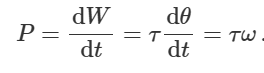dynamics
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
When has velocity reached its max on a displacment time graph?
at point of inflection, second derivative = 0
equation for velocity not including time

how does accelerations direction affect particle
when acceleration is parallel to velocity- speed is changed not direction
when acceleration is perpendicular - speed is constant, direction is changed moves along curve
how is motion related in polar coordinates
theta is related to time, motion is not related to r, r and theta always perpendicular to eachother
what are unit vectors?
length 1 and dimensionless
what is r hat
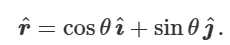
what is the vector r
is a function of theta, associated with change in mag and not direction
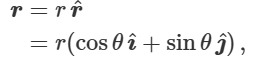
what is theta hat
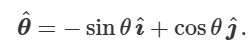
what is the velocity in polar coordinates
as magnitude and direction vary as r and theta move
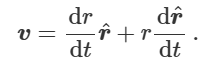
what is the velocity in polar coordinates in r and theta form including components
radial component + tangential component
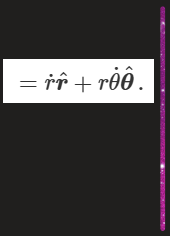
equation for angular velocity
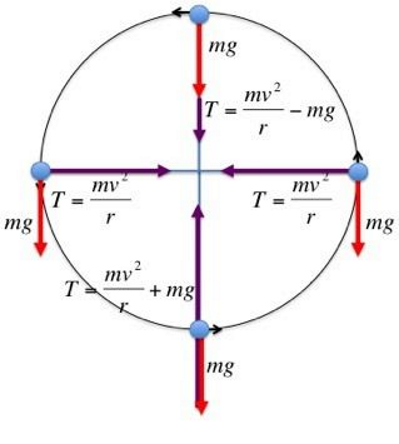
forces in a circle
velocity needed to stay on top is larger or equal to sqrt (Rg)
what is r dot r hat
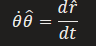
what are the radial and tangenital components in circular motion
a -radial , b-tangential
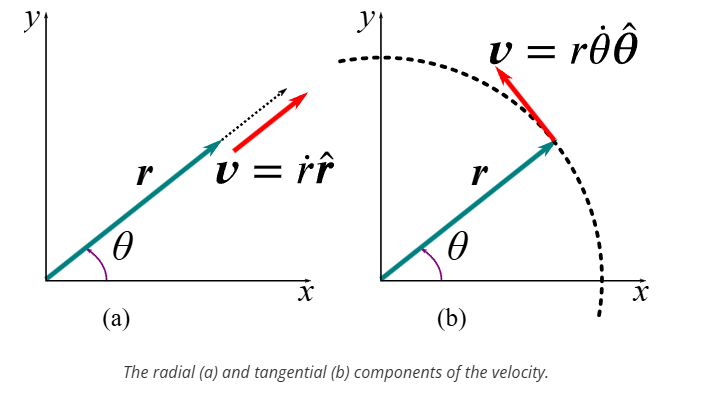
what is acceleration of an object moving in a circle
centripetal acceleration + Coriolis acceleration + linear acceleration

how to derive circular acceleration
this is because coordinate direction changes due to motion of the particle
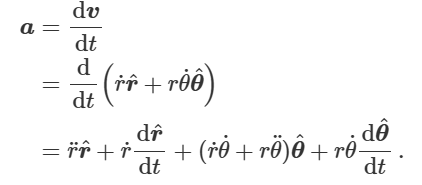
what is newton’s first law/law of inertia
object continues moving if no external force has been applied to it, in the same inertial frame if object appears to not move as it has the same instantaneous velocity
what are the forces on a passenger sitting in the car and the car turns?
as car bends person continues travelling in a straight line (N1), if there is a large centripetal force acting on passenger, they move in curved path, the force is due to friction
if force is not large enough, person slides across seat
what is newton’s second law?
F=ma, vector, force is needed to change motion not maintain in,
what is newton’s second law applied to circular motion?

what is newton’s third law?
action and reaction are equal magnitudes, different in direction and act on different bodies, what does the work doesn’t always provide the force
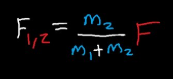
what is the contact force
m2 is the object furthest from where the force was applied
what is friction
force which opposes relative motion of 2 surfaces in contact with each other
what is static friction
on a stationary object, when friction increases as F increases, so object stays in equilibrium
what is limiting friction
when pushing force becomes large enough and frction has reached its maximum so object begins to slide
what is limiting static friction
max friction experienced by stationary body
what is dynamic friction
friction experienced by a moving object, if object is pulled at a constant speed, force is less than force needed to start sliding
what is the friction coefficient
friction / normal
what is the friction coefficient on an inclined body
tan(theta)
why is friction proportional to normal force?
