Neuroanatomy and Neurons
1/167
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
168 Terms
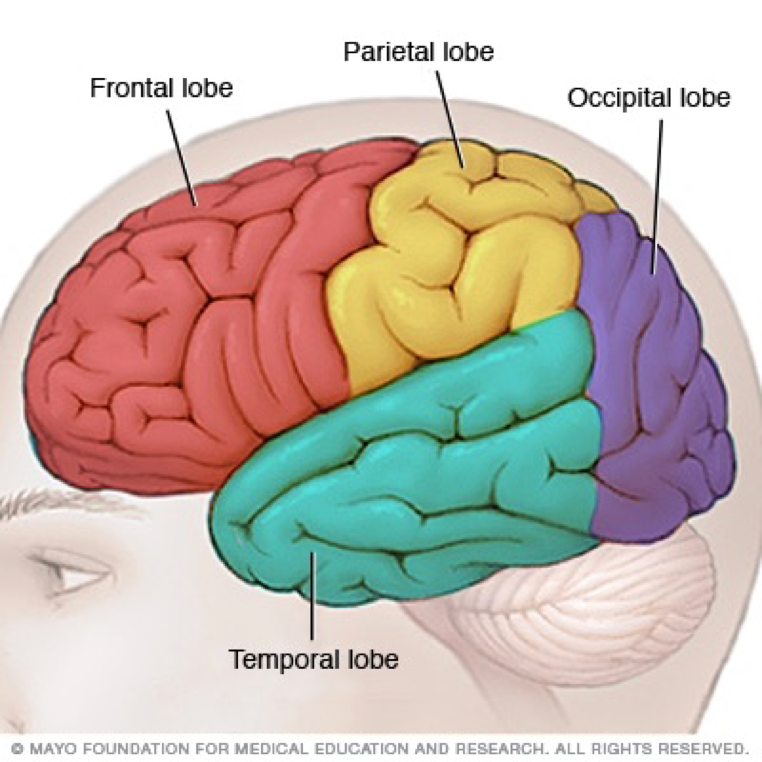
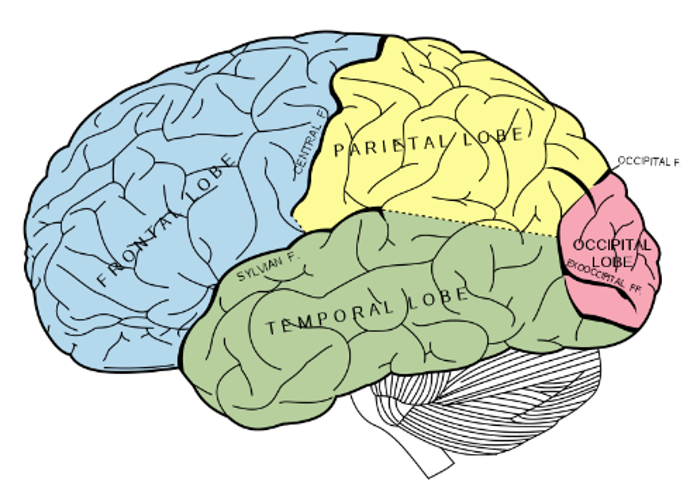
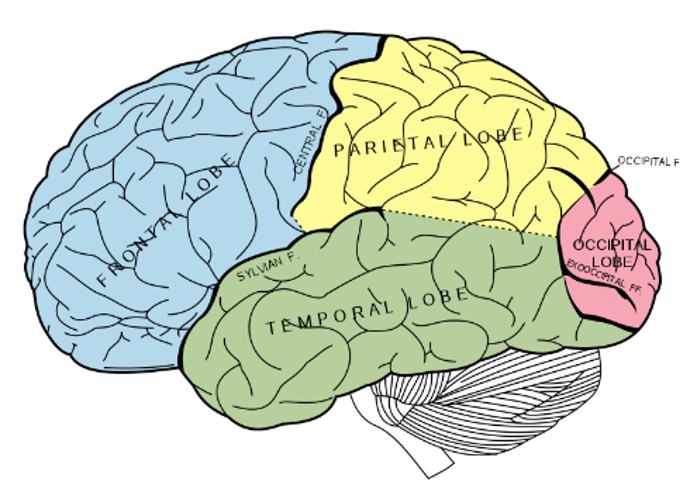
what are the 4 main lobes of the brain
frontal lobe
pariental lobe
occipital lobe
temoral lobe
where is the occipital lobe located
at the posterior (back) end of the cortex
what is the occipital lobe important for
vision
what occurs if the occipital lobe is damaged
loss of vision
what are some disorders of the occipital lobe
visual hallucinations (visual images with no external stimuli)
visual illusions (disorted perceptions)
what are visual hallucinations
visual images with no external stimuli
what are visual illusions
distorted perceptions, can take the form of objects appearing larger or smaller than they actually are, objects lacking color or objects having abnormal coloring.
how can visual hallucinations occur
can be caused by lesions to the occipital region or temporal lobe seizures.
what can occur if there was a lesion in the pariental temoral association area
can cause word blindness with writing impairments (alexia and agraphia)
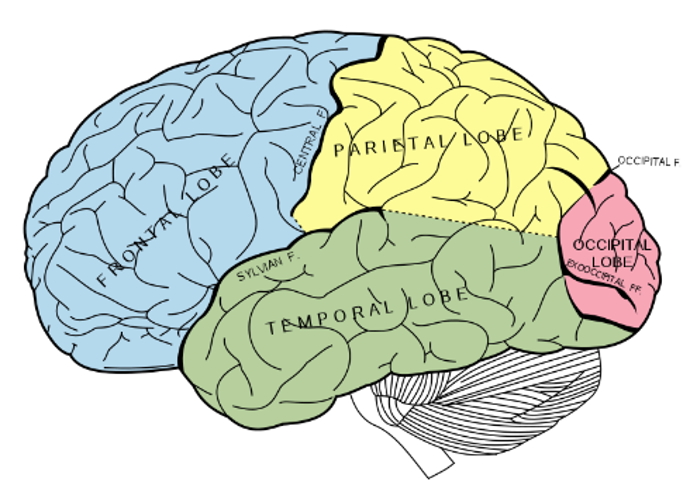
whare is the pariental lobe located
infront of the occipital lobe, behind the central fissure/sulcus
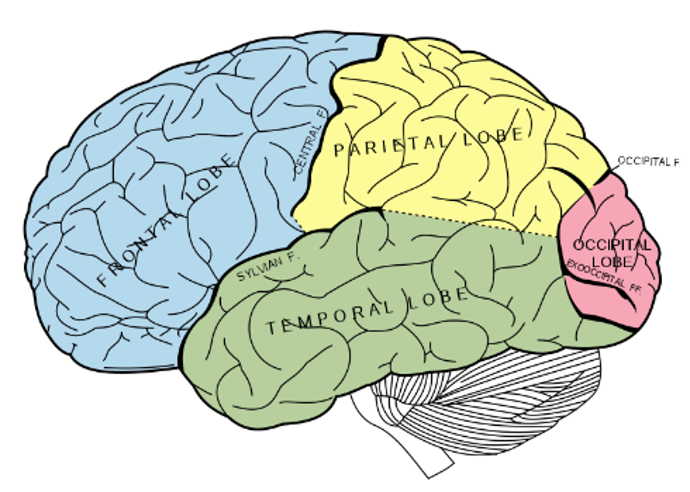
function of the pariental lobe
spatial awareness
locationg the body in space (somatosensation)
interpretaing visual information/visual recognition
taste temperature and touch
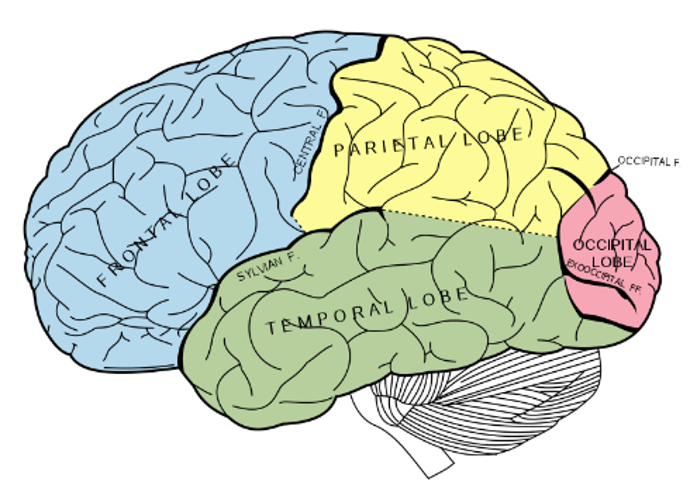
what occurs if the pariental lobe is damaged unilaterally
hemispatial neglect can result
what happens If the pariental lobe is damaged by a stroke
Attention and experience heavy spacious neglect
what happens if the pariental lobe is damaged at the right
wont be able to pay attention at the left side
what is hemispatial neglect
the inability of a person to process and perceive stimuli on one side of the body or environment, where that inability is not due to a lack of sensation
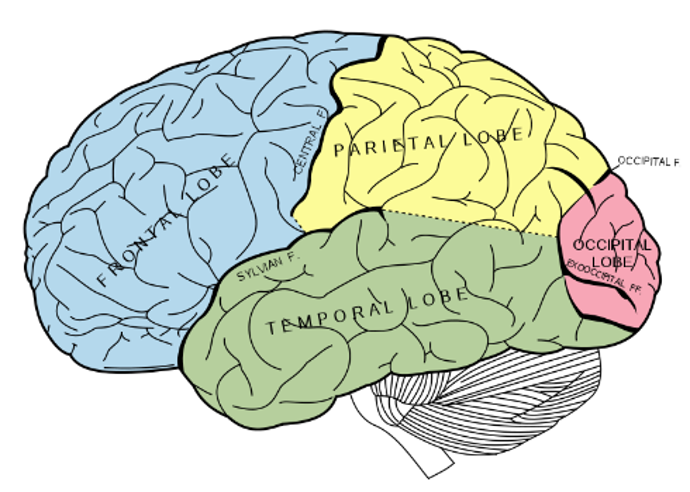
where is the temporal lobe located
underneath the other lobes under teh sylvian/lateral fissure
function of the temporal lobe
language
hearing and selective listening
receives sensory info such as sounds & speech from the ears
comprehension of meaningful speech
plays a role in emotion & memory
who identified the eight pricipale symptoms of tempral damage
Kolb & Wishaw (1990)
Kolb & Wishaw (1990) have identified eight principle symptoms of temporal lobe damage:
1) disturbance of auditory sensation and perception
2) disturbance of selective attention of auditory and visual input
3) disorders of visual perception
4) impaired organization and categorization of verbal material
5) disturbance of language comprehension
6) impaired long-term memory
7) altered personality and affective behavior
8) altered sexual behavior.
