Major Muscles Chp10
1/210
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
211 Terms
What is the Origin, or head, of a muscle?
The point of muscle attachment that does NOT move when the muscle contracts
What is the insertion of a muscle?
The point of muscle attachment that DOES move when the muscle contracts?
What is a tendon?
The tissue that attaches muscle to bone
What is an Aponeurosis?
A very broad tendon
What is an agonist, or prime mover?
A muscle that causes an action when it contracts
What is an antagonist?
A muscle that works in opposition to the agonist
What are synergists?
Muscles that work together to cause a movement
What are fixators?
Muscles that stabilize joints crossed by the prime mover, they prevent movement of the Origin of the prime mover
What does the term pectoralis indicate?
Chest location
What does the term gluteus indicate?
Buttocks location
What does the term brachial indicate?
Arm location
What does the term frontalis indicate?
Frontal bone location
What does the term carpi indicate?
Wrist location
What does the term maximus indicate?
Large size
What does the term minimus indicate?
Small size
What does the term major indicate?
Larger size than other muscle
What does the term minor indicate?
Smaller size than other muscle
What does the term longus indicate?
Long size
What does the term brevis indicate?
Short size
What does the term deltoid indicate?
Triangular shape
What does the term orbicularis indicate?
Circular shape
What does the term teres indicate?
Round shape
What does the term trapezius indicate?
Trapezoid shape
What does the term rectus indicate?
Straight orientation of fasciculi
What does the term oblique indicate?
Angular orientation of fasciculi
What does the term transverse indicate?
Across orientation of fasciculi
What is fascicle/fasciculi?
A bundle / bundles of muscle fibers
What does the term biceps indicate?
Two heads / origins
What does the term triceps indicate?
Three heads / origins
What does the term quadriceps indicate?
Four heads / origins
What does the term abductor indicate?
Contraction of this muscle moves appendage away from midpoint
What does the term adductor indicate?
Contraction of this muscle moves appendage towards midpoint
What does the term masseter indicate?
Contraction of this muscle chews
What does the term flexor indicate?
Contraction of this muscle decreases the angle between two body parts
What does the term extensor indicate?
Contraction of this muscle increases the angle between two body parts
What are the functions of the head/neck muscles?
Facial expression, chewing, movement of tongue, extrinsing eye muscles, and movement of head/neck (not associated with vertebral column)
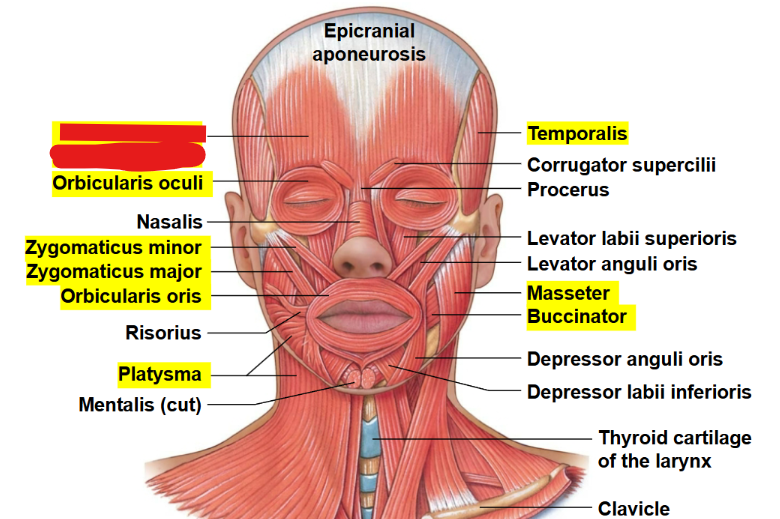
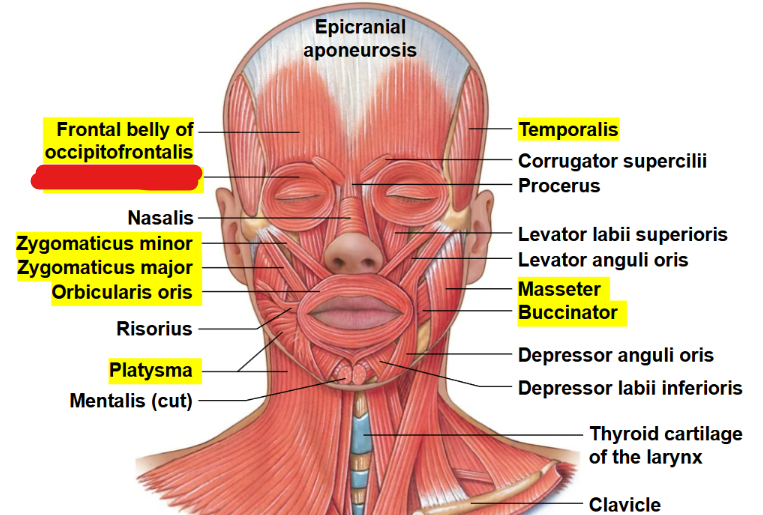
What muscle is this?
Occipitofrontalis
What muscle is this?
Orbicularis oculii
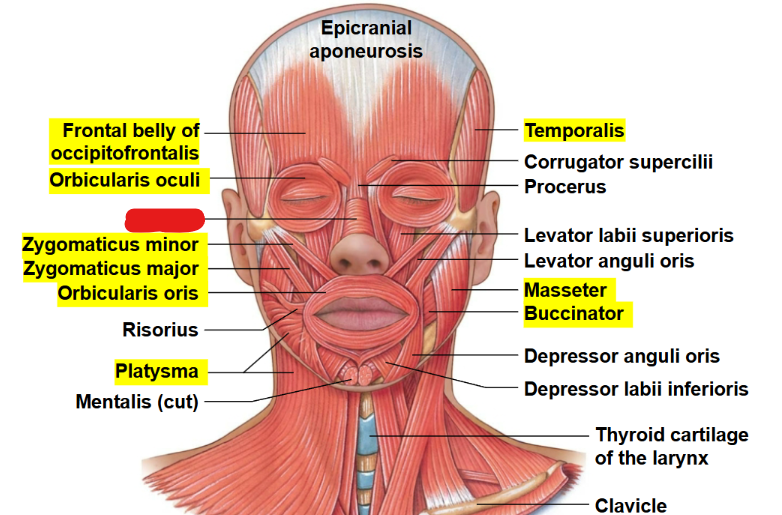
What muscle is this?
