A&P 1 Chapters 19, 20, 21
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
always check your notes and stuff b4 using these to study for tests bc this might be incomplete
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
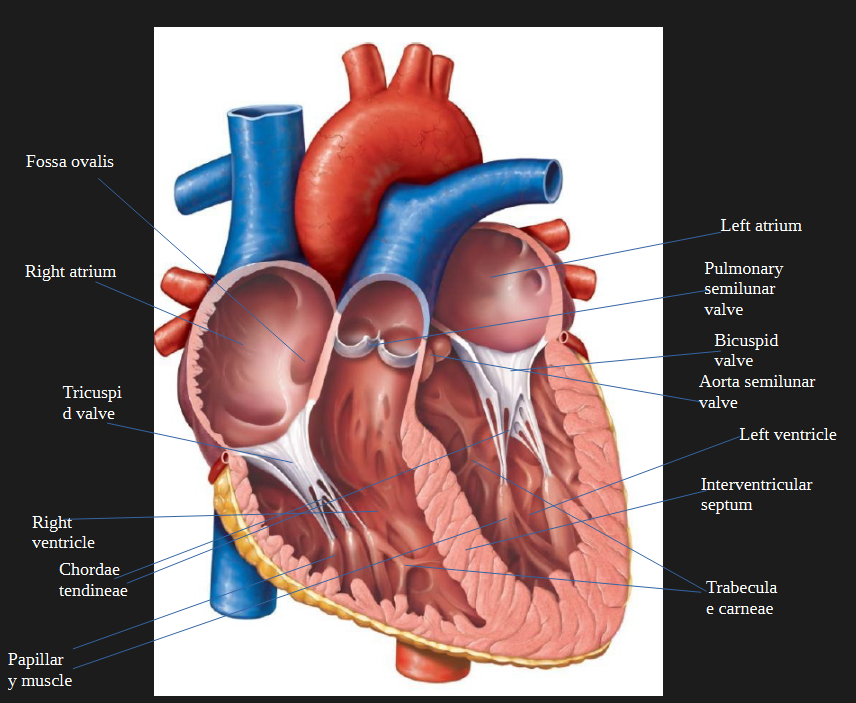
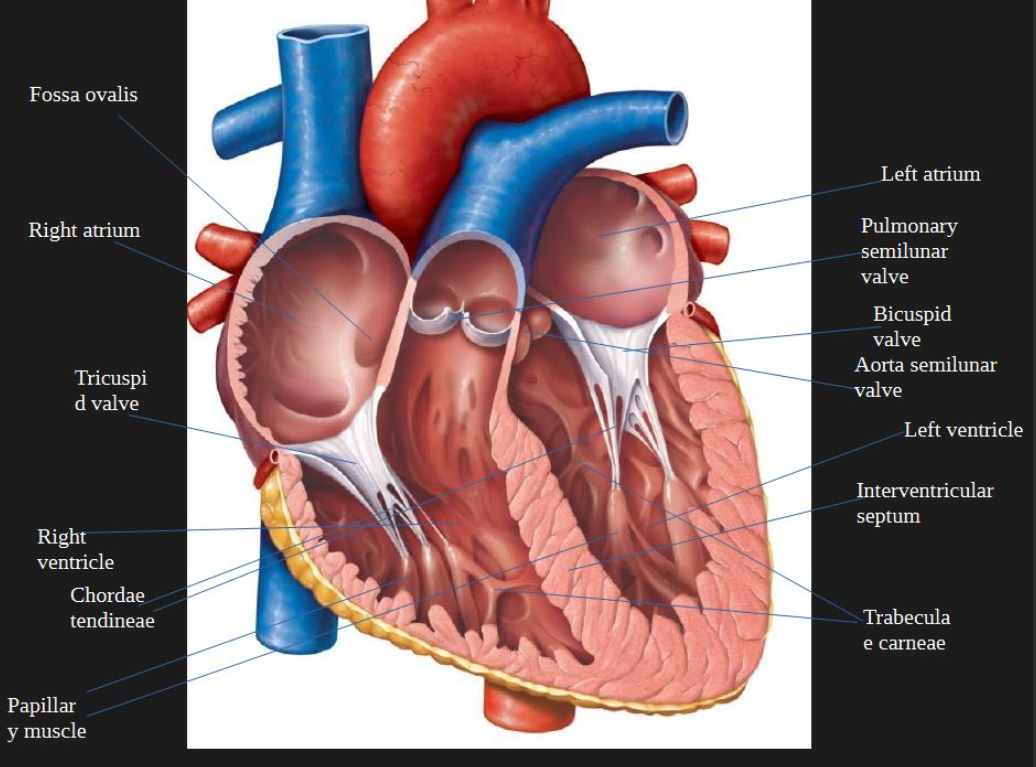
trabeculae carneae
muscle columns that line the right and left ventricle
fossa ovalis
remnant of fetal development in the inner heart
inner heart
inner heart
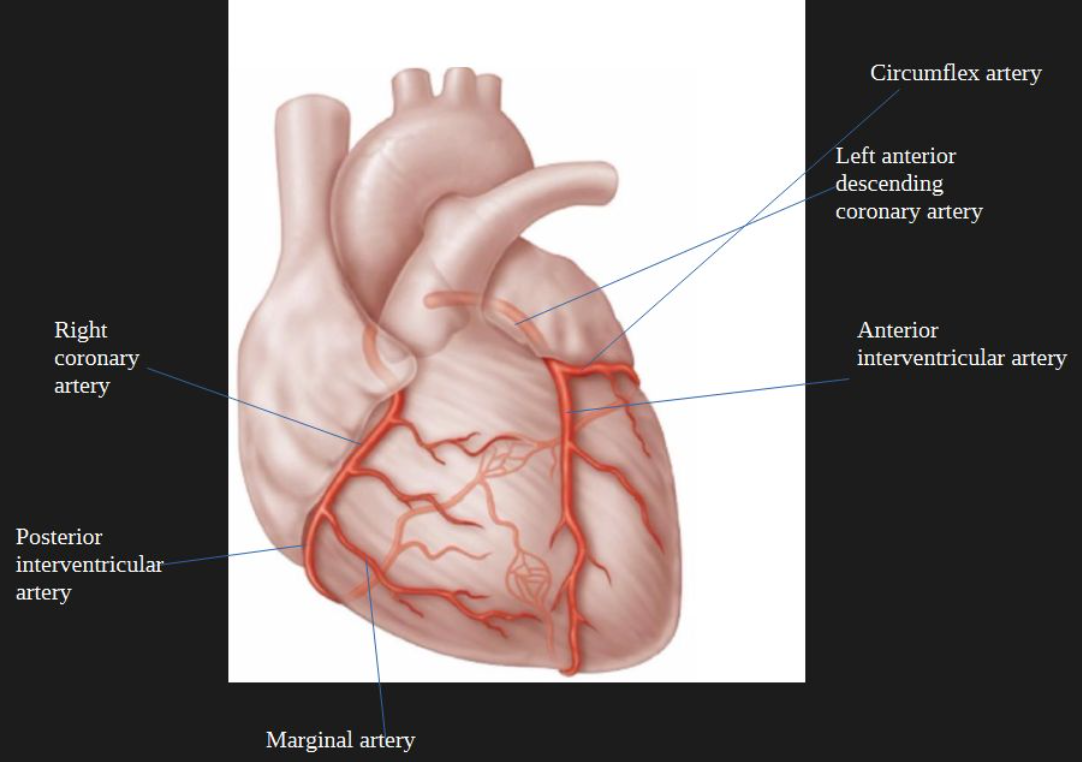
circumflex artery
supplies blood to left ventricle
marginal artery
Supplies right ventricle with blood
1
2
coronary circulation
delivery of oxygenated blood to heart wall
systemic circulation
Circulates blood to and from the body's tissues
right atrium
Blood enters ____ via vena cava.
Deoxygenated blood passes tricuspid valve to right atrium
Blood exits using tricuspid valve to right ventricle.
Exits right ventricle via pulmonary valve.
Deoxygenated blood goes to lung via right and left pulmonary arteries.
Diffusion happens: carbon dioxide is removed and grabs oxygen.
After the lungs, it comes back via the pulmonary veins, entering left atrium
Enters left ventricle via the bicuspid valve.
Oxygenated blood leaves left ventricle thru aortic semilunar valve to organs.
