BCS 111 Lecture 11
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Higher-level cognition
Cost and benefits of making a decision
How do we make a decision?
Weighing between cost a benefit
Utility maximization
Utility: the value you can get from an outcome
Reason-based choice
Are we always guided by the utility (value) of the choices?
Justification of choice instead of maximizing utility
Need a “reason” for the decision
Should I get married?
The value? The reason
The questions can also be framed
Should I get married?
look for advantages of marriage
look for a reason for the decision of getting married
Should I not get married?
Look for disadvantages of marriage or advantages of being single
look for a reason for the decision of NOT getting married
Reasoning and decision making
What’s the rationale of solving hard problem first on an exam
Deductively
All difficult problems are time-consuming.
All problems requiring elaborate thinking are the difficult ones.
All time-consuming problems require elaborate thinking. (?)
Inductively
Hypothesis testing
Solving hard problems first might improve my grade
Reasoning and decision making
Decision making process is more complicated than we thought
Understand the problem (reasoning: deductive and/or inductive)
Set a goal and formulate hypotheses
Brainstorm possible solutions (various problem-solving strategies)
Weigh cost and benefit
Final decision
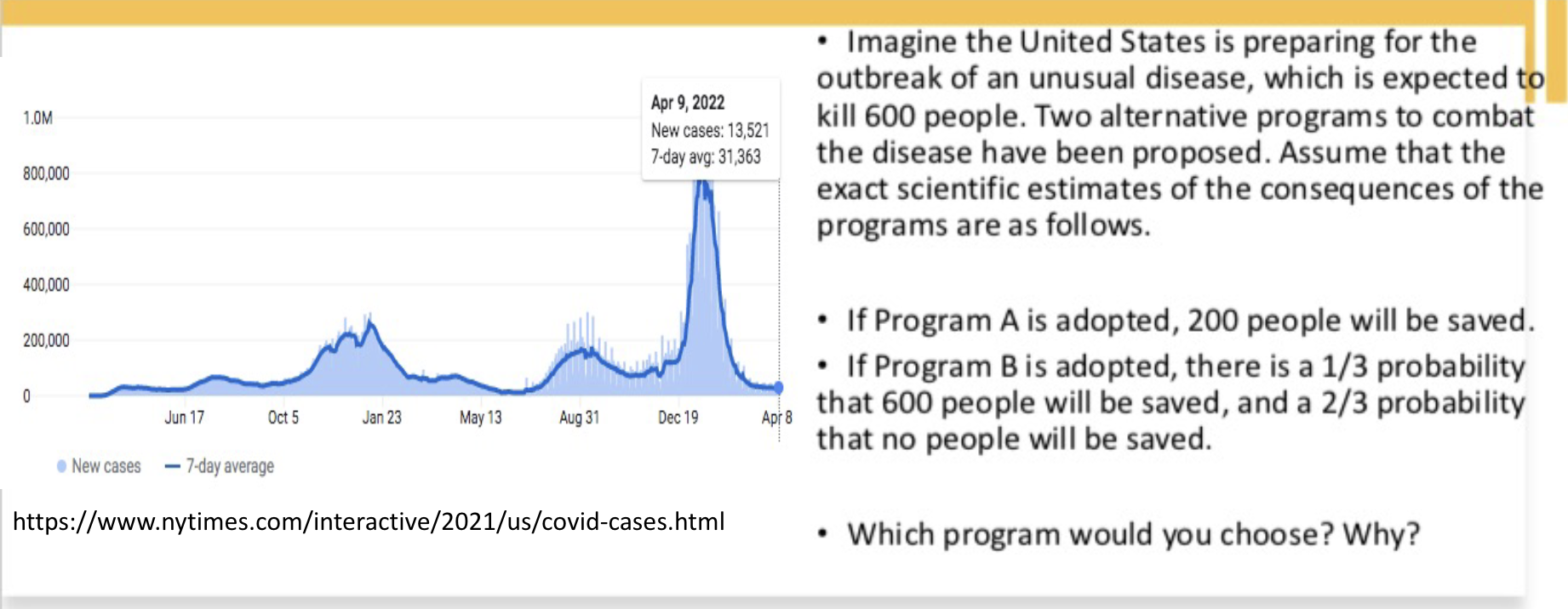
The Disease Problem (1)
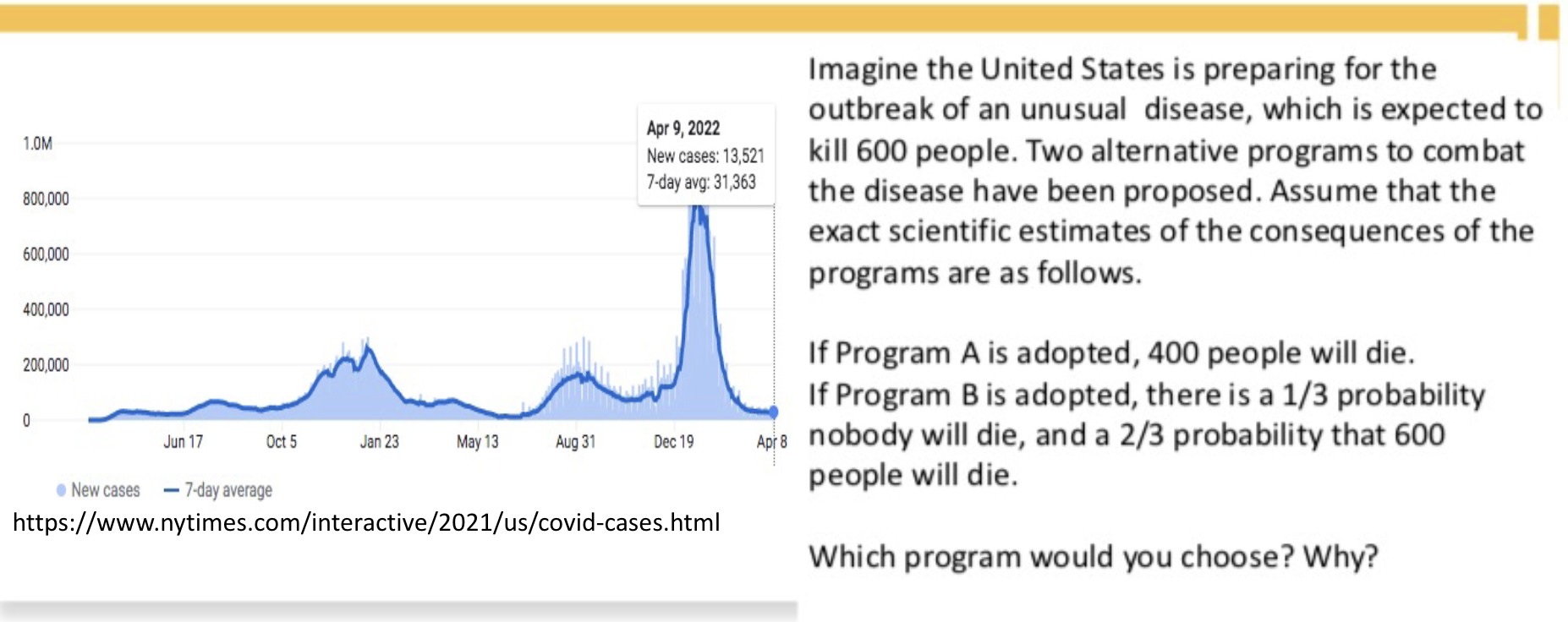
The Disease Problem (2)
Summary

Monetary reward problem (1)
Assume yourself richer by $300 than you are today. You have to choose between:
A. A sure gain of $100
B. 50% chance to gain $200 and 50% chance to gain nothing
Which option will you choose?
Monetary reward problem (2)
Assume yourself richer by $300 than you are today. You have to choose between:
A. A sure loss of $100
B. 50% chance to lose nothing and 50% chance to lose $200
Which option will you choose?
Monetary reward problem
Tversky & Kahneman (1987)
In version (1), 72% chose Program A over B.
In version (2), 64% chose B over A.
What causes this difference?
Framing of outcomes
Version (1): positively framed (# of people being saved)
Conservative decision
Version(2): negatively framed (# of people died)
Risky decision
Framing of outcomes: Influence of language on thinking!! Also supports linguistic relativism!
Decision making in investment
Assessment of risk and return
High risk but high gains?
Low risk and low gains?
