BIO65 || CH5: The Integumentary System
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
Integumentary System
Comprises the skin (integument), hair, nails, & cutaneous glands; the body's largest organ.
Made of two layers: Epidermis & Dermis
Epidermis
The epithelium layer of the skin; Consists of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium, avascular (no blood supply), with sparse nerve endings.
Dermis
The connective tissue layer of the skin.
Rich in collagen fibers, with two layers: Papillary layer & Reticular layer.
Hypodermis
Connective tissue just underneath the skin, not part of the integumentary system.
Thin Skin
Covers most of the body, hairy, with sebaceous oil glands & sweat glands.
Thick Skin
Found in specific areas like palms, soles of feet, and fingers, hairless with sweat glands, adapted for high friction.
Functions of the Skin
Include resistance to trauma & infection, water retention, synthesis of vitamin D, sensation, thermoregulation, and nonverbal communication.
Eccrine Sweat Glands
Glands that secrete sweat.
Apocrine Sweat Glands
Glands that provide an oily substance, generally sticking to hair.
Keratinocytes
Cells that synthesize the fibrous protein keratin, found in many layers of the epidermis; only found in stratum basale
Melanocytes
Cells that produce melanin, a pigment that protects DNA from ultraviolet radiation.
Tactile (Merkel) Cells
Touch receptors that aid in sensation.
Dendritic (Langerhans) Cells
Cells involved in immune surveillance and the immune system.
Layers of the Epidermis
Include Stratum Basale, Stratum Spinosum, Stratum Granulosum, Stratum Lucidum (ONLY INTHICK SKIN) , and Stratum Corneum.
Where is the hypodermis located?
Below the dermis
What types of tissues are found in the hypodermis?
Adipose and areolar connective tissue
What are the functions of the hypodermis?
Energy storage, thermal insulation, and connection to deeper tissue
Skin Color
Determined by melanin, hemoglobin, and carotene; varies across individuals.
Diagnostic Skin Colors
Include Cyanosis, Erythema, Pallor, Albinism, Jaundice, and Hematoma.
Skin Markings
Such as friction ridges, flexion lines, freckles, and moles.
Hair
An accessory organ of the skin, filament of keratinized cells that grows from hair follicles; grows on thin skin
Three Types of Hair
Include Downy Hair, Vellus Hair, and Terminal Hair.
Structure of the Hair & Follicle
Comprises the bulb, root, shaft, medulla, cortex, cuticle, hair follicle, hair receptors, and arrector muscle.
Nails
Derivative of the stratum corneum, composed of thin, dead, scaly cells with parallel rows of keratin.
Sweat (Sudoriferous) Glands
Include Eccrine (merocrine) glands, Apocrine glands, Sebaceous glands, Ceruminous glands, and Mammary glands.
Skin Cancer
Induced by UV rays, with three main types: Basal cell carcinoma, Squamous cell carcinoma, and Malignant melanoma.
Burns
Leading cause of accidental death, categorized into First-Degree, Second-Degree, and Third-Degree burns.
Cells Types of the Epidermis
Keratinocytes, Melanocytes, Tactile (Merkel) cells, Dendritic (Langerhans) cells
THICK SKIN LAYERS MNEUMONIC
Come, Let's Get Sun Burned
THIN SKIN LAYERS MNEUMONIC
Careful, Getting Sun Burned
Stratum Corneum
the most superficial layer of the epidermis consisting of dead cells
What makes the Stratum Corneum water-repellant?
Lamellar granules in this layer
How are dead cells in the Stratum Corneum replaced?
These dead cells are shed constantly and being replaced by the process described prior
Stratum Lucidum
a layer of the epidermis found only in the thick skin of the fingers, palms, and soles
What is the composition of the Stratum Lucidum?
Composed of a few layers of dead, flattened, translucent keratinocytes
Stratum Granulosum
3rd layer of the skin
What process occurs as cells move through the Stratum Granulosum?