Nasalis
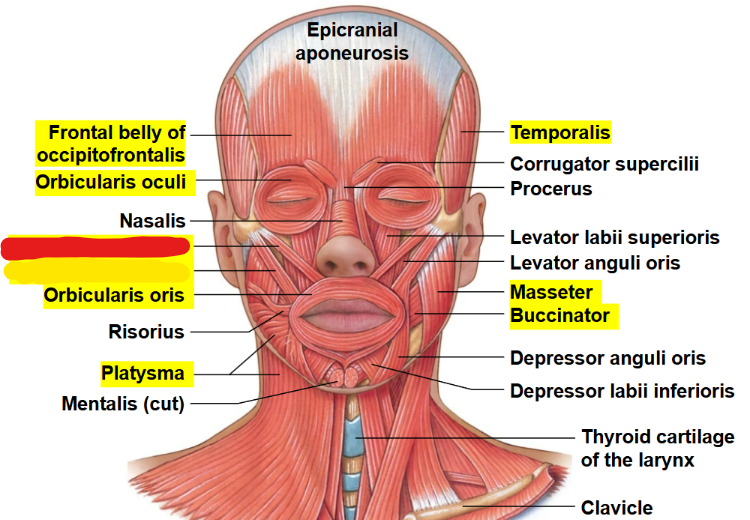
What muscle is this?
Zygomaticus minor
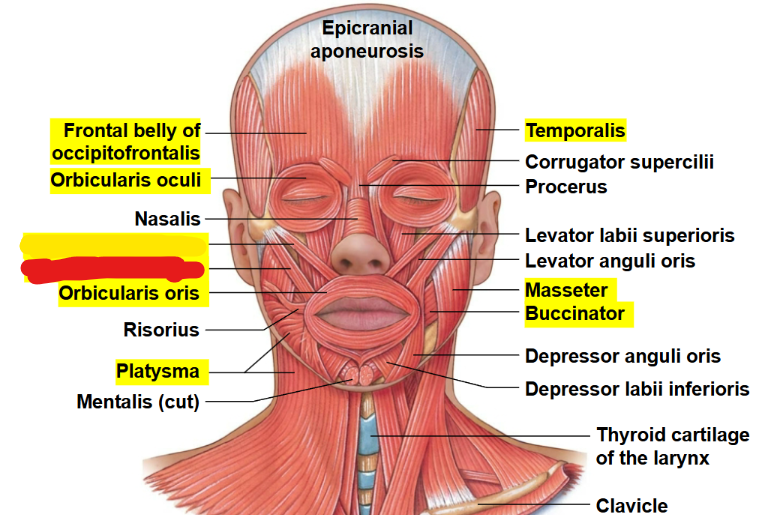
What muscle is this?
Zygomaticus major
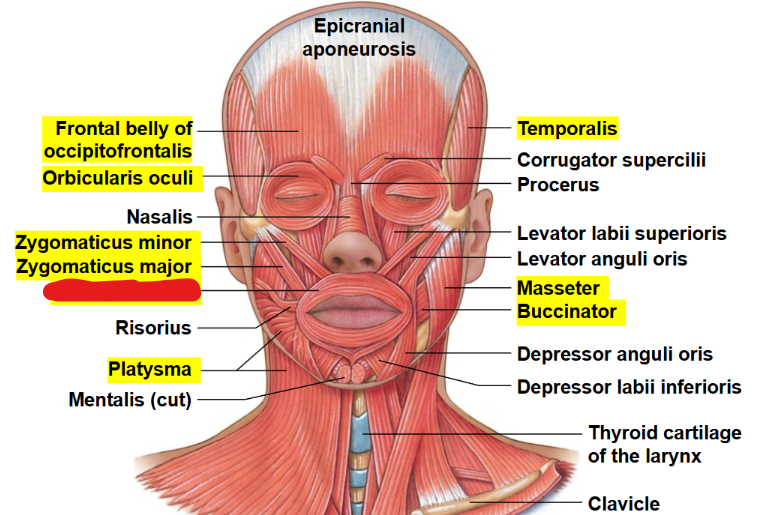
What muscle is this?
Orbicularis oris
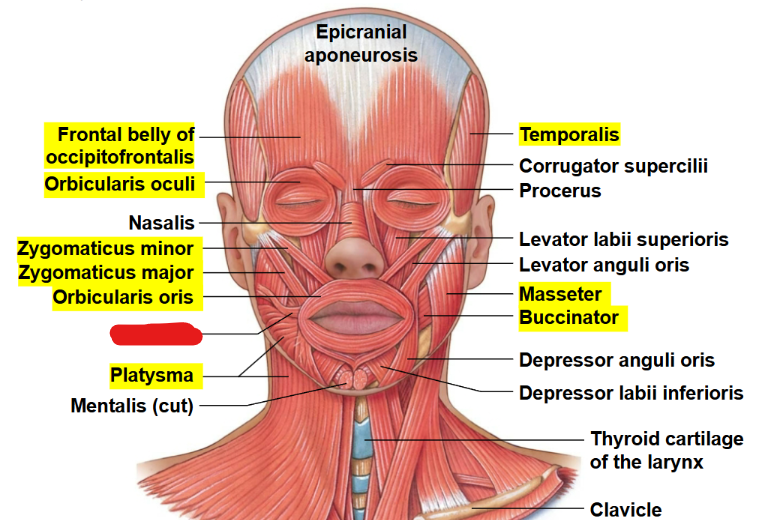
What muscle is this?