One way to test decision making in investment:
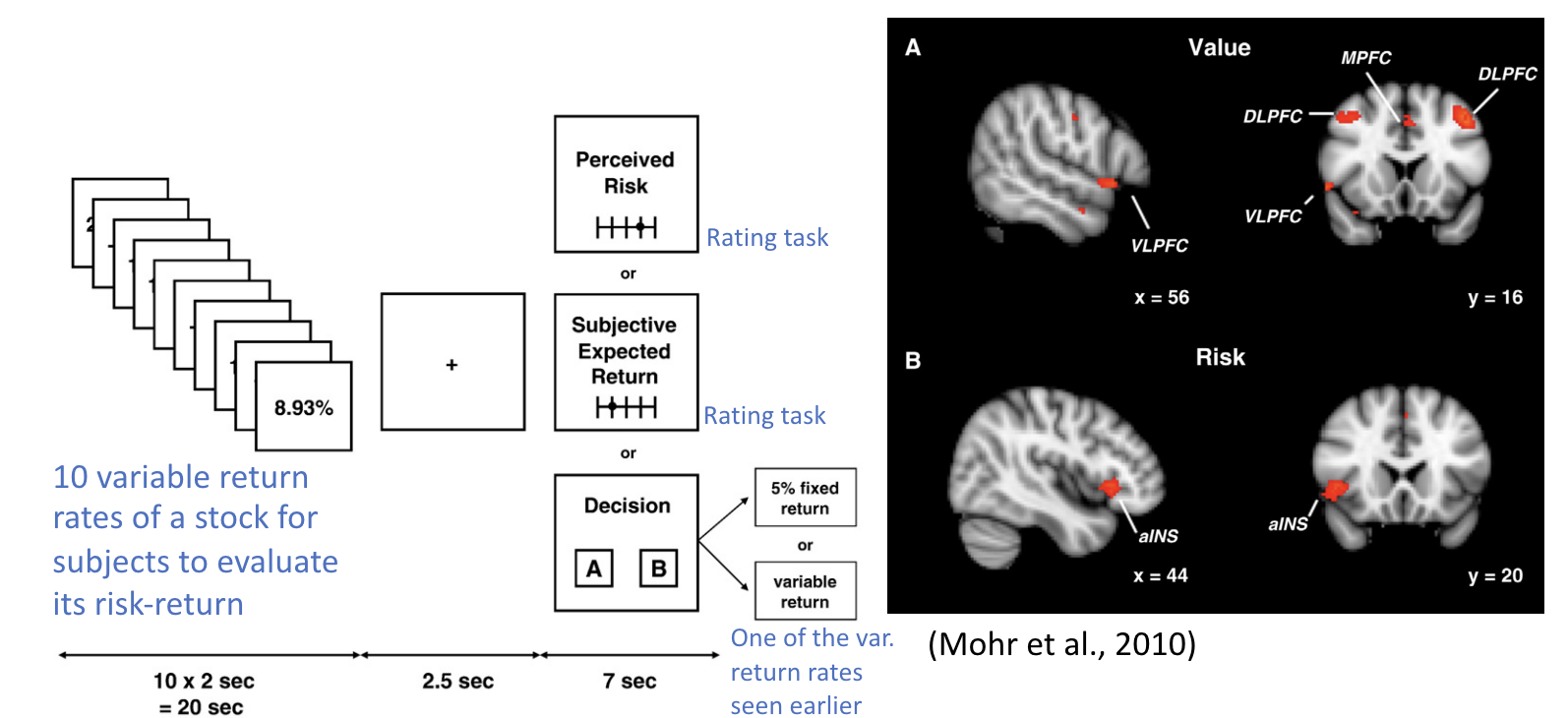
Risk Perception and Investment Decision (RPID) task (Mohr et al., 2010)
An fMRI study of decision making in investment
Subjective value (expected return – risk) is highly correlated with activities in various regions in the prefrontal cortex.
