AP Human Geo Unit 1
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Human Geography
the study of how events shaped humans and how they shaped the environment from that
Physical Geography
focusing on the natural features of an environment (includes landforms, plants, animals, & climate)
Spatial Perspective
where and why a location came to be; study of events at a location
Ecological Perspective
the relationship between humans and the environment; interactive and interdependent
Location
a position on Earth, can be relative or absolute
Absolute Location
the exact or fixed location
“315 S 7th St, Las Vegas, NV 89101” is an example of:
Absolute Location
Site
the physical characteristics of a location (landforms, climate, resources)
Relative Location
location described in relation to other places
Situation
a location’s connection to other locations
Space
an area that has an arrangement of things
Density
the quantity of an area
Pattern
how an area/space is used and developed
Environmental Determinism
physical environment controls society; humans rely on the regions features
Environmental Possibilism
physical environment challenges society; humans adapt to the environment with creativity and technology
Sustainability
maintaining land & natural resources for the future
Scale
analyzing an issue at different sizes (ex. local, regional, national, global)
Region
an area in which its features distinguish it from others (ex. continents)
Formal Region
a region with shared traits (physical, cultural, etc.)
What type of region are the Rocky Mountains?
Formal Region
Functional Region
a region that centers a node
Examples of functional regions
Roads, district services, ports, transportation systems
Node
the focal point of a functional region
Vernacular Region
perceptual region; subjective and boundaries overlap (ex. Midwest)
Globalization
how the world interconnects through communication and exchanges
Supranational organizations are an example of:
Globalization
Glocalization
