Simple Neuroanatomy
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
whats another name for anterior and posterior?
anterior- ventral, posterior- dorsal
whats another name for superior and inferior?
superior- rostral, inferior- caudal
nucleus meaning??
cluster of cell bodies (same as ganglion in PNS/ gray matter)
tracts meaning??
bundles of myelinated axons (white matter in the brain)
what do the General somatic afferent nerves do?
carry sensory info to the CNS from muscles and skin
what do the General somatic efferent nerves do?
carry motor info from the CNS to skeletal muscles
what do the General visceral afferent nerves do?
carry sensory info to the CNS from organs and blood vessels
what do the General visceral efferent nerves do?
carry motor info from the CNS to smooth muscle and glands (parasympathetic innervation)
what do the cranial nerves do?
control the special senses
what do the special somatic afferent nerves do?
vision, hearing, & balance
what do the special visceral afferent nerves do?
smell, taste
what do the special visceral efferent nerves do?
branchial arch striated muscles
what are the 5 secondary brain vesicles?
Telencephalon, Diencephalon, Mesencephalon, Metencephalon, Myelencephalon
what does the telencephalon develop into?
cerebral cortex & basal ganglia
what does the diencephalon develop into?
optic stalk, optic cup, thalamus, hypothalamus, pituary gland, pineal gland
what does the mesencephalon develop into?
midbrain
what does the metencephalon develop into?
pons & cerebellum
what does the myelencephalon develop into?
medulla oblongata
what is the brain stem made up of?
midbrain + pons + medulla
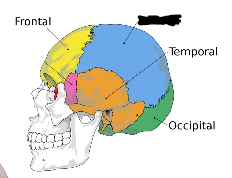
what is this?
parietal lobe
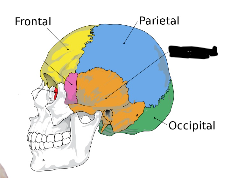
what is this?
temporal lobe
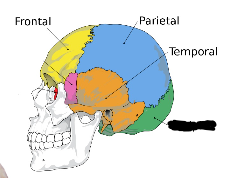
what is this?
Occipital lobe
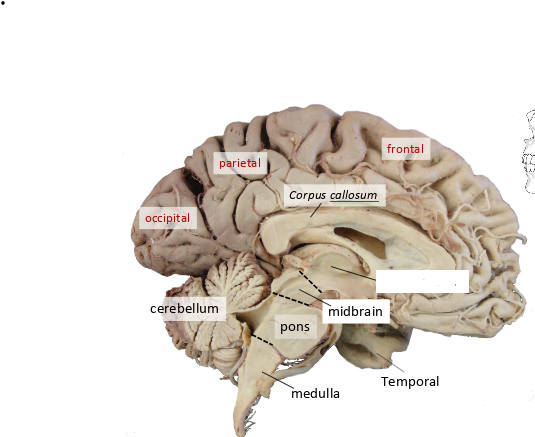
what is this?
diencephalon
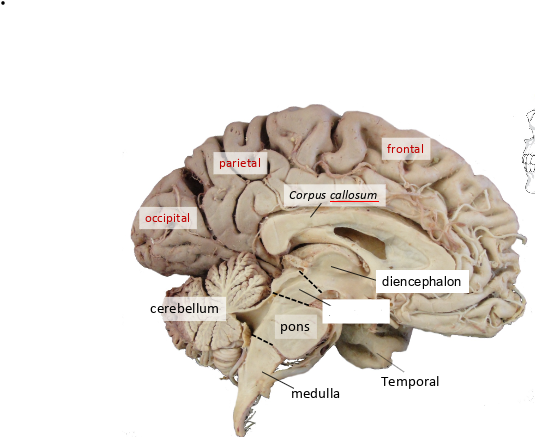
what is this?