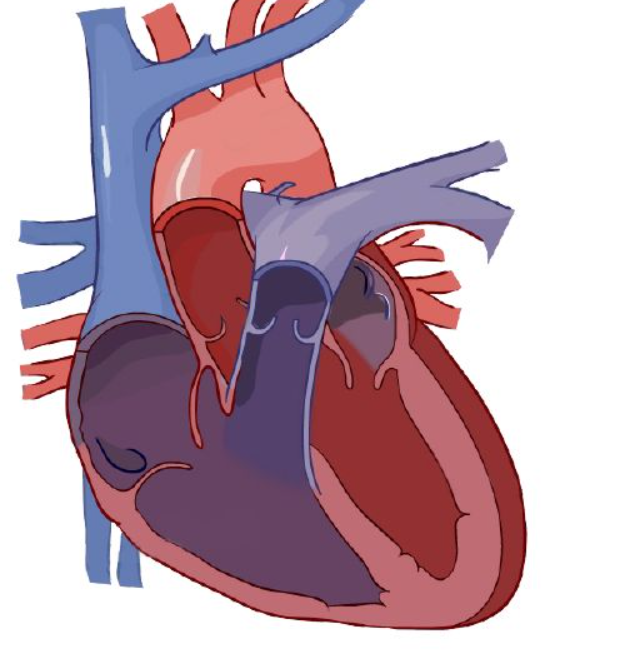
tricuspid valve
Blood enters right atrium via vena cava.
Deoxygenated blood passes _____ to right atrium
Blood exits using tricuspid valve to right ventricle.
Exits right ventricle via pulmonary valve.
Deoxygenated blood goes to lung via right and left pulmonary arteries.
Diffusion happens: carbon dioxide is removed and grabs oxygen.
After the lungs, it comes back via the pulmonary veins, entering left atrium
Enters left ventricle via the bicuspid valve.
Oxygenated blood leaves left ventricle thru aortic semilunar valve to organs.
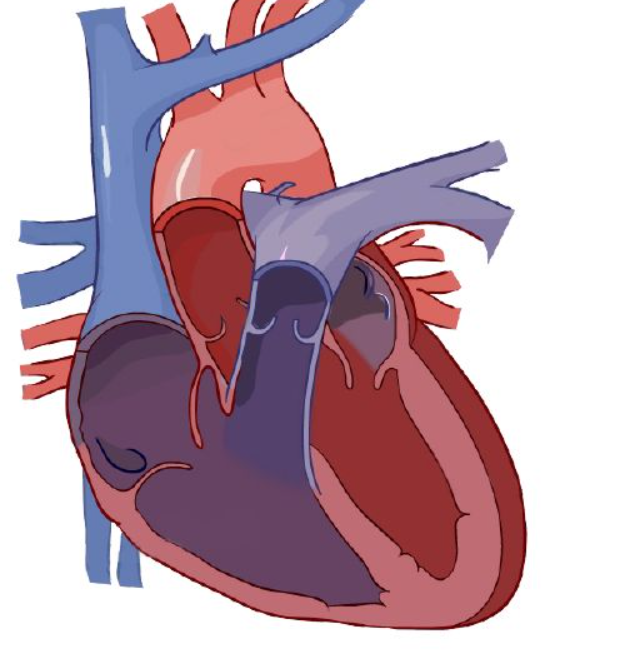
right ventricle
Blood enters right atrium via vena cava.
Deoxygenated blood passes tricuspid valve to right atrium
Blood exits using tricuspid valve to _____.
Exits right ventricle via pulmonary valve.
Deoxygenated blood goes to lung via right and left pulmonary arteries.
Diffusion happens: carbon dioxide is removed and grabs oxygen.
After the lungs, it comes back via the pulmonary veins, entering left atrium
Enters left ventricle via the bicuspid valve.
Oxygenated blood leaves left ventricle thru aortic semilunar valve to organs.
