Chapter 11: RNA and Transcription
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
RNA structures, cellular types of RNA, requirements for transcription, transcription units, RNA synthesis, consensus dequences, transcription in bacteria, transcription in eukaryotes, CRISPR RNA
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
The central dogma of molecular genetics
The flow of genetic information in cells
The primary structure of RNA
The primary structure of a nucleic acid is the sequence of nucleotides
RNA forms secondary structures
All cellular RNA types are generated by transcription: In all cells
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
All cellular RNA types are generated by transcription: Only in eukaryotes:
Pre-messenger RNA (pre-mRNA)
Small nuclear RNA (snRNA)
Small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA)
MicroRNA (miRNA)
Small interfering RNA (siRNA)
Piwi-interfering RNA (piRNA)
All cellular RNA types are generated by transcription: Only in prokaryotes:
CRISPR RNA (crRNA)
All cellular RNA types are generated by transcription - ETC.
Note: RNA replication occurs only with the genomes of some RNA virues
Transcription
Transcription is the transfer of genetic information from DNA by the synthesis of a complementary RNA molecule copied from the DNA template.
Requirements:
Template: DNA (a gene)
Enzyme: RNA polymerase
Free NTPs (nucleoside triphosphate)
No primers
RNA is transcribed from the template DNA strand
Template strand (the transcribed strand): antisense.
Non-template strand: sense.
A transcription unit
A transcription unit is a stretch of DNA that encodes an RNA molecule and the sequences necessary for its transcription.
A transcription unit: Components
promoter: the binding site for RNA polymerase and the transcription initiation apparatus
RNA-coding region: a sequence of DNA nucleotides that is copied into an RNA molecule (the gene)
terminator: a sequence of nucleotides that signals where transcription is to end (it is part of the gene)
Visual transcription unit
The gene is only the transcribed portions of the transcription unit. The final gene product must be a function RNA moleucle or protein.
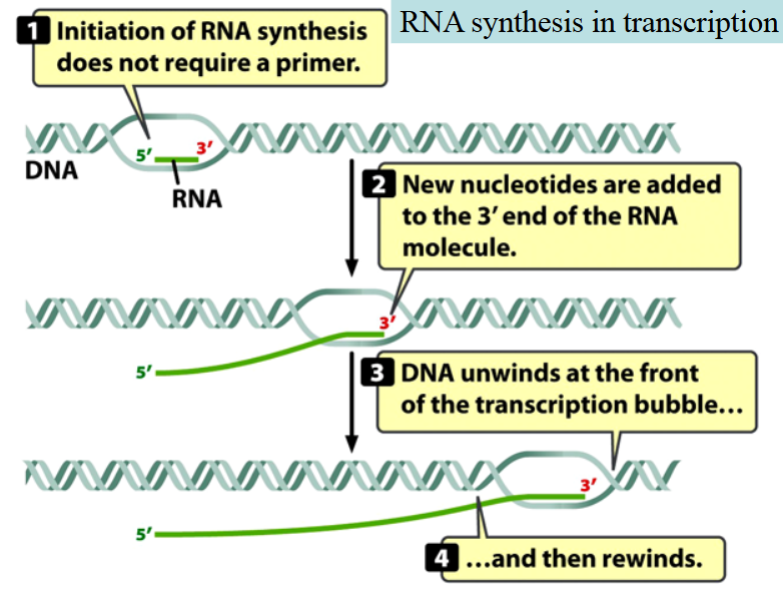
Formation of the phosphodiester bonds during RNA synthesis
Initiation and elongation of RNA synthesis in transcription
Initiation:
NTP + NTP → NTP-NMP + PPi (*the (-) showcases a bond)
Elongation:
NTP-(NMP)n + NTP → NTP-(NMP)n+1 + PPi
Notice: the initial nucleotide of the chain (5’) remained as a nucleoside triphosphate (NTP)
RNA synthesis in transcription
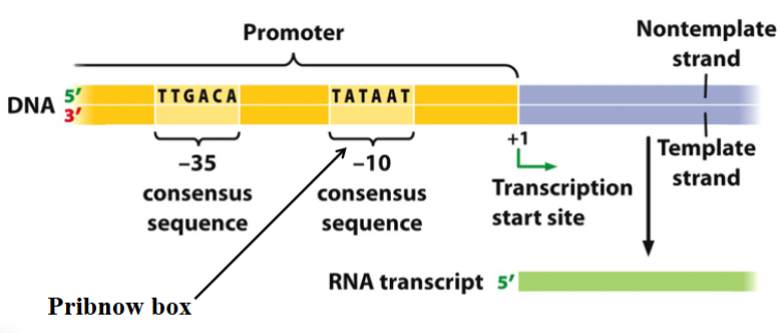
Consensus sequences in bacterial promoters
A consensus sequence comprises the most commonly found nucleotides at a specific DNA site. It is a conserved sequence. The bacterial Pribnow box has a similar function as the eukaryotic TATA box.
