Muscles
1/16
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What are the functions of muscles?
movement
generate heat
stabilizing body, form, and position
pumping and controlling fluids: blood, lymph, digestive
what are the three types of muscle tissue?
smooth
cardiac
skeletal
Cardiac
Striated, branched uninucleated fibers, its involuntary movements, occurs only in the walls of the heart. It is usually small rhythmic contractions
Skeletal
voluntary movements, striated, multinucleic, strong contractions usually attached to the skeleton
Smooth
spindle shape non-striated involuntary movements uninucleic. usually continuous strong contractions found in wall of hallow organs.
Describe the basic skeletal muscle
the skeletal muscle is comprised of multiple fasciculus and one fasciculus has various myofibers
describe myofiber structure
one myofiber contains various myofibrils and inside the myofibrils are sarcomeres that consist of thin and thick filaments and m-line and z-line.
Thin filament
are composed of actin, troponin, and tropomysin
Thick filament
contains myosin and myosin head
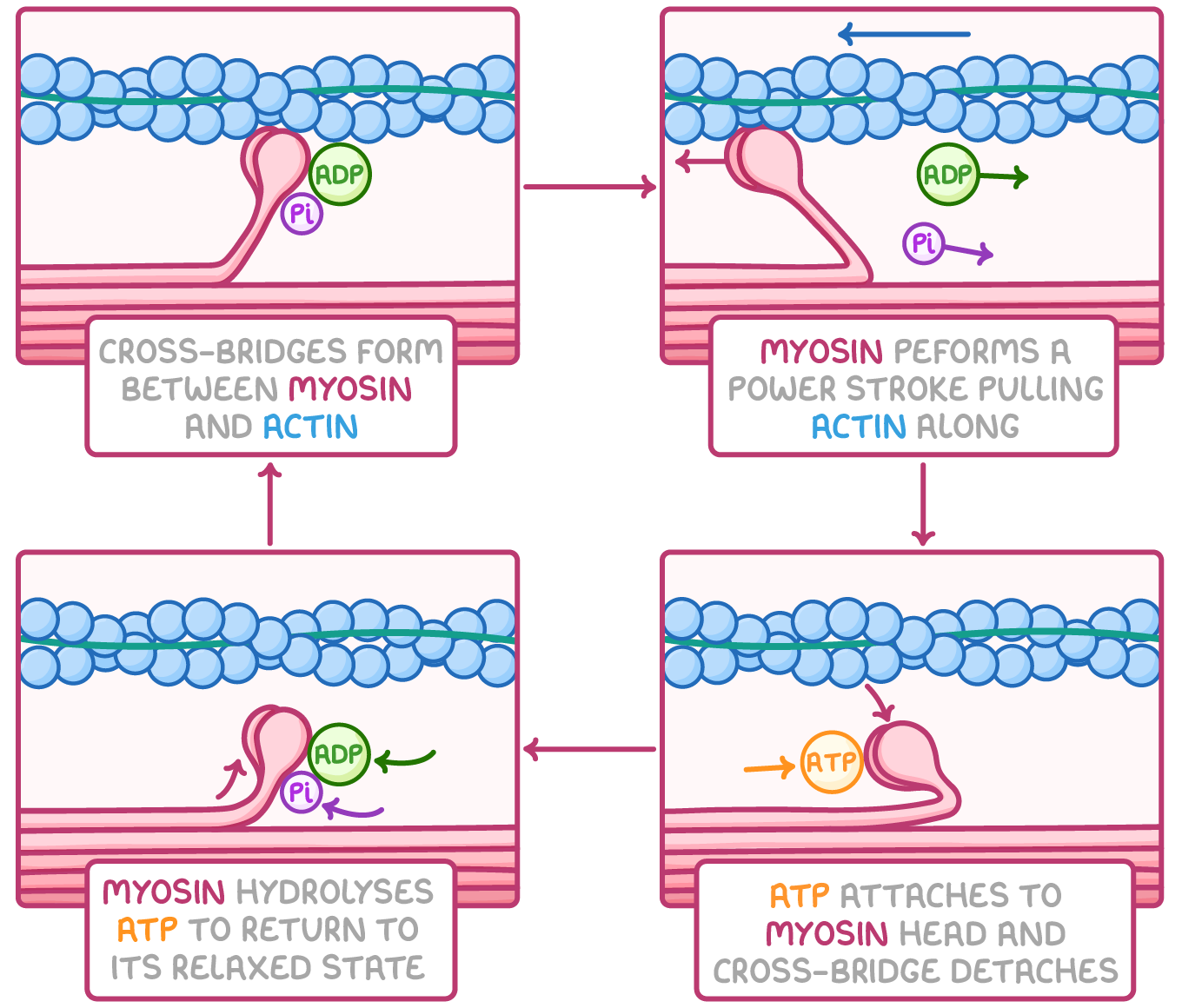
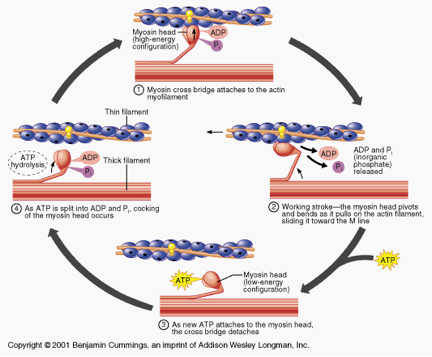
Describe the sliding filament model
ATP is bound to myosin head which is a low energy state → myosin head hydrolyzes ATP into ADP and Pi which is a high energy configuration → myosin head binds to actin forming a cross-bridge → myosin relates ADP + Pi while in a cross-bridge formation. This brings the thin filament towards the center of the sarcomere using a power stroke restoring it back to a low energy state → ATP binds to myosin head releases if from acting starting the cycle again
