A2 - Quantitative indicators for energy, water and raw material use: Mass Balances
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What can the food production chain be used for?
To use raw material efficiently
See where water is consumed
See where energy is consumed.
Law of conservation of mass
Mass can be neither created nor destroyed
Mass balance formula
Accumulation = in - out + production
Accumulation = change in time
No change in time? → accumulation = 0
Batch
No input and output
In and out are 0
Accumulation = production
Semi-batch
Periodically adding (input) or removing (output)
Continuous
Continuous input and output throughout the process
What does it mean if a process has no conversion?
Then production = 0
Steady state
When process variables (e.g. T, flow rate) are independent of time this happens in continuous processes, because there is no accumulation of products.
Continuous steady-state process without production?
Accumulation = 0 because production = 0
In = out
Transient
Process variables that change in time
mass fraction formula
Mass of the compound divided by the total mass of the material
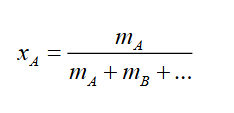
Mass fraction vs mass ratio
In case of air kg water per kg dry air is used
Therefore a ratio is used
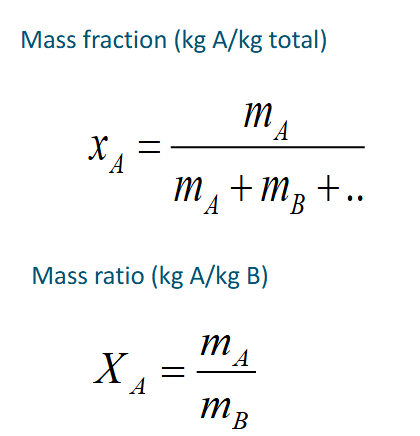
Reasons to apply recycle streams
To increase the yield from a chemical reaction
To conserve energy
Recycling of air in a dryer
To reduce the inlet concentration of an ingredient
Moisture content in a feed of a dryer.
Reasons to apply bypass
Reduce size unit operation
Product quality
Safety measure
Heating
Direct & Indirect heating
Direct: Having direct contact between the heat source (e.g. steam) and the product
Steam injection
Batch process
Indirect
Heat exchangers
Plate, tubes and pipes, scraped surfaces
Continuous process
Indirect heating
Heating exchangers
Plate
More thin and larger walls is better & more efficient
Tubes and pipes
Or scraped surfaces (for e.g. crystals)
Evaporation
Removing water from a liquid feed to produce a concentrated liquid product
e.g.:
Fruit juices (orange juice concentrate)
Vegetable juices (tomato pastes and purees)
Dairy products (condensed milk)
Sankey diagrams
Visualizing energy or mass flows
Conservation of mass or energy
Representation of flow by arrows
Arrow width = scale factor * M
Width of the arrow is related to the size of the stream
For mass, energy, all conserved quantities
All flows in go into the same side
All flows out go into the opposite side
For conserved variables, cumulative in should be equal to cumulative out
Golden rules for Sankey diagrams
Main input (raw material) usually in at the left side
Main output (product) usually out at the right side
Waste (unwanted output) goes down, emissions go up
Clear and short name to each process step
Color for different components
Short label to all arrows.