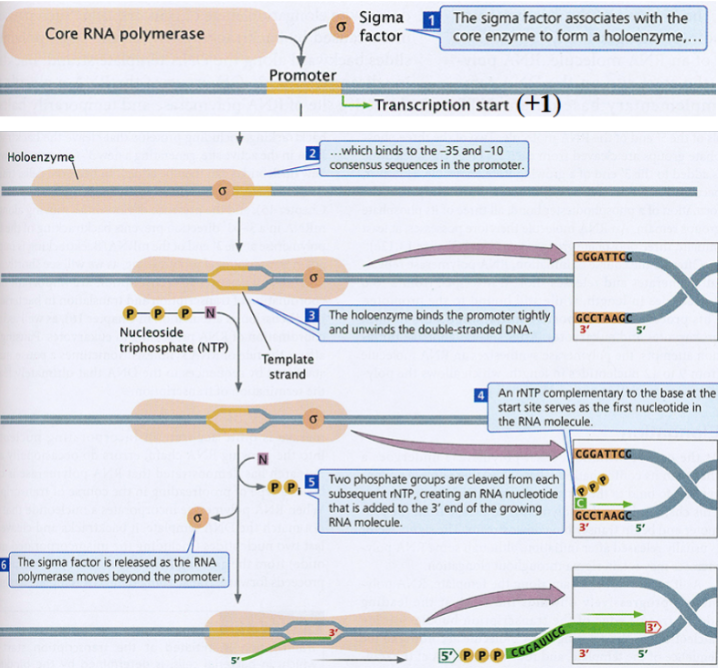
Transcription in bacteria
transcription is catalyzed by RNA polymerase
the promoter is the binding site for RNA polymerase on the DNA molecule, right before +1, and is not transcribed
the sigma factor () recognizes the promoter and directs RNA polymerase to it
the DNA double helix is unwound and denatured locally
initiation of transcription begins at the transcription initiation site (+1, the first base to be transcribed)
the sigma factor dissociates after initiation
transcription continues at ~50 nucleotides/second at 37C until the enzyme encounters the terminator sequence
Termination of transcription in bacteria
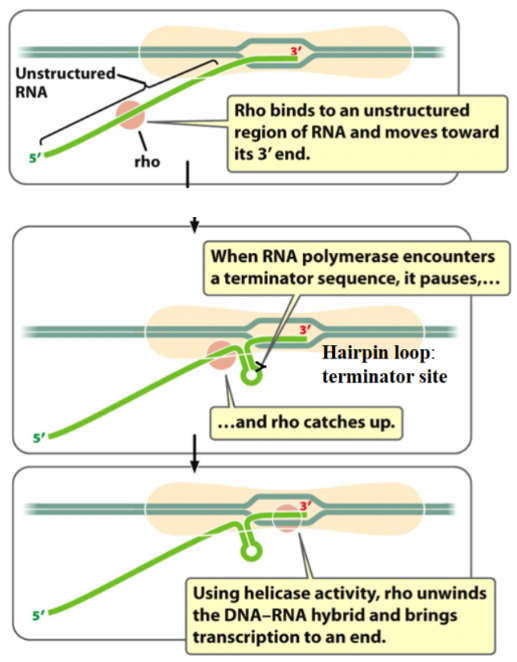
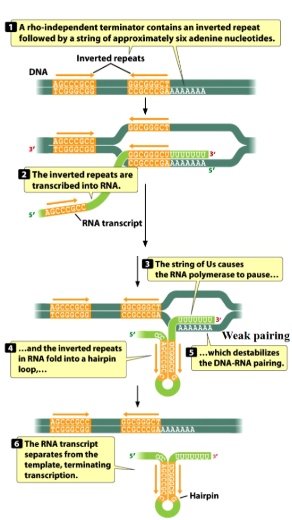
Termination in bacteria depends on the formation of the
hairpin loop secondary structure at the terminator site.