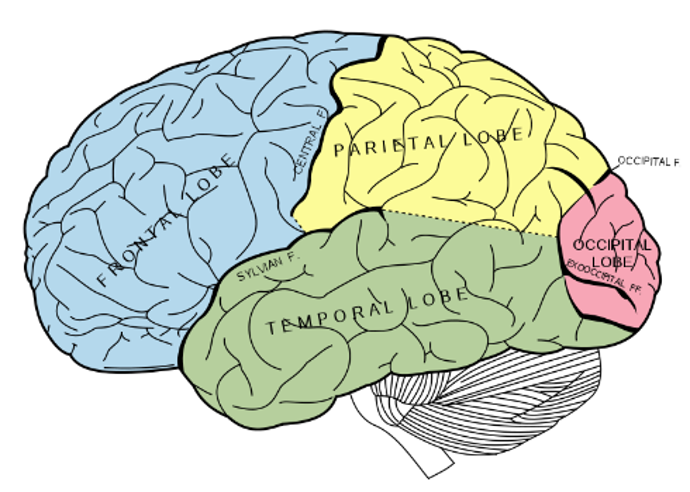
where is the frontal lobe located
at the front of the brain, anterior to the pariental loce and dorsal to the temporal lobe
what does the frontal lobe deal with
Deals with complex processes like language, planning, coordinating, carrying out plans, controlling behaviour
where is the primary motor cortex located
in the frontal lobe (precentral gyrus)
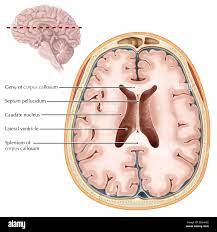
what are ventricles used for in the brain
cushioning
what are the ventrickes of the brain called
ventricles
where do the ventricles extend to
extend through the brainstem to the central canal of the spinal cord
what are ventricles filled with
CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF)
where is the cerebrospinal fluid (cfs) produced
CHLORIDE PLEXUS in the interventricular foramen
what are the 4 ventricles in the brain
–Right Lateral Ventricle
–Left Lateral Ventricle
–Third Ventricle
–Fourth Ventricle
function of the CSF (cerebrospinal fluid)
cushions the brain on impact
keeps the brain buoyant in the skull
regulates cerebral blood flow
clearing waste from the brain
what does the cns in the spinal cord carry
carries nerve fibres to/from the rest of the body
what does the CNS do in the spinal cord
continues from the medulla oblangata in the hindbrain
travels down the vertebral column
terminates at the lower boundary of the fisrt LUMBAR VERTEBRAE
how many individual vertebrae is there in the spinal cord
24 (protect the spinal cord)
