Neuroscience
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
Neuroeffector junction
Neuron communicates with muscle fiber or gland
Neuromuscular junction
Neuron communicates with skeletal muscle fibers
Association neurons
Neuron interconnections in brain and spinal cord e.g. interneurons
Astrocytes
Main type of neuroglia that provides structural support, metabolic functions, regulate passage of molecules between bloodstream and CNS
Oligodendrocytes
Wrap axons in myelin sheath to increase speed of conduction in CNS
Schwann cells
Wrap axons in myelin sheath to increase speed of conduction in PNS
Microglia
Helps regulate brain development, maintenance of neuronal networks, injury repair, waste clearance
Tract
Bundle of axons, common origin and termination in CNS
Nerve
Bundle of axons (PNS)
Nucleus
Collection of neuronal cell bodies in CNS
Ganglion
Collection of neuronal cell bodies in PNS
Cerebral cortex
2-4mm grey matter, has gyri and sulci - convolutions, cortical folding
Basal ganglia
Collection of structures including caudate nucleus, lentiform nucleus - putamen, globus pallidus (externa and interna)
Striatum
Contains caudate nucleus, putamen and sometimes Globus Pallidus
Lentiform Nucleus
Putamen and Globus Pallidus
Association fibres
Green, within hemisphere
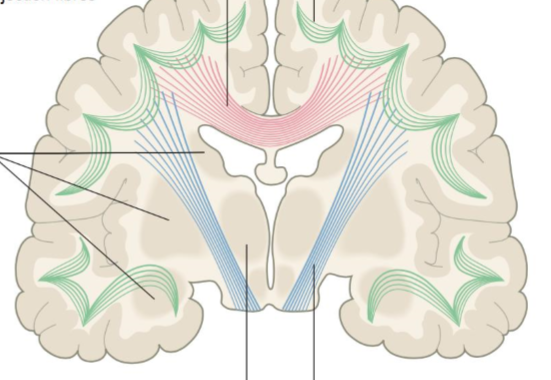
Projection Fibres
Blue, afferent - sensory, efferent - motor impulses, most travel through corona radiata
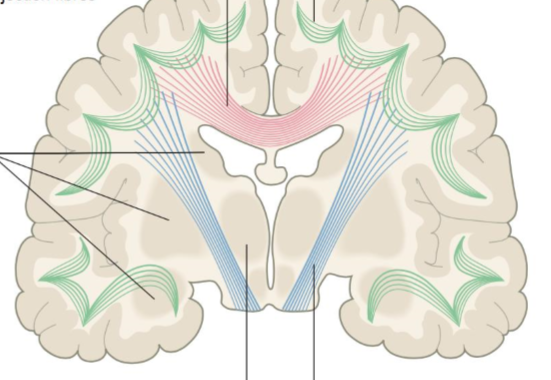
Commissural Fibers
Pink, connects corresponding cortical areas in both hemispheres e.g. corpus callosum
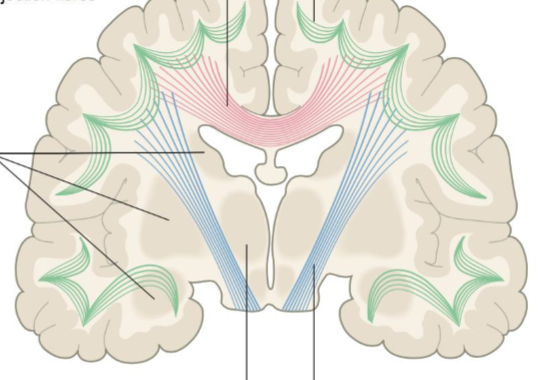
Decussation
The crossing of sensory and motor fibers at midline so that hemispheres process actions and sensations contralaterally
Base (of brainstem)
Part of brainstem that has mainly descending axons
Tegmentum
Part of brainstem that contains nuclei for CN III - XII, Reticular formation and ascending sensory tracts. Between base and cerebellum
Spinal cord
Has H shaped core of grey matter, with outside being white matter
Ventral horn with ventral roots
In the spinal cord where motor axons to periphery
Dorsal horn with dorsal roots
Sensory axons bringing info to spinal cord
Dura mater
Tough membrane attached to inside of skull
Arachnoid mater
Membrane between dura and pia that is cobweb like
Pia mater
Delicate membrane that follows surface of brain
Subarachnoid space
Space between arachnoid and pia mater filled with CSF
Frons
Forehead as a skull landmark
Occiput
Posterior skull landmark
Vertex
Superior/highest point of skull