the distribution of products globally but adapted locally
Example of Glocalization:
Available shows on Netflix varying by location
What kind of diffusion is Glocalization?
Stimulus Diffusion
Sustainable development
present needs are met, but future needs are not considered
Distance Decay
as the distance between two places increases, the interaction decreases between the two
Time-Space Compression
when the distance between places “shrink” or feel closer due to technology and faster transportation
Geo Inquiry Steps
Ask
Collect
Visualize
Share
Act
Quantitative
data measured through numbers and statistics; objective
Qualitative
data measured through observations and descriptions; subjective
Census
data that collects an official population count
GIS
Geographic Information System
What is GIS?
a system that displays layers of data on a map (ex. natural disasters, weather)
GPS
Global Positioning System
What is GPS?
a system that uses satellites to give the exact position on Earth through a device
Topography
the physical geographical features that give a land its texture
Remote Sensing
data that is collected remotely (ex. satellite images)
Cartographer
a person who makes maps
Absolute distance
distance measured through a unit of length; physical distance (ex. miles, kilometers)
Relative distance
distance measured through the connection between two places; considers social and economic factors (ex. time, money)
Absolute direction
compass (north, south, east, west)
Relative Direction
direction described through common terms (left/right, up/down, front/behind)
Large scale
zoomed-in map; presents a small area with more detail
Small scale
zoomed-out map; more generalized
Reference map
maps that focus on a generalized location and its features (streets, cities, boundaries)
Thematic map
maps that focus on a theme or type of data
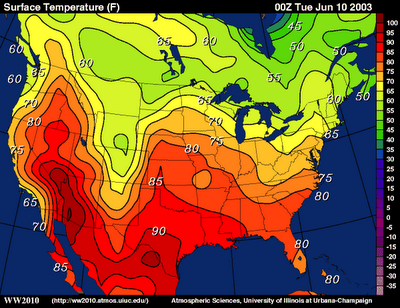
uses lines to connect places with similar values (ex. temperature, air pressure)
Isoline Map