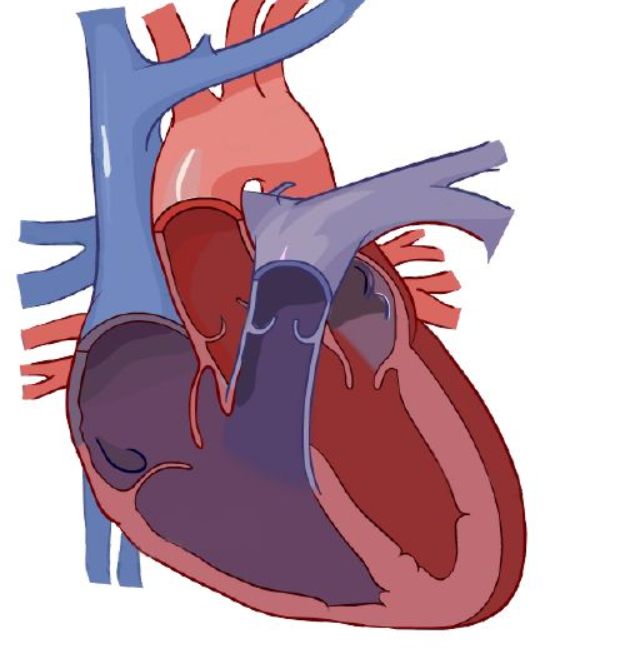
pulmonary valve
Blood enters right atrium via vena cava.
Deoxygenated blood passes tricuspid valve to right atrium
Blood exits using tricuspid valve to right ventricle.
Exits right ventricle via ______ ______.
Deoxygenated blood goes to lung via right and left pulmonary arteries.
Diffusion happens: carbon dioxide is removed and grabs oxygen.
After the lungs, it comes back via the pulmonary veins, entering left atrium
Enters left ventricle via the bicuspid valve.
Oxygenated blood leaves left ventricle thru aortic semilunar valve to organs.
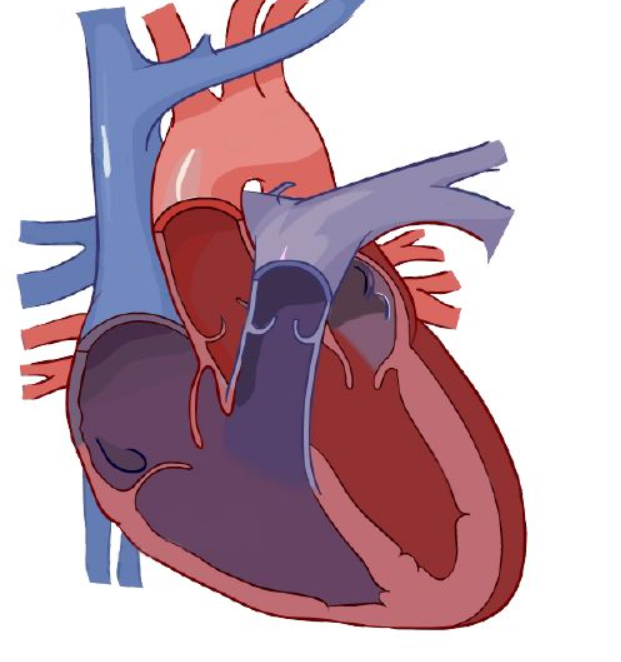
pulmonary artery
Blood enters right atrium via vena cava.
Deoxygenated blood passes tricuspid valve to right atrium
Blood exits using tricuspid valve to right ventricle.
Exits right ventricle via pulmonary valve.
Deoxygenated blood goes to lung via _____ _____.
Diffusion happens: carbon dioxide is removed and grabs oxygen.
After the lungs, it comes back via the pulmonary veins, entering left atrium
Enters left ventricle via the bicuspid valve.
Oxygenated blood leaves left ventricle thru aortic semilunar valve to organs.
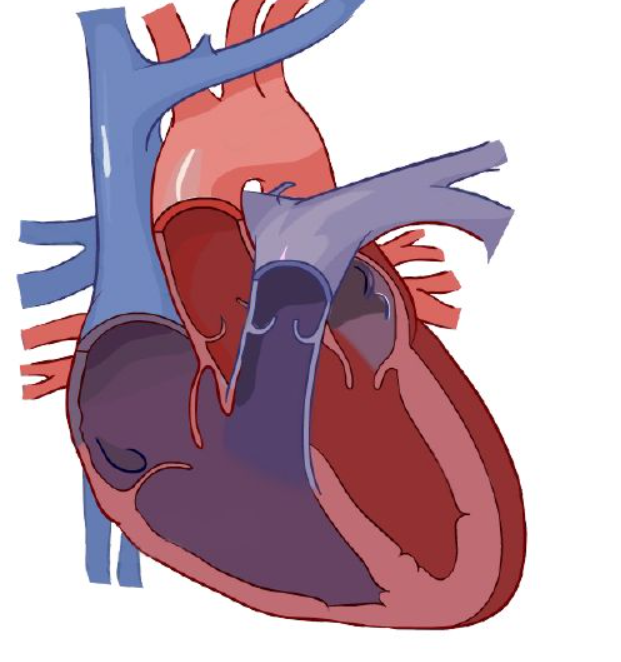
pulmonary veins
Blood enters right atrium via vena cava.