midbrain
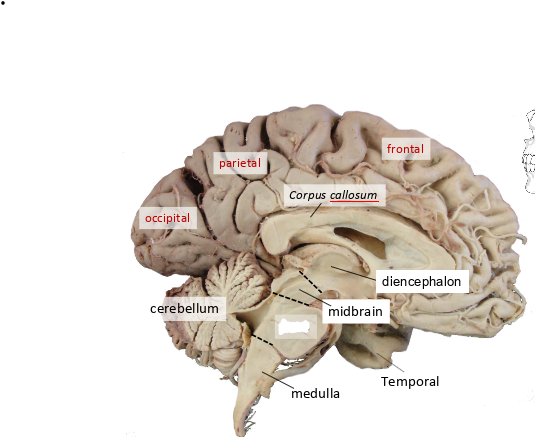
what is this?
pons
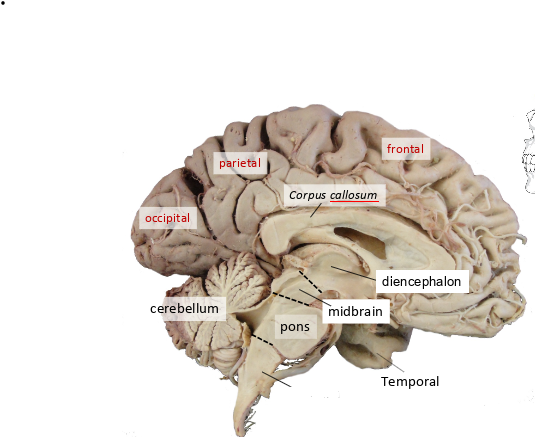
what is this?
medulla
whats the difference between sulcus and gyrus?
gyrus= ridge
sulcus=groove
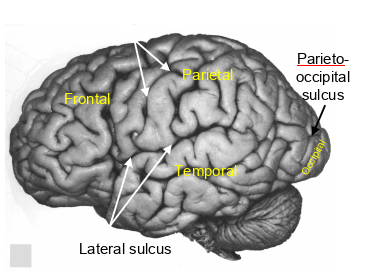
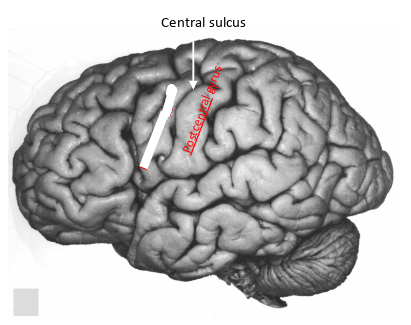
what sulcus is this?
central sulcus
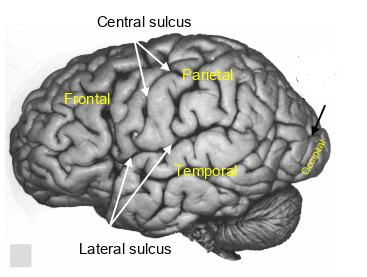
what sulcus is this?
parieto-occipital sulcus
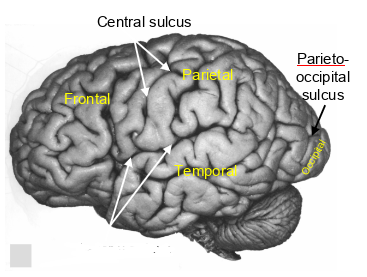
which sulcus is this?
lateral sulcus
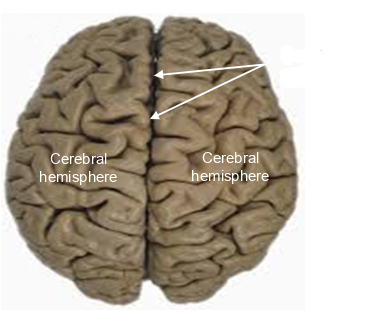
whats this pointing to?
