Elements, Compounds and Mixtures (1b)
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 1, Principles of Chemistry: Part 1, b
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Element
a substance made of atoms that all contain the same number of protons and can’t be split into anything simpler
there 118 elements
ex: Copper, Iron, Arsenic
Atom
Smallst part of an element that has the element's properties.
Compound
a pure substance made of two or more different elements chemically bonded
∞ number of compounds
can’t be separated by physical means
ex: NaCl, MgO
Mixture
combination of two or more substances mixed but not chemically bonded together.
can be separated by physical means like filtration/evaporation
ex: sand and water, oil and water
Molecule
One or more element chemically combined
Heating Curve
Graph showing how a substance changes state when heated
Cooling Curve
A graph showing how a substance changes state when cooled.
Filtration
Used to separate insoluble solid impurities from a mixture.
Fractional Distillation
Used to separate miscible substances with different boiling points
Can separate more than 2 substances
Miscible Liquids
Liquids that mix
They form one layer
Eg: ethanol and water
Immiscible Liquids
Liquids that don't mix
They form more than one layer
Eg: Oil and water
Properties of the compound vs Properties of the element it's made of
Different
Pure salt from Rock Salt
Filtration and Crystallisation
Rock salt = Pure salt + insoluble impurities
Filtration: separates the insoloble impurities from the mixture
Element, Compound, Mixture Diagram
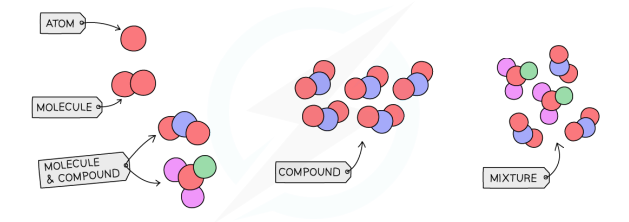
Pure Substance vs Mixture
Natural language: natural and clean, nothing added
Chemistry: pure substance = single element/compound with no other substances
ex: pure water has only H2O molecules
drinking water isn’t pure because it has additional substances like dissolved ions and chlorine
Distinguishing Purity
Pure substances melt and boil at specific temperatures ex, pure water m.p. = 0°C, b.p = 100°C
impure substances have a range of melting and boiling points because they consist of different substances
so, this data can be used to distinguish pure and impure substances
this also helps us assess the purity of drugs and foodstuffs
Assessing Purity: Process
using a melting point apparatus to heat a small portion of the sample and observe the exact melting point
compare to a data table
the closer the value is to the actual melting point, the purer the substance
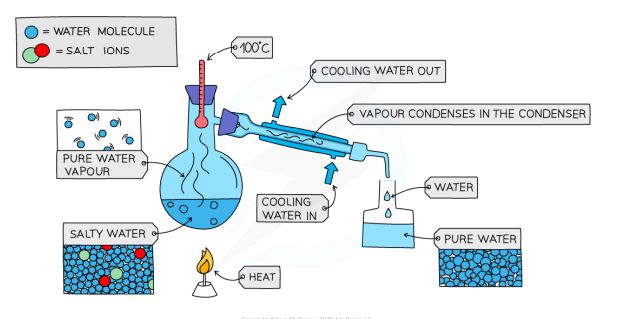
Simple Distillation
separate a liquid and a soluble solid from a solution or a pure liquid from a mixture of liquids
the solution is heated, and the liquid evaporates
the vapour rises through the neck of the round-bottomed flask
the vapour passes through the condenser, where it condenses and cools to a pure liquid that is collected in a beaker
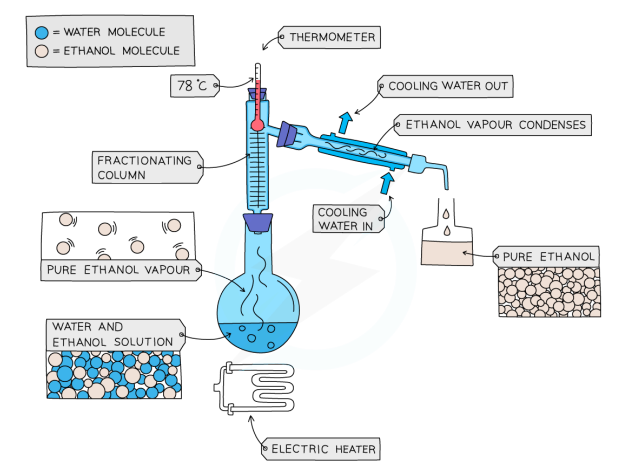
Fractional Distillation