Keratin replaces their nuclei and organelles, leading to cell apoptosis (death)
Stratum Spinosum
A layer of the epidermis that provides strength and flexibility to the skin
What is another name for the Stratum Spinosum?
Prickle cell
What happens in the Stratum Spinosum?
Keratinocytes begin to actively synthesize keratin which builds up in the cells giving them a "prickly" appearance
What is another name for the Stratum Basale?
Stratum Germinativum
How thick is the Stratum Basale?
Only 1 cell thick
What happens if the Stratum Basale is destroyed?
New skin cannot regenerate
What type of cells are mostly found in the Stratum Basale?
Keratinocyte stem cells
Papillary Layer
outer, thin layer of the dermis, directly beneath the epidermis and rich in blood vessels
Reticular Layer
Deeper & thicker layer of the dermis that supplies the skin with oxygen and nutrients
Striae
stretch marks; stretching of dermal collagen
Eumelanin
brownish black pigment
Pheomelanin
reddish-yellow pigment
Hemaglobin
Oxygen carrying pigment in red blood cells (red)
Carotene
yellow-orange pigment (carots) that concentrate in stratum corneum
Cyanosis
bluish discoloration of the skin; caused by lack of oxygen
Erythema
redness; caused by increase blood flow
Pallor
paleness; caused by lack of blood flow
Albinism
Absence of pigment in the skin, hair, and eyes; caused by genetics/heredity
Jaundice
yellowing of the skin; caused by liver failure
Hematoma
bruise; multiple colors
Friction rides of fingertips
Aid in sensitivity to texture and ability to grasp
Cause fingerprint pattern
Flexion lines (creases)
where skin near joint attaches to deeper tissue
Freckles
flat, melanized patches; vary with heredity & UV exposure
Mole (nevus)
Elevated patch of melanized skin
Hair Follicle
A sac within which each hair grows
What are the two layers of a hair follicle?
Epithelial root sheath (inner layer) and Connective tissue root sheath (derived from dermis)
Downy Hair
fine, unpigmented hair on fetus
Vellus Hair
Fine & Unpigmented, all hair in children
→ ⅔ of women's hair
→ 1/10 of men's hair
Bulb
→ Swelling at base where hair originates in dermis
→ Dermal papilla - provides nutrition
→ Hair matrix - hair's growth center (mitosis)
dermal papilla
A small, cone-shaped area at the base of the hair follicle that fits into the hair bulb
Root
Remainder of hair within follicle, dead tissue
Shaft
visible part of the hair; dead tissue
Medulla
internal layer of hair, loosely arranged cells & air spaces
Cortex
bulk of hair, several layers of long cells
Cuticle
→ Outer layer
→ Overlapping scaly cells
Hair receptors
sensory nerve fibers entwining follicles
Arrector muscle (arrector pili)
smooth muscle that causes goose bumps
Why do we have nails instead of claws?
We have flat nails, as opposed to claws, for easier manipulation.
