Ap Macro unit 4 and five
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Federal Funds rate
the interest rate at which commercial banks make overnight loans to one another
Policy rate
the interest rate at which the central bank will lend money to commercial banks
real intrest rate equation
nominal interest rate - inflation rate
Expasionary fiscal policy
Decreasing taxes and increasing government spending
Contractionary Fiscal Policy
Increasing taxes and decreasing government spending
Expansionary Monetary Policy in a limited reserves system
The central bank buys bonds, decrease the reserve requirement, decrease the discount rate
Contractionary Monetary policy in a limited reserves system
The central bank sells bonds, increase the reserve requirement, increase the discount rate
expansionary monetary policy in an ample reserves system
decrease interest on reserves, decrease the discount rate, buy bonds
Contractionary monetary policy in an ample reserves system
increase interest on reserves, increase the discount rate, sell bonds
Discount rate
The rate that the central bank charges banks when they take loans from the central bank
Interest on reserves
The rate that a central bank will pay commercial banks foe holding their reserves in the central bank
Money supply model
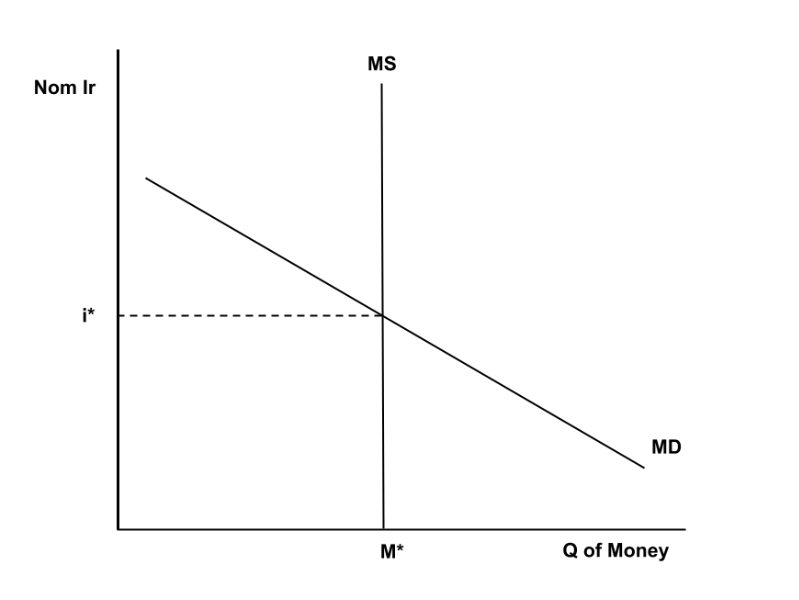
The y axis on the MS model
Nominal Interest rate
X-axis on the MS Model
quantity of Money
Money supply curve shifters
only the federal reserve can change the supply
Money demand curve shifters
a change in price level, RGDP, and transaction costs
Reserve market model
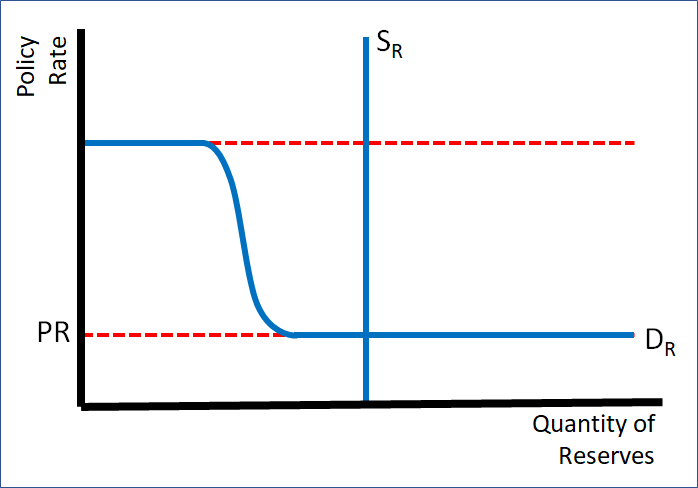
The y axis of the Reserve market Model
Policy rate
X axis on the Reserve Market Model
Quantity of reserves
Vertical line on the reserve market model
Supply of reserves
Top horizontal line on the reserve market model
Discount Rate
Bottom horizontal line on the Reserve Market Model
Demand For reserves, the dotted line is Interest on reserves
Loanable funds market Model
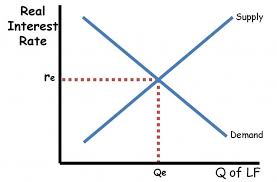
Y axis on the Loanable funds market Model
Real Interest Rate
X Axis on the Loanable Funds market Model
Quantity of loans
Downward sloping curve on Loanable funds rate model