Deoxygenated blood passes tricuspid valve to right atrium
Blood exits using tricuspid valve to right ventricle.
Exits right ventricle via pulmonary valve.
Deoxygenated blood goes to lung via right and left pulmonary arteries.
Diffusion happens: carbon dioxide is removed and grabs oxygen.
After the lungs, it comes back via the _____ _____, entering left atrium
Enters left ventricle via the bicuspid valve.
Oxygenated blood leaves left ventricle thru aortic semilunar valve to organs.
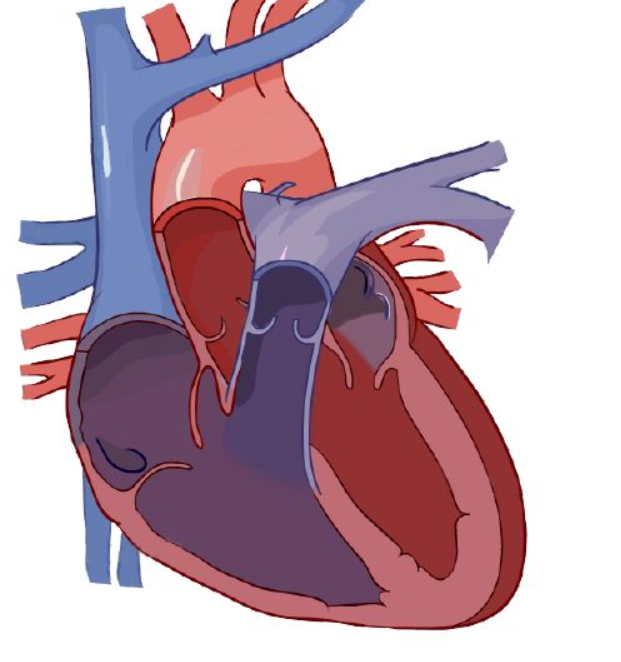
left atrium
Blood enters right atrium via vena cava.
Deoxygenated blood passes tricuspid valve to right atrium
Blood exits using tricuspid valve to right ventricle.
Exits right ventricle via pulmonary valve.
Deoxygenated blood goes to lung via right and left pulmonary arteries.
Diffusion happens: carbon dioxide is removed and grabs oxygen.
After the lungs, it comes back via the pulmonary veins, entering ______ ______.
Enters left ventricle via the bicuspid valve.
Oxygenated blood leaves left ventricle thru aortic semilunar valve to organs.
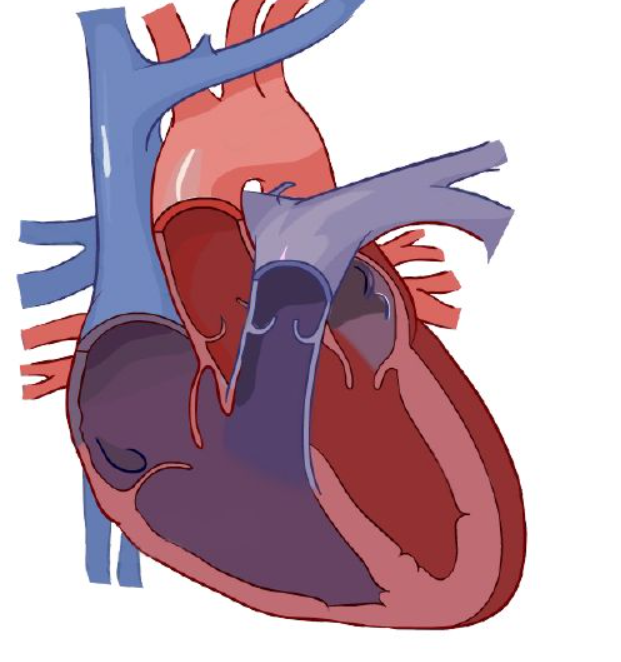
left ventricle
Blood enters right atrium via vena cava.
