Earth-like Planets: Venus, Mars, and Mercury - Properties and Surface Features
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
What is the primary method used to explore Venus's surface?
Radar mapping due to its thick atmosphere.
What is the composition of Venus's atmosphere?
Venus has a very thick carbon dioxide atmosphere, consisting of 96.5% CO2 and 3.5% N2.
What is the surface pressure on Venus compared to Earth?
The surface pressure on Venus is 90 times that of Earth.
How long does it take Venus to orbit the Sun?
Venus orbits the Sun every 225 Earth days.
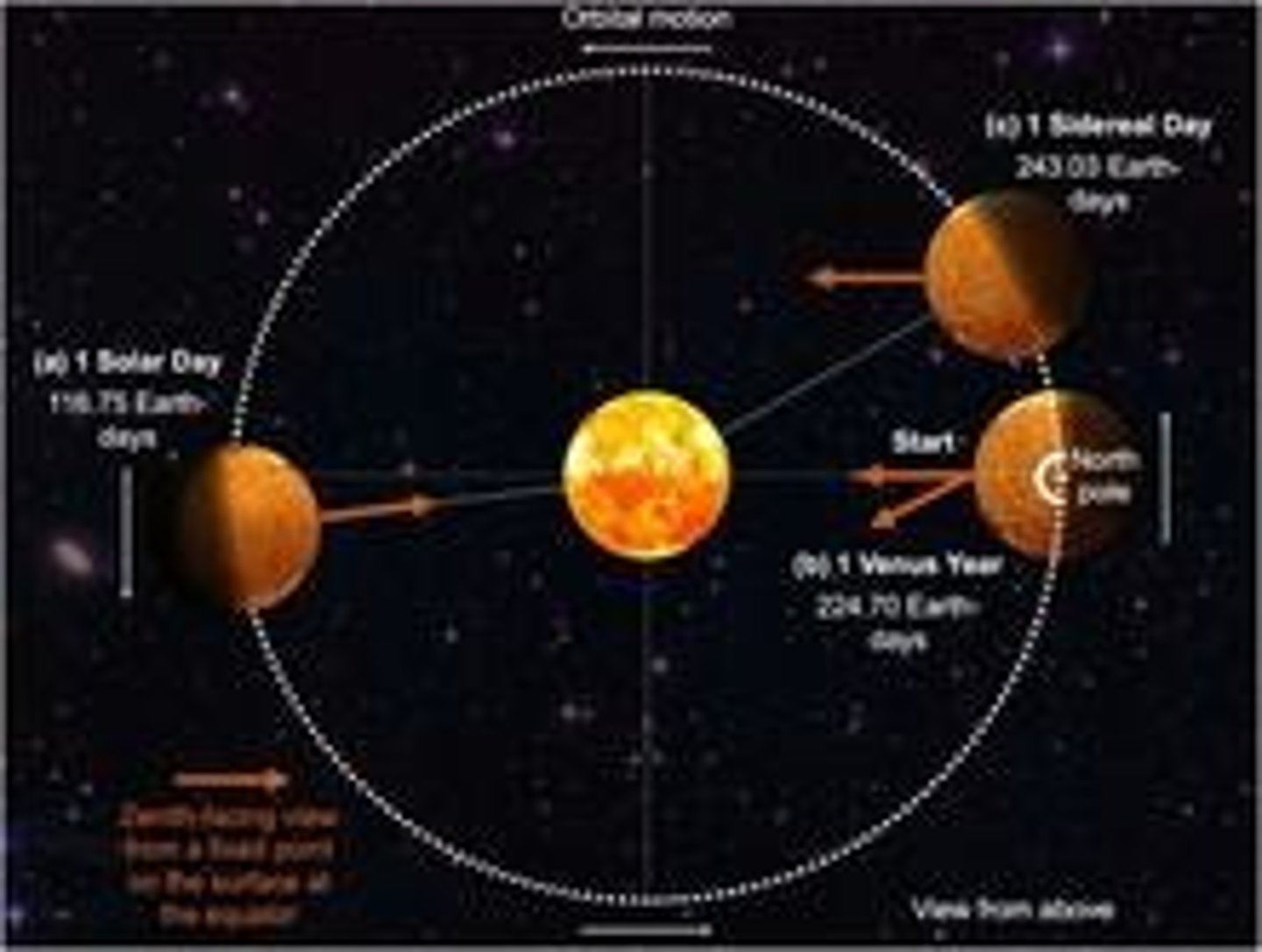
What is unique about Venus's rotation period?
Venus has a sidereal rotation period of 243 Earth days, which is retrograde.
What phenomenon accounts for Venus having little water?
