BSCI202: Lab Practical #1
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
What type of tissue is blood?
Connective
What are the formed elements in blood?
Erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells that transport oxygen from tissues throughout the body
What cells are granulocytes?
Neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
What cells are agranulocytes?
Lymphocytes and monocytes
What is the function of a neutrophil?
Phagocytize pathogens or debris
What is the function of eosinophil?
Play a role in allergic reactions and combat parasitic infections
What is the function of a basophil?
Release histamine and play a role in inflammatory responses
What is the function of a lymphocyte?
Directly attacks cells or produces antibodies (adaptive immunity response)
What is the function of a monocyte?
Develops into macrophages in tissues and phagocytize pathogens or debris
List the leukocytes from most abundant to least
Neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils
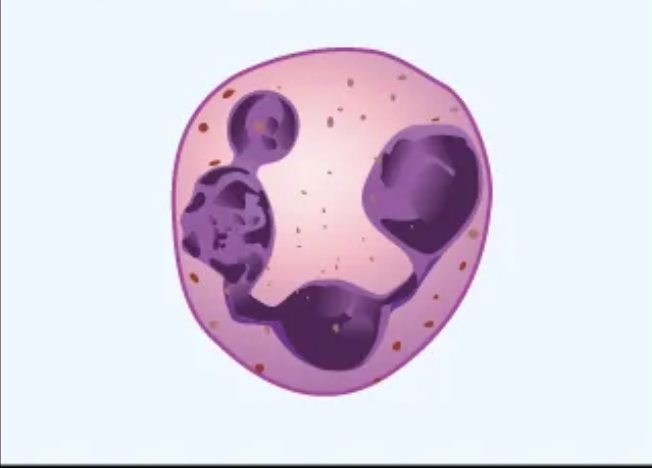
What cell is this?
Neutrophil
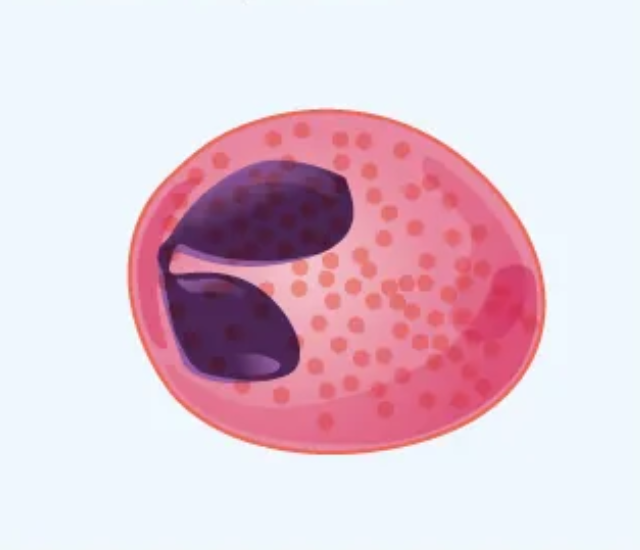
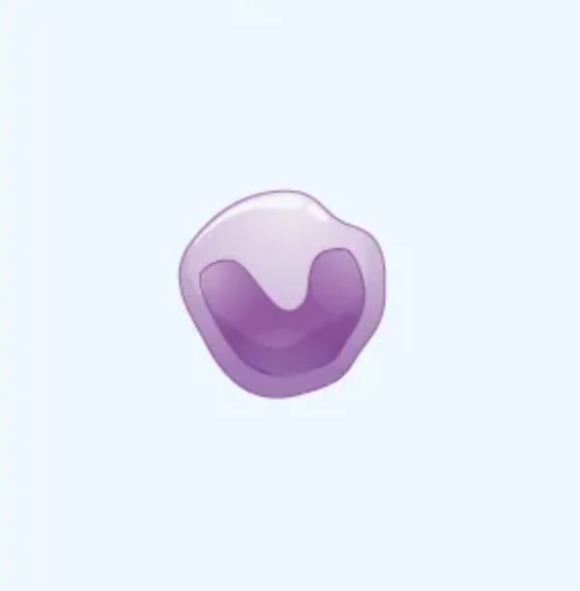
What cell is this?