the hairpin loop forms after inverted repeats in the gene are transcribed into the RNA molecule and form intramolecular base pairs
the formation of the hairpin loop destabilizes the DNA-RNA pairing, and transcription ends
in rho-dependent termination, the Rho protein, a helicase, is needed to break the DNA-RNA pairing and terminate transcription
in rho-independent termination, the weak DNA-RNA pairing at the terminator site is enough to destabilize the interaction and terminate transcription
Termination in bacteria: Rho-dependent
Termination in bacteria: Rho-independent
RNA polymerase II and transcription elongation in eukaryotes
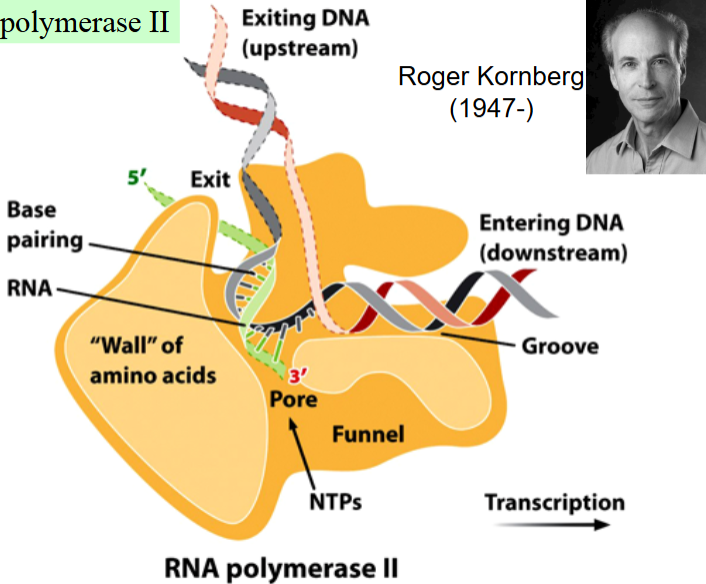
RNA polymerase maintains a transcription bubble during elongation, in which about 8 nucleotides of RNA remain base-paired with the DNA template strand.
The DNA double helix enters a cleft in the polymerase and is gripped by jaw-like extensions of the enzyme. The two strands of the DNA are unwound, and RNA nucleotides entering the enzyme through a pore are added to the 3’ end of the growing RNA molecule. As it funnels through the polymerase, the DNA-RNA hybrid hits a wall and bends at a right angle, keeping the bubble open and positioning the DNA-RNA hybrid at the active site of the enzyme. The newly synthesized RNA separates from the DNA and runs through another groove before exiting the enzyme.