Risorius
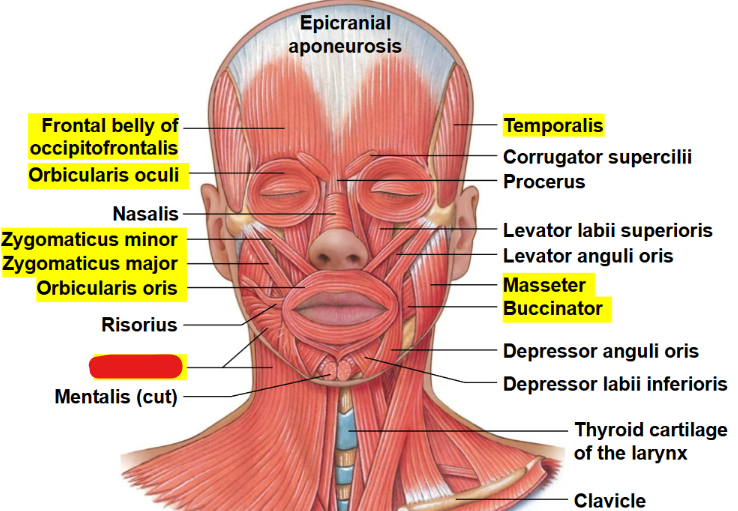
What muscle is this?
Platysma
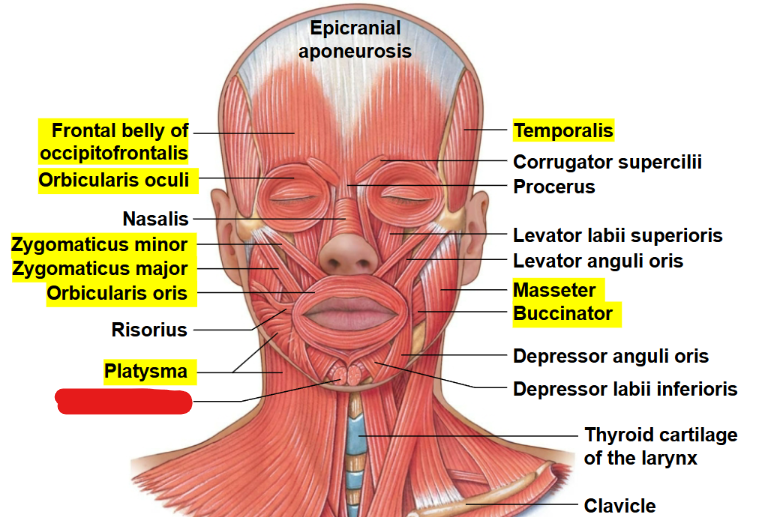
What muscle is this?
Mentalis
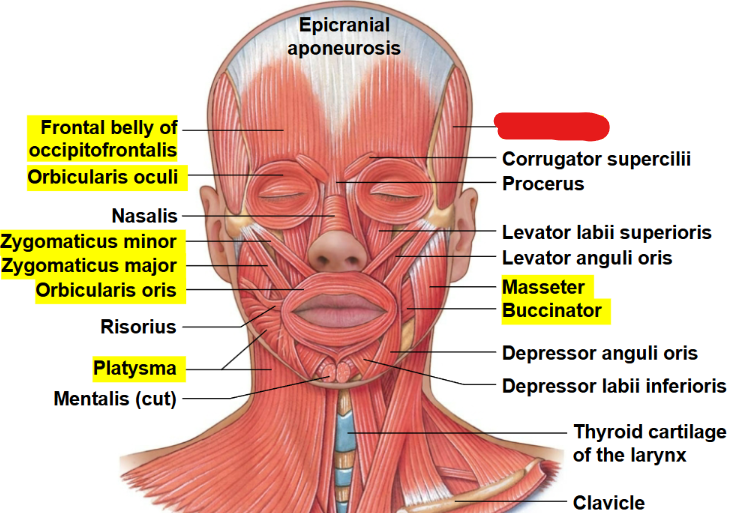
What muscle is this?
Temporalis
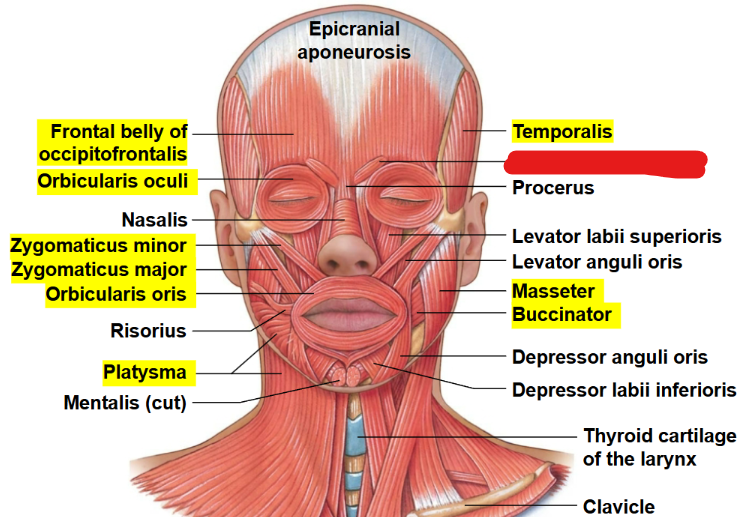
What muscle is this?
Corrugator supercilii
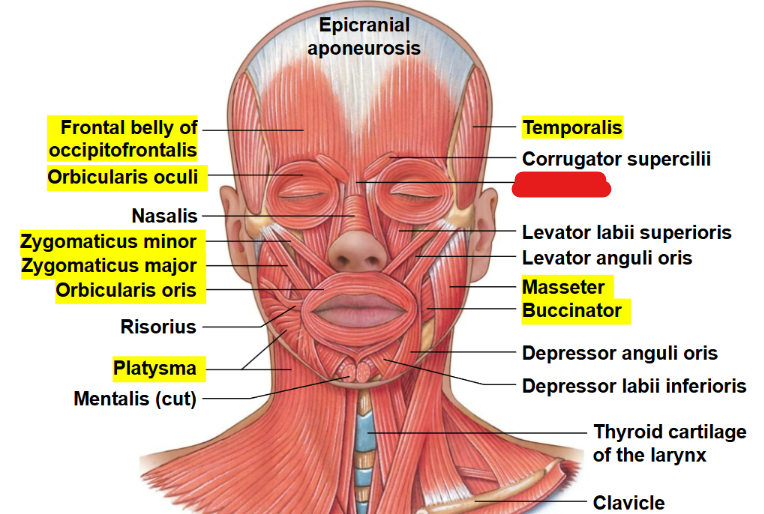
What muscle is this?