Eosinophil
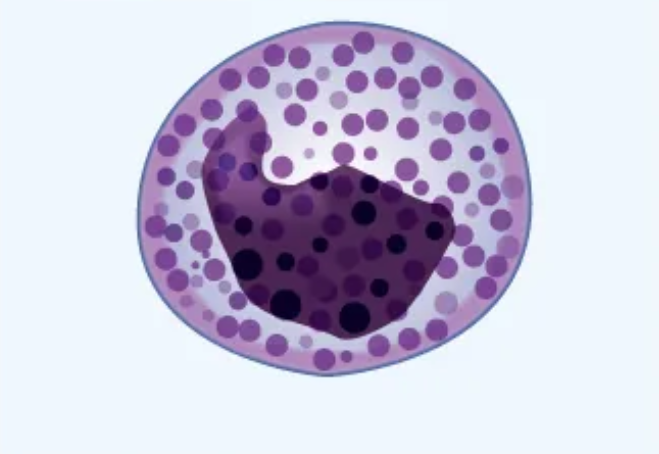
What cell is this?
Basophil
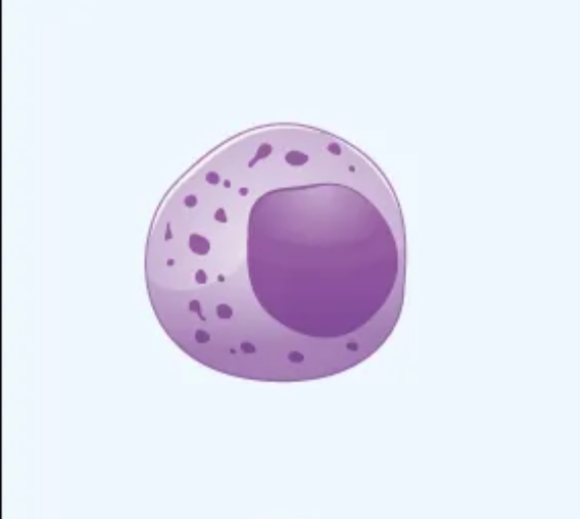
What cell is this?
Lymphocyte

What cell is this?
Monocyte
What are the types of lymphocytes?
B cells and T cells
What is the function of B cells?
Produce antibodies that destroy antigens or pathogens
What is the function of T cells?
Destroy infected cells and help regulate immune responses
What is hematocrit?
The percentage of red blood cells in the total blood volume
How do you calculate hematocrit?
Height of RBC/height of all components of the blood x 100
What is the top layer of hematocrit?
Plasma (~55% of blood)
What is the middle layer of hematocrit?
Buffy coat (less than 1% of blood)
What is the bottom layer of hematocrit?
Erythrocytes (~45% of blood)
What is the buffy coat?
Thin white layer of leukocytes and platelets
What is the normal adult female range of hematocrit?
37-47%
What is the normal adult male range of hematocrit?
42-52%
What is the normal newborn range of hematocrit?
49-61%
What is leukocytosis?
An increased number of leukocytes, caused by infection or leukemia (buffy coat is greater than 1%)
What is aplastic anemia?
Bone marrow doesn’t produce enough erythrocytes (lower hematocrit)
What is iron-deficiency anemia?
Caused by a lack of iron which leads to smaller erythrocytes (lower hematocrit)
What is hemolytic anemia?
Erythrocytes are destroyed too quickly (lower hematocrit)
What is sickle cell anemia?
Erythrocytes are sickle shaped (lower hematocrit)
What is hemorrhagic anemia?
Caused by blood loss (NOT detected by hematocrit)
What is polycythemia?
An increased number of eythrocytes (increased hematocrit)
What happens during dehydration?
Lose plasma volume (no change in RBC but increased hematocrit)
What is different for individuals living at higher altitudes?
Kidneys release more EPO and produce more erythrocytes (increased hematocrit)
How to calculate total magnification
Occular lens (10x) x objective lens
What are three functions of the lymphatic system?
Transports escaped fluids back to the blood
Defends against disease
Aids in digestion
What are two major parts of the lymphatic system?
Lymphatic vessels
Lymphoid tissues and organs
What is lymph?
Fluid within body tissues (leaks out of the capillaries)
How does lymph move?
The skeletal muscle pump and one-way valves
What is the function of lymphatic vessels?
One way system that moves lymph back towards the heart
What is the function of lymph nodes?
Filters lymph and contains defense cells (macrophages and lymphocytes)
How does lymph flow through a lymph node?
