KNS 372 Exam 2 Material
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
angular motion
all parts of a body move through the same angle
angular displacement
change in angular position or orientation of a line segment
difference in the initial and final angular positions of a moving body
vector
degrees, rads, revolutions
radian
the size of the angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc equal in length to the radius of the circle
“pure number”
how many radians is 360 degrees
2pi radians
angular distance
sum of all angular changes that have occurred
actual angular angles covered from initial to final position
scalar
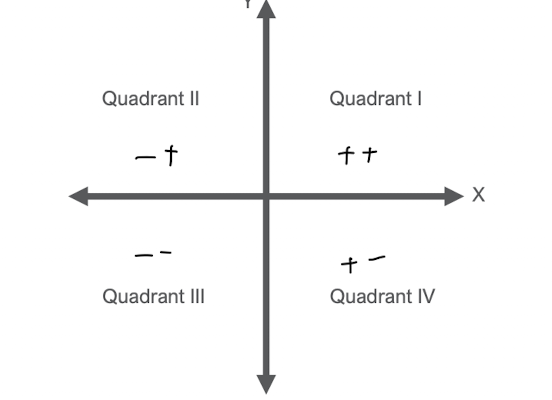
counterclockwise direction
positive
flexion
clockwise direction
negative
extension
angular velocity
angular displacement divided by change in time
angular acceleration
rate of change in angular velocity
(velocity/time)
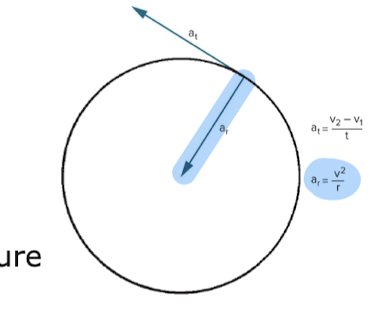
two perpendicular linear acceleration components
tangential acceleration
radial acceleration
tangential acceleration
PATH
represents the change in linear speed
is TANGENT to the curved path
linear acceleration that describes the ROC in magnitude of the tangential velocity vector
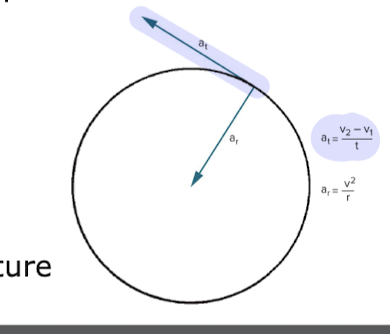
radial (centripetal) acceleration
CENTER
represents change in direction of an object following a curved path
directed toward the center of curvature (middle of the circle)
angle measurement
an angle is composed of two sides (lines) that intersect at a vertex
uses a goniometer
segment (absolute) angles
measured from an external frame of reference
(measured counterclockwise from the right horizontal in bm)
instant center of rotation
precisely located center of rotation at a joint at a given instant in time
joint (relative) angle
angle formed between two limb segments
measured as a segment moves away from the anatomical position
quadrants
zero
straight fully extended position at a joint is ____ degrees
thigh-trunk
hip angle=
thigh-leg
knee angle=
foot-leg-90
ankle angle=
inertia
resistance to a change in an object’s state of motion
directly proportional to an object’s mass
mass (m)
quantity of matter in an object
kg
force
a push or pull
f=ma
newtons, kg*m/s2
characteristics of force
magnitude (in newtons)
direction (+-)
point of application
free body diagram
sketch that shows a defined system in isolation with all of the force vectors acting on the system
net force
single resultant force derived from the composition of all the acting forces
determines the overall effect of all acting forces on a system or free body
center of gravity
point around which the body’s weight is equally balanced
aka balance point, axis of rotation
weight (wt)
amount of gravitational force acting on the body
equal to mass x gravity
Newtons
pressure (P)
force distributed over a given area
P=F/A
Pascals=N/m2
torque (T)
the rotary effect created by an eccentric force
T=Fd (perpendicular distance)
Newton-meter Nm
Impulse (J)
the product of force and the time over which it is applied
J=Ft
Newton-second (Ns)
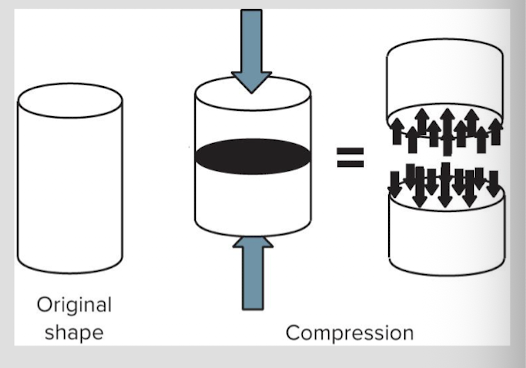
compression
pressing or squeezing force directed axially through a body
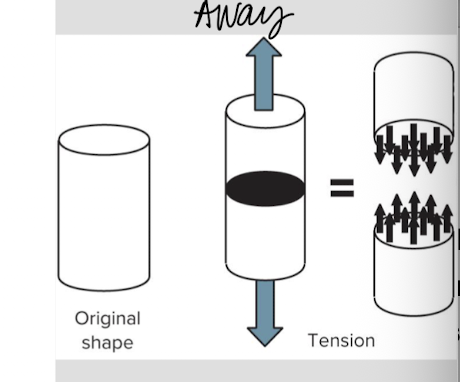
tension
pulling or stretching force directed axially through a body
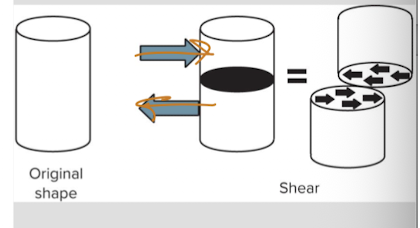
shear
force directed parallel to a surface
mechanical stress
inside the body structure
commonly used to describe force distribution within a body when an external force acts on it
N/m2
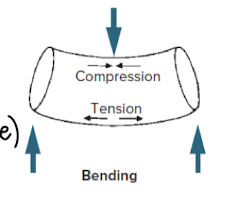
bending
asymmetric loading
produces tension on one side and compression on the other