Perceived risk is highly correlated with activities in aINS (anterior Insula)
Decision making in gambling
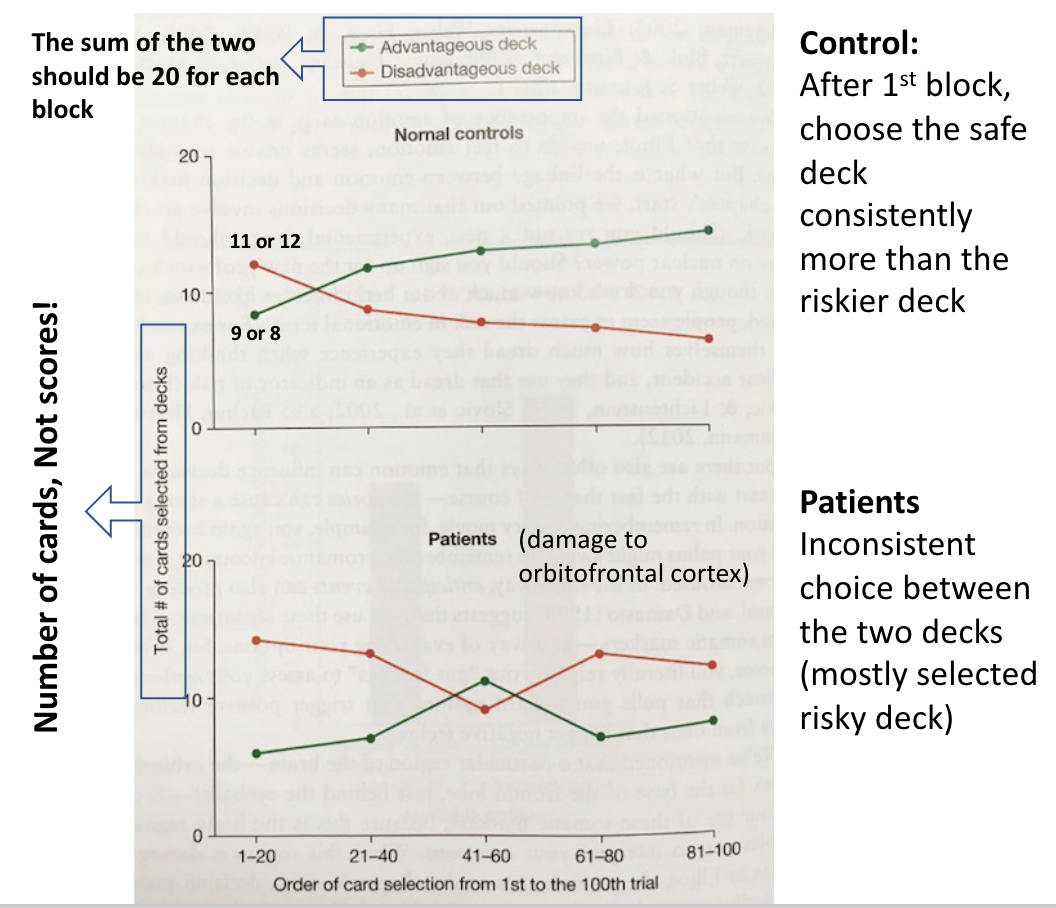
Another way to test decision making and risky behavior: the Iowa Gambling Task or “IGT” (Bechara et al. 1994; Verdejo-Garcia et al. 2007)
4 decks of card: Subjects pick one card at a time from any deck
Predetermined order of cards and gains/losses in each deck
Some decks are riskier, while others are “safer”
Substance abuse and decision making
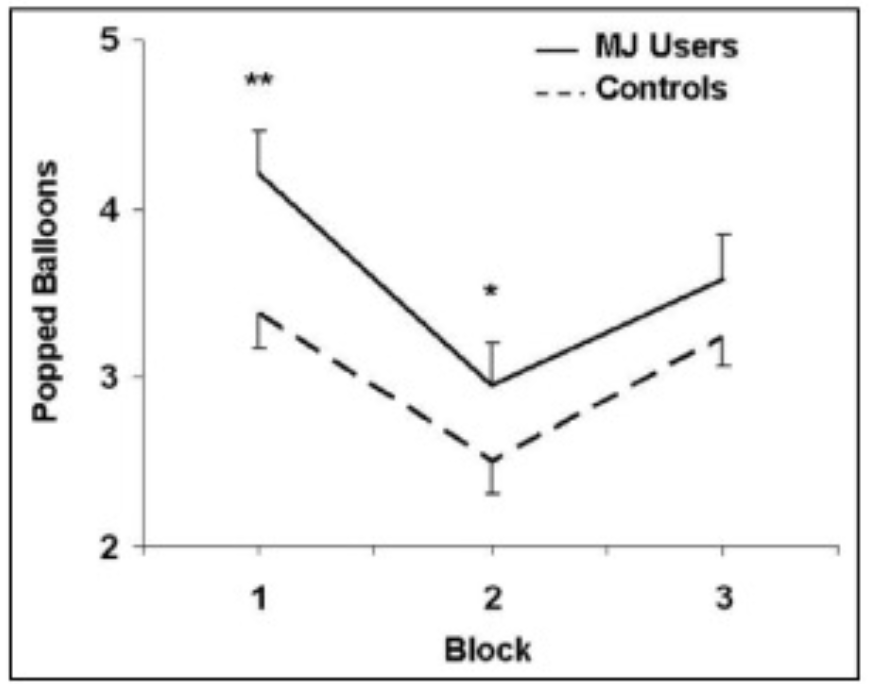
Balloon task: marijuana users vs. non-users (controls)
MJ users took a riskier approach than controls.