Deoxygenated blood passes tricuspid valve to right atrium
Blood exits using tricuspid valve to right ventricle.
Exits right ventricle via pulmonary valve.
Deoxygenated blood goes to lung via right and left pulmonary arteries.
Diffusion happens: carbon dioxide is removed and grabs oxygen.
After the lungs, it comes back via the pulmonary veins, entering left atrium
Enters ____ _____ via the bicuspid valve.
Oxygenated blood leaves left ventricle thru aortic semilunar valve to organs.
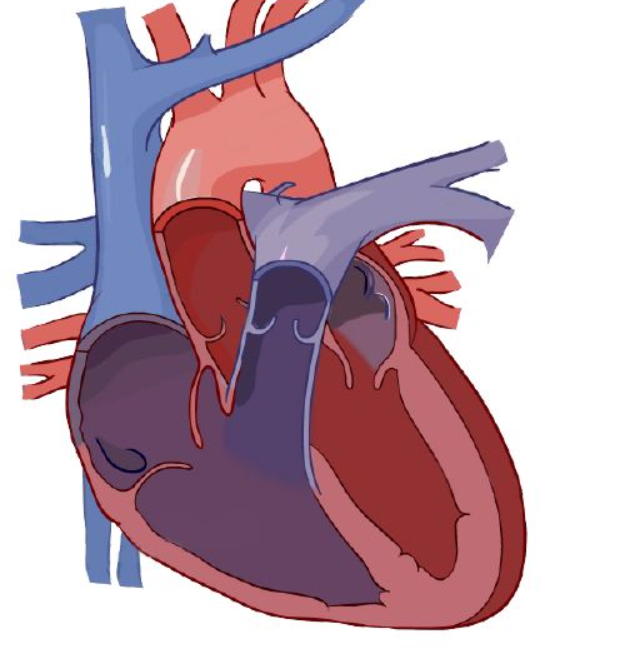
bicuspid valve
Blood enters right atrium via vena cava.
Deoxygenated blood passes tricuspid valve to right atrium
Blood exits using tricuspid valve to right ventricle.
Exits right ventricle via pulmonary valve.
Deoxygenated blood goes to lung via right and left pulmonary arteries.
Diffusion happens: carbon dioxide is removed and grabs oxygen.
After the lungs, it comes back via the pulmonary veins, entering left atrium
Enters left ventricle via the ____ ____.
Oxygenated blood leaves left ventricle thru aortic semilunar valve to organs.
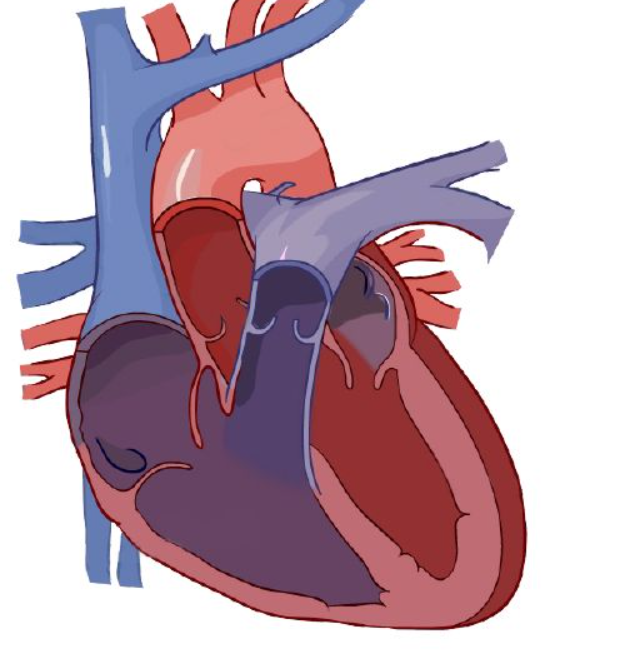
aortic semilunar valve
Blood enters right atrium via vena cava.
Deoxygenated blood passes tricuspid valve to right atrium
Blood exits using tricuspid valve to right ventricle.
Exits right ventricle via pulmonary valve.
Deoxygenated blood goes to lung via right and left pulmonary arteries.
Diffusion happens: carbon dioxide is removed and grabs oxygen.
After the lungs, it comes back via the pulmonary veins, entering left atrium
Enters left ventricle via the bicuspid valve.