demand for loans
upwards sloping curve on loanable funds rate mode
Supply of loanable funds
Loan demand shifters
change in private borrowing, change in public borrowing
Loan Supply Shifters
change in private savings, change in public savings
M1
Cash, Checking accounts, Travelers Checks
M2
Savings assets, Checking deposits, Money Market assets, +M1
Uses of money
Medium of exchange, unit of account, store of value
Recessionary gap on the Aggregate demand model
expansionary fiscal policy and monetary policy. Needs to increase the money supply and lower the nominal interest rate
Expansionary gap on the Aggregate Demand Model
contractionary fiscal policy and monetary policy. Need to decrease the money supply and increase the monetary policy
increase in money supply
decrease in nominal interest rate
decrease in money supply
increase in nominal interest rate
Short run Phillips curve shifter
a shift in ad results in movement along the curve, a shift in AS moves the SRPC in the opposite direction the shift occurred
Phillips curve model
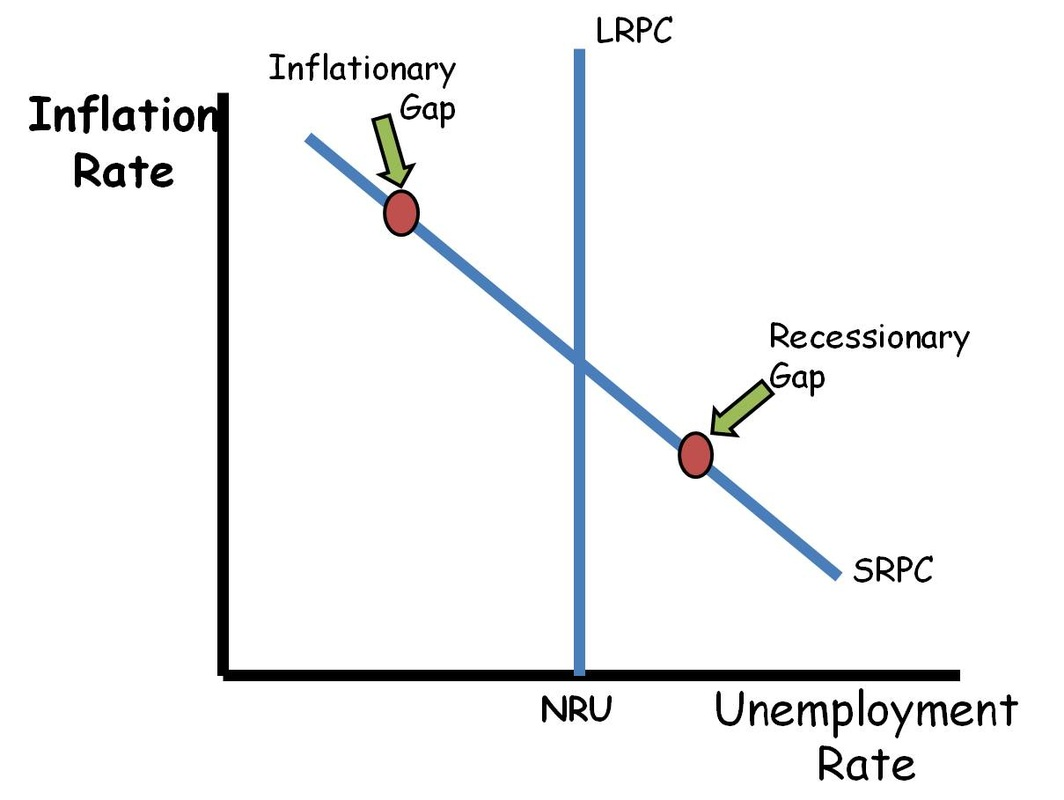
y axis for the phillps curve model
Inflation rate
x axis for the phillips curve model
unemployment rate
downward sloping line on the Phillips curve model
Short run phillips curve
upward sloping line on the philips curve model
long run phillips curve
stagflation
caused by a decrease in aggregate supply which results in an increase in unemployment and inflation along with slow economic growth
velocity of money (v)
the amount of times a dollar is respent in a year
Quantity of money theory
Money Supply (M) x Velocity (V) = Price level (P) x Quantity of Output (Y)
Nominal Gdp formula
Price level (P) x Quantity of Output (Y)
Crowding out
The government deficit spends increasing demand for loans because there is less taxes being collected or an increase in spending. Interest rates increase due to this which decreases private sector borrowing in the short run “Crowding out” the private borrower
GDP per capita
GDP / population, is used to measure a nations standard of living
Productivity
output / input , ie. $80 / 4 hours
Long run Phillips curve shifter
the curve shifts the opposite direction of an LRAS shift