longitudinal fissure
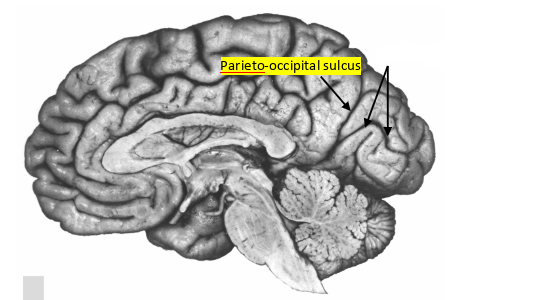
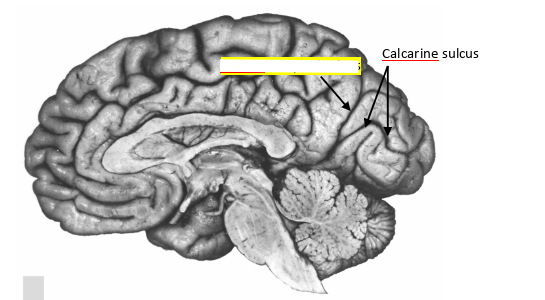
what sulcus is this?
calcarine sulcus
what sulcus is this?
Parieto-occipital
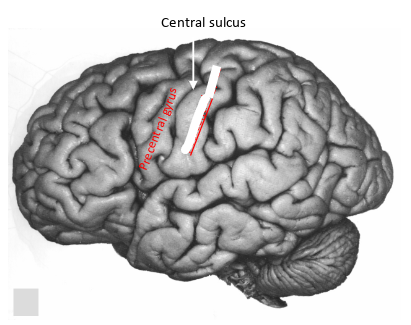
whats this gyrus and what does it do?
precentral gyrus- primary motor area
whats this gyrus and what does it do?
pest control gyrus- primary somesthetic (somatosensory) area
what is this area called?
primary auditory area
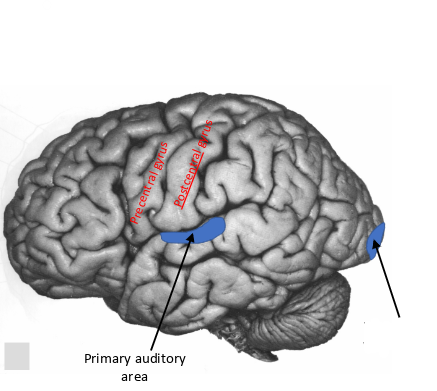
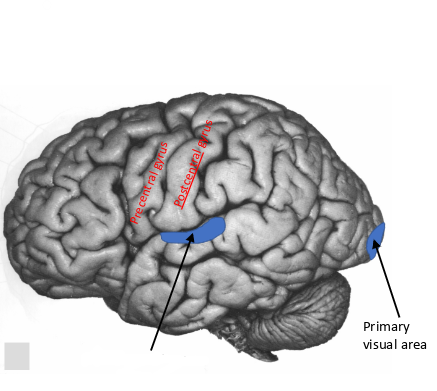
what is this area called?
primary visual area
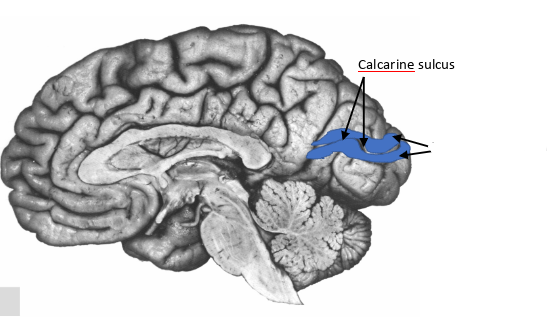
what are these pointing to?
primary visual area
who in the 19th century numbered areas of the cortex correctly?
Korbinian Brodmann
how did Broodmann decide what to number each region?
based on fine structures and neuronal components of its six layers
what are ventricles in the brain?
spaces within the brain filled with CSF
what are functions of the CSF
supports brains weight, prevents compression of its blood supply, buffers againts blows to the head, can wash out metabolic waste products
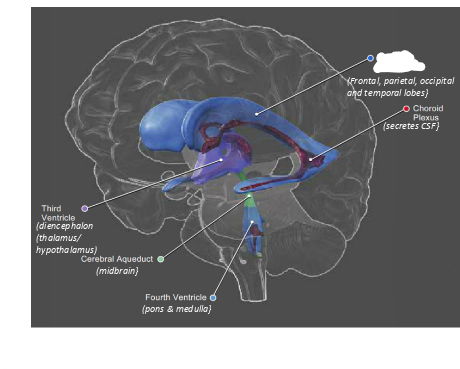
what is blanked out?
