Multiplication of Viruses Part I
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
TRUE OR FALSE
All viruses kills the cell they infect
FALSE
Tumor viruses don't kill the cell
Structural changes in the host cells that are caused by viral invasion is called?
Cytopathic Effect
A large cell like structure formed by the joining together of two or more cells is called
Syncytium
Which virus can form syncytium ?
Measles virus
What was the first assay used to detect viral infectivity in a DNA virus known as Vaccinia virus
CAM Pock-Assay
Vaccinia virus is a non-pathogenic form of
Small pox virus
How was CAM Pock-assay carried out?
1. First infect the aliquot of vaccinia virus into the chorioallantoic membrane
- Pock lesions would form where the virus infected
- you can count the pock
What limitations did CAM Pock-assay have?
not many virus form pock or lesion. on the chorioallantoic membrane
What is the most accurate and widely used test to measure the number of infectious particles?
Plaque assay
What are the steps for Plaque assay?
1. Grow cells that are susceptible to virus in culture plate.
2. The membrane of cell culture is grown to full confluence.
3. Growth medium is decanted and cell cultures are inoculated with aliquot of seal dilution of virus stock
4. After inoculating, culture dish is overlayed with agar
5. Neutral red stain is added to the agar.
6. Neutral red stain is taken up bye the viable cells.
7. Dead cells form plaque and releases the neutral red stain and will look amber in color
8. The plaques are counted
Why is agar added to the culture dish?
To inhibit the movement of newly released virus particles.
Why is plaque assay considered to the most effective one?
Because it has shown each of the plaque is initiated or can be initiated by infection of a single cell with a single virus particle.
What is Multiplicity of Infection (MOI)?
Ratio of number of infectious particle per cell.
How can viral titer be calculated?
(Mean # plaque/mL)*( Reciprocal of dilution)
What is the significance of the Poisson distribution?
It measure the number of plaque cells infected based on MOI
TRUE or FALSE
An increase in MOI means a decrease in cells infected
FALSE
Answer: increase
A high MOI means?
All cells to be killed
What kind of line can you get in one-hit kinetics and what is the slope of the line?
Straight line with a slope go one
it shows a direct proportion between the plaque and the concentration of virus inoculated.
What does end point titration assay measure?
How far can you dilute the viral suspension and still see the end point.
What is used as the end point in end point titration ?
Cytopathic effect
Who came up with calculating 50% in vivo endpoint titration?
Reed and Muench
TRUE or FALSE
Endpoint titration can be done in vivo and in vitro
TRUE
What can endpoint titration be used to quantify?
Viral infectivity
What is the chickenpox vaccine?
Virivax
What is the shingles vaccine?
Zostavax
What is the vaccine for measles, mumps, and rubella?
MMR II
Varicella vaccine is titrated using
Plaque assay
A 0.5 mL dose of Varicella vaccine contains how many plaque-forming units (PFU)?
Minimum of 1350 PFU
A single dose of zoster vaccine contains how many PFU?