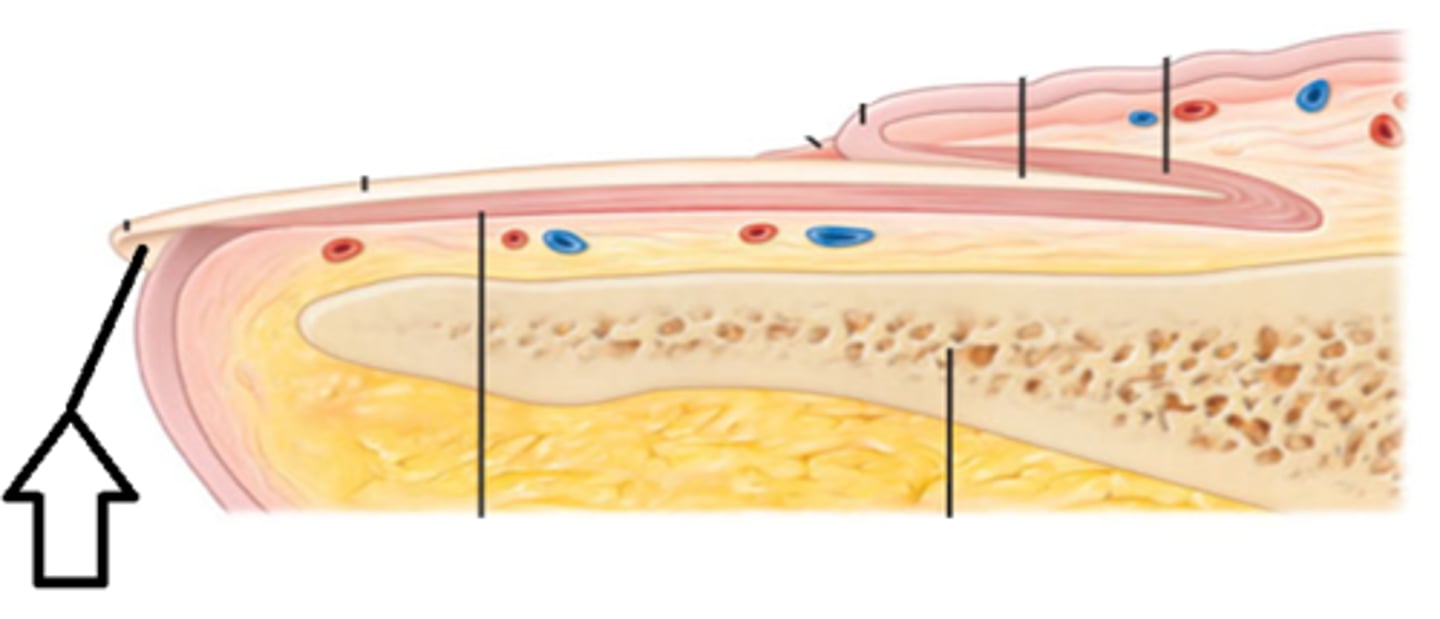
Nail Plate
Hard part of nail. Includes free edge, nail body, nail root.
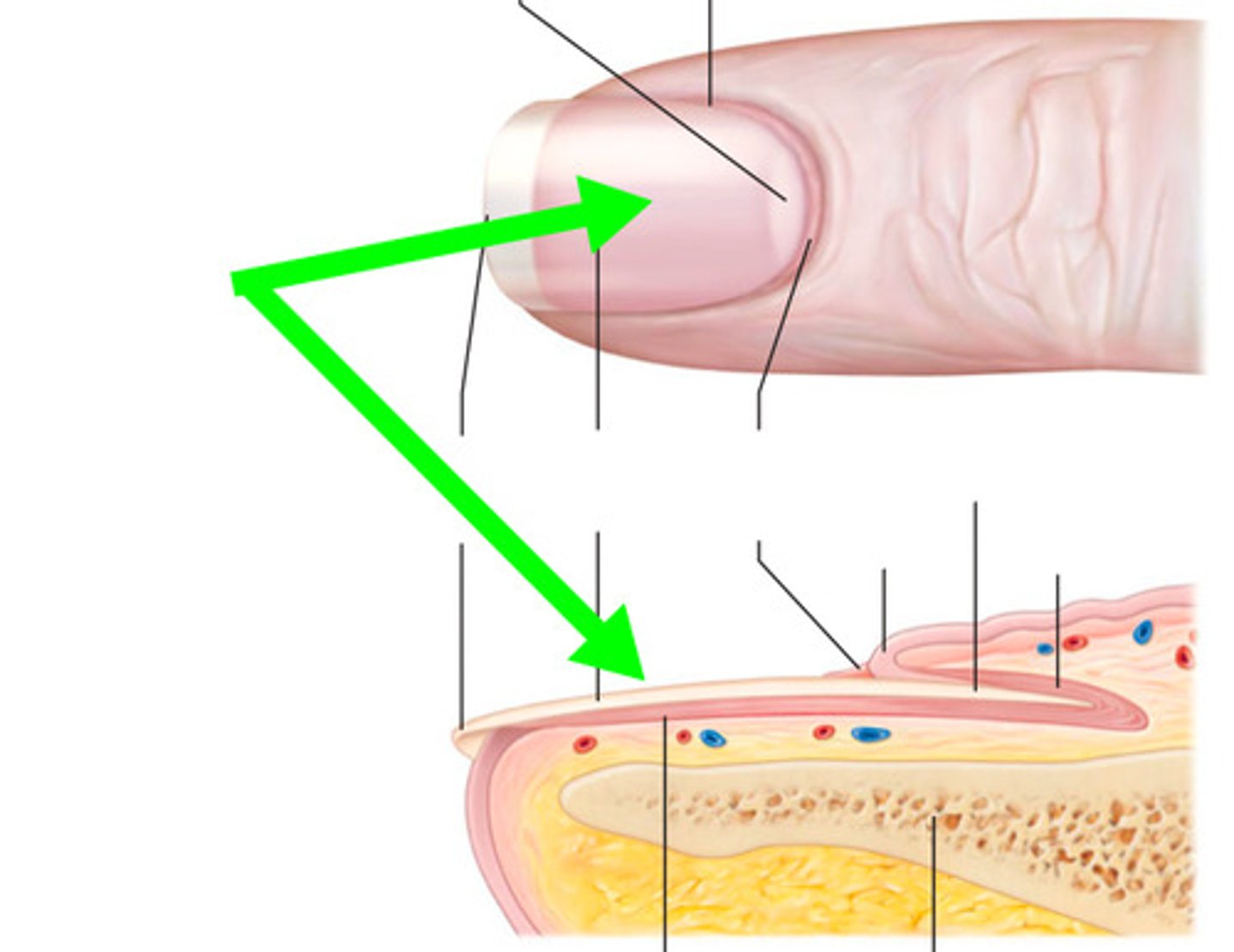
Nail fold
Fold of normal skin that surrounds the nail plate; nail groove
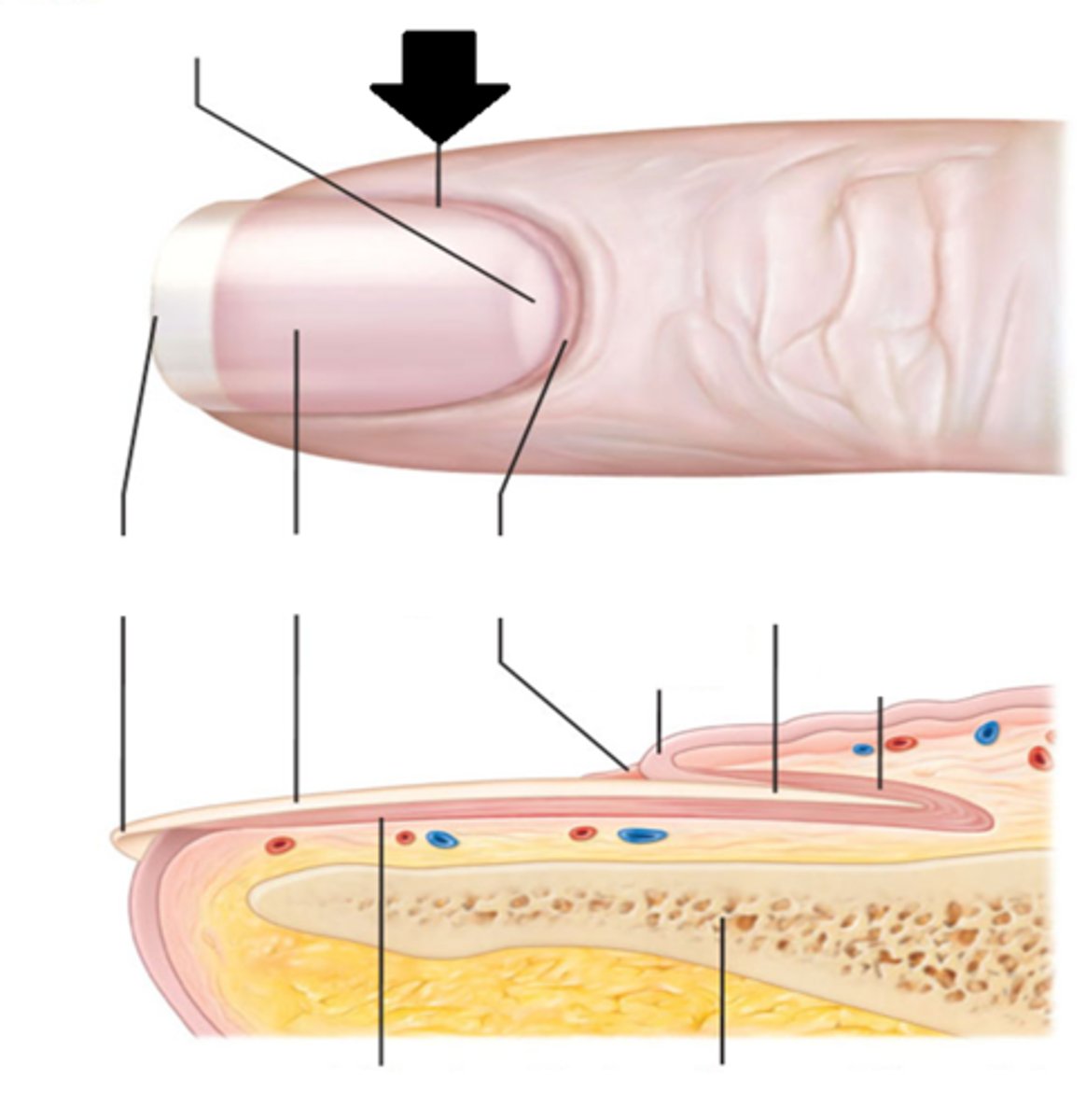
Nail bed
skin underlying the nail plate
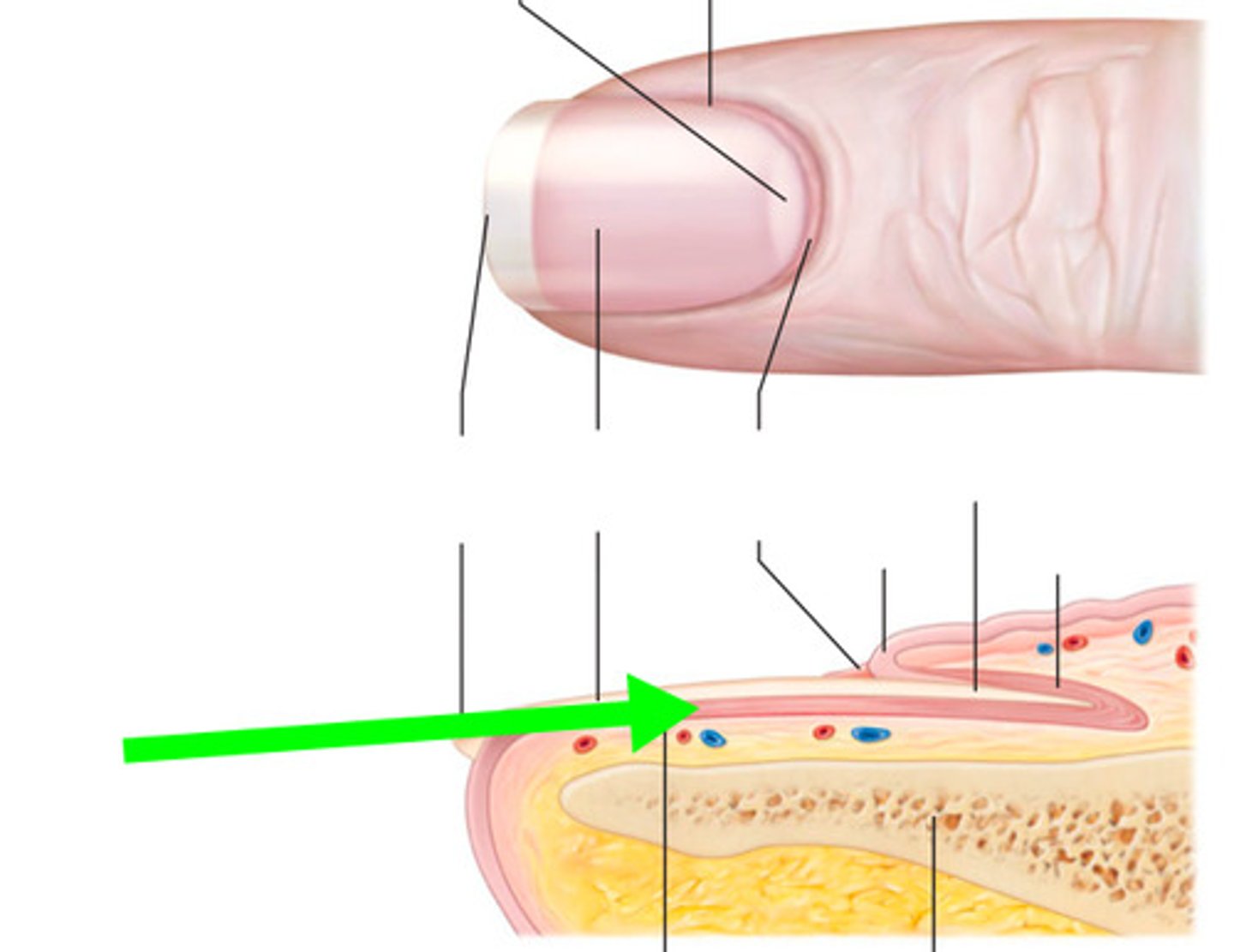
Hyponychium
