Consultation and prescribing skills
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
TO GAIN CONSENT
…FOR ANY GIVEN SITUATION.
ENGAGE with the person
Gain CONSENT to question
- Why? How?
What feels right for:
You
The person
The situation
Structuring the consultation
•Adapting speech
o Non jargon language
•Adapting body language
•Active listening
•Asking sensitive questions
•Questions with purpose
•Avoid irrelevant questions
•Health Literacy
cultural competence
•CONFIDENCE AND COMPETENCE
o Trust and Rapport
Consultation skills
Golden Minute
Calgary-Cambridge Guide
TED
ICE
LICEF
4 Es- Health coaching Model
Neighbour- Closing consultations
SOCRATES
MR-CAT
Golden minute
•The FIRST 60 seconds is where the patient should NOT be interrupted and be part of the patient's history taking.
Asking relevant OPEN questions will allow the patient to share almost 80% of what has brought them in
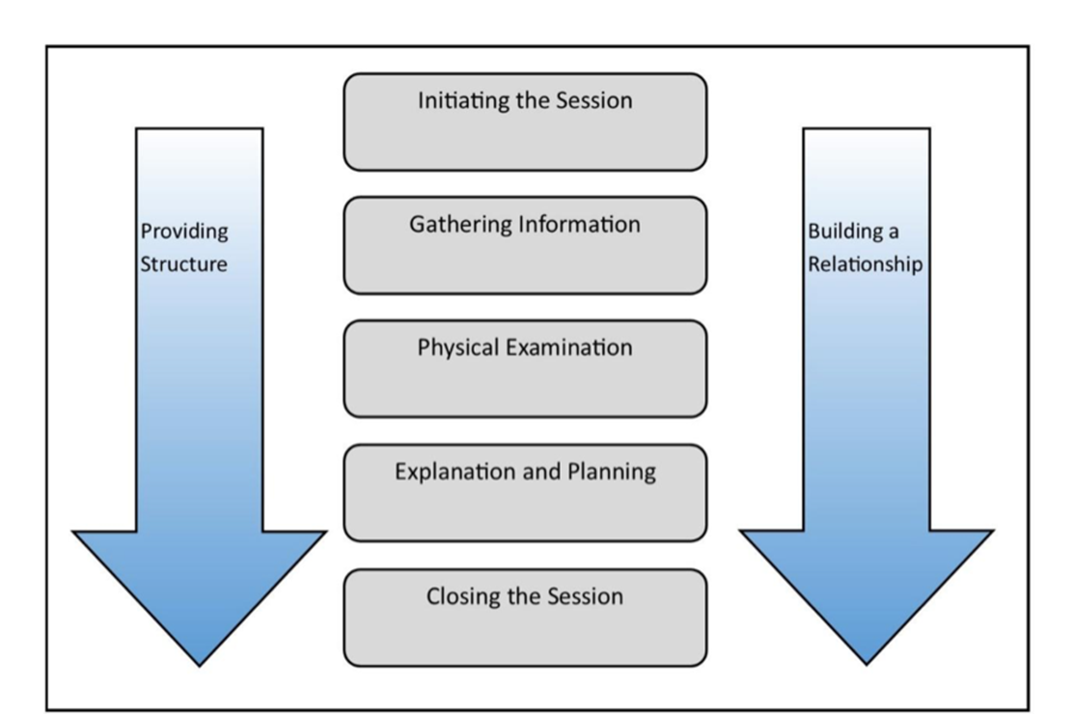
Calgary - Cambridge model
Initiating session- Introduce yourself, build rapport, establish agenda
Gathering information- Explore- use model- ICE
Physical examination- Not always required and if needed should occur at this point
Explanation and planning- provide appropriate information. Develop action plan
Closing the session- summarise key messages- 'safety-net ' the patient
TED
•TELL
Tell me more about ….
•EXPLAIN
Explain to me why/what....
•DESCRIBE
Can you describe....
ICE
IDEAS
CONCERNS
EXPECTATIONS
LICEF
•L – Lifestyle
•I – Ideas
•C – Concerns
•E – Expectations
•F - Feelings
The 4 E’s model
Explore- patient knowledge, perception and lifestyle goals
Educate- Link information to patient agenda, use 'teach back' method
Empower- Help patient to make decisions on taking medicine
Enable- ensures patient works out how they will incorporate taking medicines into their lives for e.g. some statins used at night when sleeping but this can’t be done for patients who work night shifts.
Neighbour model
CONNECTING
-develop rapport and empathy
SUMMARISING
-reasons and ICE
HANDING OVER
-agreed agenda and management plan- empower patient
SAFETY-NETTING
-contingency plans
HOUSEKEEPING
-check yourself- are you okay to continue?
SOCRATES

Where is the pain?
What were you doing when the pain started?
What does the pain feel like?
Does the pain go anywhere else?
Do you have any other symptoms with the pain?
How long have you had the pain?
Does anything make the pain better or worse?
On a scale of 1-10 how severe is the pain?
MR-CAT
•Building Rapport
•Active Listening
•Questioning Techniques
•Providing Information
•Empathy and Sensitivity
•Patient Involvement
•Summarising and Clarifying
•Non-Verbal Communication
Clinical empathy
embarrassed
difficulty in explaining
feeling the worst
symptoms induced by anxiety
show you understand what the patient has concerns about
Sensitive questions
Address:
Your own anxiety about approaching certain topics
The person’s anxiety to approach certain topics
HOW to ask the questions!
Reassure the person:
Decrease their anxiety
Addressing facts rather than judgements
Be specific in your questioning rather than general
How?
Unnecessary questions
•Does it matter if you ask something that is unnecessary or that they have already told you?
- wastes time (patient’s and pharmacist’s)
- indicates you aren’t listening to or engaging with the person – this relates to trust and empathy
- can damage confidence in pharmacist (which can impact on adherence)
- unnecessary questions are UNNECESSARY!
Closing and safety netting
closing and follow up
time frame
further advice
professionalism
documentation
Patient agenda
person centred consultation - tailored information
exploring hidden agendas and unvoiced agenda
Prescribing skills
Adopted from the military to give brief, concise and focused information
When would you use it?
•Escalation
•Urgency
•Handover
Warwick 4 frame model
PC
HX of PC
Red flags
PMH, DRUGS AND ALLERGY
Social and family Hx
ICE