DNA Mutations
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
DNA Mutations
Changes in the DNA sequence that can lead to variations in genes. These mutations can occur naturally or as a result of environmental factors.
natural mutations occur during…
DNA replication/recombination
they are random & spontaneous
Large scale mutations
long segments of DNA changed via
translocations, duplications, & inversions
Small scale mutations
small, single base segments of DNA changed via
point mutation/substitution mutations
1 base incorrect in DNA = 1 mRNA incorrect
types of substitution mutations: point mutations
Silent mutation
Nonsense mutation
Missense mutation
Silent mutation
still codes for correct protein → little to no loss in protein structure/function
Nonsense mutation
codes for STOP sequence, UGA, UAG, UAA → early termination
Missense mutation
codes for different protein
conservative: codes for similar functional group protein → function preserved/slightly altered
non-conservative: codes for different functional group protein → function significantly altered
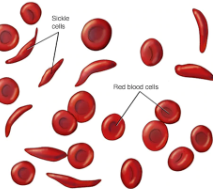
Example of point mutation
Sickle Cell Anemia
single substitution: A → T
results in Valine protein = sickle cell hemoglobin (should be Glutamic acid)
this shape can cause blockage that prevents blood flow = less oxygen
= missense mutation
types of insertions & deletions: Chromosomal mutations
frameshift mutation
Insertion/deletion of 3 nucleotides/bases
frameshift mutation
extensive missense mutations → incorrect protein
immediate nonsense mutations → stop codon
Insertion/deletion of 3 nucleotides/bases
no frameshift; extra or missing amino acid protein
example of insertion/deletion or chromosomal mutation
Cystic Fibrosis: trapped mucus in airways
deletion in CFTR gene = non functioning CFTR channel in lungs