Procerus
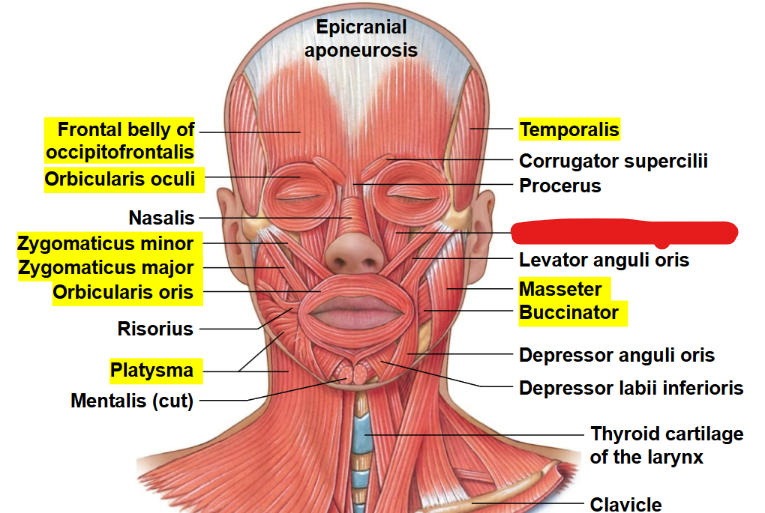
What muscle is this?
Levator labii superioris
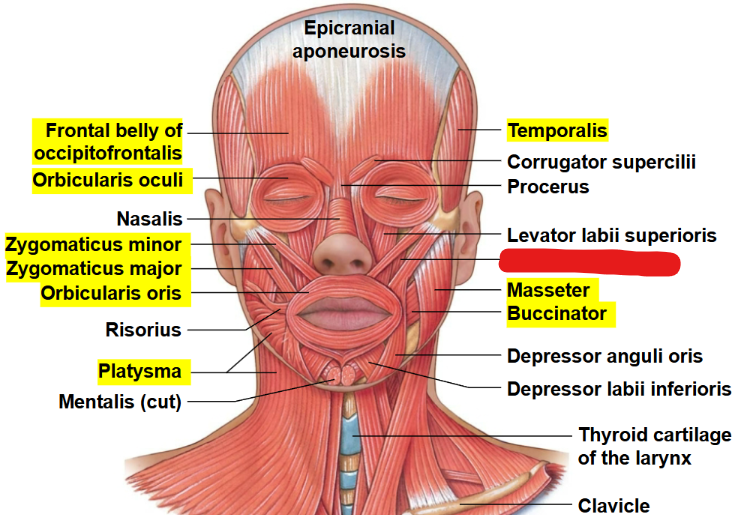
What muscle is this?
Levator anguli oris
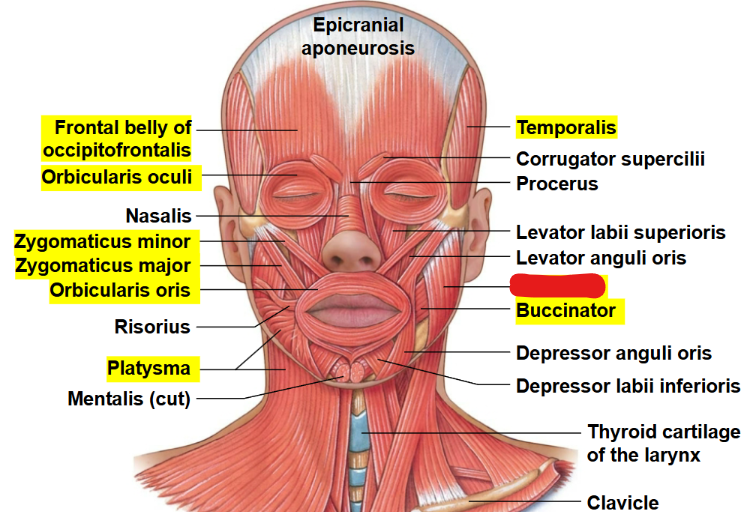
What muscle is this?
Masseter
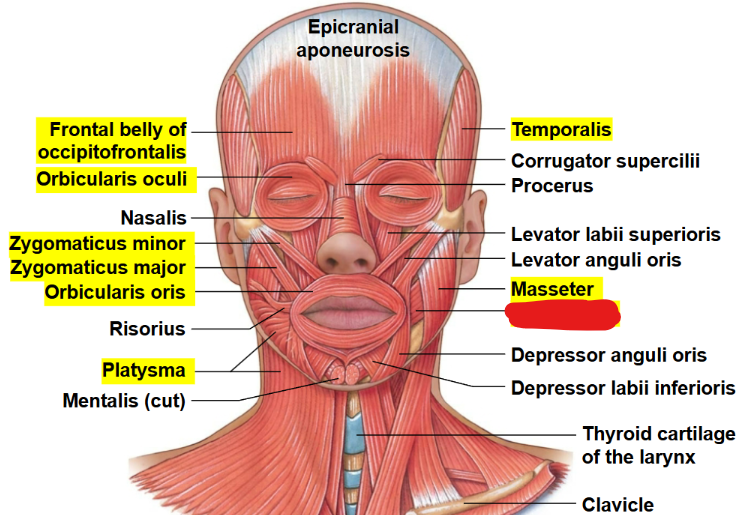
What muscle is this?