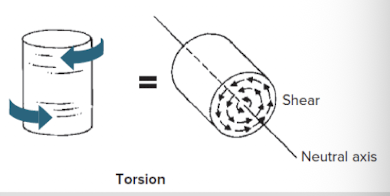
torsion
occurs when a structure is caused to twist about its longitudinal axis, typically when one end of the structure is fixed
combined loading
presence of more than one form of loading
MOST COMMON
deformation
change in shape
effects of loading
deformation
acceleration
yield point
“elastic limit”
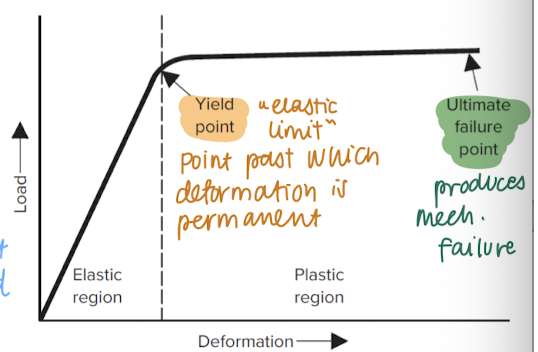
point past which deformation is permanent
ultimate failure point
produces mechanical failure
repetitive loads
repeated application of a subacute load that is usually of relatively low magnitude
can also result from repeated sustenance of forces
“chronic, stress injury”
“microtrauma”
acute loads
application of a single force of sufficient magnitude to cause injury to a biological tissue
“acute macro trauma”
law of inertia (1)
a body will maintain a state of rest or constant velocity unless acted on by an external force that changes the state
law of acceleration (2)
a force applied to a body causes an acceleration of that body of a magnitude proportional to the force, in the direction of the force, and inversely proportional to the body’s mass
law of action and reaction (3)
when one body exerts a force on a second body, the second body exerts a reaction force that is equal in the magnitude and opposite in the direction to the first
ground reaction force (GRF)
every contact of a foot with the floor or ground generates an upward reaction force
(related to performance and injury)
law of gravitation
any two particles of matter attract one another with a force directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance separating them
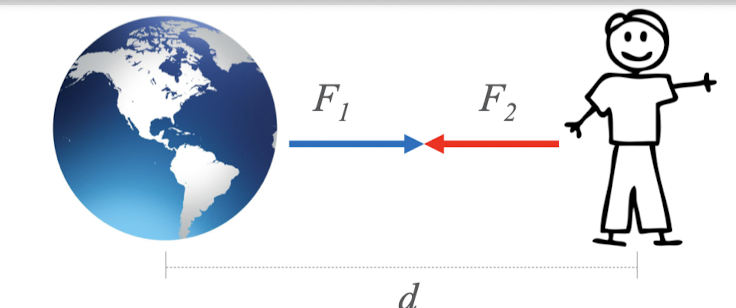
frictional forces
opposes sliding or motion between objects in contact
maximum static friction (Fm)
maximum amount of friction that can be generated between two static surfaces
dynamic (kinetic) friction (Fk)
friction force present during motion
friction
a force acting at the interface of two surfaces in contact during the motion or impending motion of one surface
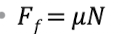
coefficient of friction
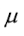
index of the interaction between 2 surfaces in contact
unitless # indicating the relative ease of sliding
normal (perpendicular) reaction force (R or N)
the force exerted by a surface on an object that is in contact with it, acting perpendicular to the surface
momentum
quantity of motion
M=mv
kg*m/s or N*s
Vector
conservation of momentum
in the absence of external forces, the total momentum of a given system remains constant in a closed system
M1=M2
perfectly elastic collision
“bouncy” collision
no energy lost
initial velocities and final velocities are the same
sum of momentums are the same
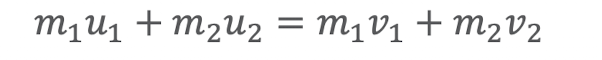
perfectly inelastic collisions
“sticky” collisions
no rebound or bounce
travel at the same speed afterwards (stuck together)
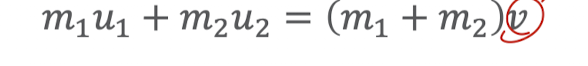
coefficient of restitution
ratio of pre- (u) and post-collision (v) velocity
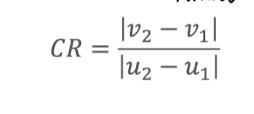
0
coefficient of restitution for a perfectly inelastic collision
1
coefficient of restitution for a perfectly elastic collision
breaking impulse
decelerating (dec. horizontal momentum)
negative impulse, positive momentum (opposite directions)
propulsive impulse
accelerating (inc. horizontal momentum)
positive impulse, positive momentum (same directions)
impulse-momentum relationship
rate of change in momentum produced by the force changes the impulse
Impulse=change in momentum
reduce momentum
impulse and momentum in opposite directions, impulse will…