High number of popped balloons in Block 1: Why??
Exploring/trying the task to maximize outcome
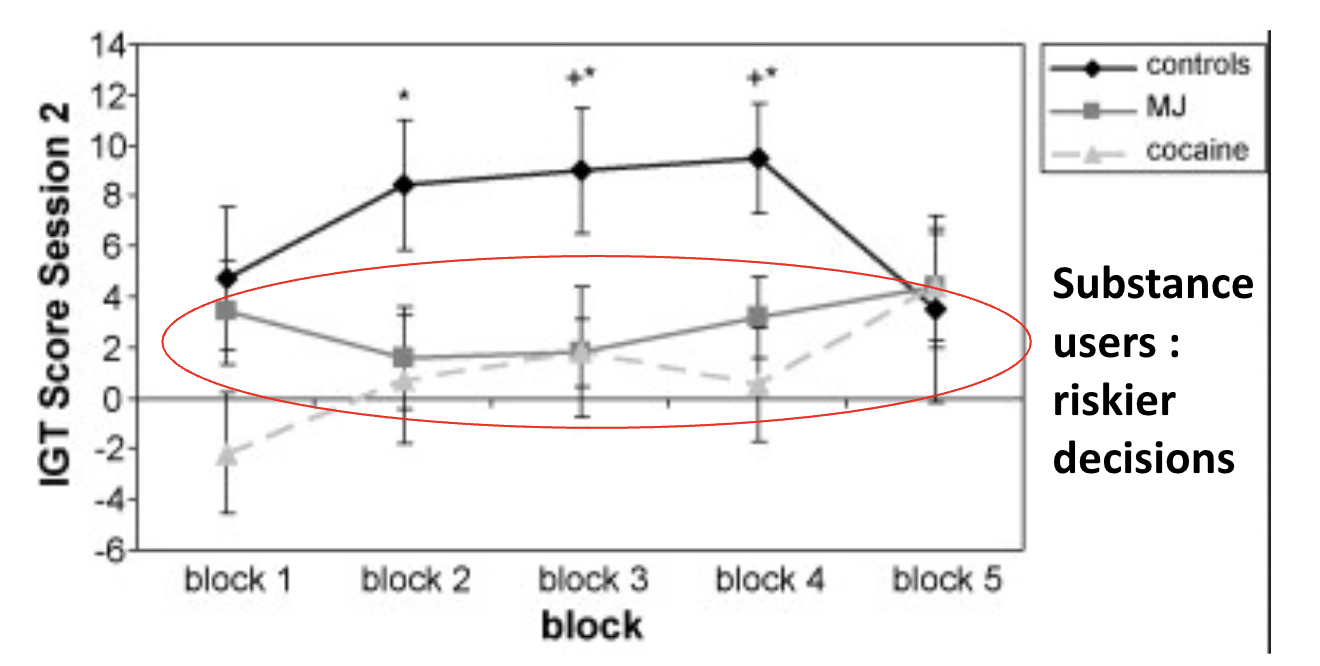
Substance abuse and decision making
Each block = select 20 cards
Why no diff. among 3 groups in block 5?
Emotion control and decision making
Emotion control
• Impaired orbitofrontal cortex → impaired emotion control → riskier decision
Other factors affecting decision making
Age
Younger → riskier decisions?
Older → more conservative decisions?
Other factors affecting decision making
Age
Negative correlation between age and cognitive functions (memory, processing speed)
Leading to negative correlation between age and quality of decision making (Henninger et al. 2010) (due to cognitive aging)
Another factor affecting decision-making: stress/pressure
Recognition-primed decision (RPD) (Klein,
1989, 1993)- Key concepts:
Decision “primed” by recognition of a situation:
If familiar:
Quickly select an action (instead of planning first) sometimes based on intuition
If unfamiliar:
Reassess/Seek more info
Mental simulation of the selected action: experience needed in order to “imagine” the possible outcomes
`
Decision making in children
What about children? How do children make decisions?
Rational?
Reason-based?
Utility-maximization?
