Biology and Behavior
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
What is neuropsychology and what does it study?
Neuropsychology is the scientific study of how the structure and function of the nervous system, particularly the brain, influence cognition, emotion, and behavior.
What are the three main types of neurons in the nervous system?
Sensory (Afferent) Neurons, Motor (Efferent) Neurons, Interneurons
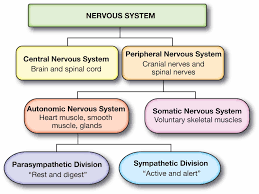
How is the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) organized, and what are its key subdivisions?
Somatic Nervous System (voluntary)
Autonomic Nervous System (automatic)
Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS) – Fight-or-Flight
Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS) – Rest-and-Digest
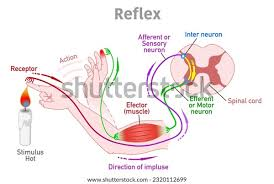
How do reflex arcs use interneurons to coordinate rapid responses and brain communication?
1. Stimulus - Activates sensory receptors (e.g., heat, pain)
2. Sensory (Afferent) Neuron - Sends signal to spinal cord
3. Interneuron (Integration Center) - Processes signal; triggers motor neuron and routes info to brain
4. Motor (Efferent) Neuron - Sends signal to muscle or gland
5. Effector - Muscle or gland executes the response (e.g. muscle contraction)
What are the two major divisions of the nervous system?
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Composed of the brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Includes cranial nerves, spinal nerves, and ganglia
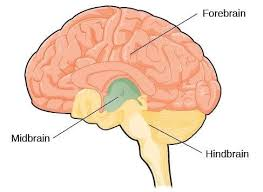
What are the three major subdivisions of the brain?
Hindbrain, Midbrain, and Forebrain
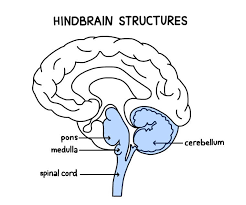
What are the key components of the hindbrain?
CMR = Core Motor Regulation
Cerebellum
Medulla Oblongata
Reticular Formation
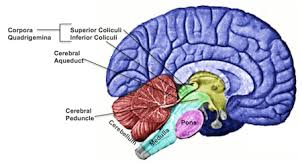
The midbrain contains…
the superior and inferior colliculi
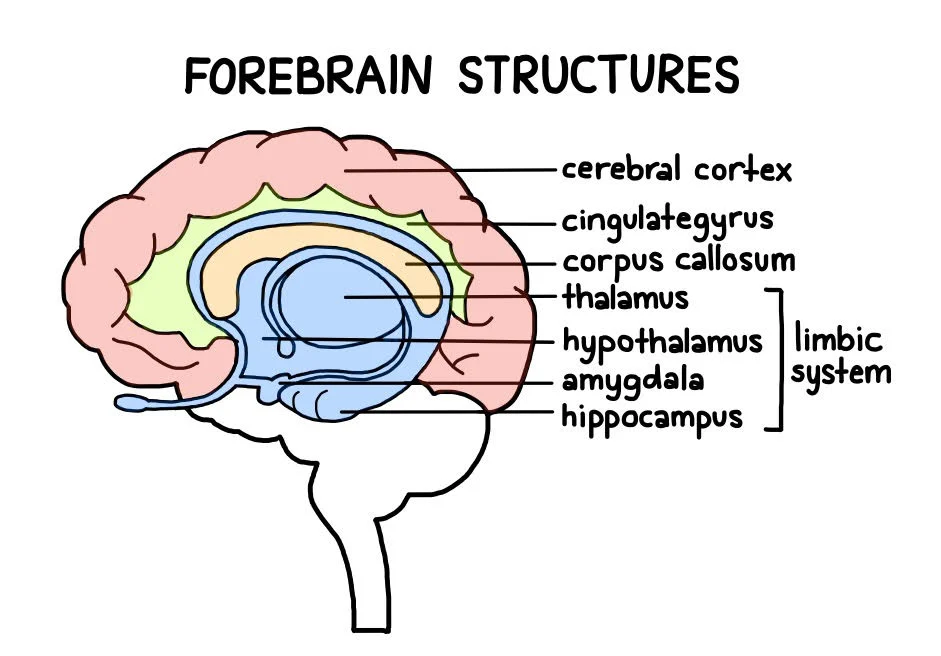
What are the major components of the forebrain?