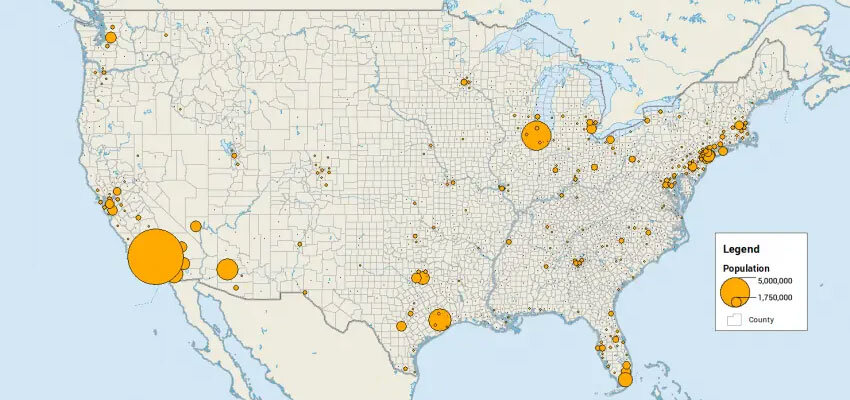
a symbol is used to show the intensity of an area (ex. earthquake magnitudes, population density)
Graduated symbols map
dots are used to show the occurrence of an area (ex. births, deaths, crimes)
Dot density map
colors/shades are used to distribute data between areas
Choropleth map
Map projections
visualizations of the globe on a flat surface; have many different purposes and uses
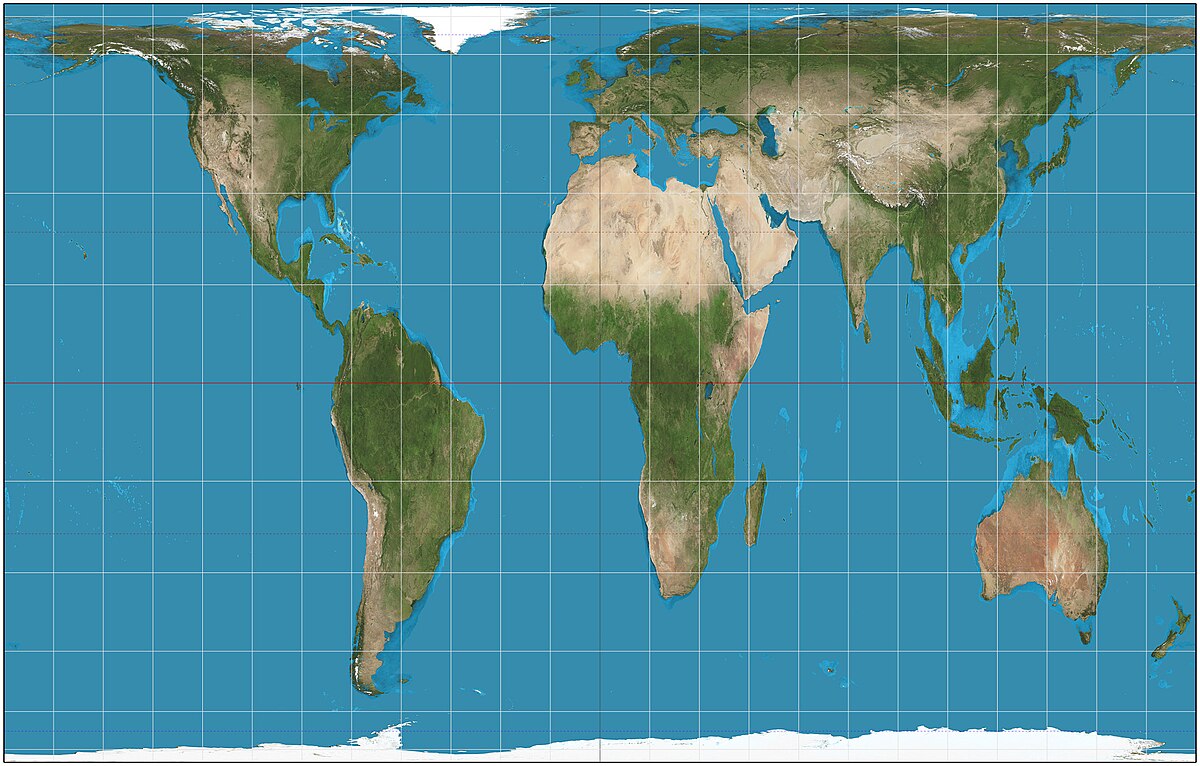
preserves land shape but distorts size as it moves farther away from the equator; used for navigation and sea-travel
Mercator Projection
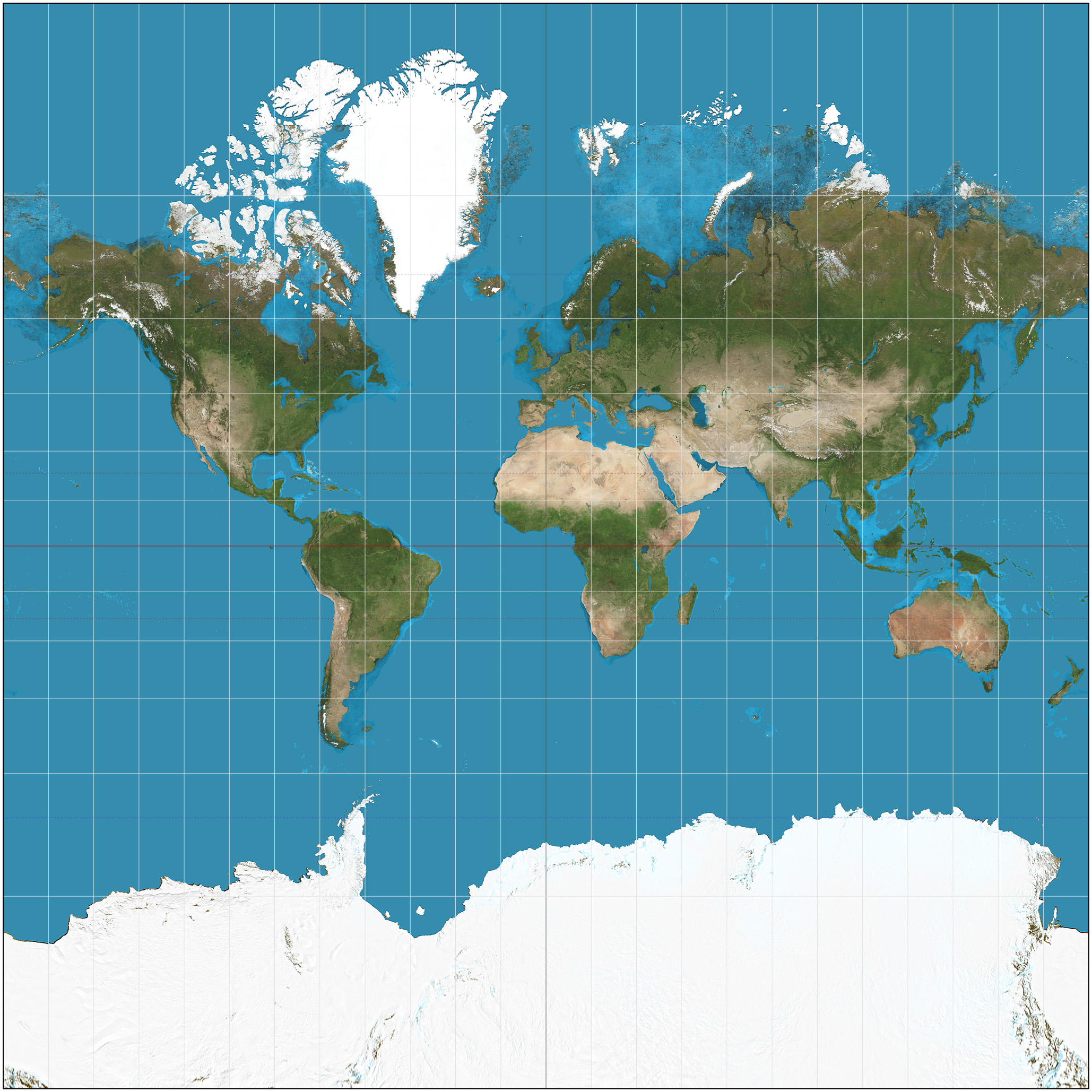
preserves land mass size but distorts the shape; not eurocentric
Gall-Peters Projection
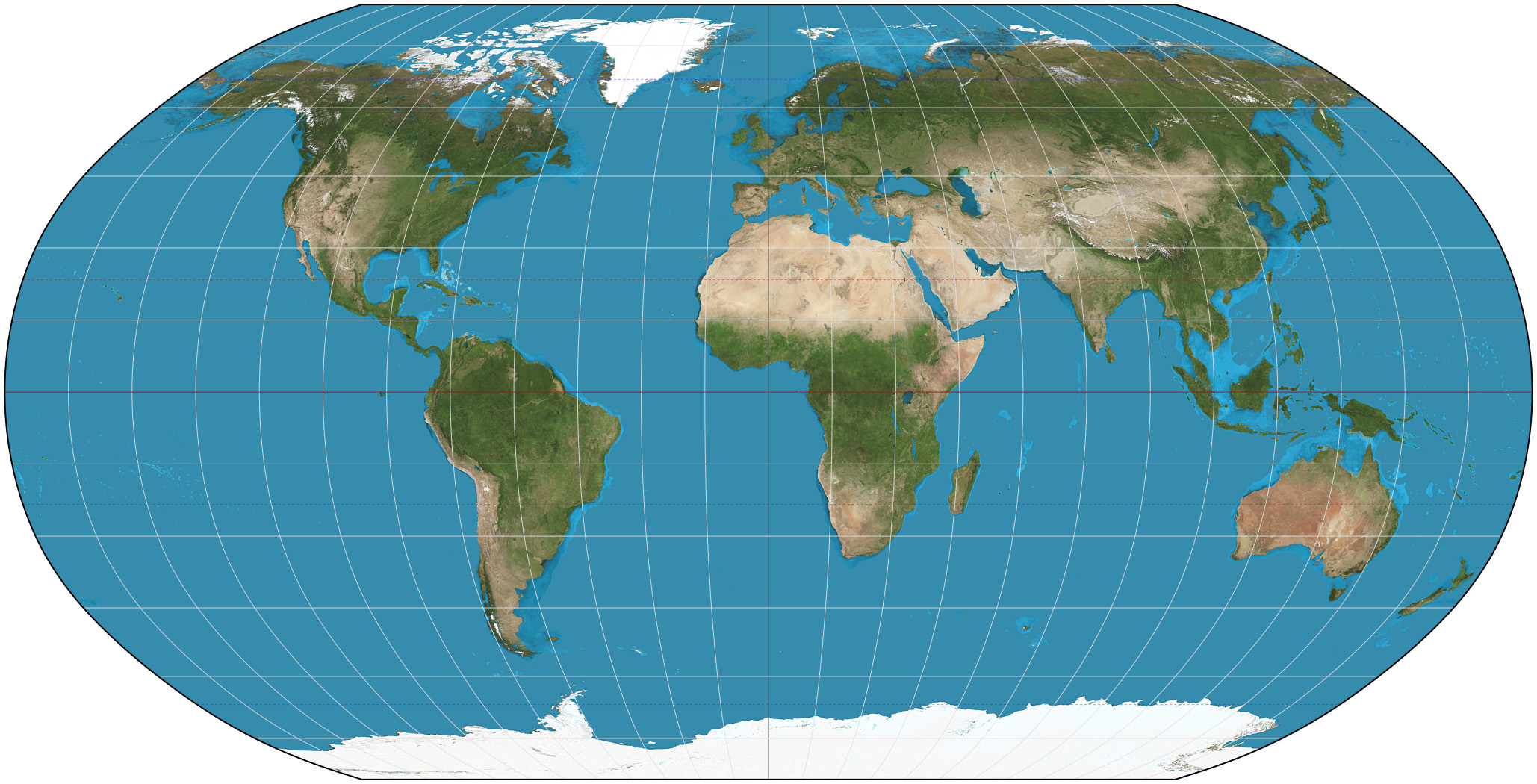
minimizes and balances distortion of all features; used for aesthetic appeal
Robinson Projection
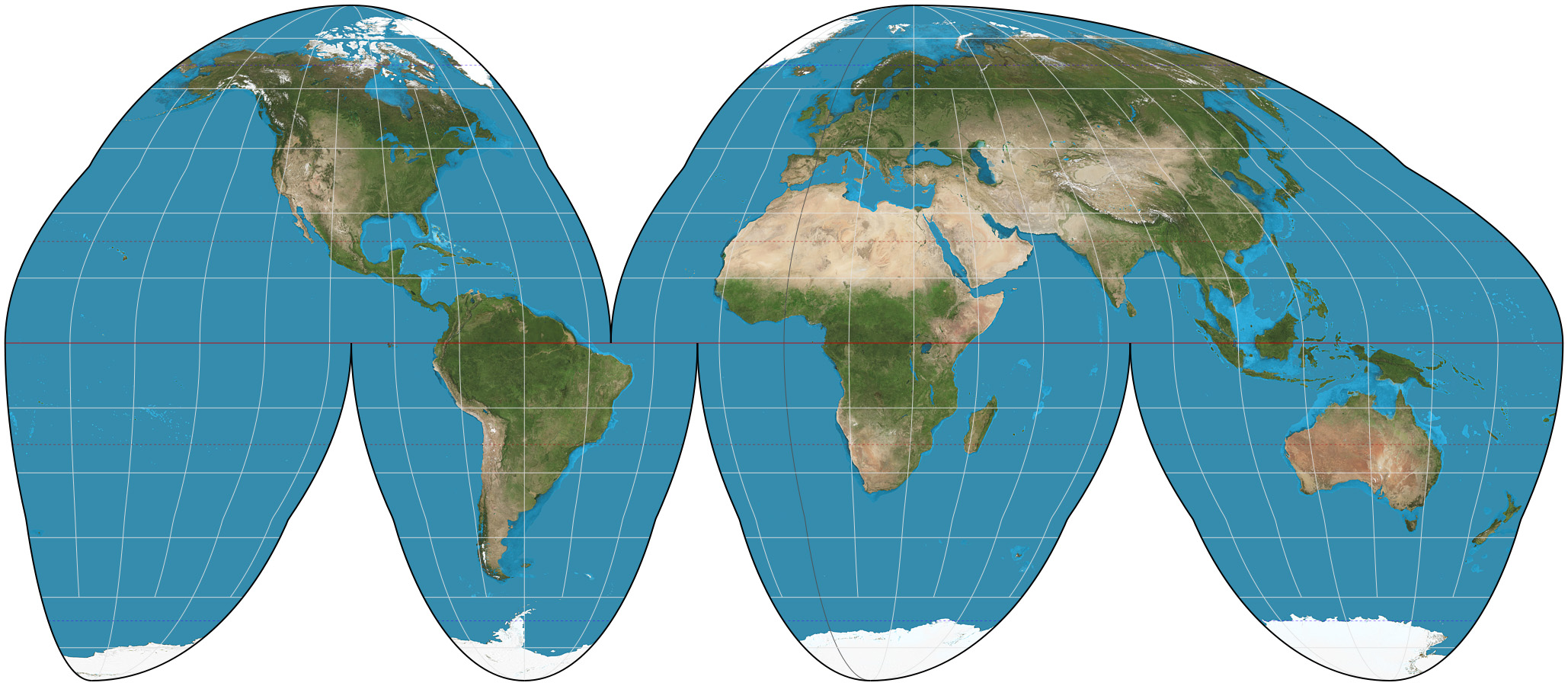
Goodie’s Homolosine Projection
projects polar areas in a disk-like shape
Azimuthal Projection