area of contact between objects is small, pressure is high at contact points and become flattened until weight is supported, strong intermolecular forces between them, moving objects need these forces to be broken, when broken they skim past each other ( less force needed for dynamic friction), when load increases, surface flattens further, greater force required
what is the speed of motion in a vertical circle
increases on way down, decreases on way up
what are the components of speed in a circle?
tangential = mg sin(theta)
radial = mg cos(theta) - T
what are the magnitudes on components in a circle
tangential = g sin(theta)
radial = -v²/R
what is the tension at any point in the circle
where theta = 0 in the south direction
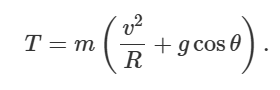
what is the critical speed in a circle
must be at top otherwise string wouldn’t be taunt
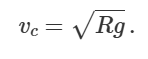
what happens if weight is less than centripetal force
object leaves track and travels short parabola, loses KE, full loop is complete
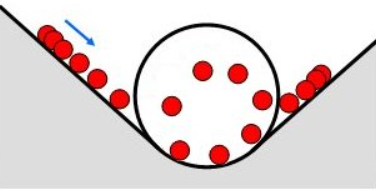
what is work for objects in equilibrium
force x distance travelled x cos(theta)
what is the work done on an object when multiple forces act on an object

what is the work done when force varies?
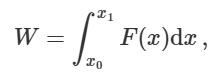
what is the work done by a spring?
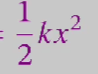
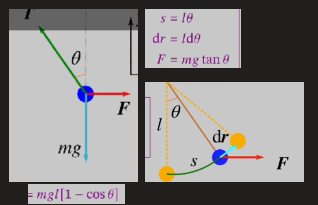
on a pendulum what is the work done
what is work done in 3d
force is a function of r
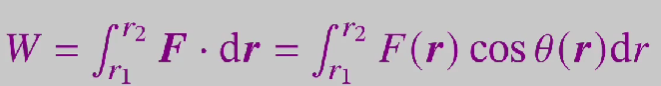
what is the change in work done
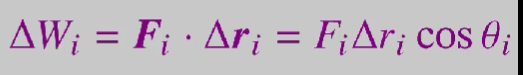
what is the work-energy theorem
work done by resultant force = change in kinetic energy of particle, when velocity is constant there is no work done
what is power
rate of doing work = force x velocity = work / time
equation of power in terms of work done
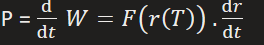
what is centre of mass
point that moves as if all mass was concentrated there and all external forces act on it
what is the equation to find centre of mass
for 3D replace r with vector r
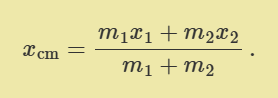
what is rigid body and its centre of mass
system of packed particles
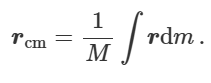
how to find acceleration of centre of mass
all forces acting on body are external, all internal forces cancel (N3)
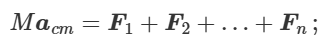
what happens when an object moving in parabolic trajectory gets split in half
same external forces act on each, mass has decreases, trajectory continues, centre of mass of trajectory is the same as full objects trajectory
what is the kinetic energy of a system
KE of centre of mass + KE of particles relative to where they are to centre of mass
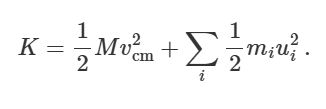
what is the reduced mass
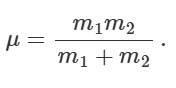
what is the kinetic energy using reduced mass
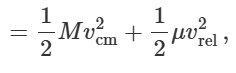
what is gravitational potential energy
seperation between 2 objects causes attraction, shared between both objects, as GPE increases KE decreases
what is the GPE of an object
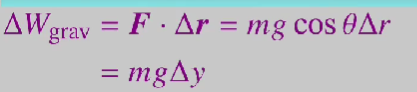
what is work done on a body when lifted
by gravity is negative, potential increases
what is elastic potential energy
energy associated with state of compression
what happens if elastic and gravitational force do work on a body
total mechanical energy is conserved, potential energy is sum of both
what are properties of a conservative force
work done is reversible, independent of path, expressed as difference between initial and final values of U
what is the elastic force
object collides with spring, speed is reducded until it is 0, block moves in opposite direction and gains speed,KE will be the same when it returns, mechanical energy is conserved