Oxygenated blood leaves left ventricle thru ____ ____ ____ to organs.
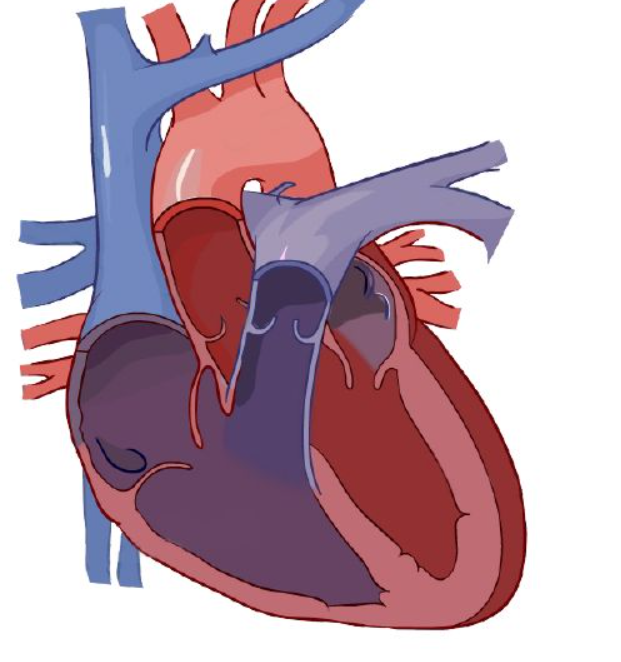
Bundle branches
Transmits action potentials to Purkinje fibersq
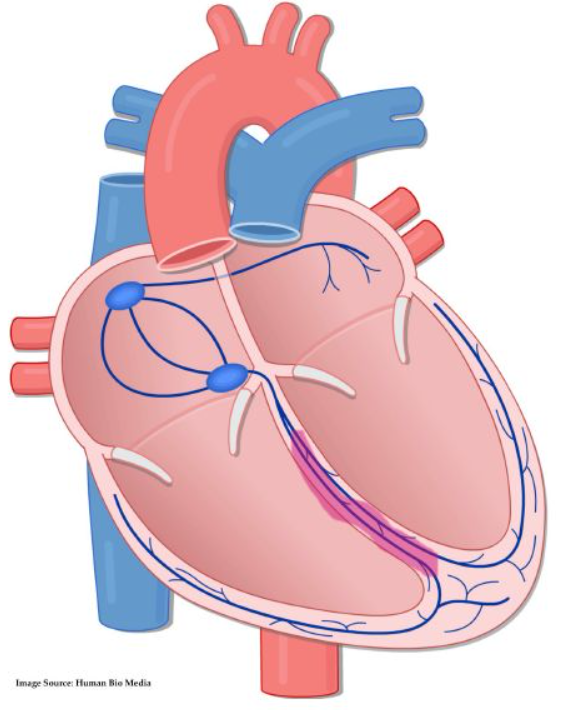
AV node
carries impulse toward ventricle
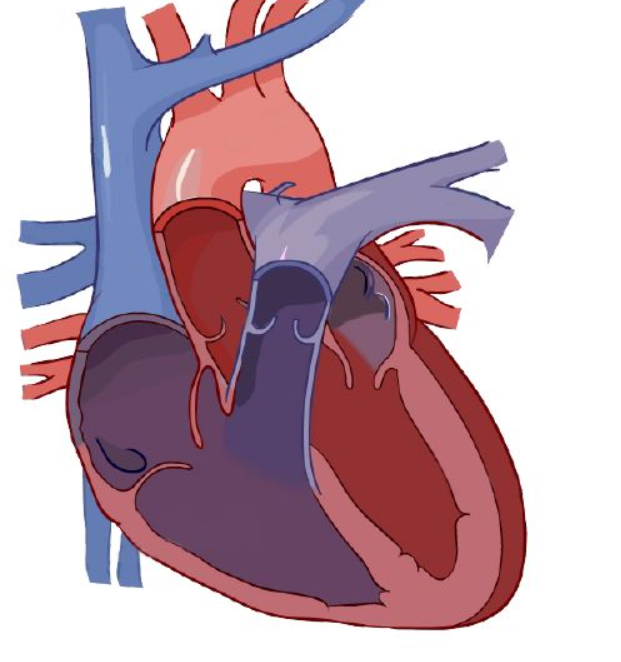
right ventricle
What chamber pumps blood out of the heart, toward the lungs?
