electricity and device 1
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What is insulation on wires used for?
To keep us safe by stopping electricity from escaping.
What do electrons do in a copper wire without a power source?
They move randomly.
What occurs when a wire is connected to a battery in a loop?
Electrons move in one direction, forming electric current.
Define electricity.
A type of energy created by moving electrons.
What components make up an atom?
Protons (+), Neutrons (no charge), and Electrons (-).
Where are the parts of an atom located?
Protons and neutrons are in the center (nucleus), while electrons move around outside.
What is a conductor?
A material that allows electricity to flow easily, such as copper.
What is an insulator?
A material that blocks electricity, like rubber or glass.
Why are wires covered with plastic or rubber?
To keep the electricity safely contained inside.
What is a circuit?
A path for electricity to travel through.
What happens in a closed circuit?
Electricity flows continuously around the circuit.
What happens in an open circuit?
The path is interrupted, preventing electricity from flowing.
What does voltage represent?
The push that moves electricity through a circuit.
What is the meaning of 1 volt?
It gives 1 joule of energy to each group of electrons (1 coulomb).
What does more voltage indicate?
More push and an increased flow of electrons.
What is a paired cable?
Two wires twisted together, where one sends current and the other returns it or connects to ground.
Why are wires twisted in a paired cable?
To reduce external noise or interference.
Define potential difference.
The energy difference between two points, also known as voltage.
What occurs with no voltage present?
No current flows.
What is earthing?
Connecting parts to the ground for safety.
Why is the ground considered 0 volts?
It provides a safe path for excess current away from people.
Where is single-phase power used?
In homes for lighting, fans, and electrical plugs.
What types of wires are involved in single-phase power?
Live (brown or black) and Neutral (blue).
What is 3-phase 3-wire AC primarily used for?
Industrial machinery.
How many live wires does 3-phase 3-wire AC contain?
3 live wires and no neutral.
What is 3-phase 4-wire AC used for?
Industrial machines (3 phases) and lights/sockets (1 phase + neutral).
What wires are present in a 3-phase 4-wire system?
3 live wires, 1 neutral, and possibly 1 earth wire.
.L1 – Brown
L2 – Black
L3 – Grey
neutral – Blue
Why is a neutral wire used?
The neutral wire is used to complete the electrical circuit and provide a return path for current in an AC system. It is essential in systems where phase-to-neutral voltage is needed, such as in single-phase power and 3-phase 4-wire system.
Where is DC commonly used?
DC (Direct Current) – Used in:
Batteries – phones, laptops, cars
Electronics – TVs, computers (internally)
Solar panels – generate DC
Electric vehicles – motors and batteries
DC = Comes from batteries, runs electronics and vehicles
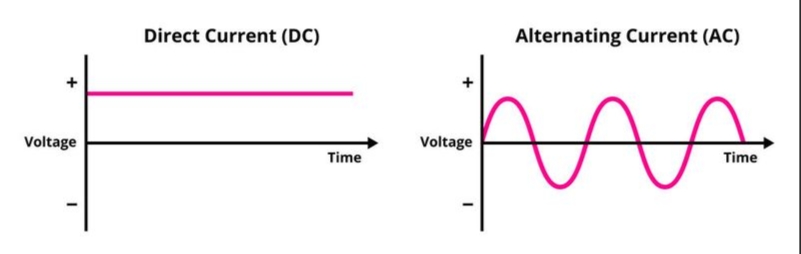
Compare AC and DC.
AC alternates direction; DC flows in one direction only.
What is electric current?
The flow of electric charge through a circuit.
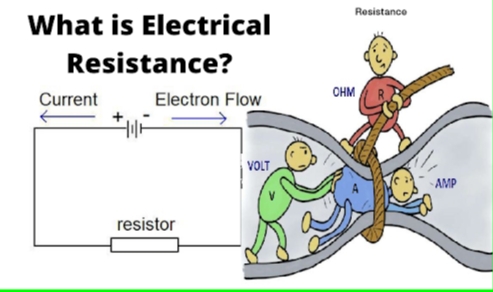
Define resistance.
Resistance: Resistance is how much a material or object resists or slows down the flow of electricity. The higher the resistance, the harder it is for electricity to pass through.
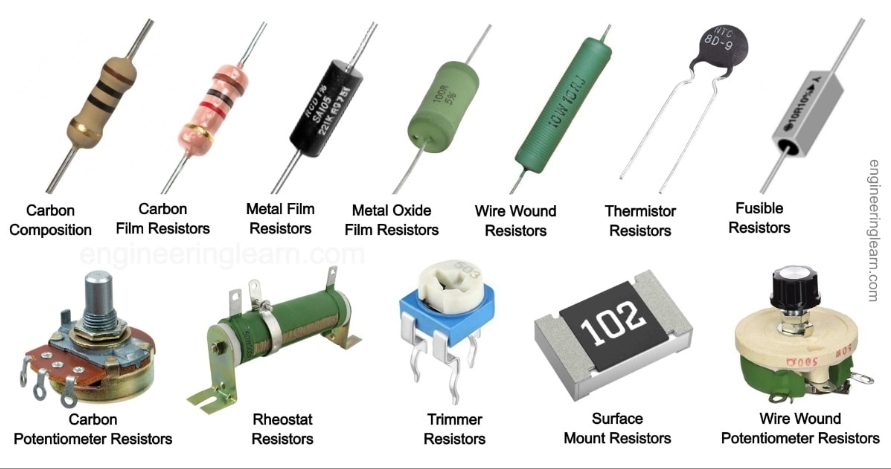
What is a resistor?
Resistor: A resistor is a small device that slows down the flow of electricity. It helps control how much electricity goes through a circuit.
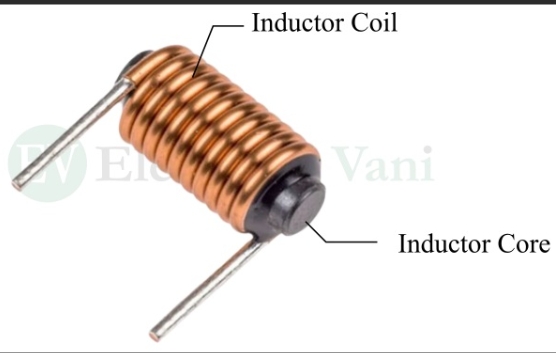
What is an inductor?
An inductor helps keep the flow of electricity more steady and smooth, especially when the electricity is switching on and off. Does that make it clearer?