used to separate two or more miscible liquids
solution is heated to the temperature of the substance with the lowest m.p
this substance will evaporate first, and vapours will pass through a condenser
the liquid will be condensed and collected in a beaker
once all of the substance is collected, the other liquid will be left behind
Fractional Distillation of Ethanol and Water
Ethanol b.p = 78 °C, Water b.p = 100 °C
mixture is heated until it reaches 78 c, and the ethanol boils and distills out of the mixture and condenses into the beaker
when the temperature starts to increase to 100 °C, heating should be stopped. Water and ethanol are now separated
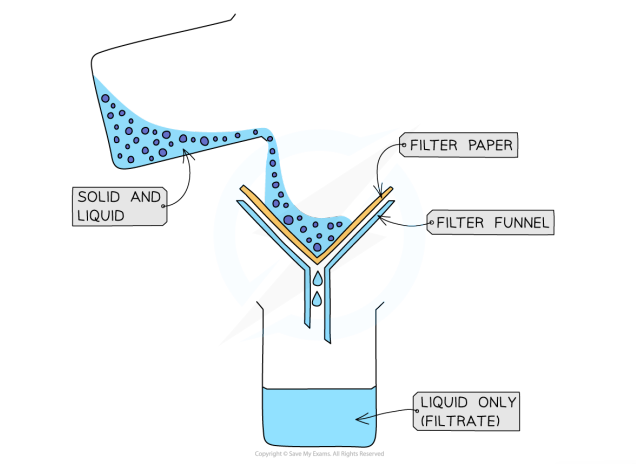
Filtration
used to separate undissolved solids from a mixture of solids and a liquid (centrifugation can also be used for this mixture)
filter paper is placed in a filter funnel above a beaker
the mixture is poured in
the filter paper will only allow small liquid particles to pass through as filtrate
solid particles are too large, so the stay behind as filtrate
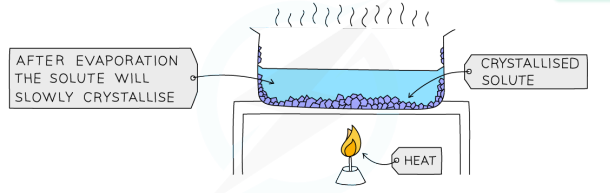
Crystalllisation
used to separate a dissolved solid from a solution, when the solute is more soluble in hot solvent than cold
solution is heated, allowing the solvent to evaporate and leave a saturated solution behind
test if the solution is saturated by dipping a glass rod into the solution (if the solution is saturated, crystals will form on the glass rod)
saturated solution will cool slowly
crystals will grow as solids come out of the solution due to decreasing solubility
crystals are collected by filtering, they are washed with cold distilled water to remove impurities and then allowed to dry
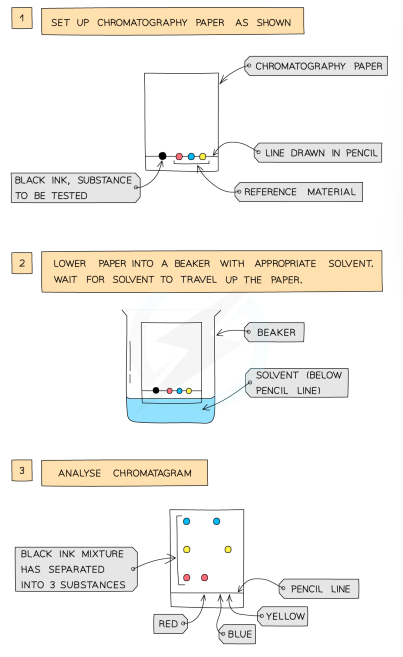
Paper Chromatography
used to separate substances with different solubilities in a given solvent
a pencil line drawn on chromatography paper, and spots of the sample are placed on it (pencil is used as ink would run into the chromatogram along with the samples)
the paper is then lowered into the solvent container (the line must be above solvent line so samples don’t wash into the solvent container)
solvent travels up the paper by capillary action, taking the coloured substances with it
different substances have different solubilities, so will travel at different rates (this causes the substances to separate, higher solubility = travel further)
this will show the different components of the ink/dye
Interpreting Chromatograms
pure substances = only one spot
impure substance = multiple spots
same substance = identical chromatograms
mixture = separates to show different components as separate spots
use a known compound to identify spots
Rf Values
used to identify components of mixtures
always the same for a particular compound
solvent changed = Rf value changes
allows to identify compounds because it can be compared with known values
Rf = distance moved by substance / distance moved by solvent