Buccinator
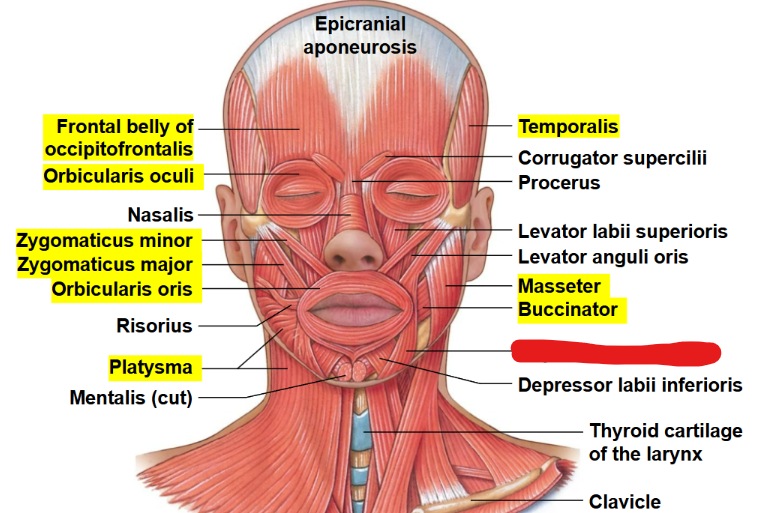
What muscle is this?
Depressor anguli oris
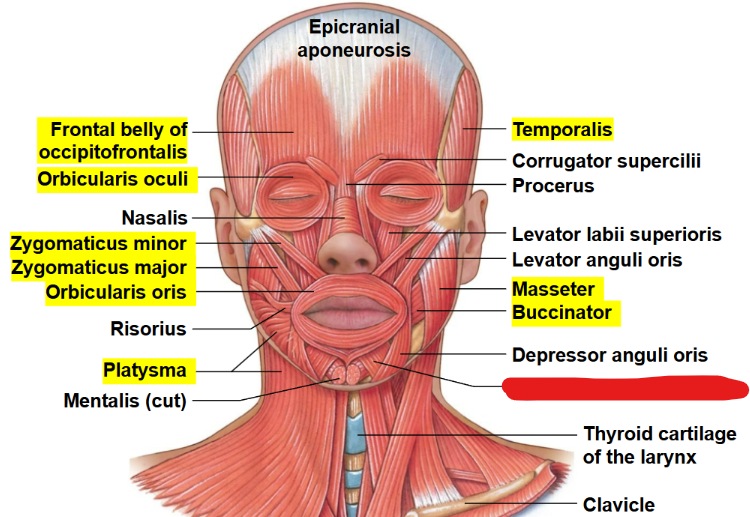
What muscle is this?
Depressor labii inferioris
What are cutaneous muscles?
Muscles that insert into the skin, action causes facial, lip, and eyelid movement. Produces facial expression
What is the Origin, insertion, and action of the Occipitofrontalis?
Origin: Occipital bone
Insertion: Skin of eyebrows, nose
Action: raising eyebrows, crinkling forehead
What is the Origin, insertion, and action of the Orbicularis Oculii?
Origin: Maxilla and Frontal Bone
Insertion: Skin
Action: Closes eye
What is the Origin, insertion, and action of the Orbicularis Oris?
Origin: Maxilla and Mandible
Insertion: Lips
Action: Closes mouth, purses lips
What is the Origin, insertion, and action of the Buccinator?
Origin: Mandible and Maxilla
Insertion: Orbicularis Oris
Action: Compressing and flattening cheeks. Whistling, blowing, and sucking
What is the Origin, insertion, and action of the Zygomaticus Major and Zygomaticus Minor?
Origin: Zygomatic bone
Insertion: Angle of the mouth and upper lip
Action: Drawing corners of mouth up, smiling
What is the Origin, insertion, and action of the Masseter?
Origin: Zygomatic arch
Insertion: Ramus of the mandible
Action: Mastication, or chewing motion
What is the Origin, insertion, and action of the Temporalis?
Origin: Temporal bone
Insertion: Mandibular ramus and Coronoid process
Action: Mastication or chewing
What are the muscles required for Mastication, or elevation of the mandible?
Temporalis and Masseter
What is the Origin, insertion, and action of the Platysma?
Origin: Second rib
Insertion: Mandible
Action: Tenses the skin of the neck, and lowers the mandible
What muscle is the major head flexor?
Sternocleidomastoid
What muscles accomplish extension of the head?
Splenius capitis, semispinalis, and trapezius muscles
What muscles accomplish lateral movements of the head?
Sternocleidomastoid, and scalene muscles
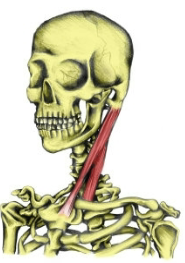
What muscle is this?
Sternocleidomastoid
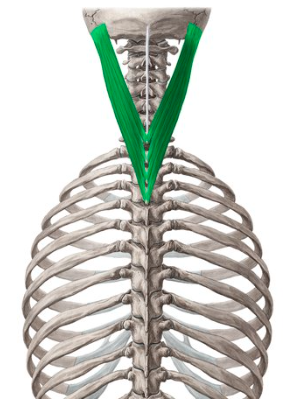
What muscle is this?
Splenius capitis
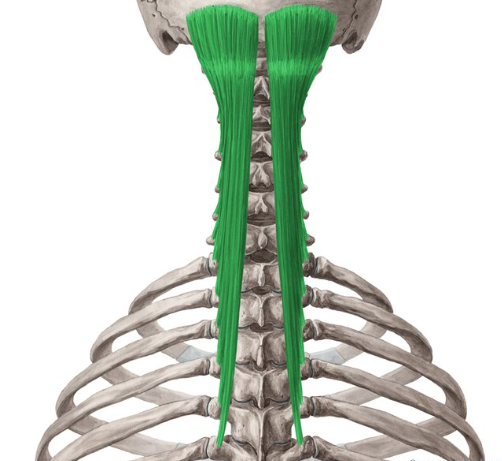
What muscle is this?