name the components of the spine
cervical
thoracic
lumbar
sacral
coccygeal
where do nerve fibres emerge from the spinal cord
between the verebrae to form 31 sets of dorsal and ventral roots
is dorsal, motor or sensory
sensory
is ventral motor or sensory
motor
what does the peripheral nervous system consists of
motor neurons
sensory neurons
somatic nervous system
autonomic nervous system
sympathetic division
parasympathetic division
what does the somatic nervous system control
controls voluntary movement
what does the autonomic nervous system control
contols the involuntary responses
what is the sympathetic divasion also now as
fight or flight
what is the central nervous system composed of
brain and spinal cord
where does the peripheral nervous system lie
lies outside of the brain and spinal cord/skull and spine
what does the peripheral nervous system allows the brain to do
■communicate with muscles and organs via nerve fibres
what carries information from the sensory receptors towards the CNS
sensory/afferent nerves
what do motor/efferent nerves carry
carry info from the CNS to muscle glands via vntral roots
what are reflexes
A mechanism whereby the spinal cord can step in and make a decision, bypassing the brain!
what is the blood brain barrier
a selectively permeable wall between the CNS and the rest of the body
what does the blood brain barrier protect the brain from
from toxic substances from the blood
peripheral VS CNS
PNS
not encased
not protected
can be exposed to toxins, injuries
