L13 - Normal Animal Behaviour 2
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Behavioural fear responses
Responses include attack, flight, or immobility.
Warning calls
Signals given to conspecifics before attack.
Species-specific behaviour
Unique behaviours and anatomy of each species.
Vigilance
Awareness of animal behaviour to ensure safety.
Heightened sense of smell
Animals may react to scents undetectable to humans.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Gear worn to protect handlers during interactions.
Blind spot
Area behind hindquarters where animals cannot see.
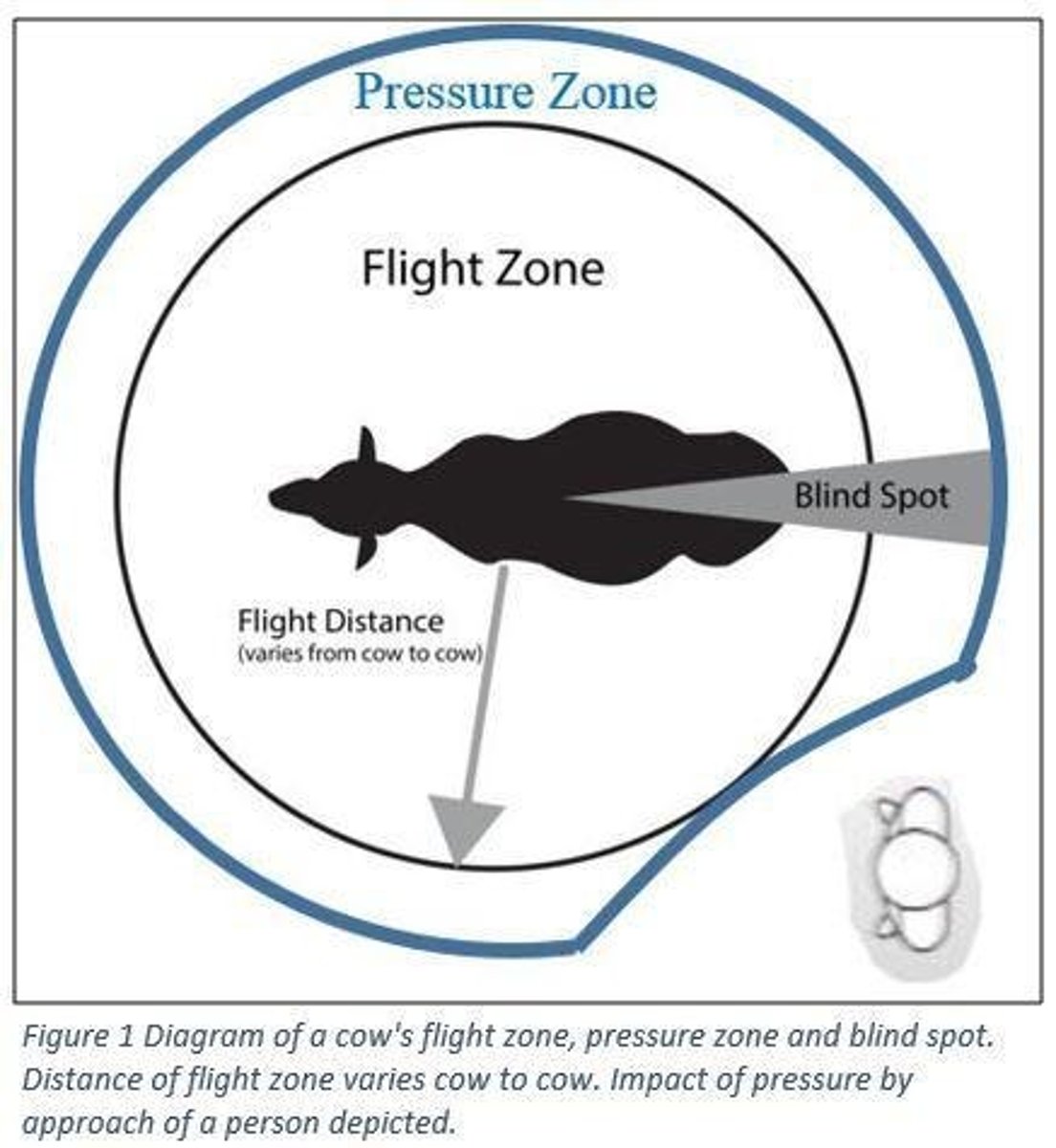
Announce approach
Touch animal's front/side to signal presence.
Cows' kicking behavior
Kicks begin at front, avoid the arch region.
Handling facilities
Designed spaces for safely managing large animals.
Exit strategy
Always leave a way to escape during handling.
Animal movement
Important when moving animals into vehicles or chutes.