Semispinalis capitis
What is the Origin, insertion, and action of the Sternocleidomastoid?
Origin: Sternum and Clavicle
Insertion: Mastoid process of the Temporal bone
Action: Flexes and rotates the neck
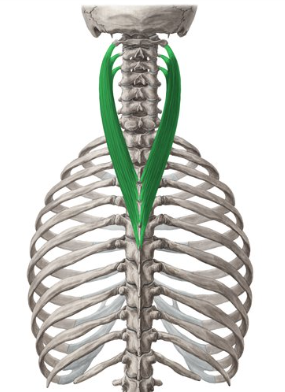
What muscle is this?
Splenius cervicis
What two muscles are part of the Splenius?
Splenius Capitis and Splenius Cervicis
What is the Origin, insertion, and action of the Splenius?
Origin: Cervical vertebrae
Insertion: Mastoid process of the Temporal Bone, and Occipital bone
Action: Both of the muscles extend the neck, separately they rotate and laterally flex the neck to similar sides
What is the Origin, insertion, and action of the Semispinalis Capitis?
Origin: Processes of lower cervical and upper thoracic vertebrae
Insertion: Occipital bone
Action: Extends and rotates the head, bends the head on either side
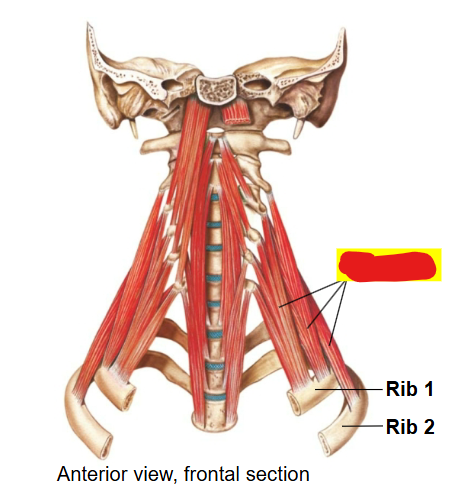
What muscles are these?
The Scalenus
What is the Origin, insertion, and action of the Scalenus?
Origin: Cervical Vertebrae
Insertion: First two ribs
Action: Elevates ribs and flexes the neck
What is the function of the muscle group Erector Spinae?
Elevates and strengthens the spine, extends the back
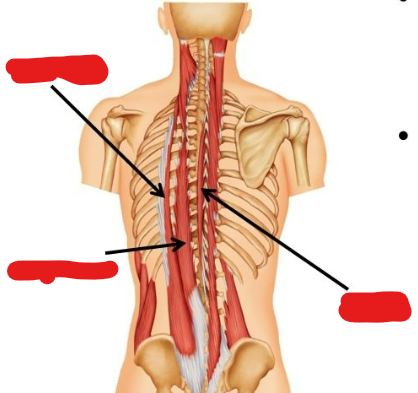
What are the different muscles in the Erector Spinae?
Iliocostalis, spinalis, and longissimus
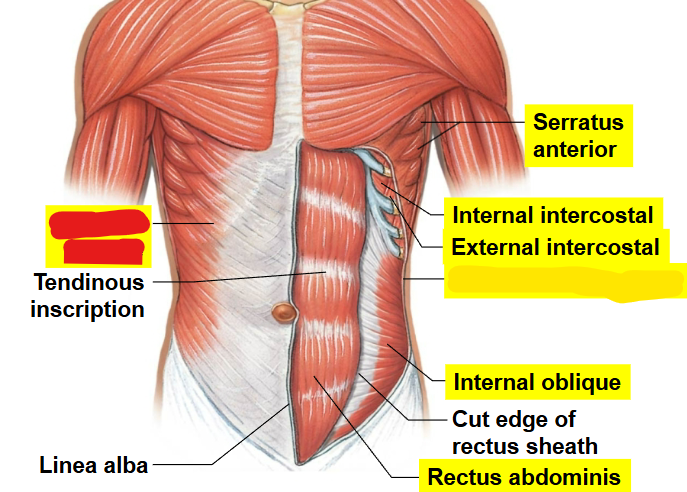
What muscle is this?
External oblique
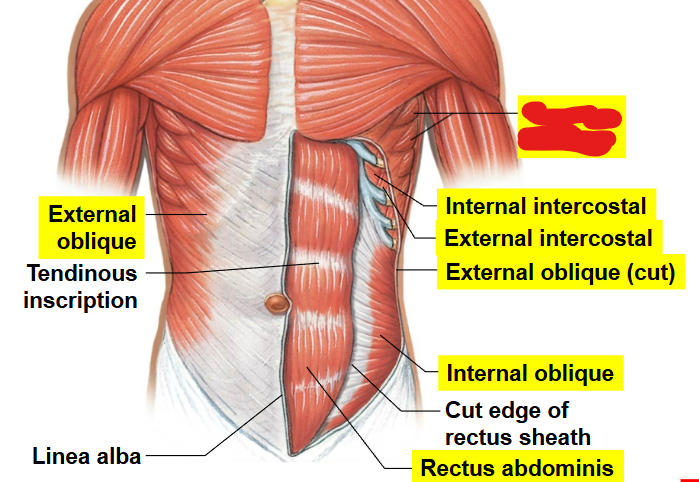
What part of the muscle is this?
Tendinous inscription
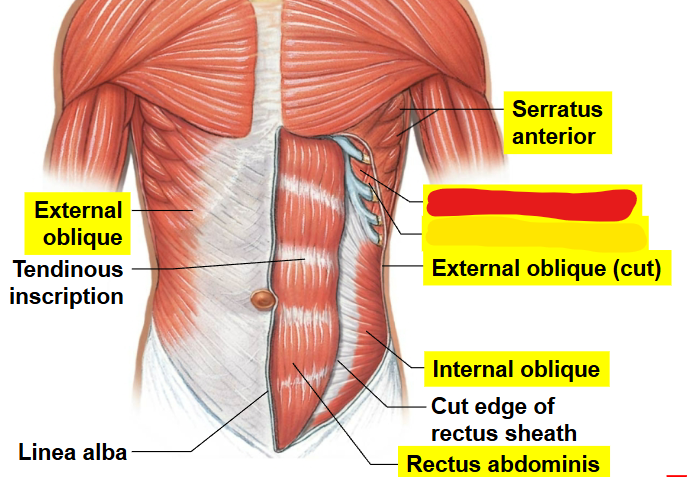
What muscle is this?