The Hungry Brain Loves Complex Thinking
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Basal Ganglia
Limbic System
Cerebral Cortex
What are the major methods used to study brain function and structure?
"L.E.A.R.N. the Brain"
Lesions
Electrical Simulation
Activity Recording - Real-time neural signals (EEG/MEG)
Regional Blood Flow
Neuroimaging
What is the role of the thalamus?
a relay station for sensory information
Hypothalamus role?
The hypothalamus maintains homeostasis and integrates with the endocrine system through the hypophyseal portal system that connects it to the anterior pituitary
Basal ganglia role?
central to refining movement and maintaining postural control
What are the key components of the limbic system and its role?
contains the septal nuclei, amygdala, and hippocampus, controls emotion and memory
septal nuclei function:
The septal nuclei are involved with feelings of pleasure, pleasure- seeking behavior, and addiction
What role does the amygdala play?
controls fear and aggression
Hippocampus function:
The hippocampus consolidates memories and communicates with other parts of the limbic system through an extension called the fornix
What are the four lobes of the cerebral cortex?
F-POT
The cerebral cortex is divided into four lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal
What are the key functions of the frontal lobe?
FEELS
Frontal Executive
Emotion
Language
Strategy
What are the key functions of the parietal lobe?
The parietal lobe controls sensations of touch, pressure, temperature, and pain; spatial processing; orientation; and manipulation
What does the occipital lobe do?
controls visual processing
What does the temporal lobe control?
TEMPORAL
Tunes
Emotions
Memory
Perception Of Real Auditory Language
Which hemisphere is dominant for language in most individuals?
Left Hemisphere Dominance
What do neurotransmitters do?
Neurotransmitters are released by neurons and carry a signal to another neuron or effector (a muscle fiber or a gland).
Where is acetylcholine used in the nervous system?
Acetylcholine is used by the somatic nervous system (to move muscles), the parasympathetic nervous system, and the central nervous system (for alertness).
what does dopamine do?
maintains smooth movements and steady posture.
What do endorphins and enkephalins do?
act as natural painkillers
epinephrine and norepinephrine function:
Epinephrine and norepinephrine maintain wakefulness and alertness and mediate fight-or-flight responses. Epinephrine tends to act as a hormone, and norepinephrine tends to act more classically as a neurotransmitter.
γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glycine function:
act as brain “stabilizers.”
What is glutamate’s role in the brain?
acts as an excitatory neurotransmitter
Glutamate excites neurons, increasing the likelihood of action potential firing
Serotonin function:
modulates mood, sleep patterns, eating patterns, and dreaming
How does the endocrine system connect to the nervous system?
through the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary, as well as a few other hormones.
What is cortisol?
a stress hormone released by the adrenal cortex
testosterone and estrogen:
Testosterone:
Primary Sources: Testes, adrenal cortex
Key roles: Libido, aggression, muscle growth
Estrogen:
Primary Sources: Ovaries, adrenal cortex
Key roles: Libido, mood, reproductive cycle
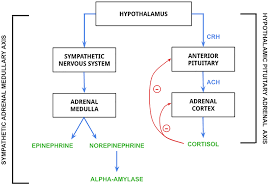
Where are epinephrine and norepinephrine secreted?
adrenal medulla
are epinephrine and norepinephrine related to the sympathetic or parasympathetic nervous system?
they cause physiological changes associated with the sympathetic nervous system
nature vs. nurture
a classic debate regarding the relative contributions of genetics (nature) and environment (nurture) to an individual’s traits.
For most traits, both nature and nurture play a role.
The relative effects of each can be studied.
