CVM - Lecture 5: The Cardiac Cycle
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
This is the amount of stretch on the ventricular wall due to blood filling it
Describe preload
The resistance which ventricles must overcome in order to eject blood
Describe afterload
end diastolic volume: the amount of blood at the end of diastole
EDV
end systolic volume: the amount of blood at the end of systole
ESV
Stroke volume: the amount of blood ejected by the ventricles. EDV-ESV
SV (define and how to calculate)
The number of cardiac cycles per minute
HR
cardiac output: SV x HR
CO
stroke volume increases in response to an increased preload
Describe the Frank Starling law
Optimal length-tension relationship in cardiac sarcomeres for cross-bridge formation
What is the basis of Frank Starling law?
Congestive heart failure reduces stroke volume by overstretching the ventricles, impairing optimal cross-bridge formation and weakening contraction. Diuretics can reduce fluid overload and improve heart function.
How can congestive heart failure affect stroke volume and why?
1. Late diastole: ventricles fill passively with blood from atria
2. atrial systole: extra blood is pumped into the ventricles by atrial contraction
3. isovolumic ventricular contraction: ventricles begin to contract, producing enough pressure to shut the AV valves but not yet to open the semilunar valves
4. ventricular ejection: ventricles contract further, causing ventricular pressure to surpass arterial pressure. This forces open semilunar valves and ejects blood
5. Isovolumic ventricular relaxation: ventricles begin to relax and pressure drops below arterial pressure, causing blood to flow back into semilunar cusps and semilunar valves to shut. At the end of phase 5, ventricular pressure falls below atrial pressure and AV valves open.
Describe the cardiac cycle in 5 phases
This is a brief spike in aortic pressure, following the shutting of aortic valves. This happens because, as aortic valves shut, a slight negative pressure is created at the proximal aorta in conjunction with the elastic recoil from the aortic walls.
What causes the dicrotic notch?
A: Aortic valve opens
B: Aortic valve shuts
C: AV valve shuts
D: AV valve opens
E: Beginning of blood ejection from ventricles as semilunar valves open
F: Begin of passive filling of ventricles as AV valves open
Describe what happens at points A-F
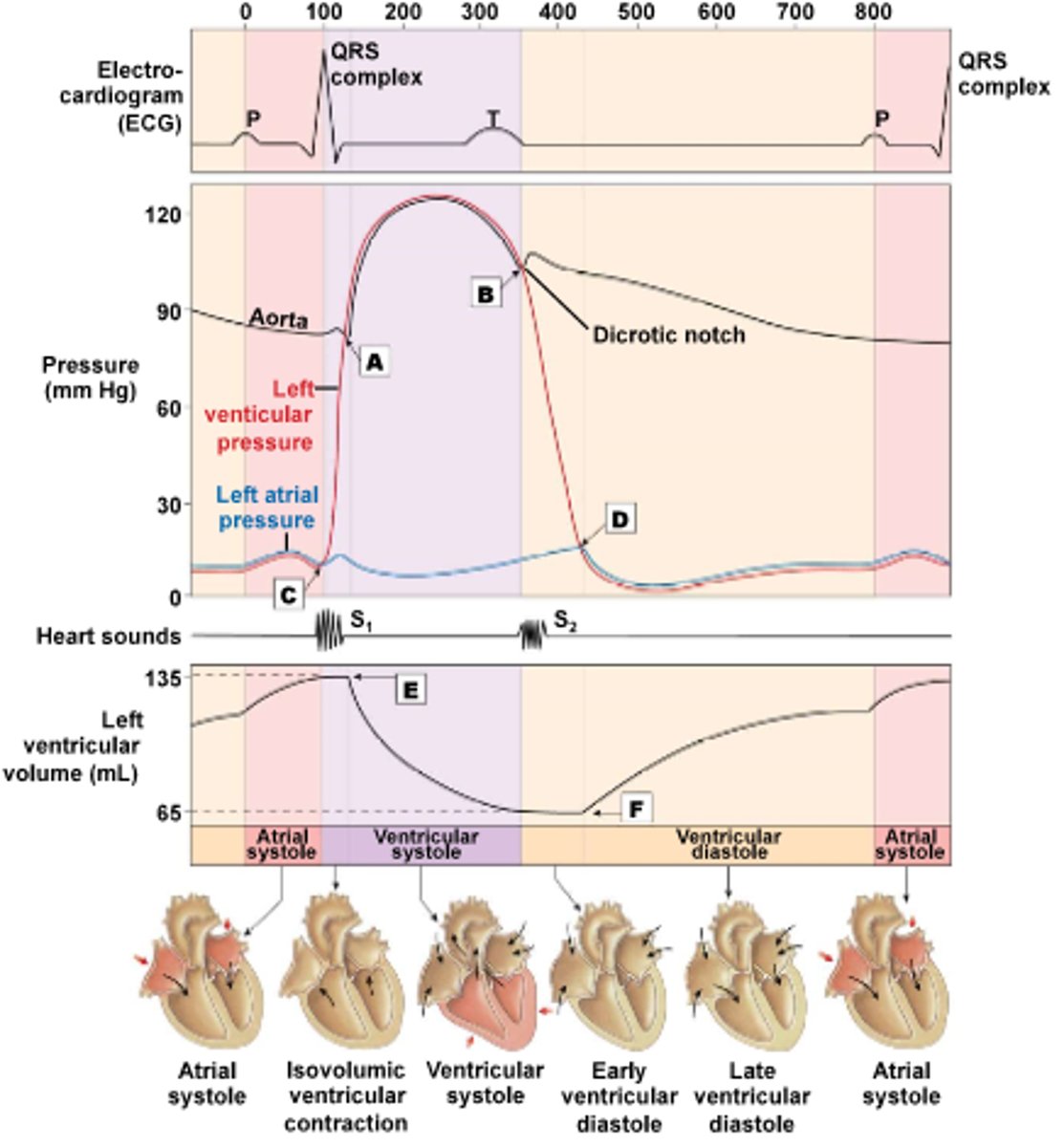
Shutting of AV valves
What does the s1 sound of the heart represent?
Shutting of the semilunar valves
What does the s2 sound of the heart represent?