Serratus anterior
What muscle is this?
Internal intercostal
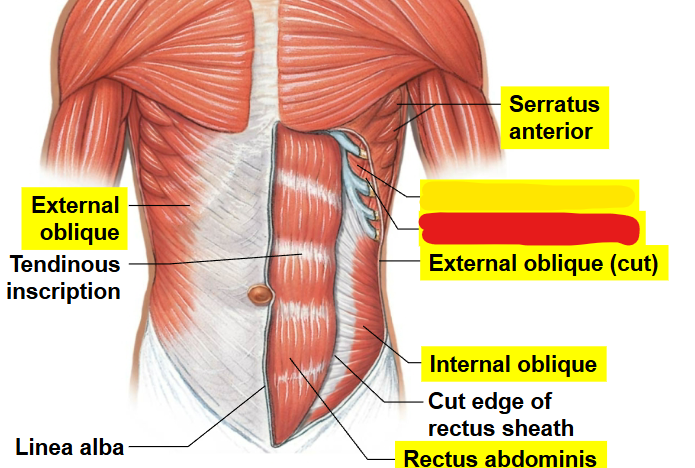
What muscle is this?
External intercostal
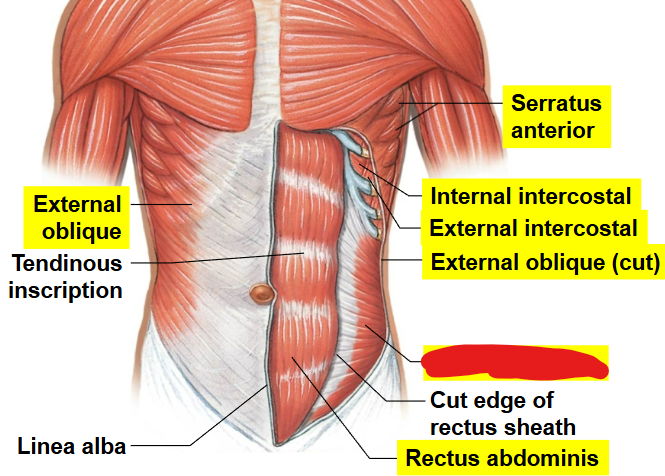
What muscle is this?
Internal oblique
What is the function of the External Intercostal muscle?
Inspiration of air
What is the function of the Internal Intercostal muscle?
Expiration of air
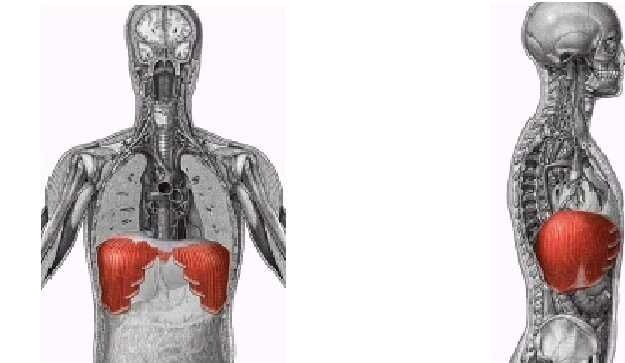
What muscle is this?
Diaphragm
What muscles is the abdominal wall composed of?
Internal Oblique, External Oblique, Transversus Abdominus, and Rectus Abdominus
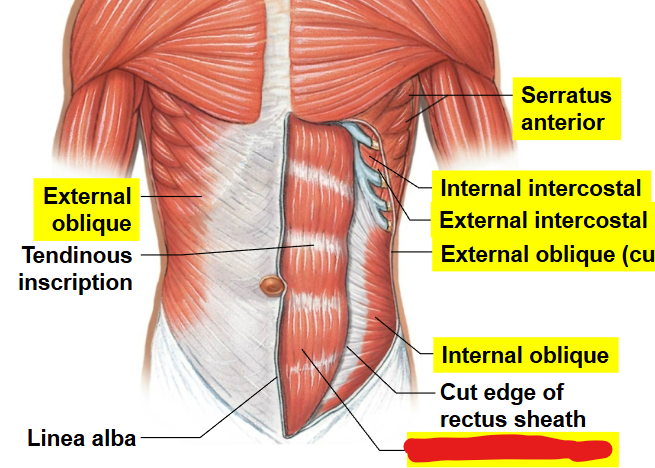
What muscle is this?
Rectus Abdominis
What is the Origin, insertion, and action of the Rectus Abdominus?
Origins: Pubic Crest and Pubic Symphysis
Insertion: Xiphoid process and costal cartilages of the 5th - 7th ribs
Action: Flexes vertebral column
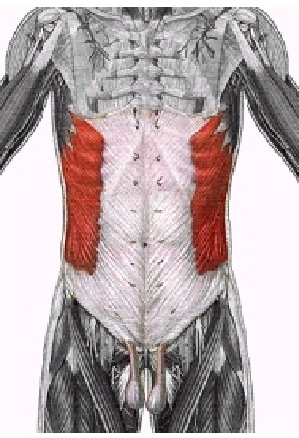
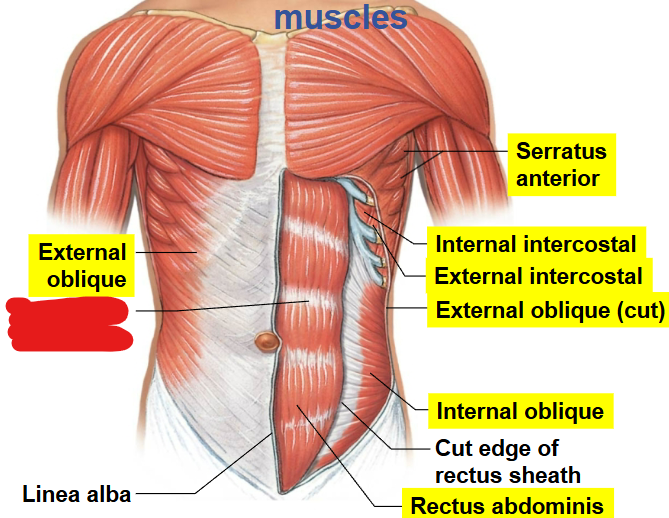
What muscle is this?