lateral ventricles
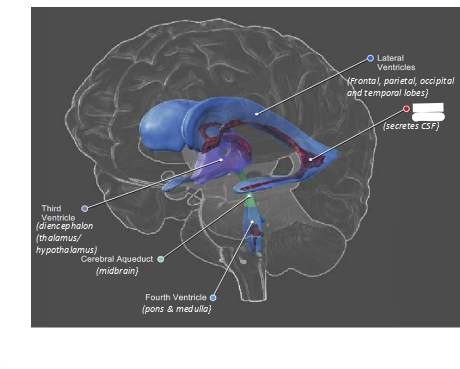
what is this?
chloroid plexus
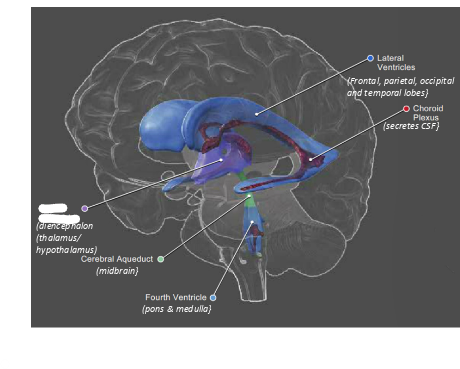
what is this?
third ventricle
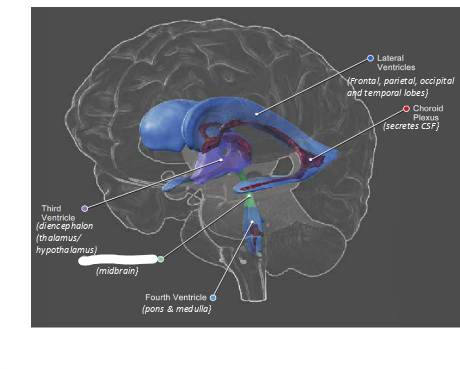
what is this
cerebral aqueduct
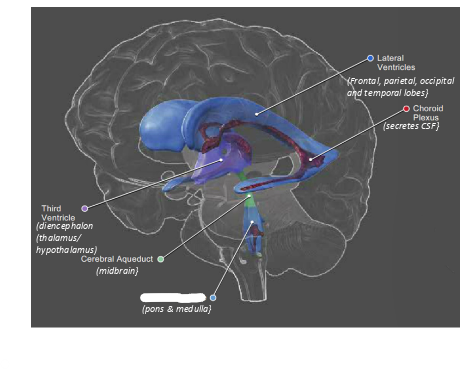
what is this?
fourth ventricle
what are the two large arteries that supply the brain on each side?
internal carotid arteries
vertebral arteries
what are the 3 layers of membranes surrounding the brain?
Dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
what is the dura mater made up of?
meningeal (inner layer), periosteal (outer layer)
what is the arachnoid mater made up of?
thin subarachnoid space containing CSF
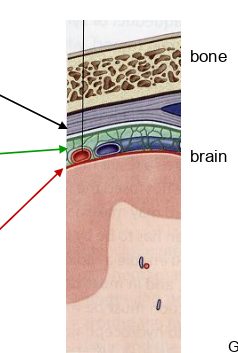
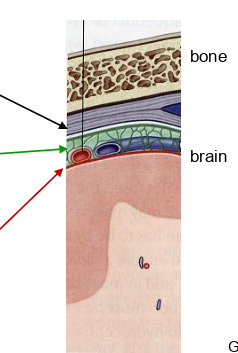
what is the black arrow pointing to?
dura mater
what is the green arrow pointing to?