What is a transformer?
A transformer is a device that changes the voltage of electricity.
For long-distance travel, it raises the voltage (called step-up).
Near homes, it lowers the voltage to make it safe (called step-down).
It has no moving parts and uses magnetic fields and coils of wire to work.

What is a capacitor?
A small device that stores and quickly releases electricity.

AMPS or current
Amps measure how much electricity is being used."
Current is the name of the flow of electric charge (moving electrons).
Amps (amperes) is the unit used to measure current.

what is a AC Current
Alternating current
Electricity changes direction back and forth, very fast.
Example: Power from your wall at home.
AC = back and forth
DC current
DC (Direct Current):
Electricity flows in one direction, like a straight line.
Example: Batteries.
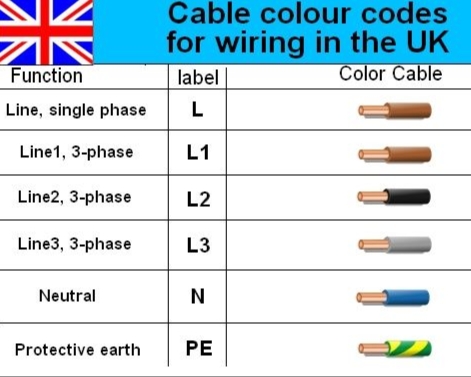
Common color codes for 3-phase 3-wire systems
.L1 – Brown
L2 – Black
L3 – Grey
where is AC used in
1. Power Transmission & Distribution
Reason: AC can be easily transformed to high voltages (for long-distance transmission) and then back to lower, usable voltages.
Examples: Power lines, substations, utility grids.