Refined handling procedures
Adjust techniques based on observed animal behaviour.
Poor welfare outcomes
Negative effects during handling can hinder treatment.
Firm but gentle handling
Technique to build trust and confidence with clients.
Skilful handling
Improves patient coping during veterinary procedures.
Diagnostic parameters
Proper handling aids in accurate health assessments.
One Health
Interdependence of human and animal health.

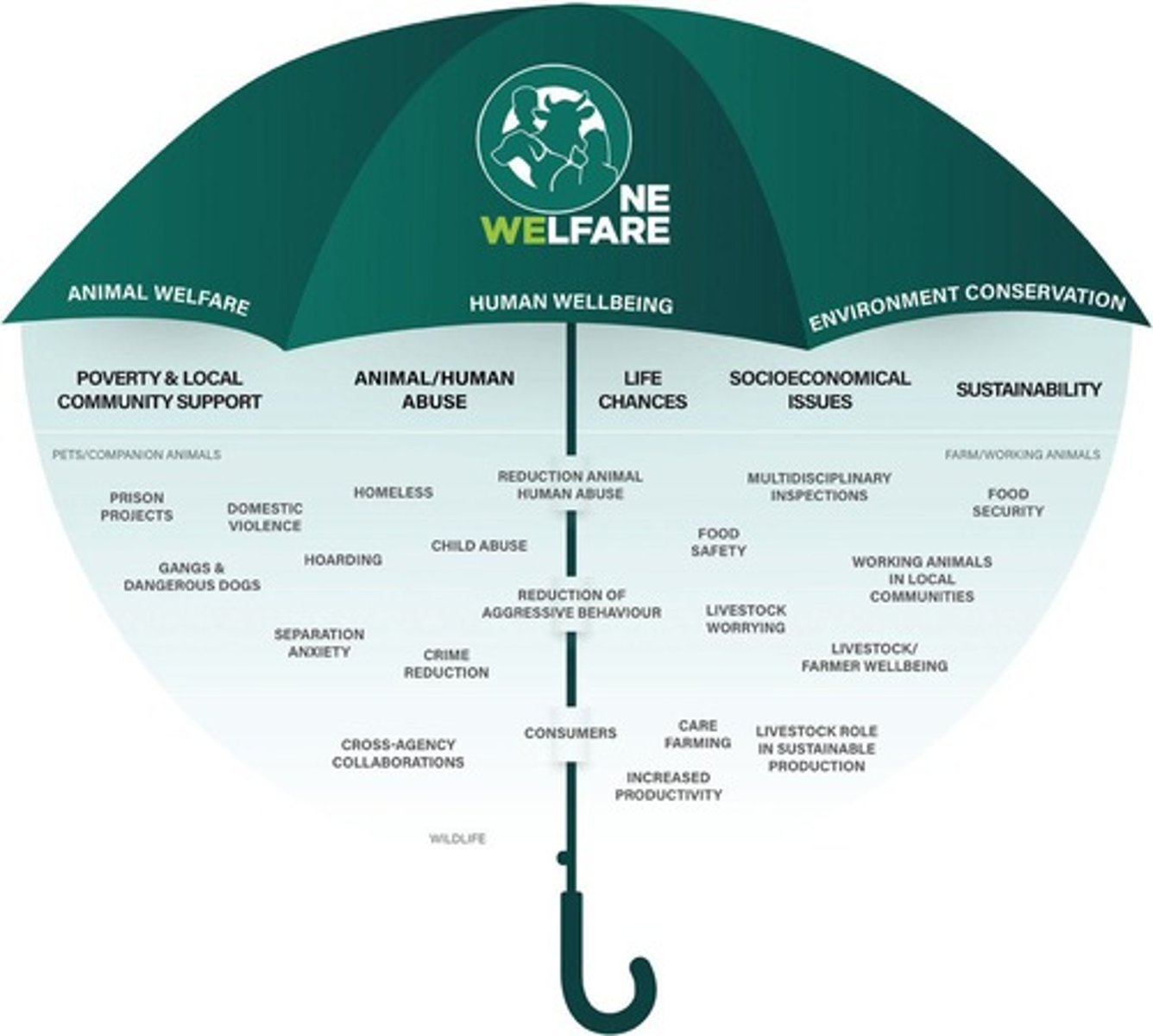
One Welfare
Links animal welfare, human wellbeing, and environment.
Human-Animal Relationship (HAR)
Interactions between humans and animals affecting welfare.
Occupational well-being
Farmer satisfaction linked to better animal welfare.
Cooperative care
Training animals to participate willingly in care.
Normal behaviour
Expected actions of healthy animals.
Stereotypies
Abnormal behaviours indicating potential welfare issues.
Evolutionary history
Understanding natural behaviours shaped by domestication.