arachnoid mater
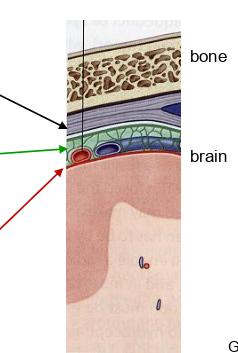
what is the red arrow pointing to?
pia mater
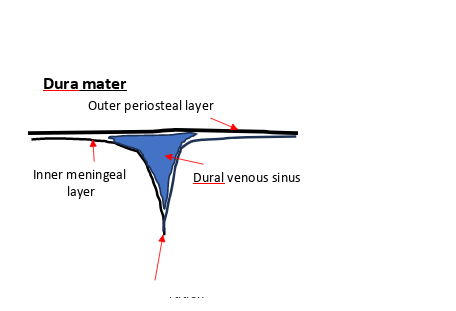
what is the arrow pointing to
dural partition
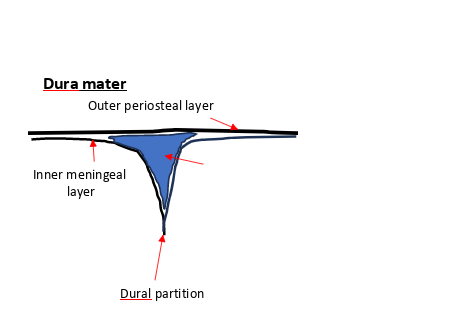
what is this pointing to
dural venous sinus
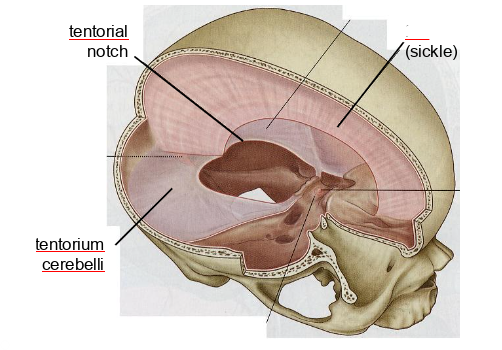
what dural partition is this
falx cerebri
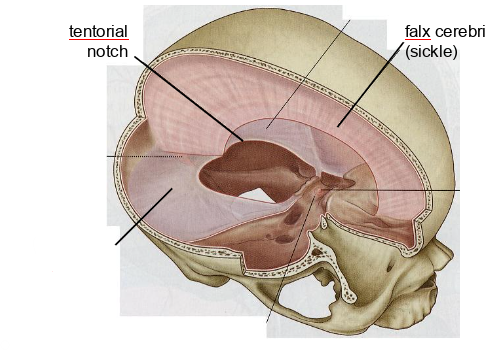
what dural partition is this
tentorium cerebelli
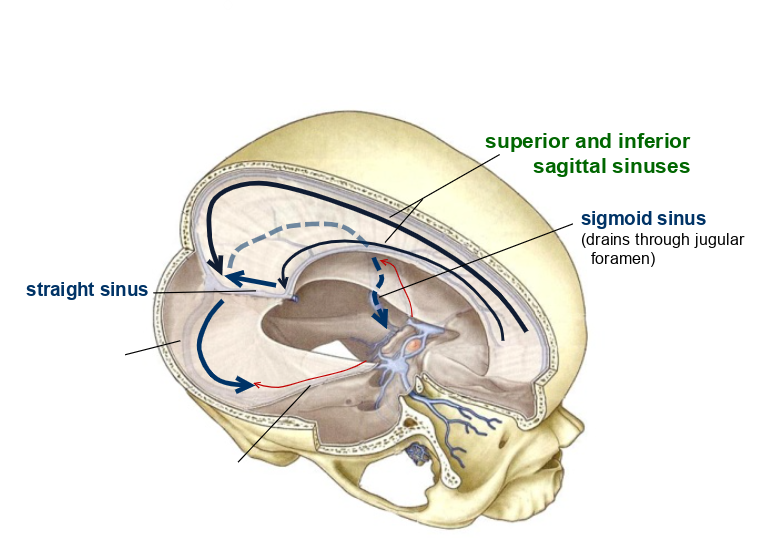
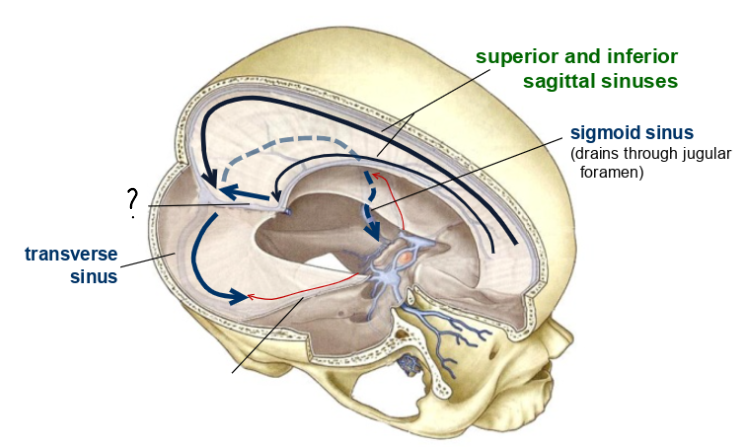
what is this?