A runaway greenhouse effect.
What are pancake-shaped volcanoes on Venus?
Volcanoes that are about 25 kilometers across and 2 kilometers tall, formed by eruptions of highly viscous lava.
What is the largest impact crater on Venus?
The largest impact craters in the Lavinia region have diameters of 50 kilometers.
What is the significance of Fotla Corona on Venus?
It shows curved fracture patterns and is associated with pancake and dome volcanoes.
What is the appearance of Venus's surface as captured by Venera landers?
The surface appears orange due to the thick atmosphere absorbing bluer colors of light.
What is Olympus Mons?
The largest volcano on Mars and probably the largest in the solar system.
What is Valles Marineris?
A canyon complex on Mars that is 3000 kilometers long and 8 kilometers deep.
What did Giovanni Schiaparelli claim to see on Mars in 1877?
He described seeing canals on Mars.
Who was Percival Lowell?
An astronomer who claimed to have observed canals on Mars and opened an observatory to explore them.
What is the significance of the Martian meteorite?
It is a fragment of basalt ejected from Mars that eventually arrived on Earth.
What is the Tharsis bulge?
A large volcanic plateau on Mars that includes Olympus Mons.
What is the resolution of Mars photographs taken by the Hubble Space Telescope?
The resolution is about 20 kilometers.
What are the primary components of Venus's atmosphere?
96.5% carbon dioxide and 3.5% nitrogen.
What is the temperature increase like in Venus's atmosphere?
Temperature rises steeply below the clouds due to the greenhouse effect.
What is the size of the caldera at the top of Olympus Mons?
The caldera is 65 kilometers across.
What is the significance of the dust devil tracks on Mars?
They indicate wind activity and surface conditions on Mars.
What are the characteristics of the surface of Mars?
Mars has polar caps and dark surface markings but lacks detailed topographic features in early photographs.
What is the primary reason for the weak weather on Venus?
Slow rotation produces a very weak Coriolis effect.
What is the relationship between Venus's day and year?
A solar day on Venus lasts about 117 Earth days, longer than its year.
What evidence suggests tectonic activity on Venus?
Surface fractures and ridges indicate tectonic forces at work.
What are the Lavinia region's characteristics on Venus?
It features rough impact craters that appear brighter in radar images.
What is the significance of the radar images of Venus?
They reveal surface features and geological structures hidden by the thick atmosphere.
What phenomenon on Mars is responsible for redistributing dust?
Dust devils
What is the width of the area shown in the high-resolution photo of dust devils?
About 3 kilometers
What are yardangs?
Long straight ridges aligned with the dominant wind direction on Mars
What is the height of the cliff walls in Ophir Chasma?
Up to 10 kilometers
What does the Martian North Polar Cap primarily consist of?
Mostly water-ice residual cap
What are Nanedi Valles interpreted as?
Valleys of ancient rivers fed by rain or underground springs
What do the dark streaks on the wall of Garni Crater suggest?
Temporary flow of surface water
What are recurring slope lineae on Mars?
Locations where salty liquid water flows on or just below the surface
What evidence of evaporating ice was observed by the Phoenix lander?
Three spots of ice that sublimated away over four Martian days
What do the images from the three Martian landers show?
Flat, windswept plains littered with rocks
What is significant about the Sojourner rover?
It was the first wheeled vehicle on Mars
What is the diameter of Victoria Crater?
800 meters
What was the operational period of the Spirit rover on Mars?
2004 to 2010
What does the image from the Curiosity rover in Gale Crater show?
An ancient lakebed of cracked mudstones
What is the composition of Mars' atmosphere?
96% CO2, 2% Ar, 2% N2
What is depicted in the 'Face on Mars' images?
A formation that resembles a face, seen in low and high resolution
What are the names of Mars' two moons?
Phobos and Deimos
How do Phobos and Deimos compare to Earth's Moon in terms of distance?
Both moons are much closer to Mars than the Moon is to Earth
What is the significance of the Martian landscape shown in the Pathfinder lander images?
It shows the effects of ancient water flow
What is the primary feature of the Martian landscape observed by the Opportunity rover?
Dune fields in the interior of craters
What does the term 'gullies' refer to in the context of Mars?
Dark streaks caused by the flow of water on slopes
What does the term 'outflow channels' refer to?
Channels interpreted as ancient river valleys on Mars
What geological feature is associated with the Valles Marineris canyon system?
Connected valleys with evidence of landslides
What is indicated by the presence of cross-bedded sandstone in Gale Crater?
Evidence of liquid water passing over sediment
What role do dust devils play in Martian exploration?