anemia
Lowered count of hematocrit called:
Polycythemia
Elevated count of hematocrit called:
basophil
WBC that promotes inflammation by releasing histamine
eosinophil
WBC that responds to parasites and worms
antinflammatory response
monocyte
White blood cell that differentiates to macrophages which engulf pathogens
Kidneys
What do erythropoietin-stimulating cells target?
hyperthyroidism
Symptoms associated: Weight loss, increased appetite, heat intolerance, incr sensitivity to heat, tachycardia, palpitations, arrhythmia, diarrhea, anxiety, nervousness, irritability, insomnia, tremors, increased hair and nail growth, incr sweating
Leptin
Secreted by adipocytes for fat storage
-high = suppresses hunger centers in hypothalamus
Pancreas
Insulin is secreted by beta cells in what organ?
Insulin
Decreases concentration of glucose in sugar in blood
Beta blockers
interferes with the binding of epinephrine which prevents hormone from raising blood pressure and heart rate
Beta blockers, androgens; glucorticoids, mineralcorticoids
What chemicals are secreted by the adrenal medulla?
androgens
Involved in sex drive and early sexual development secreted by adrenal cortex
adrenal cortex
Regulates ion balance, glucose, stress.
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Raises calcium levels in blood if it's below set point
Thyroid hormones (TSH), Calcitonin
Thyroid gland secretes:
follicle-stimulating hormone
Stimulates development and maturation of gametes (eggs and sperm)
gonadotropins (luteizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone)
Targets gonads (ovaries and testis)
adrenocorticotropic hormone
What hormone releases cortisol, elevates glucose and stores fat for energy?
thyroid-stimulating hormone
Targets the thyroid gland
growth hormone
Involved in the growth of muscles and bones
Musculoskeletal system
Growth hormone targets the:
mammary gland
Prolactin targets the:
36-48%
Hematocrit rate for F
basophil
WBC that promotes inflammation by releasing histamine
Kidneys
What do erythropoietin-stimulating cells target?
monocyte
White blood cell that differentiates to macrophages which engulf pathogens
Neutrophils > Lymphocyte > Monocyte > Eosinophil > Basophil
White blood cells: From commonality to uncommonality --
4,500-11,000
Average range of white blood cells:
eosinophil
WBC that responds to parasites and worms
antinflammatory response
lymphocyte
WBC involved in and controls immune response which make antibodies
neutrophils
WBC that's a general macrophage; responds to bacterial infection
Type I diabetes
Low insulin production from pancreatic cells which attacks the beta cells in pancreas
gigantism, pituitary dwarfism
Issues with growth hormone when young
fibrinogens
Plasma protein involved in clotting
epicardium
Outermost layer of the heart wall
-has areolar tissue, dense fibrous layer
superficial fibrous pericardium
Outer wall of the pericardium consisting of dense CT
-anchors and protects the heart
epinephrine, noepiphrineprine
Hormones secreted from adrenal medulla
Anterior pituitary gland
Of the halves of the pituitary gland, which one is the true gland?
atria
As their name implies, the heart chambers that receive blood returning through both circulatory circuits are called
right atrium
Receives deoxy blood from systemic circuit
left atrium
Receives oxy blood from pulmonary circuit
Erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets
Which are considered formed elements of blood?
Platelets
Which of the following is NOT a component of plasma?
Hemoglobin
What molecule in blood carries oxygen?
Transport, protection, regulation
Three major functions of blood
Oxytocin, ADH
Hormones secreted by posterior pituitary
TSH, calcitonin
Thyroid gland secrete which hormones?
PTH
Parathyroid gland secretes
Glucorticoids, mineralcorticoids, androgens
Adrenal cortex secrete:
Norepinephrine, epiphineprine, beta blockers
Adrenal medulla secrete:
Insulin, glucagon
Hormones secreted by pancreas:
chordae tendineae, papillary muscle
The ___________ and __________anchor the bicuspid and tricuspid valves to prevent them from inverting.
Plasma
Water, proteins, ions, hormones layer of the blood
Buffy coat
WBCs & platelets layer of the blood
Erythrocyte
Red blood cell part of the blood
Where is erythropoeitein secreted from?
Kidneys