Skin between the free edge and fingertip of the natural nail
Lunule
an opaque white crescent at proximal end of nail
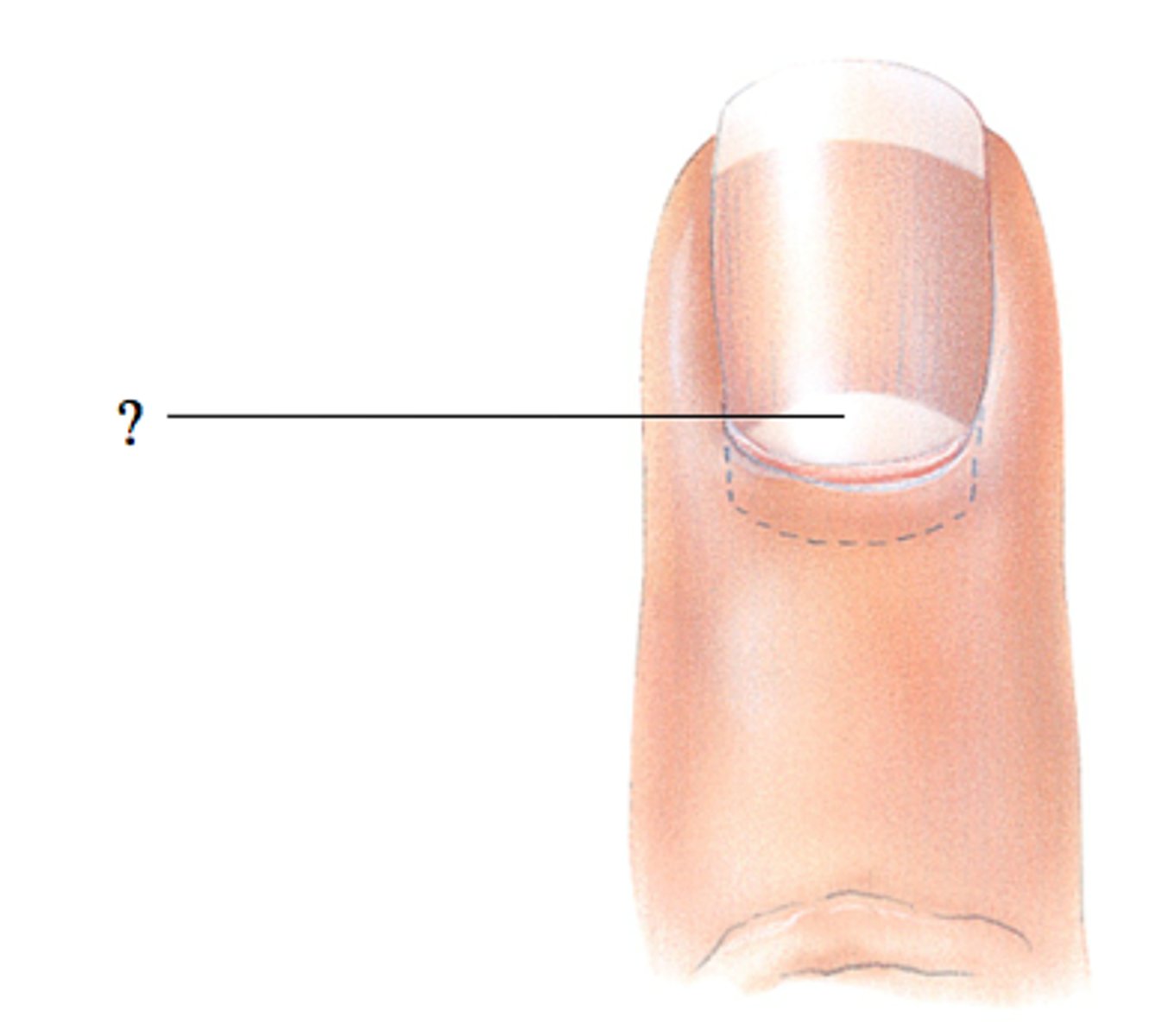
Eponichium
cuticle of nail
Cutaneous Glands
sebaceous glands and sweat glands
Where are eccrine (merocrine) glands especially abundant?
On palms, soles, and forehead
What do simple ducts of eccrine glands lead to?
Pores at the skin surface of the epidermis
What is the main function of eccrine glands?
To produce water and salty perspiration to cool the body
Eccrine (merocrine) glands
glands that produce sweat; found over most of the body
Apocrine glands
Sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat
Where are apocrine glands found?
Groin, anal region, axilla, areola, and beard
What do apocrine glands produce?
Sweat with many fat molecules
What causes the odor associated with apocrine gland sweat?
Bacterial metabolism of fats
How do apocrine glands respond?
To stress and sexual stimulation
When do apocrine glands develop?
During puberty (not active until puberty)
What is the believed function of apocrine glands?
To secrete pheromones
Sebaceous glands
secrete sebum (oil) into the hair follicles where the hair shafts pass through the dermis
What is the main function of sebaceous glands?
Produce oily secretion called sebum
Where do sebaceous glands usually open into?
Hair follicle
How do sebaceous glands help in maintaining skin and hair health?
They keep skin and hair from becoming brittle
Sebum
oily substance secreted by sebaceous glands
Ceruminous Glands
produce ear wax (cerumen)
Cerumen
ear wax