They help keep solar panels of rovers free of dust
What is a key characteristic of the surface of Mars as seen by the Viking landers?
It is littered with rocks ranging from tiny pebbles to meter-size boulders
What is the significance of the images taken by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter?
They provide high-resolution views of Martian features
What are the two main sides of the Moon?
The side that faces Earth and the far side that faces away from Earth.
What are the dark areas on the Moon's surface called?
Maria.
What is the significance of Apollo 11?
It was the first mission to land humans on the Moon.

Why will footprints on the Moon likely be preserved for millions of years?
There is no atmosphere, ocean, or geological activity to erase them.
What phenomenon causes the same side of the Moon to always face Earth?
Tidal locking.
What is the diameter of Tycho Crater?
About 82 kilometers.
What percentage of the Moon's surface is made up of highlands?
83%.
What are lunar maria primarily composed of?
Basaltic lava.
What is the age of the Mare Orientale impact basin?
Formed 3.8 billion years ago.
What is a key characteristic of lunar rocks compared to terrestrial rocks?
Lunar rocks are chemically distinct from terrestrial rocks.
What is the primary cause of cratering on the Moon?
Impact from meteoroids.
What is the typical diameter of Meteor Crater in Arizona?
About 1.2 kilometers.
What happens during the formation of an impact crater?
A projectile vaporizes, creating a shock wave and ejecting material.
What is the appearance of the Moon at different phases?
It varies based on the position of the Moon relative to the Earth and Sun.
What is the significance of the Apollo 15 mission?
It provided detailed geological studies of the Moon's surface.
What is the main reason no liquid water exists on the Moon?
The lack of atmosphere prevents stable liquid water.
What is the central feature of King Crater?
It shows typical features associated with large impact structures.
What is the role of shadows in lunar craters?
Shadows can preserve frozen water due to eternal darkness.
What is the height of the central mountain in Tycho Crater?
2 kilometers above the crater floor.
What does the term 'ejecta blanket' refer to?
Material that falls back to fill the crater after an impact.
What is the primary geological activity observed on the Moon?
Impact cratering.
What is the significance of the Apollo Project's lunar samples?
They provide insights into the Moon's composition and history.
What is the main visual difference between volcanic and impact craters?
Their profiles are quite different in structure.
How does the Moon's rotation relate to its orbit around Earth?
The Moon rotates once for every orbit around Earth.
What is the primary reason for the black sky observed from the Moon?
The lack of atmosphere prevents scattering of light.
What does the term 'maria' refer to in lunar geography?
Flat plains of basaltic lava on the Moon's surface.
What is the significance of Harrison Schmitt's role on the Moon?
He was a geologist who contributed to lunar geological studies.
What is the Moon's geological status?
The Moon is now believed to be geologically dead.
How long ago did large planetesimals impact the Moon?
About 3.8 billion years ago.
What volcanic activity occurred on the Moon?
Some volcanic activity about 3 billion years ago created lunar maria.
What are the three early models of the Moon's formation?
Co-formation, capture, and rotational split.
What does the Giant Impact Model explain?
It explains the observed properties of the Moon and suggests it formed from a giant impact.

What is the significance of the Giant Impact Model?
It is widely accepted but may never be definitively proven.
What is Mercury's core size compared to the Moon?
Mercury's metallic core is about the same size as the Moon.
What percentage of Mercury's volume does its core occupy?
57% of its volume.
What are the three theories explaining Mercury's large core?
1. Evaporation of outer layers due to heat. 2. A giant impact removed outer layers. 3. Drag from the solar nebula removed lighter elements.
Why should Mercury not have a magnetic field?
Based on its slow rotation period, it should not generate a magnetic field.
What is the actual rotation period of Mercury?
59 days, which is 2/3 of its orbital period.
What causes Mercury's spin-orbit coupling?
Tidal forces from the Sun slow Mercury's rotation until it matches its orbital speed.
What is unique about Mercury's rotation and its elliptical orbit?
Mercury's rotation speed matches its orbital speed at perihelion, where tidal forces are strongest.
What type of surface does Mercury have?
A mixture of heavily cratered and smooth regions, likely ancient lava flows.
What does the topography of Mercury's northern hemisphere show?
It shows a difference in elevation of roughly 10 kilometers.
What are 'hollows' on Mercury?
Lighter areas formed as easily vaporized minerals escape.
What is the Caloris Basin?
The largest known structural feature on Mercury, partially flooded and covering almost two million square kilometers.

What is the Discovery Scarp?
A long cliff on Mercury, nearly 1 kilometer high and over 100 kilometers long, formed after craters.
Where is water ice found on Mercury?
In permanently shadowed low-lying craters near the north pole.