Minimum of 19,400 PFU
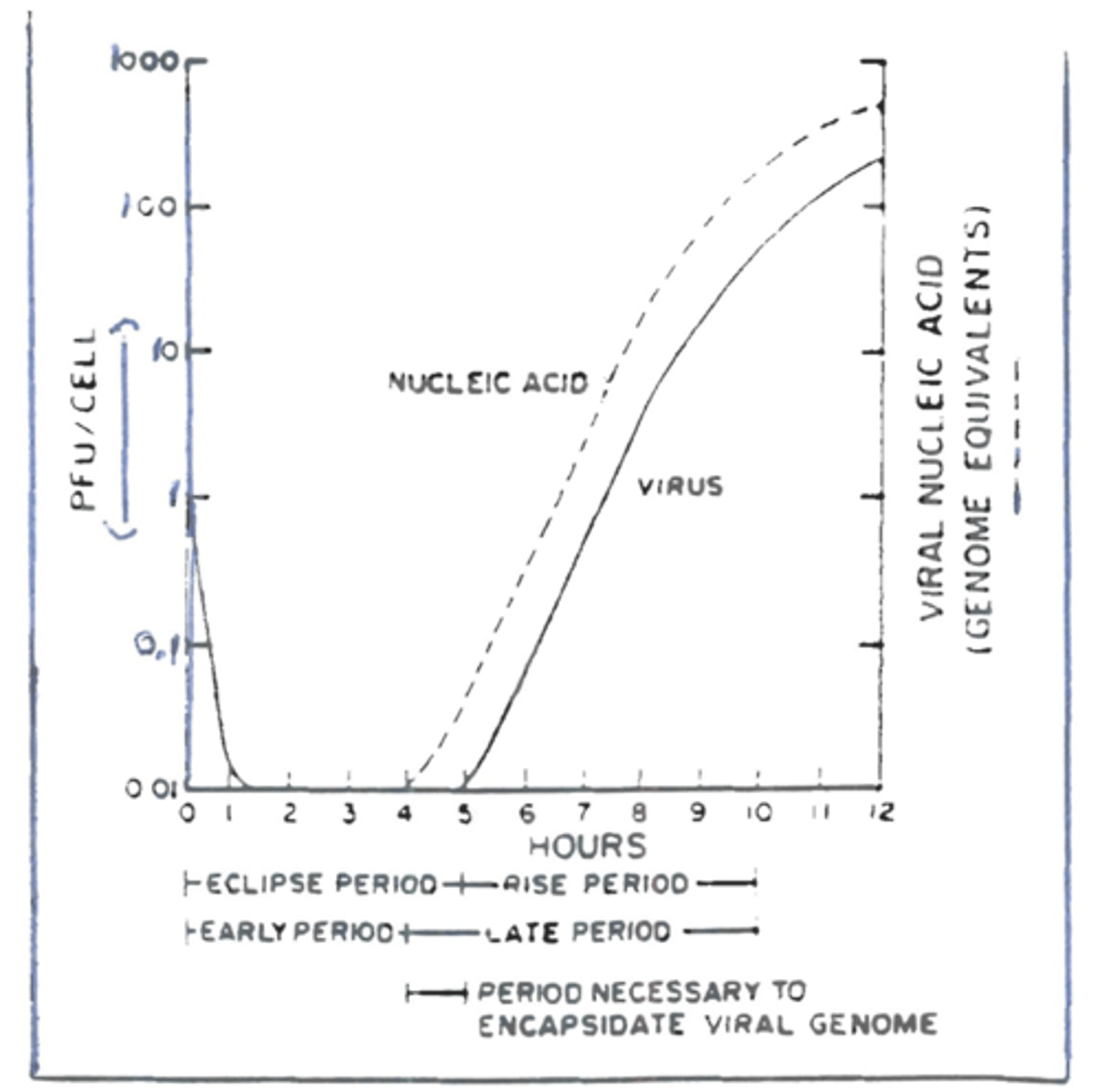
What does the one-step growth curve do?
Used to make determinations about the life cycle of a virus on a particular host.
The one-step growth curve is only applicable to?
Large DNA viruses such as herpes viruses, Adenoviruses and pox viruses
Why is the one-step growth curve only applicable to large DNA Viruses?
Because the steps in multiplication of small viruses overlap each other.
What are the early period steps in one step growth curve?
1. Virus attaches to cell
2. Virus penetrate
3. Virus uncoated
4. Viral early genes are expressed
Which period corresponds to the period that follows uncoating of virus and precedes the appearance of intracellular progeny virions?
Eclipse period
What do early viral genes encode?
Enzyme and regulatory proteins
What is the late period in One-step Growth curve categorized by?
Structural proteins
What does structural proteins include?
Capsid protein and proteins that are inserted onto the the envelope of virus
The One-Step Growth Curve
A virus without a genome is _____
dead
What are the steps in Viral Replication?
1. Recognition of target cell
2. Attachment
3. Penetration
4. Uncoating
5. Macromolecule synthesis
6. Assembly of virus
7. Budding of enveloped virus
8. Release of virus
What are two things required for viral attachment?
- Viral attachment protein and cell receptor that is compatible with the viral attachment protein