regeneration occurs here
two divisions: somatic and autonomic nervous systems
CNS
Encased in bone (skull, spine)
protected by the BLOOD BRAIN BARRIER
less likely to be exposed
less regenaration occurs here
no divisions
what does the somantic nervous systme controls
voluntary muscular movement in the body
what is the somantic nervous system made up of
cranial nerves, spinal nerves and many smaller association nerves
where is the cranial nerves in the somantic nervous system exit
from underneath of the brain
where do the spinal nerves exit in the somantic nervous system
from the spinal cord
how many cranial nerves are there
12 pairs
what are cranial nerves responsible for
both sensory and motor information transmission
what do the cranial nerves attach to
connect directly into the brain or into the very beginnings of the spinal cord (at the brain stem), by-passing the spinal column.
name all the cranial nerves
OLFACTORY
OPTIC
OCULOMOTOR
TROCHLEAR
ABDUCENS
TRIGEMINAL
FACIAL
VESTIBULOCOCHLEAR
GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL
HYPOGLOSSAL
VAGUS
ACCESSORY
optic
visual info (belongs to the CNS)
olfactory
sense of smell
1.OCULOMOTOR
2.TROCHLEAR
3.ABDUCENS
Coordinate eye movements
TRIGEMINAL
information from the teeth, gums, face, anterior tongue
FACIAL
facial expressions
VESTIBULOCOCHLEAR
hearing & balance
GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL
taste, salivation
HYPOGLOSSAL
tongue movement
VAGUS
parasympathetic innervation – blood pressure, heart rate