Temporae
Temple skull landmark
Calvaria
Skullcap
Cran
Skull “bowl” that has 3 sections - anterior, medial, and posterior
Lacrimal bones
Contains duct for tears
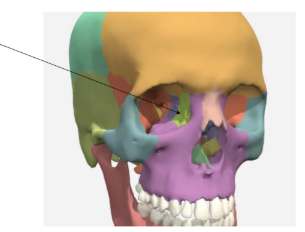
Inferior nasal concha
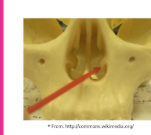
Vomer
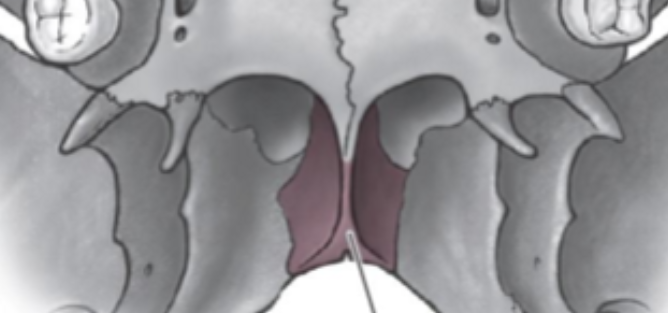
Palatine bone
Transverse palatine suture
Horizontal process
Pyramidal Process
Posterior nasal spine
Posterior third of hard palate
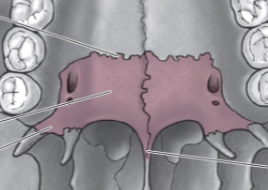
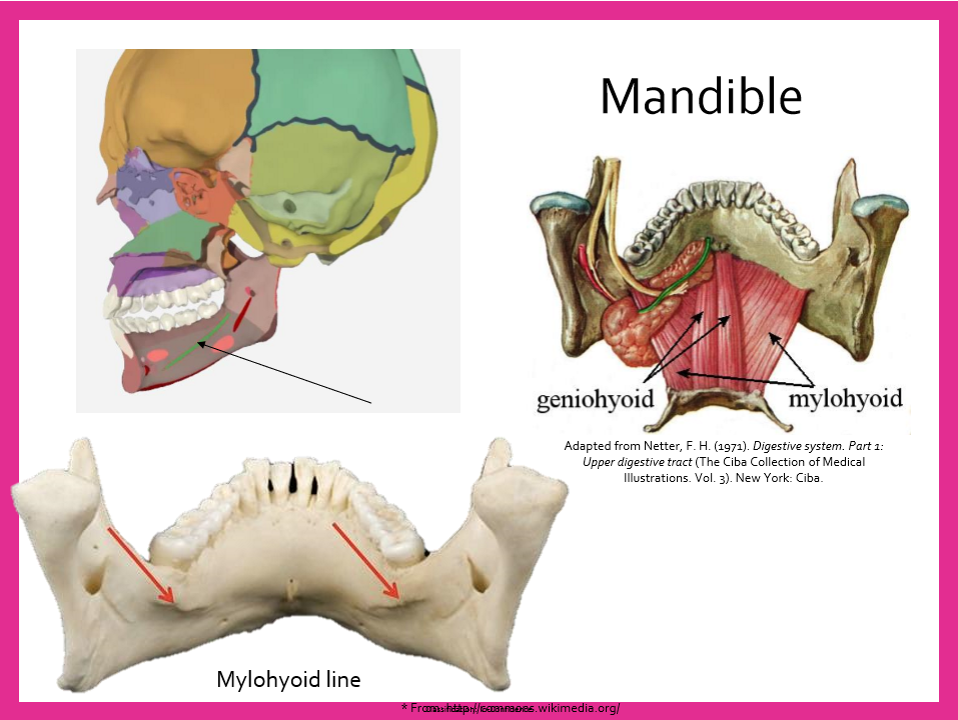
Mental symphysis
Mandible landmark

Mental protuberance
Mental Tubercles
Mandible landmarks
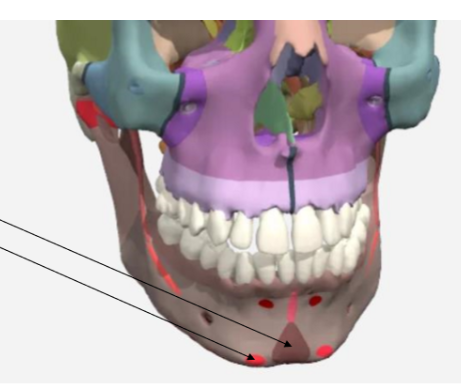
Mylohyoid line
Aorta
Main artery, carries blood from left ventricle to all parts of body except lungs
Internal and External carotid arteries
Common carotid artery branches into…
Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA)
Anterior Cerebral Artery (ACA)
Internal carotid artery branches into…
Middle cerebral artery (MCA)
Supplies blood to lateral surface of frontal, parietal and temporal lobes
Anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
Supplies blood to medial surface of frontal and parietal lobes, corpus callosum, basal ganglia
Basilar artery
Vertebral arteries merge to form this artery at lower border of pons
Posterior Cerebral Artery (PCA)
The basilar artery splits to form these 2 arteries that supply inferior and medial temporal lobes, and lateral and medial occipital lobes, midbrain
Circle of Willis
Arteries are linked by communicating vessels - anterior communicating artery, posterior communicating artery - at base of brain
Ischemia
Type of CVA > 80%, blocked artery resulting in part of brain losing blood supply
Thrombosis
Type of ischemia, involving the narrowing of an artery due to gradual accumulation of debris, usually in areas of turbulence, many occurring during sleep/inactivity as lower BP allows vessels to narrow or close
Embolism
Type of ischemia, fragment of material (broken off blood clot, tissue from tumor, plaque) gets lodged - sudden, often during period of activity
Hemorrhage
Type of CVA ~ 10-15% caused by rupture or leakage of cerebral blood vessels - cerebral bleeding - deprives downstream vessels, puts pressure on surrounding brain
Intracerebral hemorrhage
Type of hemorrhage, bleeding within brain tissues
Epidural/extradural hemorrhage
Type of hemorrhage, often results from meningeal artery - outside dura
Subdural hemorrhage
Type of hemorrhage, between dura and arachnoid