External Abdominal Oblique
What is the Origin, insertion, and action of the External Abdominal Oblique?
Origin: Last 8 ribs
Insertion: Linea alba, pubic tubercles, and iliac crest
Action: Lateral flexion and trunk rotation
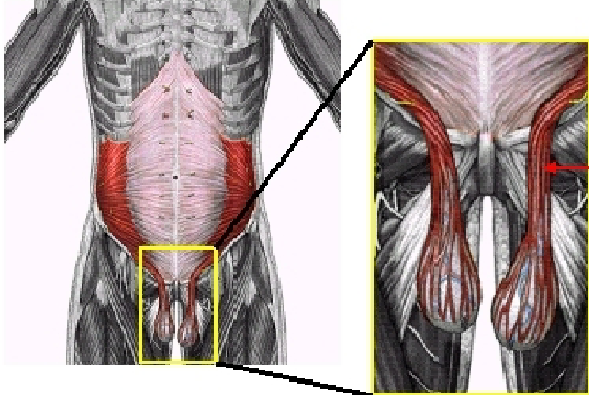
What muscle is this?
Internal Abdominal Oblique
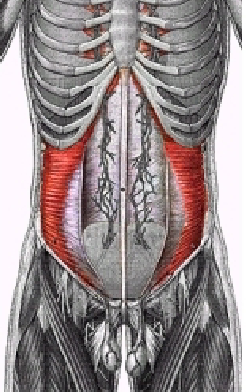
What muscle is this?
Transverse Abdominus
What are insertion points of the Internal Abdominal Oblique?
Spermatic Cord and Testicles
What are origins of the Transverse Abdominus?
Inguinal ligament, iliac crest, and cartilage of lowest 5 ribs
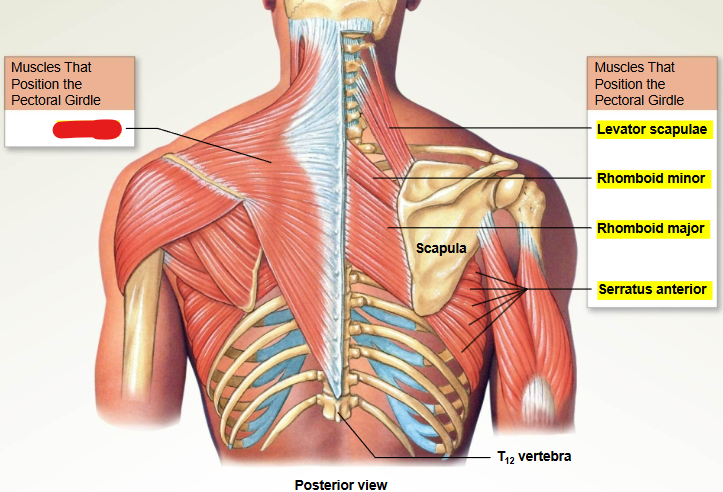
What muscle is this?
Trapezius
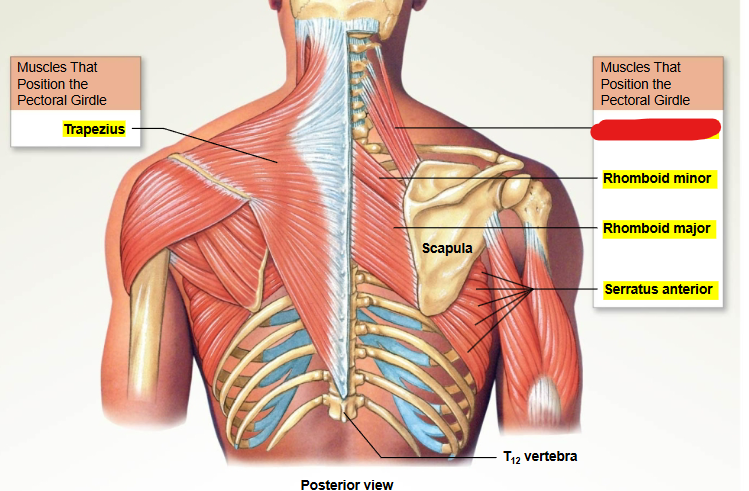
What muscle is this?
Levator scapulae
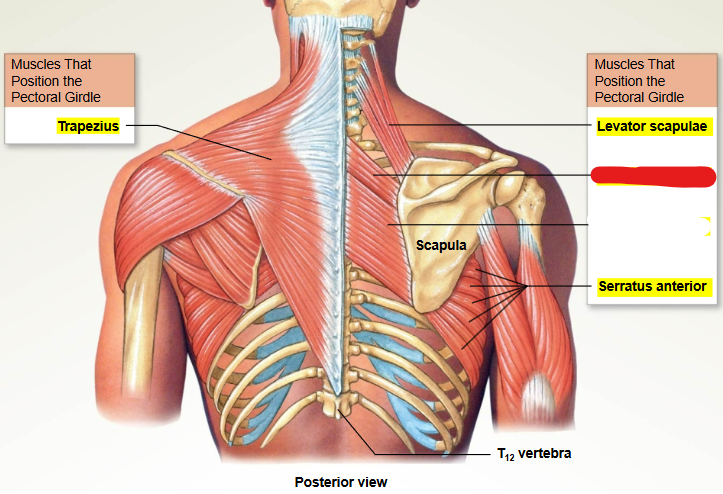
What muscle is this?
Rhomboid minor