ACCESSORY
shoulder and head movement
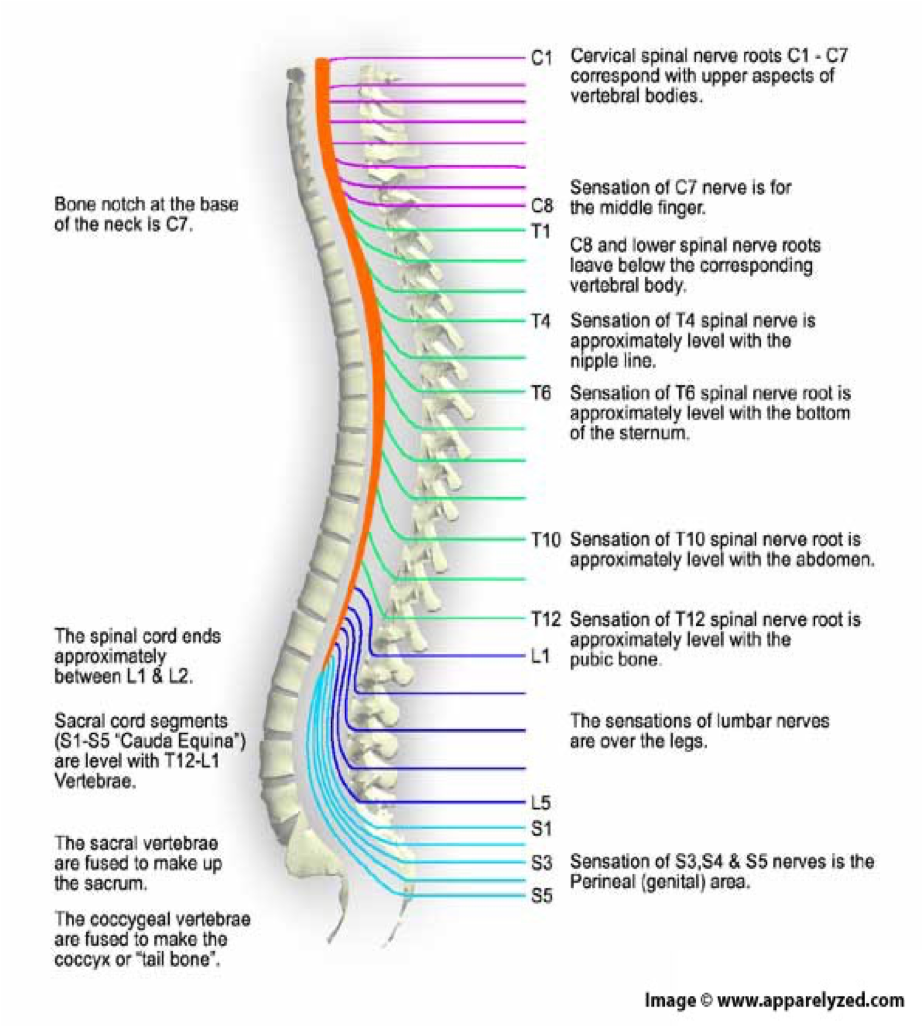
how many spinal nerves are there
31 pairs
C1-8
pairs of cervical nerves
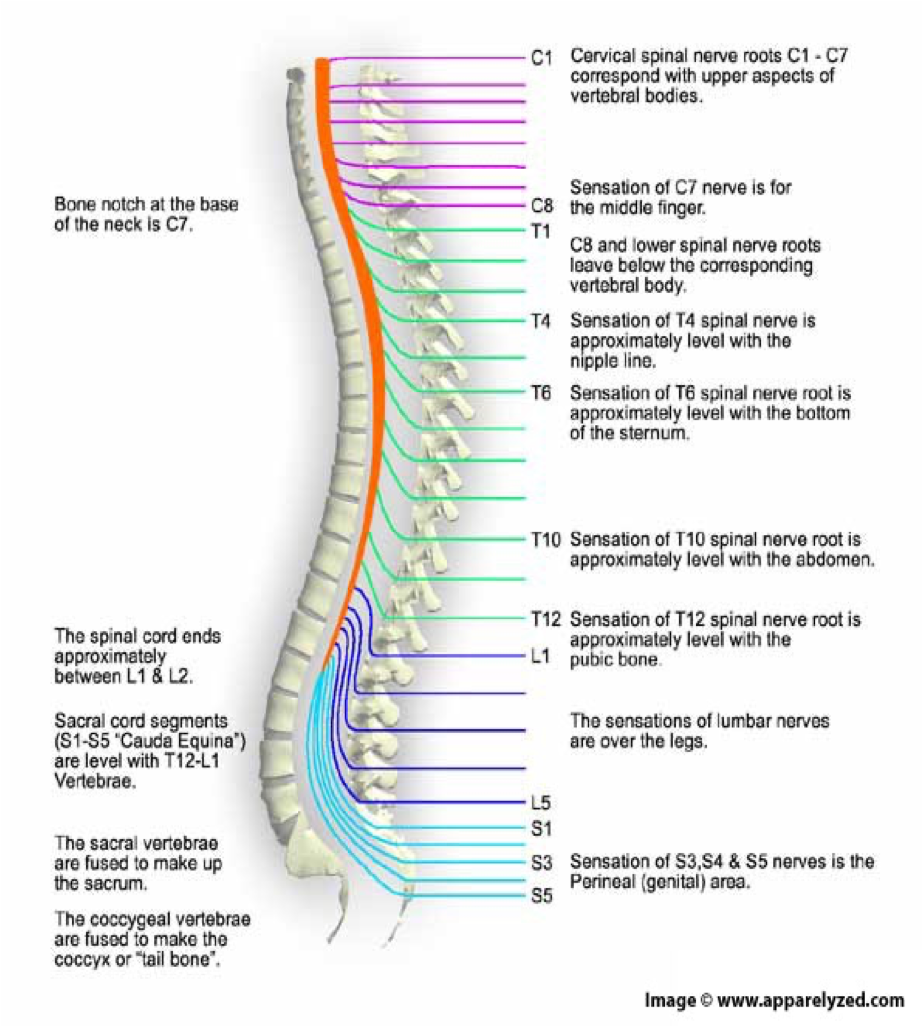
T1-12
12 pairs of thoracic nerves
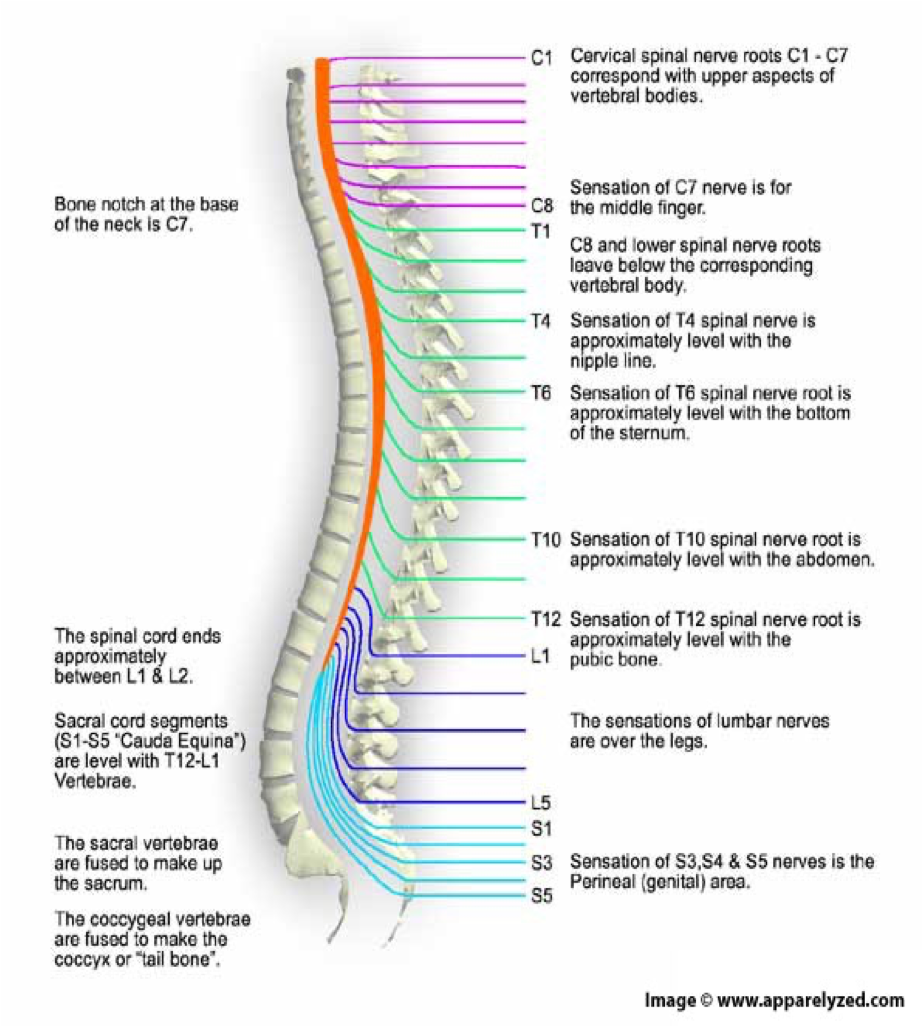
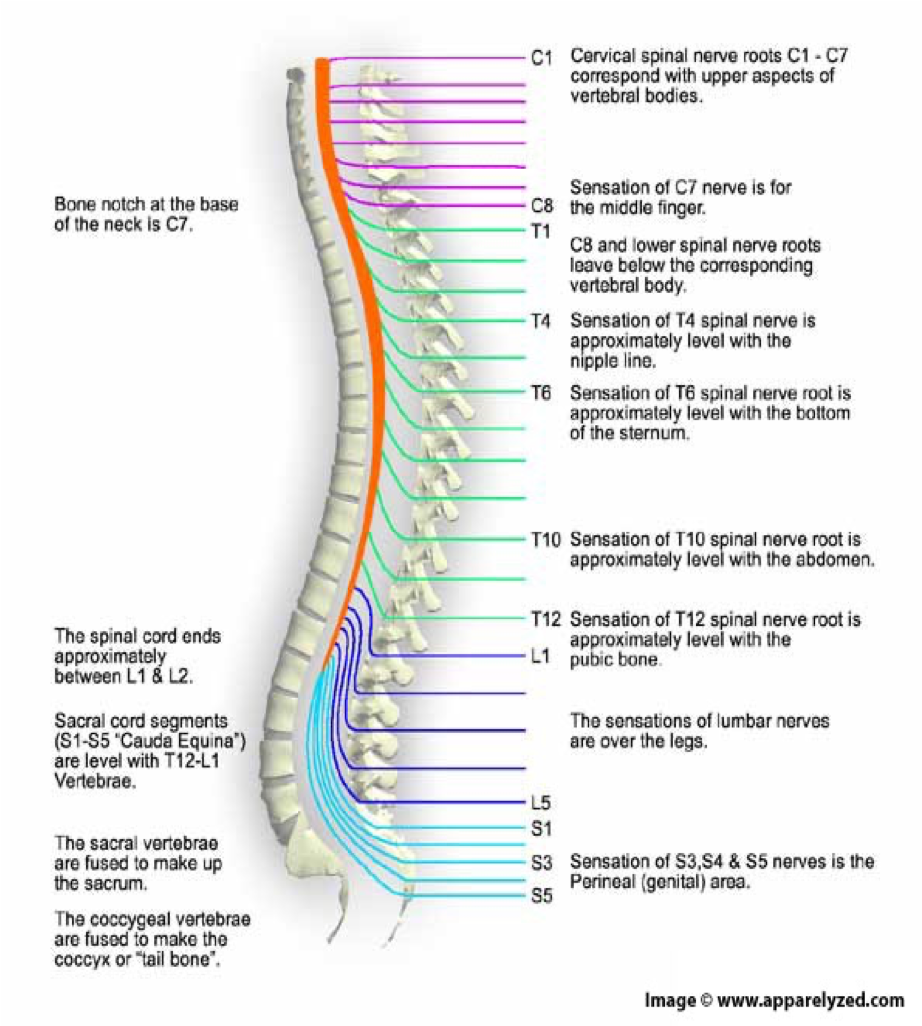
L1-5
5 pairs of lumbar nerves
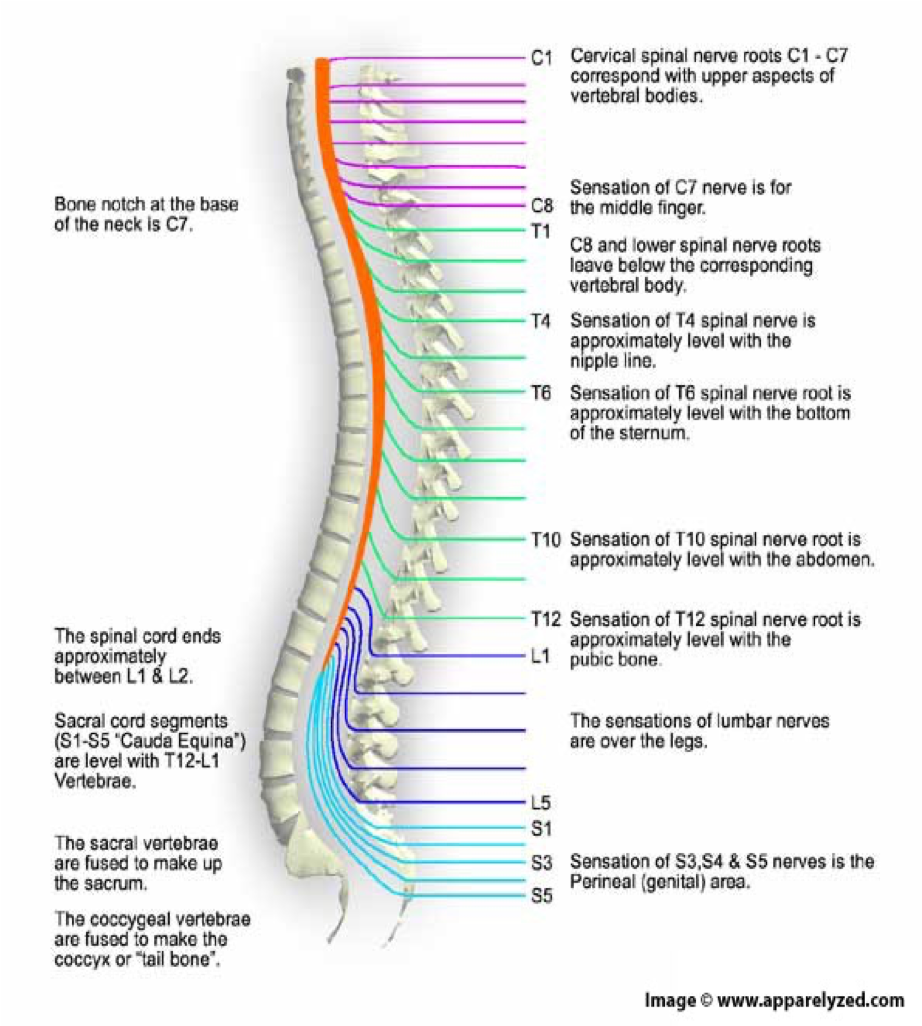
S1-5
5 pairs of sacral nerves
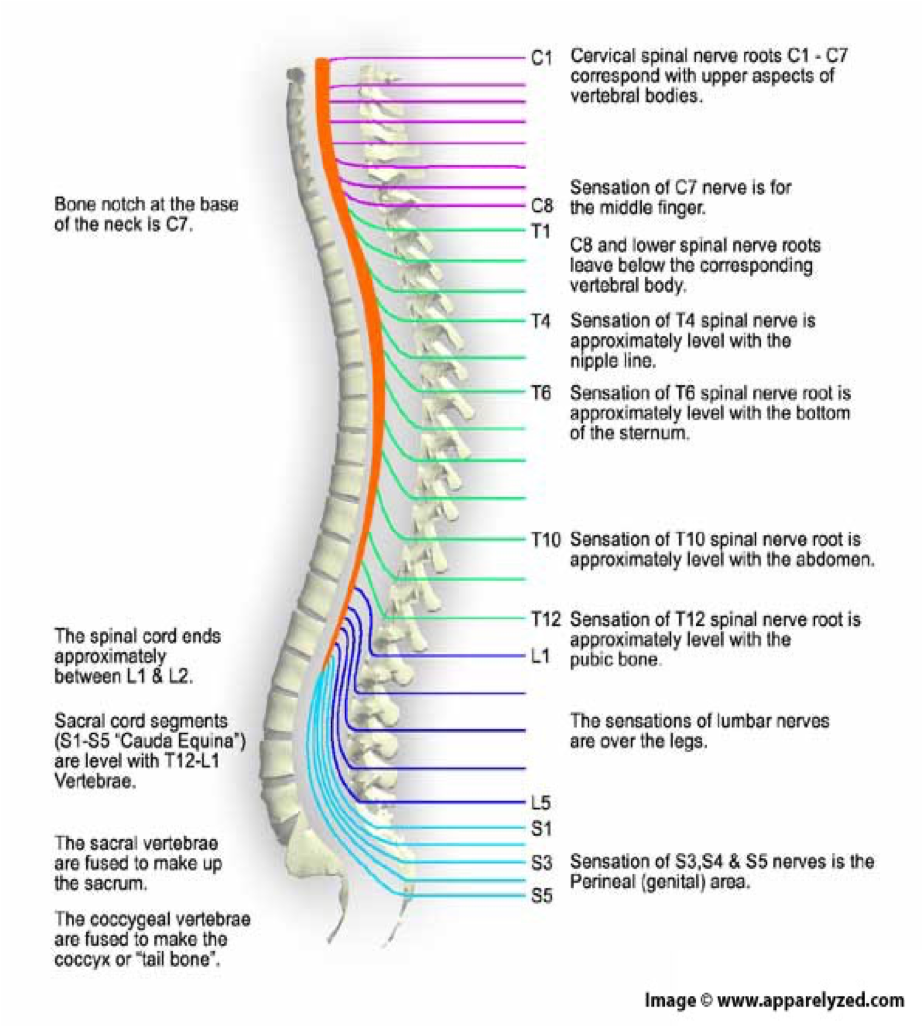
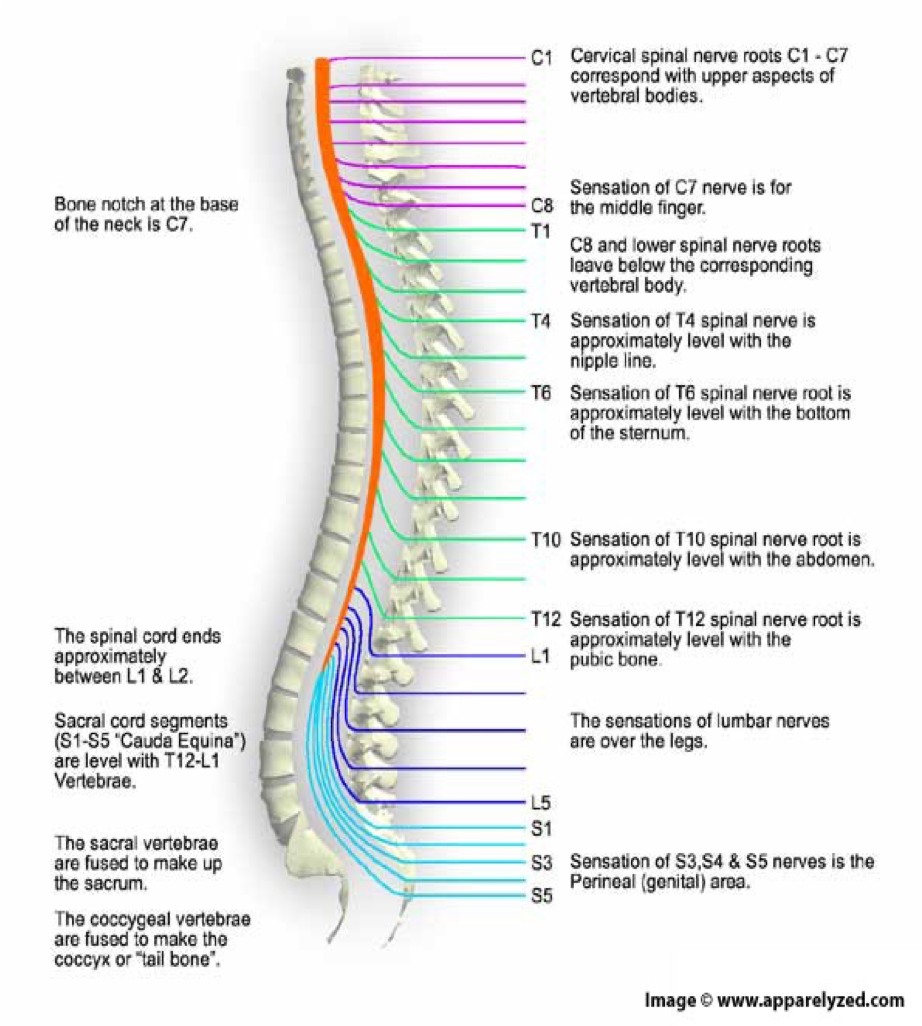
1 pair of…
1 pair of coccygeal nerves
whay does the autonomic nervous system controls
■Controls involuntary or SMOOTH MUSCLE activity (i.e.organs)
–Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, Perspiration, Digestion
what does the autonomic nervous system works with
works independently of the SNS and the CNS
what are the other 2 subdivision sog the autonomic nervous system
sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
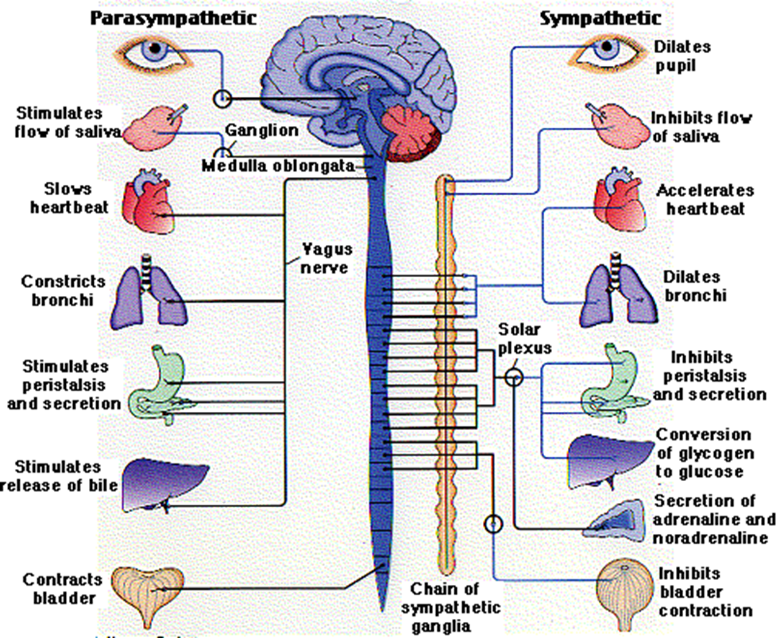
what are sympathetic nerves
autonomic nerves that prepare your internal system for emergency action
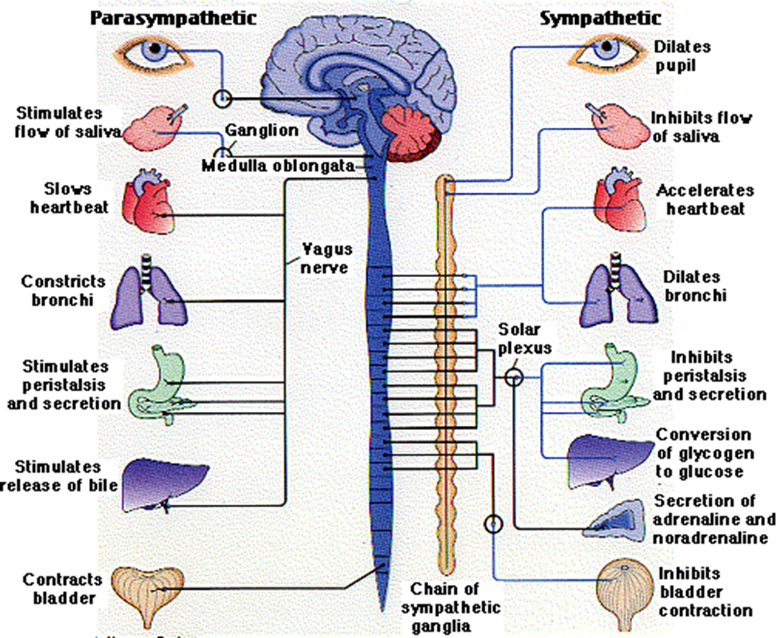
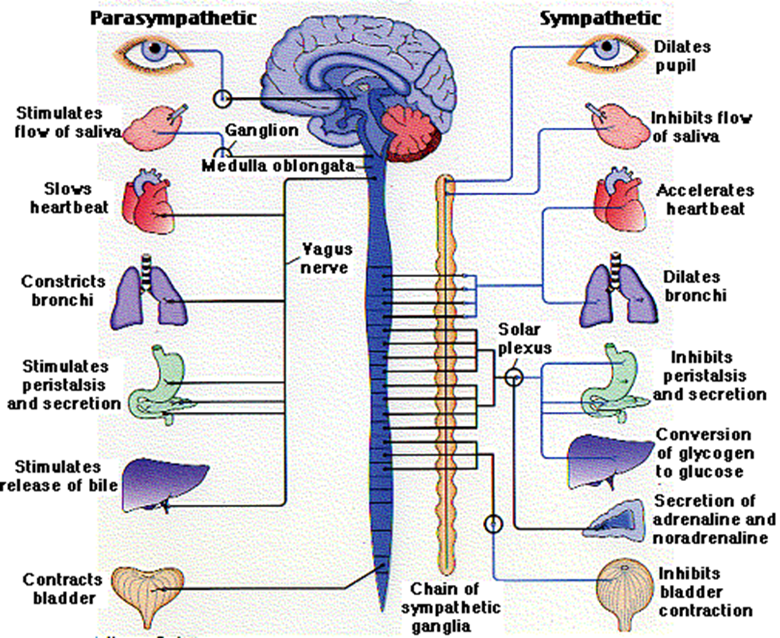
what is the parasympathetic nerves
autonomic nerves that prepare your internal systems for calm
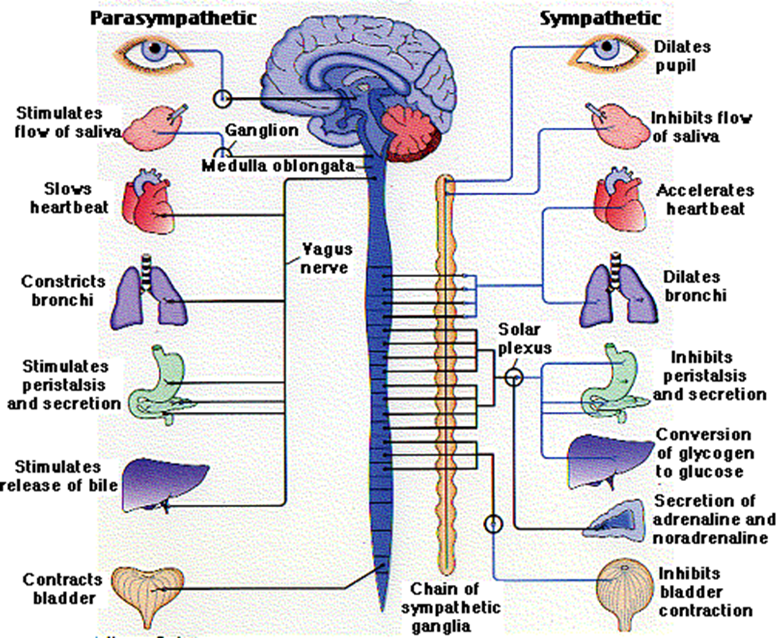
characteristics of sympathetic nervous system (ANS)
■“FIGHT OR FLIGHT”
■Originates from the THORACIC and LUMBAR regions of the spinal cord
■Form the sympathetic ganglion chain
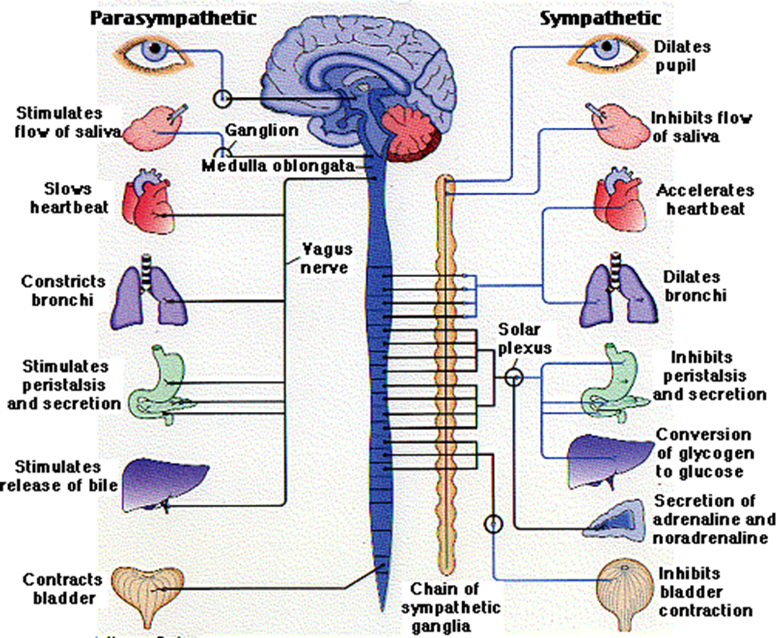