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Type of hemorrhage, caused by disorders of vascular formation such as aneurysm, or arteriovenous malformation
Ectoderm
Top layer of trilaminar embryonic disk, which thickens and forms neural plate, gives rise to nervous system
Mesoderm
Middle layer of trilaminar embryonic disk, becomes cardiovascular, musculoskeletal, urinary and reproductive systems
Bottom layer of trilaminar embryonic disk, becomes respiratory and gastrointestinal systems
Neuropores
Open ends of neural tube
Choroid Plexus
Where CSF is produced
Metencephalon
Pons and cerebellum
Diencephalon
Part of brain that includes thalamus and hypothalamus
Mesencephalon
Midbrain
Myelencephalon
Medulla
Telencephalon
Cerebral hemispheres
Environmental teratogens
Substances that cause developmental defects - drugs, chemicals, infections
Anencephaly
Type of abnormal embryonic development - defective fusion of neural tube - cranial end remains open and forebrain doesn’t develop
Spina bifida
Type of abnormal embryonic development - defective fusion of neural tube - caudal end remains open, malformation of lower spinal cord
Hydrocephalus
Type of abnormal embryonic development - enlargement of ventricles due to CSF accumulation, raised intracranial pressure
Olfactory Area
Inferior temporal and insula
Gustatory area
Anterior insula and frontal operculum
Unimodal
Primarily receives input from a single sensory area
Heteromodal
Recieves input from multiple sensory of multimodal areas
Premotor area
Planning of voluntary movement, integration and interpretation of motor information, contains motor maps for movement of larger muscle groups
Supplementary motor area
Anterior to M1 & Superior to premotor area (medial surface) - maps for postural stabilization, initiation of speech
Broca’s Area (BA 44 & 45)
Dominant hemisphere (usually left)
Pars Triangularis and Pars Opercularis of inferior frontal gyrus
Programs speech movements and phoneme sequencing
Prefrontal Area
Executive functions - planning, problem solving, directing and maintaining attention, decision making. Working memory - retain info long enough to plan and execute behavioural response to a stimulus, personality
Somatosensory Association Cortex (BA 5)
Adjacent to S1 - interpretation of sensory info - lesion can result in astereognosia
Astereognosia
Inability to recognize objects by touch
Posterior parietal cortex (BA 7)
Somatosensory & visual integration, visuospatial perception and attention - representation & manipulation of objects, perception of movement
Lesions → neglect syndrome, apraxia (don’t understand things out of context)