RNA polymerase II
Termination of transcription of protein-coding genes in eukaryotes
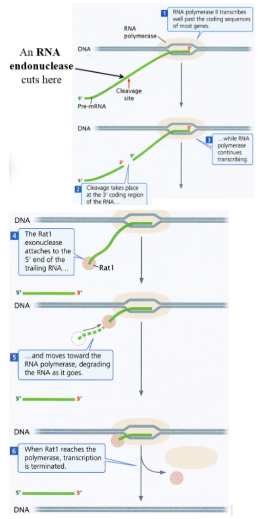
Termination in eukaryotes does not occur by itself but
requires the activity of the Rat1 exonuclease.
after the protein-coding region of the gene is transcribed, the RNA molecule is cleaved by an RNA endonuclease at a consensus cleavage site
then, Rat1, a 5’ => 3’ RNA exonuclease, binds to the unprotected 5’ end of the trailing, non-coding RNA fragment and begins to degrade it until it catches up with the RNA polymerase, which is still transcribing the DNA
the complete degradation of the trailing fragment terminates transcription
Termination of transcription of protein-coding genes in eukaryotes
CRISPR RNA: adaptive immunity in prokaryotes
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) are DNA arrays consisting of a number of short palindromic sequences separated by spacer sequences. The spacers are derived from invading DNA molecules such as bacteriophages or plasmids. They are the basis of a form of adaptive immunity found in bacteria and archaea.
CRISPR RNA: adaptive immunity in prokaryotes - The three stages of the CRISPR-CAS system
Acquisition
Expression
Interference
The three stages of the CRISPR-CAS system: 1. Aquisition
Foreign DNA enters the cell, and it is identified, processed, and inserted into the CRISPR array as a new spacer (a memory of the invading DNA).
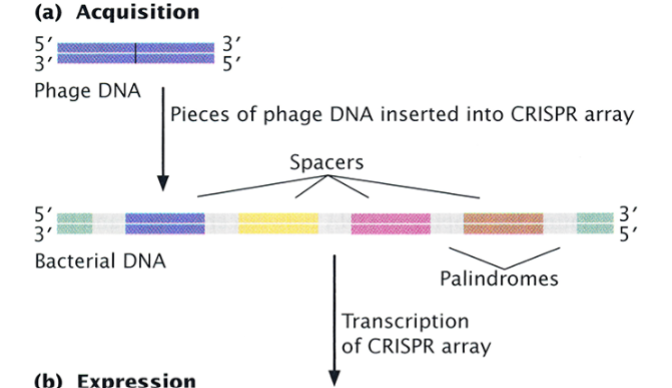
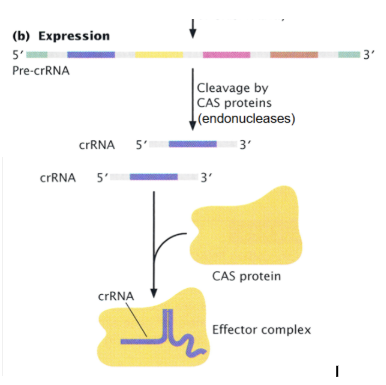
The three stages of the CRISPR-CAS system: 2. Expression
The entire array is transcribed into a long CRISPR precursor RNA, then cleaved by a CAS (CRISPR-associated) protein into CRISPR RNAs (crRNAs), each one containing one spacer homologous to a foreign DNA.
Each crRNA combines with a CAS protein to form an effector complex.
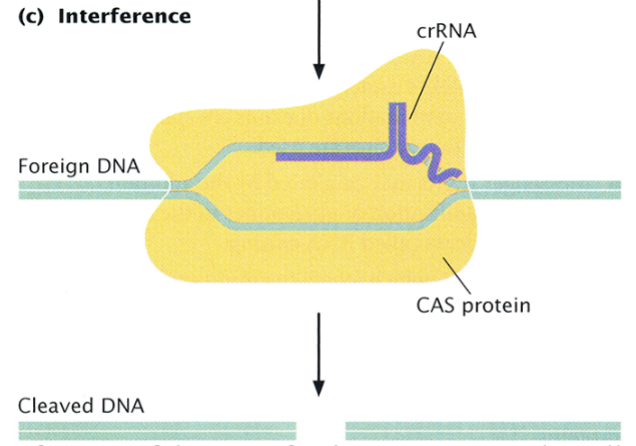
The three stages of the CRISPR-CAS system: 3. Interference
If the same foreign DNA enters the cell again, the effector complex recognizes it by its base-pair complementarity to the crRNA, and the CAS protein cleaves it with its endonuclease activity.