Chapter 8: Energy and Enzymes
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
coupling reactions
energy obtained from exergonic reactions (food) to power endergonic needs
first law of thermodynamics
energy is neither created nor destroyed but can be transformed
second law of thermodynamics
the amount of disorder in a system increases over time
kinetic energy
energy of motion
thermal energy
energy of moving molecules
potential energy
energy stored in position or configuration
chemical energy
energy stored in chemical bonds that can be transferred to other bonds or taken from other bonds with weaker bonds with higher potential energy than stronger bonds
gibbs free energy
composite of heat/bond energy and entropy effects and determines whether a reaction is spontaneous or not
spontaneous
when gibbs is less than 0 and reaction does not require energy input to occur
exergonic
energy output
endergonic
energy output
nonspontaneous
when gibbs is greater than 0 and reaction requires energy input to occur
energetic coupling
process between exergonic and endergonic reactions allows chemical energy released from one reaction drive another via redox or transfer of phosphate groups
oxidization
loss of electrons
reduction
gain of electrons
ATP hydrolysis
process in which ATP’s terminal phosphate is broken off to ADP adding energy to the system which can be coupled to endergonic reactions to make them spontaneous
substrates
reactants that undergo a chemical reaction by binding to an enzyme at the active site to allow proper orientation
conformational change
when enzyme does not fit substrate until substrate makes contact with it
specificity
characteristic of enzymes in which each enzyme only works with specific substrate
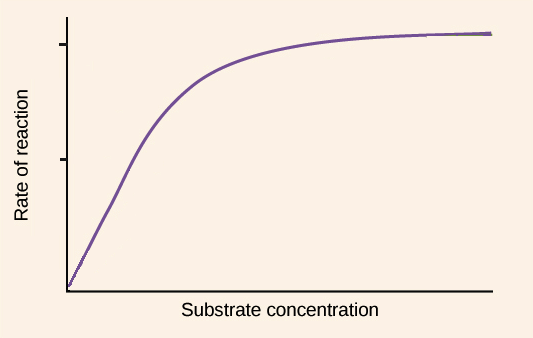
saturation
characteristic of enzymes in which active sites of all enzymes become filled up at a threshold concentration of substrate
saturation kinetics
characteristic of enzymes in which the speed of reaction reaches maximum
competition
characteristic of enzymes in which sometimes there are molecules that are similar enough to the substrate that they bind to the active site, reducing the reaction rate
cofactors
inorganic ions such as Zn2+, Mg2+, Fe2+ that reversibly react with enzymes and detach easily
coenzymes
organic molecules such as NADH and FADH2 that interact with enzymes and detach easily (include vitamins)
prosthetic groups
non amino acid atoms or moleecules permanently attached to enzymes
regulating molecules
regulate cell’s enzymatic activity that may change enzyme’s structure, ability to bind to its substrate, or may either activate or deactivate an enzyme’s function
competitive inhibition
reversible regulatory reaction where molecule competes with the substrate for the active site
allosteric regulation
reversible regulatory reaction molecule binds at a location other than the ctive site, causing a change to enzyme’s shape, and can activate or deactivate the enzyme
phosphorylation
most common form of covalent modifcation in which kinases covalently add phosphate groups to their substrates to active or phosphatases take it off to deactivate
kinases
enzymes that phosphorylate
phosphatases
enzymes that dephosphorylate (remove covalently linked phosphate groups from substrate
peptide cleavage
the enzymatic hydrolysis of peptide bonds to release smaller peptide fragments or amino acids
proteolytic cleavage
process where proenzyme takes off something covering the active site to make it accessible
feedback inhibition
as concentration becomes abundant it feed back to stop reaction and amount of initial substrate is not depleted and stored or used for other reactions
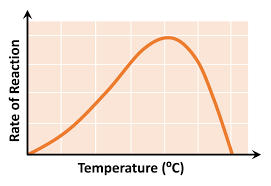
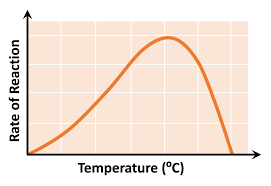
temperature graph
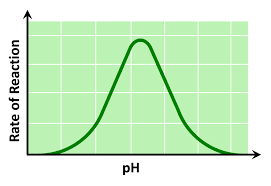
pH graph
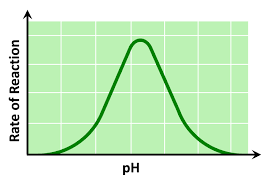
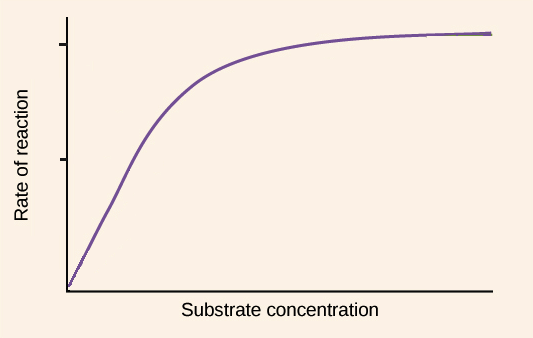
substrate concentration graph