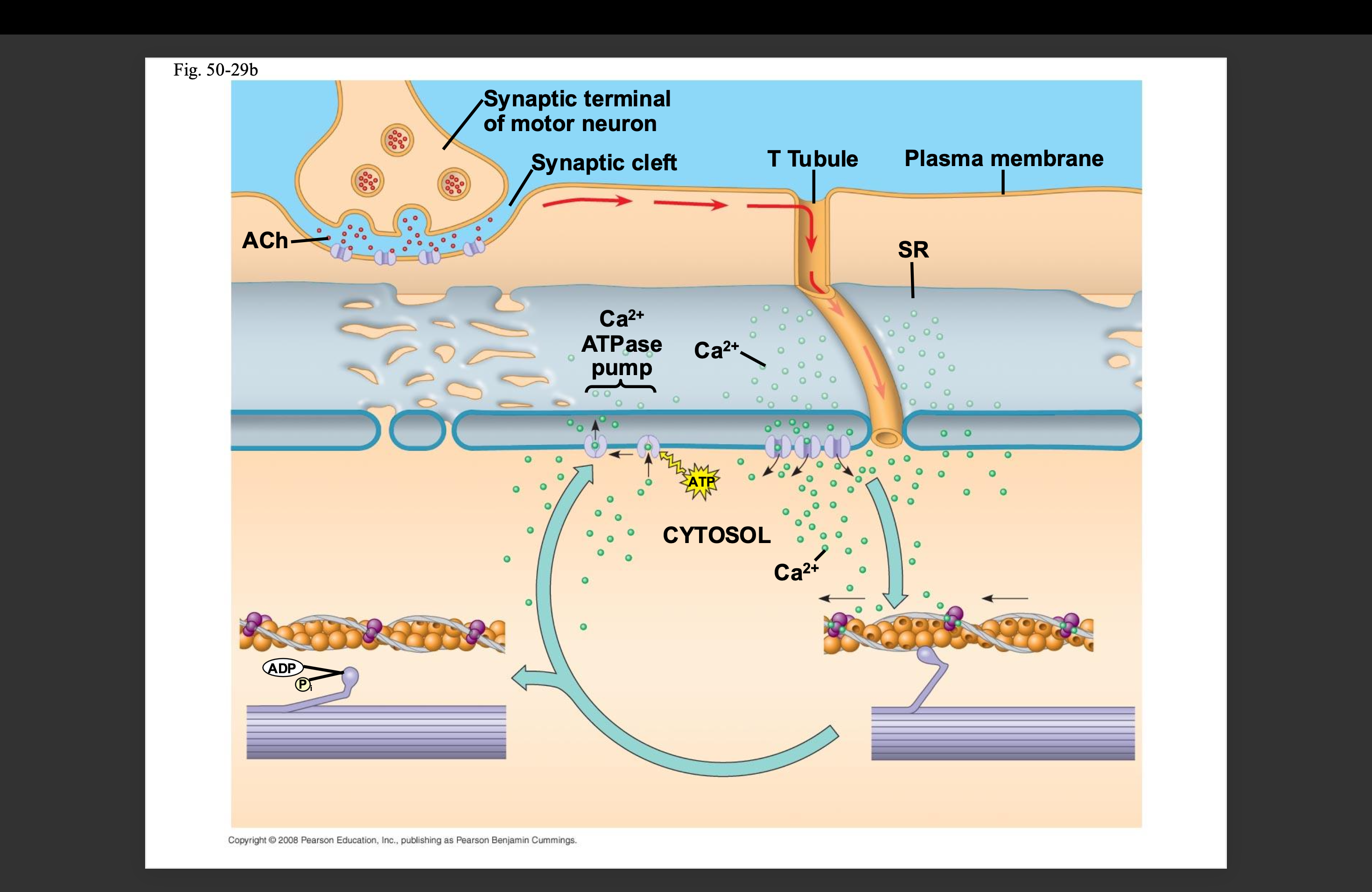
What is the process to get the sliding-filament model started?
A motor neuron releases acetylcholine and diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to receptor proteins on the muscle fiber, triggering an action potential → The action potential goes down t-tubules which triggers calcium ions to be release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum → calcium ions bind to the troponin complex exposing the myosin binding sites → a cross bridge forms and the sliding filament model comes into play → movement stops and calcium ions return to the sarcoplasmic reticulum → contraction ends and muscle fibers relax
Motorunit
a single motor neuron and all the muscle fibers that it stimulates. Fibers work together like a unit.
Large motorunit
like legs or arms and the neuron controls more muscle cells
Small motor unit
would be the fingers or eyes and they control less muscle cells
Fast Twitch
brief rapid powerful contractions. People who have fast twitch muscles contain less mitochondria and myoglobin and is anaerobic
Slow Twitch
Sarcoplasmic reticulum pumps calcium ions more slowly which lasts longer. These muscles contain more mitochondria and myoglobin and is aerobic
What is the main difference between the two twitches?
the rate at which the myosin head hydrolyzes ATP.