what are actions associated woth the sympathetic ANS
–Dilating bronchia (air towards lungs)
–Accelerating heart
–Increasing secretion of sweat
–Inhibiting digestion
–Inhibiting bladder contraction
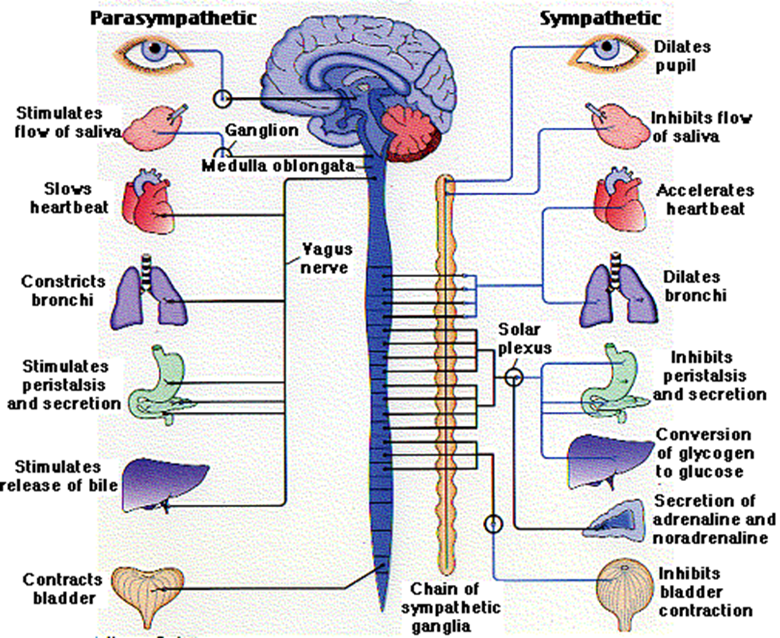
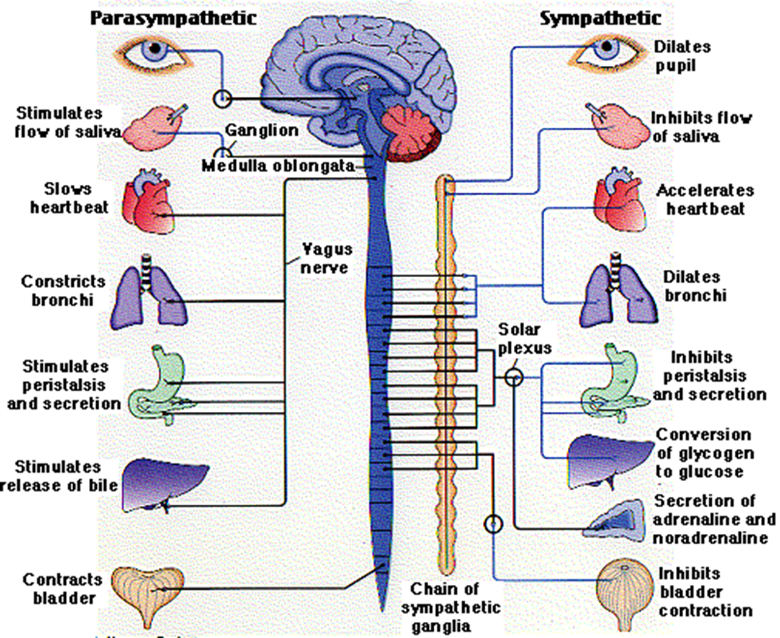
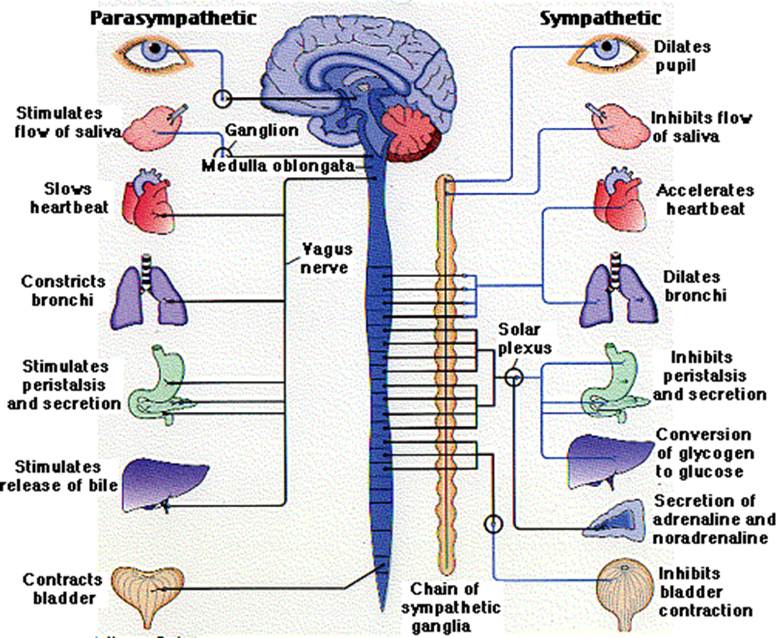
charactersitics of the parasympathetic ANS
■“REST AND DIGEST”
■Returns the body to a normal state after sympathetic activation
■Effectively does the opposite of the sANS
what are the 2 nervous system cells
neurons
glia
what do neurons do
transmits info
what does the glia do
support functions
who put the idea that neurons are the basicbuilding blocks of the nervous system
Santiago Ramon y Cajal in the late 19th century
what are nerves made up of
made up of the tail ends (AXONS/NERVE FIBRES) of neurons
what do axons do
Axons extrude from the neuron body, carrying information in the form of ELECTRICAL IMPULSES
Neurons are....
specialised communication cells
how do neurons communicate
communicate using electrochemical signals
Glia are support cells with a wide range of functions:
–Attacking invading organisms
–Promoting neuron repair
–Providing insulation for the electrochemical communications between neurons
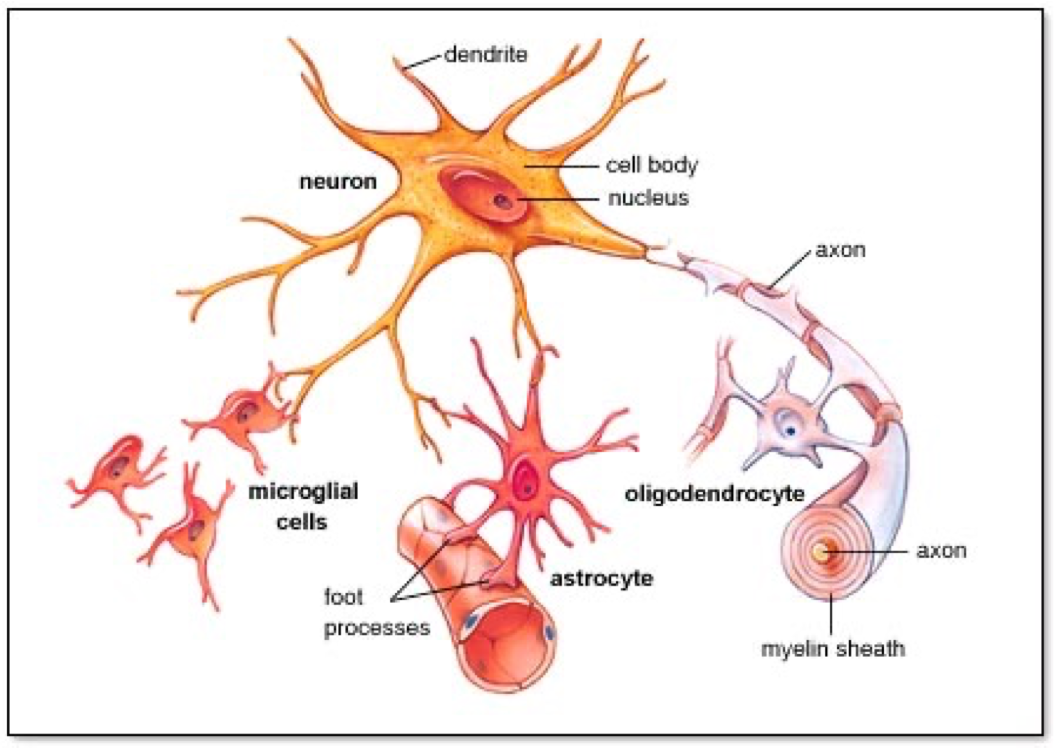
what are the 2 diff glial cells
Microglia
Macroglia
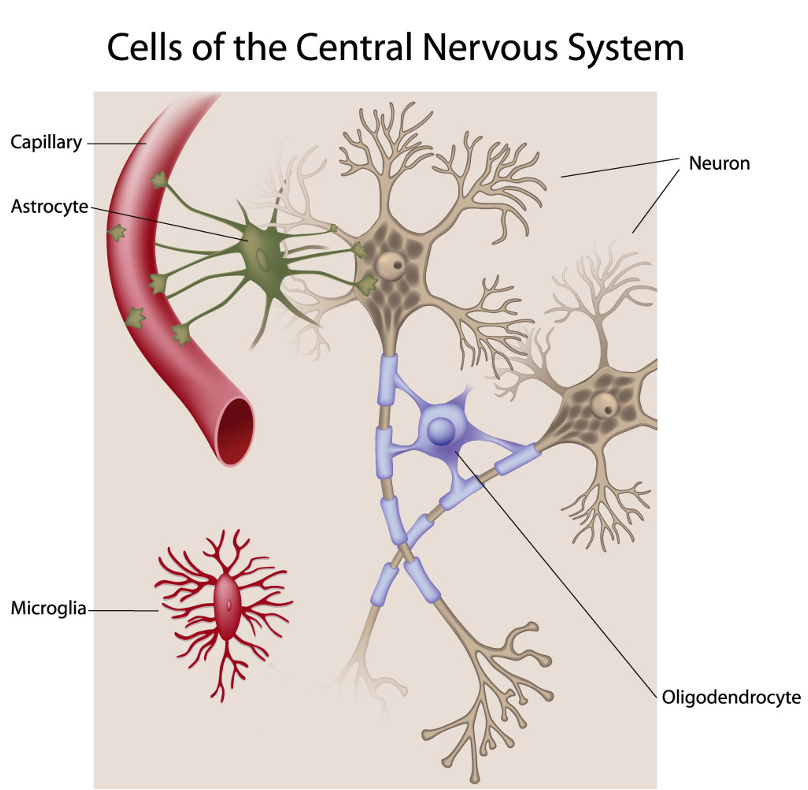
what is cytoarchitecture
is the study of the cellular composition of the central nervous system's tissues under the microscope.