transverse sinus
what is this?
straight sinus
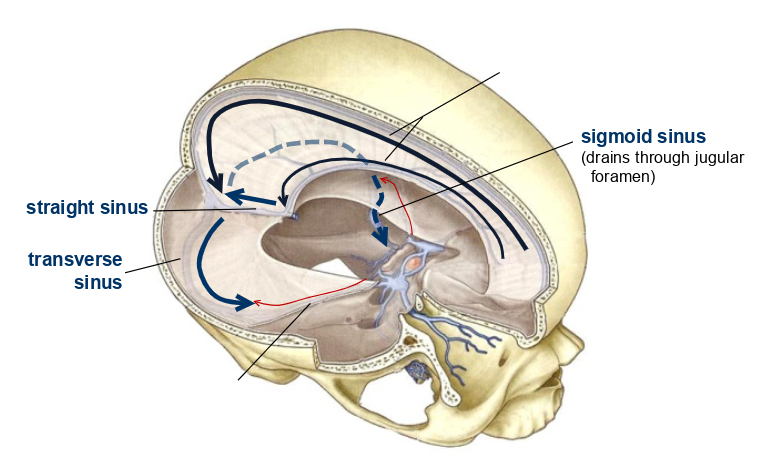
what are these called?
superior and inferior sagittal sinuses
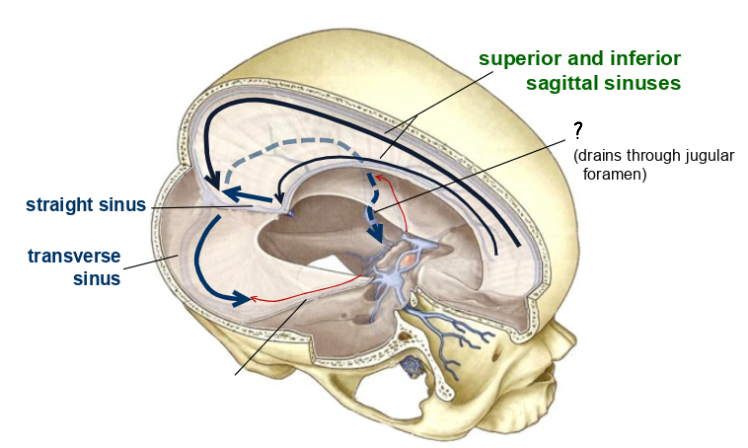
what is this
sigmoid sinus
what does the sigmoid sinus continue into?
internal jugular vein
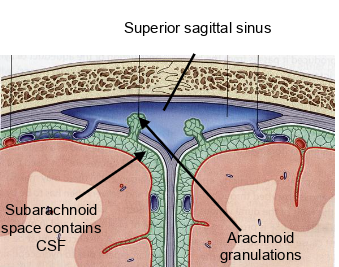
CSF in the subarachnoid drains how?
through arachnoid granulations into the venous blood in the superior sagittal sinus