Before fully developing the above mechanisms, they rely on something else: environmental reliability (or credibility)
Children decision-making: Kidd, Palmeri & Aslin (2013)
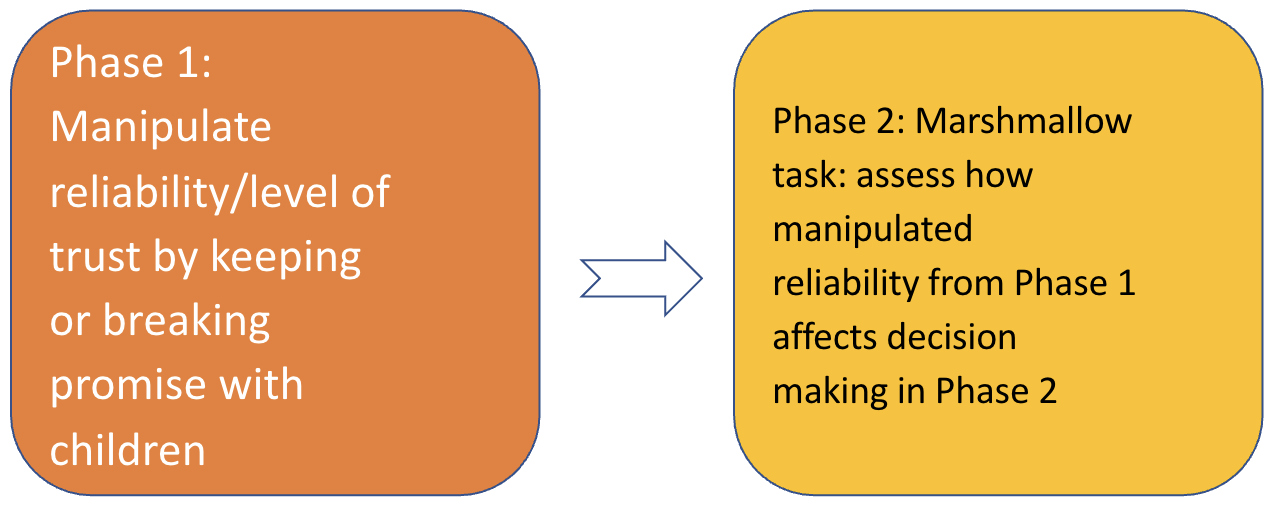
(cont)
Phase 1: manipulate reliability
Choice 1:
Reliable condition: a sealed jar of crayons; promised to bring a fancy set of art supplies if children can wait
Unreliable condition: return without the promised supplies
(cont 2)
Phase 1: manipulate reliability Choice 2 (not a manipulation; just another choice):
Reliable condition: a pack of stickers; promised to bring another better pack if they can wait
Unreliable condition: return without the promised stickers
Phase 2
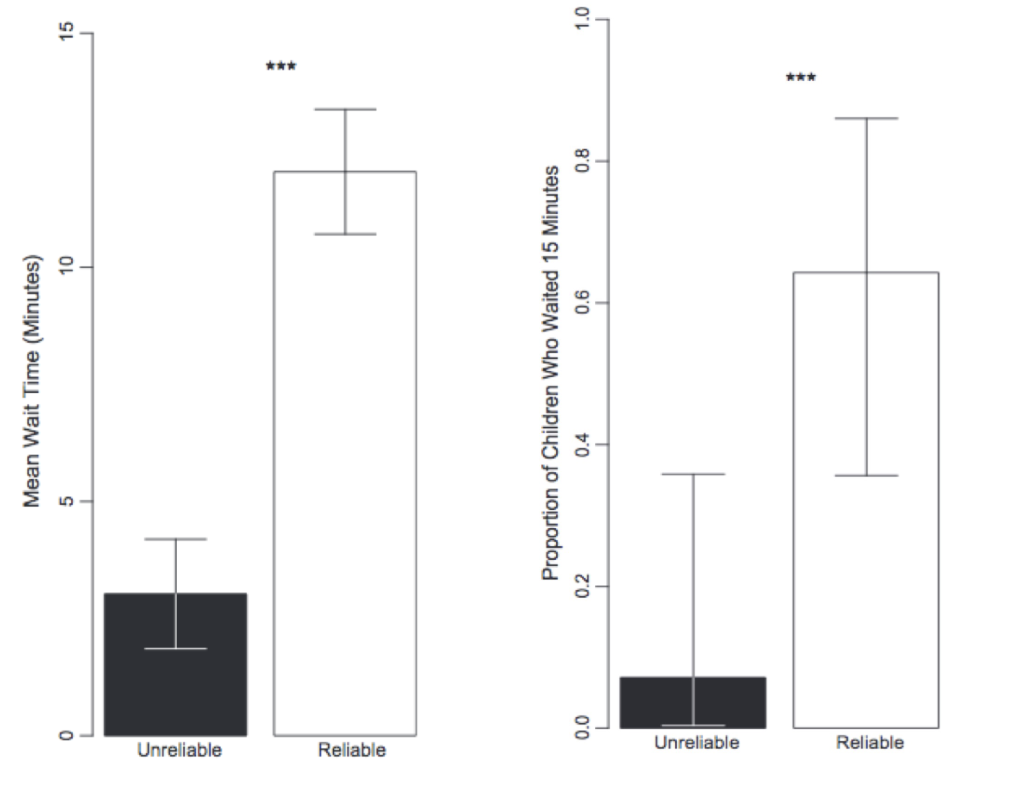
Marshmallow task
“…You can eat this one marshmallow right now. Or—if you can wait for me to go get more marshmallows from the other room [15 mins]—you can have two marshmallows to eat instead… I’ll leave this [marshmallow] here, and if you haven’t eaten it when I come back, you can have two marshmallows instead!”