What do family studies do?
look at the relative frequency of a trait within a family compared to the general population
What do twin studies do?
compare concordance rates between monozygotic (identical) and dizygotic (fraternal) twins
What do adoption studies do?
compare similarities between adopted children and their adoptive parents, relative to similarities with their biological parents.
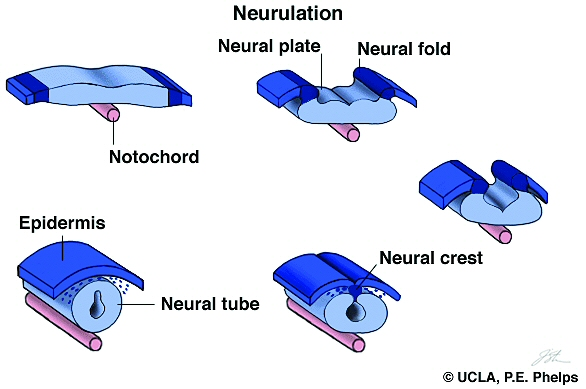
How does the nervous system develop through neurulation?
The nervous system develops through neurulation, in which the notochord stimulates overlying ectoderm to fold over, creating a neural tube topped with neural crest cells.
During neurulation, what does the neural tube and neural crest become?
The neural tube becomes the central nervous system (CNS).
The neural crest cells spread out throughout the body, differentiating into many different tissues
What are primitive reflexes and why do they matter?
Involuntary, brainstem-mediated motor responses present at birth
Most primitive reflexes serve (or served, in earlier times) a protective role.
They can reappear in certain nervous system disorders.
Rooting Reflex - Key Primitive Reflex
Stimulus: Stroke to the cheek
Response: Infant turns head toward stimulus
Function: Facilitates feeding (locating nipple)
Moro Reflex (Startle) - Key Primitive Reflex
Stimulus: Sudden loss of support or loud noise
Response: Arms extend outward, then retract; often followed by crying
Function: Protective response to falling
Babinski Reflex - Key Primitive Reflex
Stimulus: Stroke along the sole of the foot
Response: Big toe extends upward, other toes fan out
Function: Unknown in infants; pathologic if retained in adults
Grasping reflex - Key Primitive Reflex
Stimulus: Object placed in palm
Response: Fingers close around object
Function: Primitive grasping behavior
What are developmental milestones?
Predictable skills and behaviors most children achieve by specific ages
Most children follow these closely, with minor variation (~1–2 months)

How do Gross and fine motor abilities progress?
head to toe and core to periphery.
How do social skills develop?
from parent-oriented (Social smile, separation anxiety) to self-oriented (Autonomy, tantrums, parallel play) to other-oriented (Cooperative play, empathy, sharing)
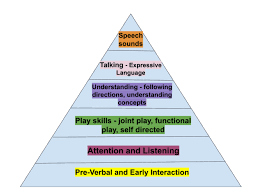
how do language skills develop?
they become more complex over time
What do motor neurons do?
transmit motor information from the brain to the body
what do sensory neurons do?
transmit sensory information from receptors to the brain
What is the function of the hindbrain?
responsible for balance and motor coordination
What is the function of the midbrain?
manages sensorimotor reflexes that promote survival
What is function of the forebrain?
Associated with emotion, memory, and higher-order cognition
What cognitive functions are associated with the nondominant hemisphere?
Nondominant hemisphere (usually right): Spatial awareness, emotional tone, holistic processing, sense of direction
What are catecholamines and what the significant ones?
hormones produced by the adrenal glands during the flight or fight response
Dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine are significant ones
What neurotransmitter can cause hallucinations in people with Schizophrenia?
dopamine
What does the pineal gland do?
responsible for producing melatonin, which controls the body’s circadian rhythm
What diseases are associated with dopamine and how?
Schizophrenia:
associated with high levels of dopamine or high sensitivity to dopamine
Parkinson’s disease:
associated with the destruction of the dopaminergic neurons in the basal ganglia
Do identical or fraternal twins share more similar traits?
Identical twins share the same genetic makeup, which can result in more similar personality traits compared to fraternal twins, who share about 50% of their genes, like typical siblings.