what is a non-conservative force
object has less KE than it started, friction does negative work in both directions, total mechanical not conserved
what is the total final mechanical energy
initial mechanical energy + work done by non-conservative forces = change in KE
what is the potential energy in 3D
only for conservative forces
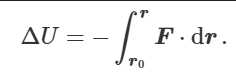
what happens to potential if force is in same direction as displacement
decreases
what do conservative forces do to potential energy
push towards lower potential energy
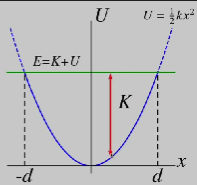
elastic potential graph
total mechanical constant, forbidden region as v cannot be negative
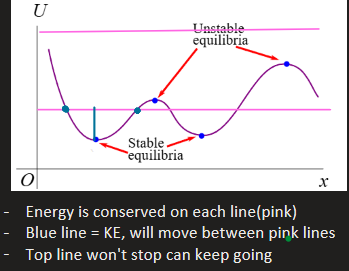
where are the stable and unstable equilibria
what is momentum
vector, mass x velocity, is always conserved
what is the rate of change of momentum
proportional to resultant force, is in the same direction
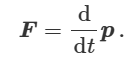
what is the momentum of a centre of mass
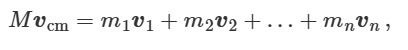
what is impulse
rate of change of momentum
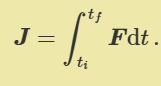
what is the average force of a system
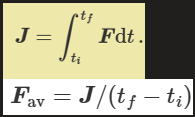
what is an elastic collision
KE is consevered
what is a perfectly inelastic collision
KE is not conserved, objects stick together
what is a partially inelastic collision
KE is not conserved, objects move apart
what happens when one object is stationary when hit
moving object comes to rest, rest object has its velocity
what happens in an elastic collision
realtive velocity = -relative velocity after
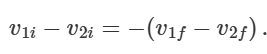
how to find x-components of velocity
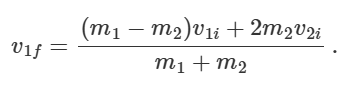
what happens in perfectly inelastic collisions if KE is greater after
potential energy was lost
what is the coefficient of restitution
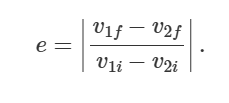
what is a glancing collision
do not hit at centres, conservation of momentum applied in x and y directions
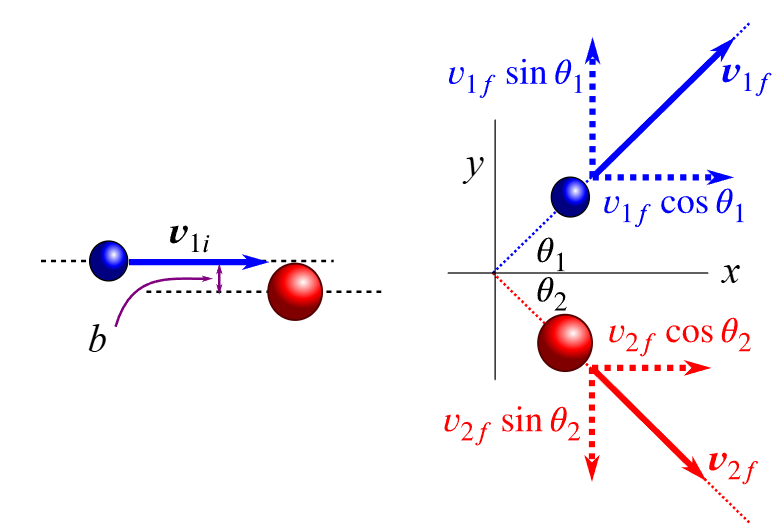
what is an impact parameter
initial distance between centres
what are the angles particles go when they collide
add up to 90degrees, velocities have dot product = 0
what are rotations of rigid bodies
angular displacment is the same for all, ds ( r x dtheta) is different
what is angular velocity
w
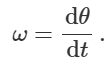
what is angular acceleration
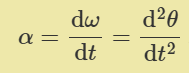
what is the tangential velocity of rotating body
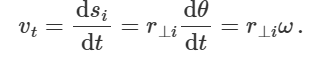
what is the tangential acceleration of rotating body
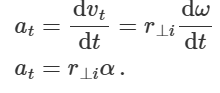
what is radial acceleration of rotating body
= centripetal accleration
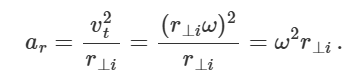
how to find direction of vector
or use of right hand
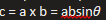
what is KE of rotating body
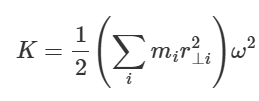
what is moment of inertia
kg m², depends on how mass of object is distribute, further from centre = greater MoI
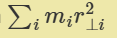
how to calculate moment of inertia
dm = density dV
dV = r dr dz dtheta
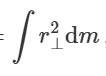
moment of inertia of objects
solid sphere- 2/5MR²
thin sphere - 2/3MR²
ring - MR²
solid circle - 1/2MR²
what is the torque
force x perpendicular distance (cross product), friction force x coefficient of friction
equation of torque from inertia
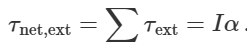
what is torque due to gravity
total gravitational force actin on CoM
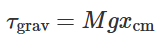
what is parallel axis theorem
proof/example in notes
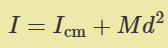
what is work done on rotating objects