structure of teh neuron image
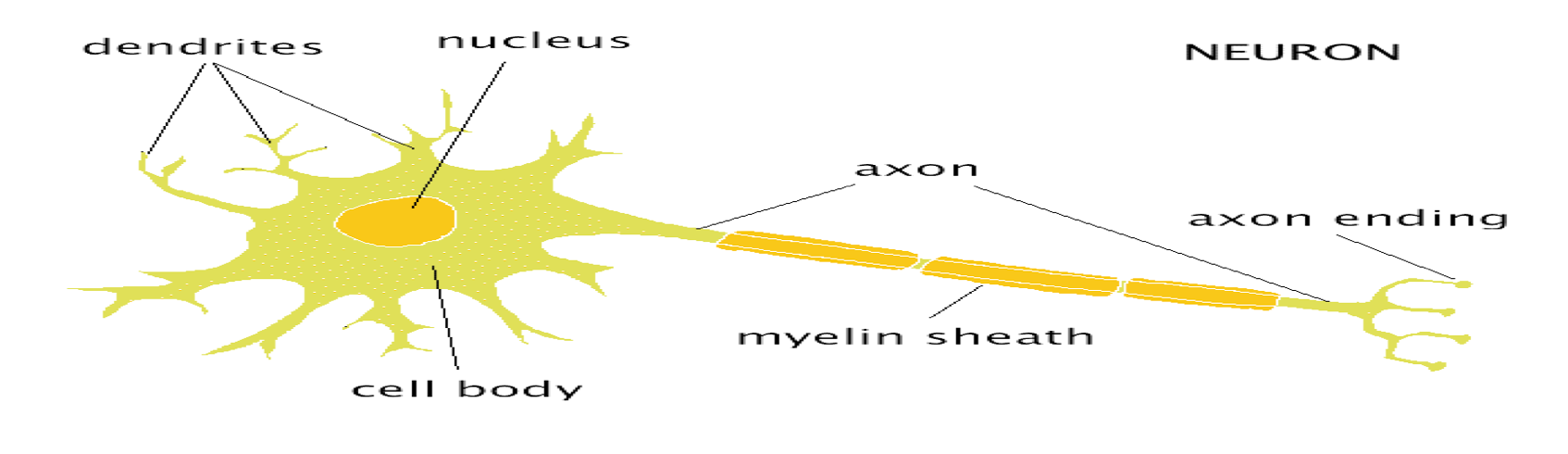
SOMA
The cell body, metabolic centre
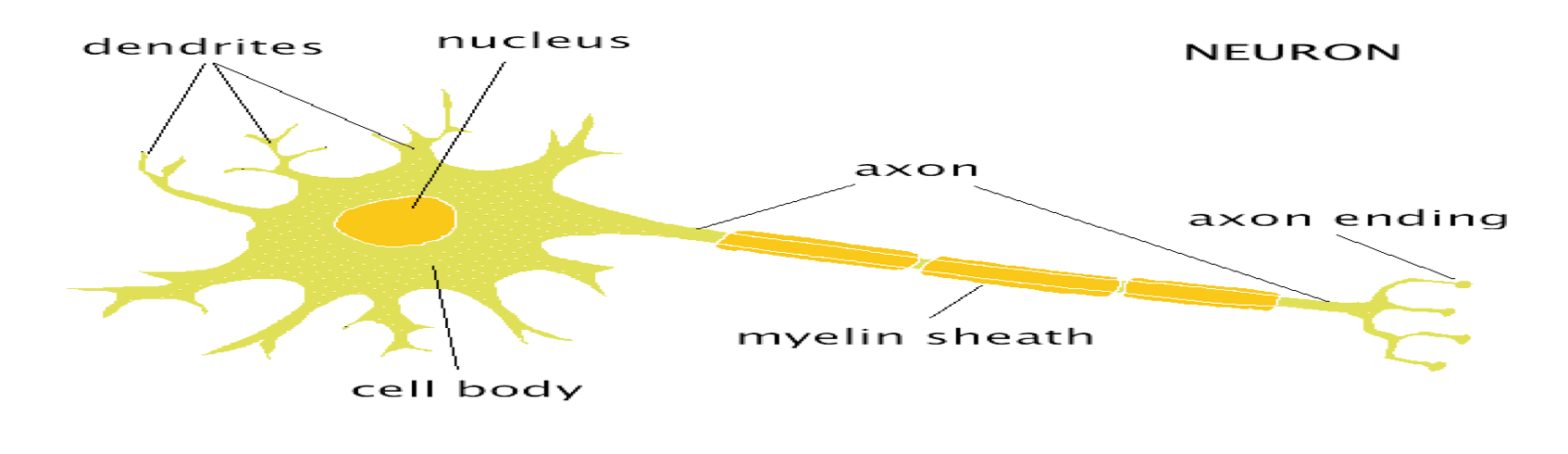
DENDRITES
bring information to the soma from other cells/neurons
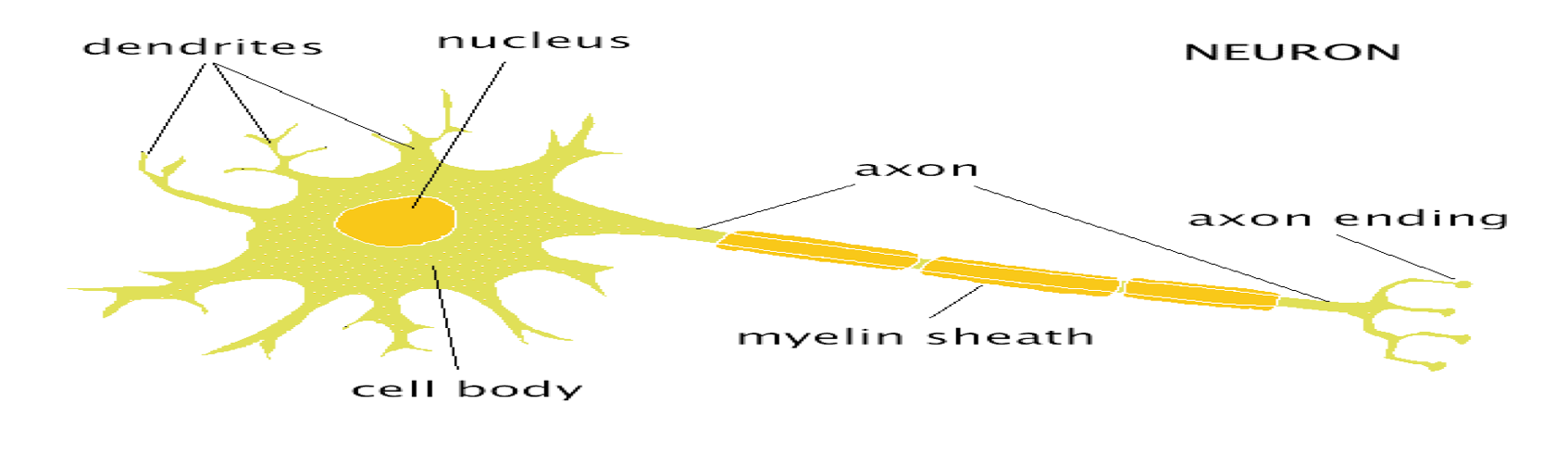
axon
Project from the soma to other cells, carry information away