Enters through afferent vessels and exits through efferent vessels
Are there more afferent or efferent vessels?
More afferent (having less efferent helps flow for better filtration)
What are the primary lymphoid organs?
Bone marrow and thymus
What is found primarily in the cortex?
Collections of lymphocytes (B cells and T cells)
What is found primarily in the medulla?
Macrophages and plasma cells
What is the cortex?
The outer region of the lymph node
What is the medulla?
The inner region of the lymph node
What cell matures in the bone marrow?
B cells
What cells mature in the thymus?
T cells
Where are blood cells produced?
In the bone marrow
What are the secondary lymphoid organs?
Spleen, lymph nodes, tonsils, adenoid, appendix, Peyer’s patches
Where are lymph nodes commonly located (regions)?
Cervical, axillary, and inguinal
What is the function of the spleen?
Filters blood and destroys worn out blood cells
Which lymphoid organs filter foreign substances?
Spleen (filters blood) and lymph nodes (filters lymph)
Which lymphoid organs trap and destroy pathogens?
Tonsils (throat area) and peyer’s patches (small intestine)
What cells produce antibodies?
Plasma cells
What are the five major classes of antibodies?
IgM, IgG, IgD, IgA, and IgE
What antibody class is the first to appear during a primary immune response?
IgM
Which antibody class is most abundant?
IgG
What is the function of IgG antibodies?
Provides long term immunity (key player in secondary immune response)
What are antigens?
Proteins on RBC membranes
What are antibodies?
Y shaped proteins that attack foreign antigens
What antigens and antibodies are present in type A blood?
A antigens and anti-B antibodies
What antigens and antibodies are present in type AB blood?
A and B antigens and no antibodies
What antigens and antibodies are present in type O blood?
No antigens and anti-A and anti-B antibodies
What antigen is found in positive blood types?
Rh (D) antigen
Who is the universal blood donor?
O negative
Who is the universal recepient?
AB positive
What is agglutination?
Clumping of cells caused by antibodies binding to antigens
What blood type is indicated if anti-A serum causes agglutination?
Blood type A
What blood type is indication if anti-D serum causes agglutination?
Rh-positive (positive blood type)
What are the two semilunar valves?
Pulmonary and aortic
What are the two atrioventricular valves?
Tricuspid (right) and mitral (left)
What seperates the left and right atria?
Interatrial septum
What seperates the left and right ventricles?
Interventricular septum
Describe the systemic circulation route
Left ventricle → aortic valve → aorta → systemic arteries → capillaries → systemic veins → venae cavae → right atrium
Describe the pulmonary circulation route
Right ventricle → pulmonary valve → pulmonary trunk → pulmonary arteries → lungs → pulmonary veins → left atrium
What happens to the heart during systole?
Contraction
What happens to the heart during diastole?
Relaxation
What is the pericardium?
A double walled sac protecting the heart
What is the epicardium?
Outermost layer of the heart wall composed of simple squamous epithelium (AKA visceral pericardium)
What is the myocardium?
The middle layer of the heart wall composed of cardiac muscle (striated and intercalated disks)
What is the endocardium?
The innermost layer of the heart wall composed of simple squamous epithelium
What are the two main components of the pericardium?
Outer fibrous pericardium and inner serous pericardium
Which chamber has the thickest myocardium?
Left ventricle (pumps blood to entire body)
Which valves are open during diastole?
AV valves (allow blood to flow from atria to ventricles)
Which valves are open during systole?
SL valves (allow blood to exit the ventricles)
What does the P wave represent?
Atrial depolarization (before contraction)
What does the QRS complex represent?
Ventricular depolarization and atrial repolarization
What does the T wave represent?
Ventricular repolarization (before relaxation)
What is the function of the right atrium?
Receives deoxygenated blood from superior and inferior vena cava (systemic circulation)
What is the function of the right ventricle?
Pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs (pulmonary circulation)
What is the function of the left atrium?
Receives oxygenated blood from pulmonary veins
What is the function of the left ventricle?
Pumps oxygenated blood into the aorta (systemic circulation)
Electrical Conduction System of the heart
SA node → Atrial contraction → AV node → Bundle of His → Bundle branches (right and left) → Purkinje fibers → Ventricular contraction
What occurs during the PR interval (ECG)
Signal travels from SA node to AV node