Marshmallow task
What will the results look like if environmental reliability plays no role in this task?
i.e. What if “self-control” was the main factor influencing young children’s decision making?
Then both bars would be low
Therefore, it is not self control
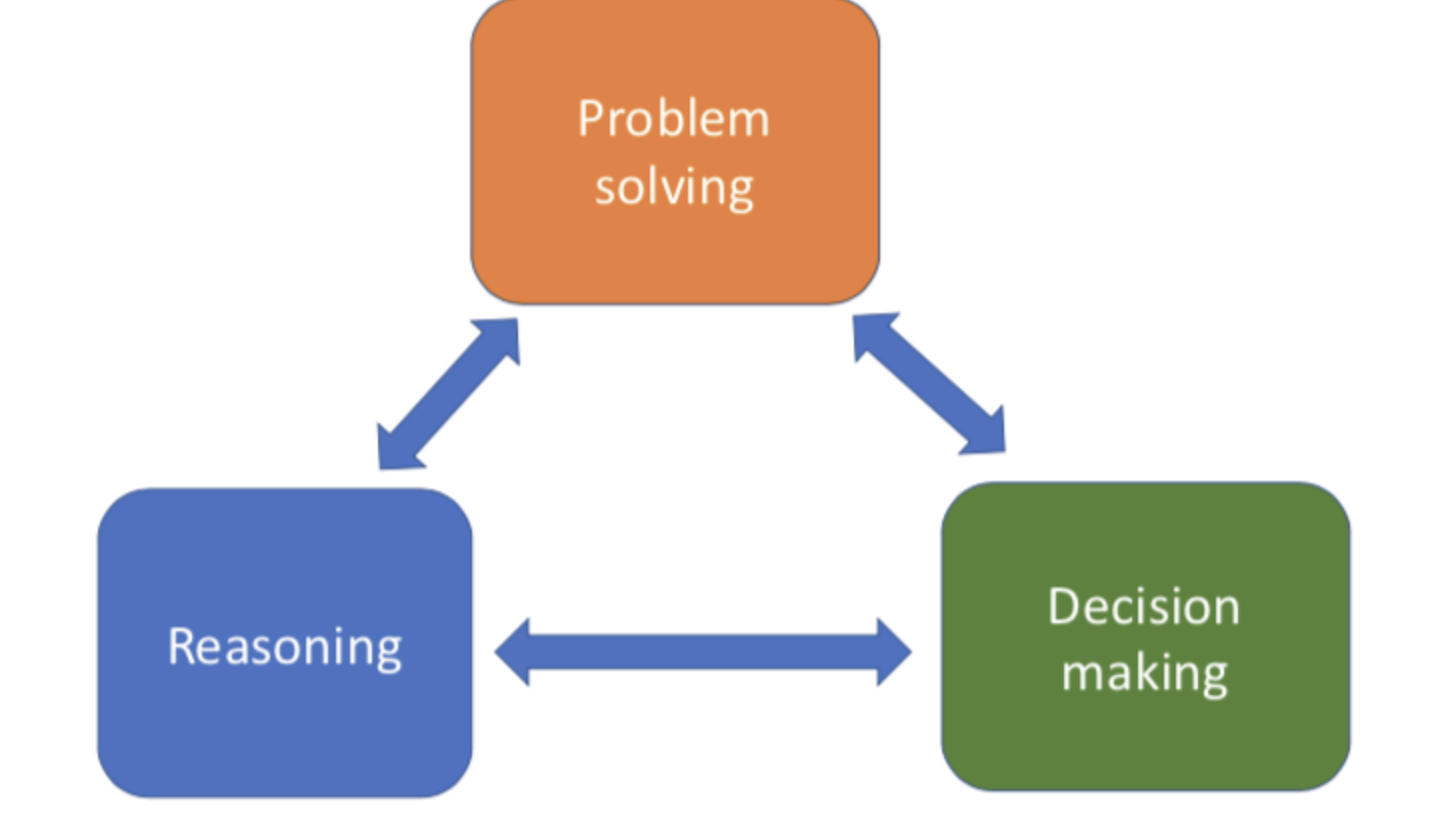
Decision making wrap-up: three main mechanisms
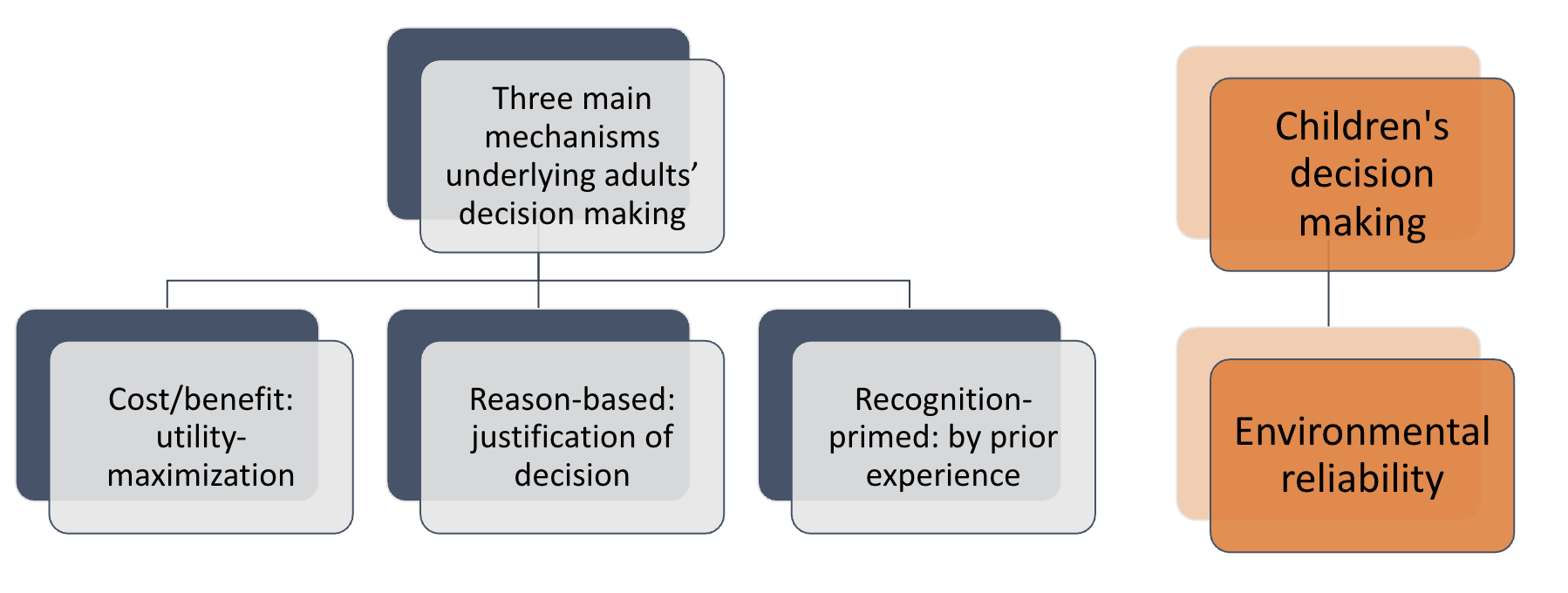
Wrap up: Decision making
Highly interacts with reasoning and problem
solving
E.g., reasoning of the problem at hand in order to form a decision
E.g. forming hypotheses deductively and inductively before making a decision (e.g. solving easy vs. hard problems first on an exam)
Framing of outcomes as evidence for linguistic relativism
Higher amount of substance abuse as well as emotional disorder can lead to riskier behavior and decisions