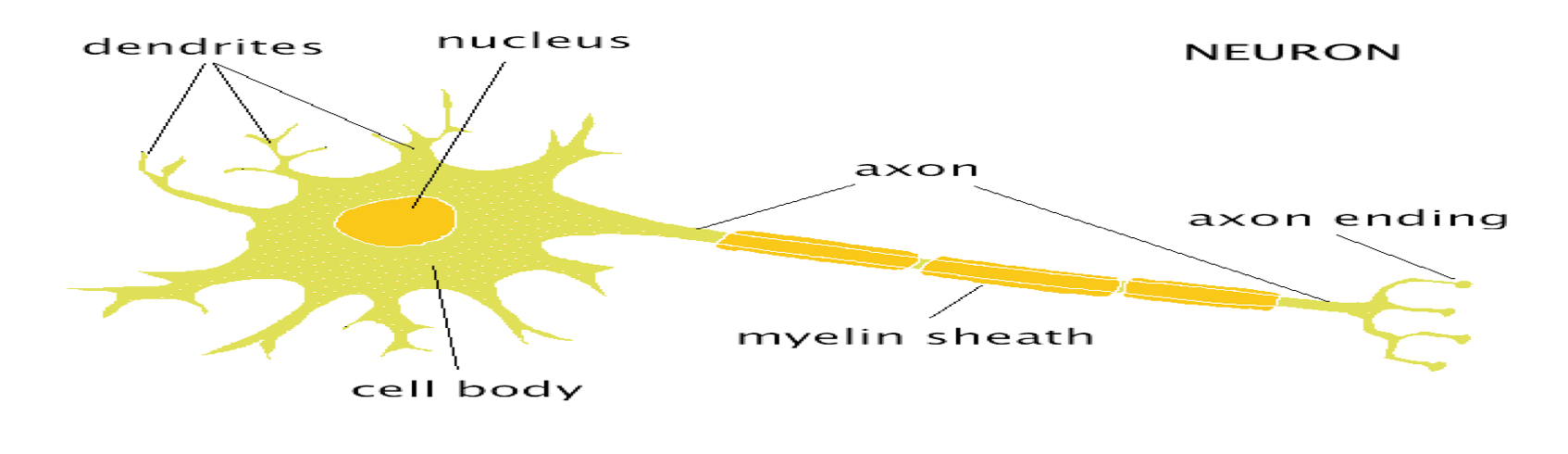
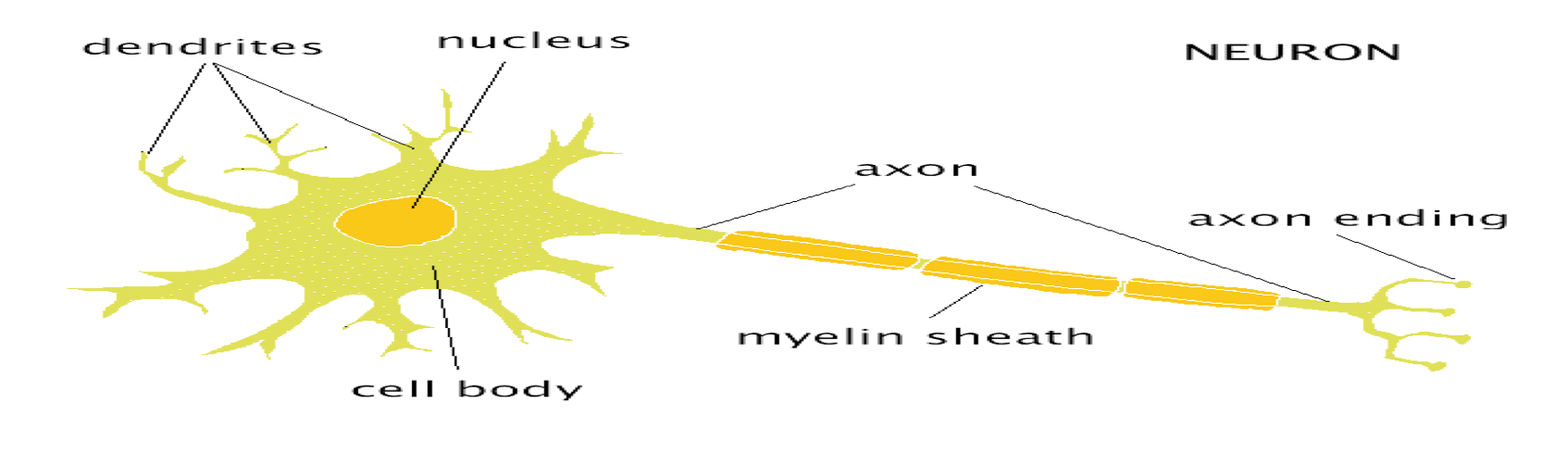
AXON HILLOCK
■Junction between soma and axon
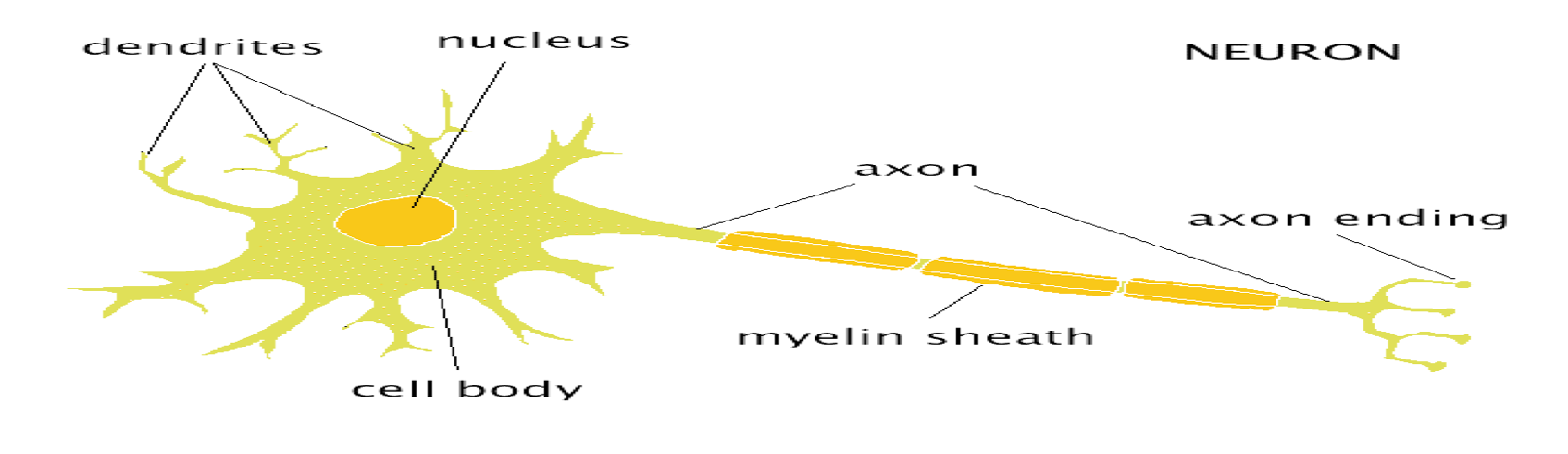
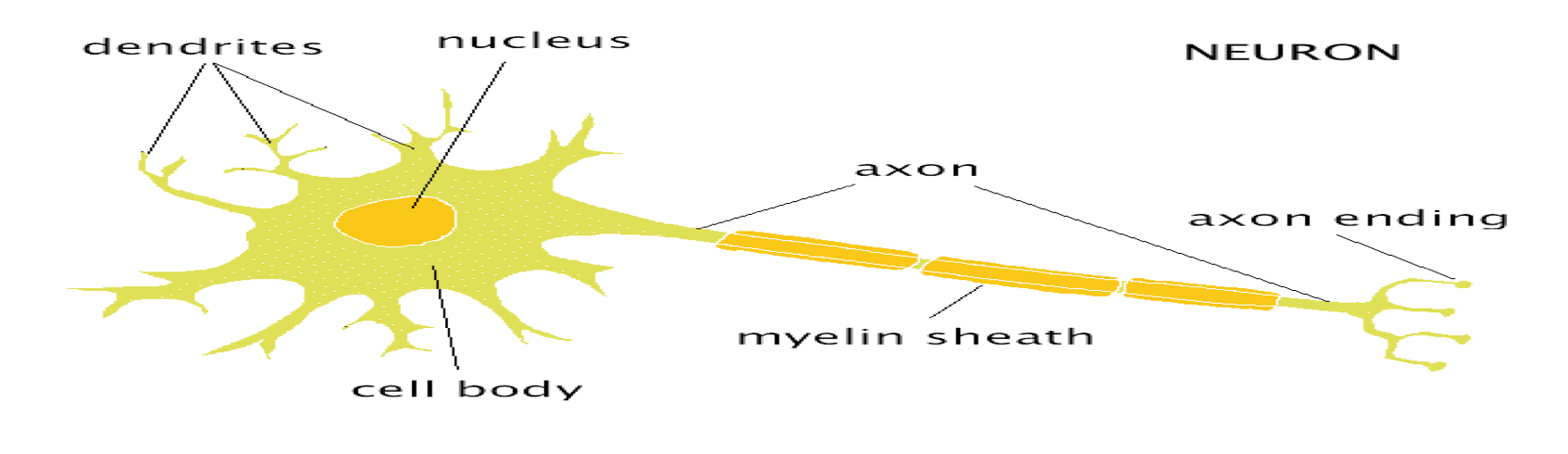
MYELIN SHEATH:
Layer of fat surrounding most axons
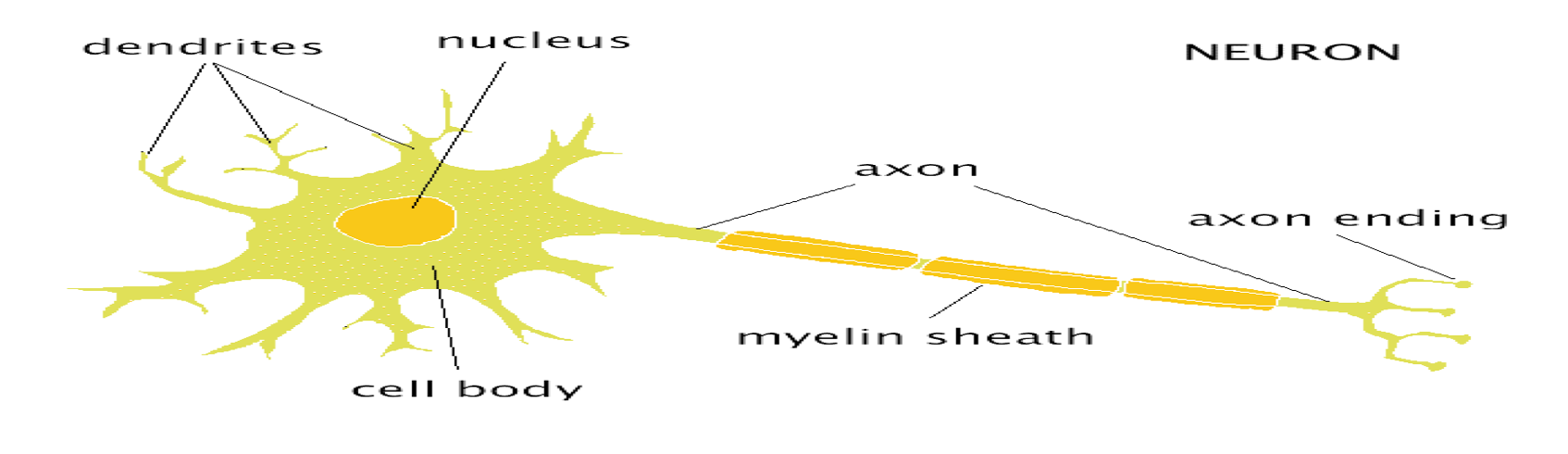
NODES of RANVIER
gaps between myelin sections