Criminalistics Intro test - basic knowledge - Sam R
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Who is the “Father of toxicology”?
Mathieu Orfila
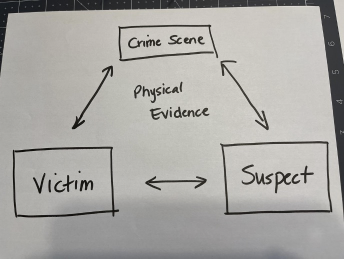
What is the exchange of evidence principle
the idea that “Every contact leaves a trace”
criminals can be connected to crimes by the dust carried from the scene
created by Edmond Locard
who regulates the activities that influence our daily lives?
the government
What is the well-known crime where a forensic engineer was involved?
9/11 (to look at the structure of the buildings)
What is the landmark case that set a precedent for the 3 strikes law
A man attacked a woman named Poly. He had previously been convicted of numerous aggressive crimes. This created the 3-strikes rule. If he had been in jail sooner, Poly wouldn’t have been attacked.
What is a landmark case and why are they important?
It is a crime case that sets a precedent for future cases. It is important/studied because of its historical and legal significance.
What is the oldest crime lab?
established in 1923 by the LAPD
August Vollmer
What is the largest crime lab?
FBI
founded in 1932 by J. Edgar Hoover
What is the definition of Forensic Science?
the application of science to criminal and civil laws enforced by police agencies in a criminal justice system.
who was responsible for anthropometry?
Alphonse Bertillon
Who wrote Sherlock Holmes?
Sir Arthur Conan Doyle
What is the explanation for rapid growth of crime labs?
the progression of technology, backlogged DNA samples, and the advancement of DNA profiling
How many public labs are opening?
about 400
What are the units of forensic science?
Physical Science Unit
Biology Unit
Firearms Unit
Document Examination unit
photography unit
toxicology unit
latent fingerprints unit
polygraph unit
voiceprint unit
CSI unit
What does each unit do?
Physical science - analyzes drugs, glass, paint, explosives, and soil
Biology - identifies and profiles DNA, compares hairs and fibers, and botanical materials (woods and plants)
Firearms - examines discharged bullets, cartridge casings, shotgun shells, and residues
Document Examination - analyses handwriting, paper, ink, and altered documents
Photography - uses digital imaging, infrared, ultraviolet, and X-ray photography for evidence
toxicology - examines body fluids and organs to detect the presence of drugs and poisons.
latent fingerprints - processes latent impressions
Polygraph - lie detection (tool, not admissible in court)
Voiceprint - analyses sound patterns (telephone treats, tape-recordings)
CSI - collects and preserves physical evidence
What is the CSI effect?
The dramatization of TV’s portrayal of forensic science gives unrealistic expectations and jury perceptions.
What does criminalistics actually focus on?
it focuses on the services of the crime lab, where physical and natural science techniques are applied to analyze crime scene evidence
What is the landmark case of Fry vs. US?
This case made polygraph tests inadmissible in court and they can only be used as a tool for detectives to gather evidence/theories about a case.
What are the 4 major crime labs?
FBI, DEA, ATF, and USPS
What is the FBI?
investigative powers
What is the DEA?
Drug Enforcement Administration (production, sale, and transportation)
What is the ATF?
Bureau of Alcohol Tabacco Firearms
Alcohol, documents, weapons, explosives, gun control
What is the USPS?
United States Postal Service
What is the diagram of the evidence exchange principle?