Inferior parietal cortex (BA 39, 40)
Multimodal association cortex - visual, auditory, somatosensory info
Role in receptive language in dominant hemisphere - phonology, reading, spelling
Role in spatial & symbolic representation of abstract concepts
Superior Longitudinal Fasciculus/Arcuate fasciculus
Important tracts connecting inferior parietal cortex to Inferior frontal gyrus and Superior temporal gyrus
Visual Association cortex (BA 18, 19)
Surrounds V1 on medial surface, extending onto lateral surface, interpretation of what we see
Dorsal Stream (of Visual Association cortex)
Where - location and movement of objects
Ventral stream (of Visual association cortex)
What - form and colour of objects
Auditory association cortex
Distinguis sounds as speech, music or noise
Occipitotemporal gyrus/ fusiform gyrus
Inferior surface of temporal lobe - synthesizes and elaborates complex aspects of info - link visual object/word/face to meaning (recognize objects - names of objects)
Visual agnosia
Lesion in fusiform gyrus - can see and describe object, but don’t know what it is, may be able to recognize it using touch or smell
Prosopagnosia
Visual agnosia for faces
Basal ganglia
Regulating cortically initiated motor activity
Suppressing movements extraneous to precise and targeted motor activity
Adjusting automatic motor movements - arm swinging, facial expressions
Learned reflex control
Emotions, personality, cognition
Athetosis
Constant slow twisting movement in muscles - mostly in upper limb & Speech muscles
CN I - Olfactory
Conducts information from nasal chemoreceptors to olfactory bulb via olfactory nerves. Information travels from olfacotry bulb to olfactory tract
CN II - Optic
Light strikes retina, rods and cones convert light energy into a neural signal, excitatory or inhibitory synapses onto bipolar cells
Synapse onto ganglion cells - axons of ganglion cells are the nerve
Homonymous hemianopia
Contralateral field loss in both eyes - lesion in optic tract or optic radiations
CN III - Oculomotor
Elevates upper eyelid
Moves eyeball up, down and medially
Motor component of pupillary reflex, consensual reflex, accomodation reflex
CN - III Oculomotor Nerve Lesions
Ptosis - inability to elevate eyelids
Lateral Strabismus - eyeball deviates outwards
CN IV - Trochlear
Innervates superior oblique muscle
Keeps eyes horizontally level (stops rotation during contraction)
CN IV - Trochlear Lesions
Vertical medial strabismus - difficulty moving eyeball down and laterally
May report difficulty walking down stairs