Week 1 – Image Critique (AP Soft Tissue Neck, Lateral Soft Tissue Neck, Hyperflexion/Hyperextension Lateral C-Spine, AC Joints Without Weights)
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering week 1 image critique topics for AP soft tissue neck, lateral soft tissue neck, hyperflexion and hyperextension lateral C-spine, and AC joints without weights.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What indicates no rotation in an AP soft tissue neck?
Symmetrical sternoclavicular (SC) joints.
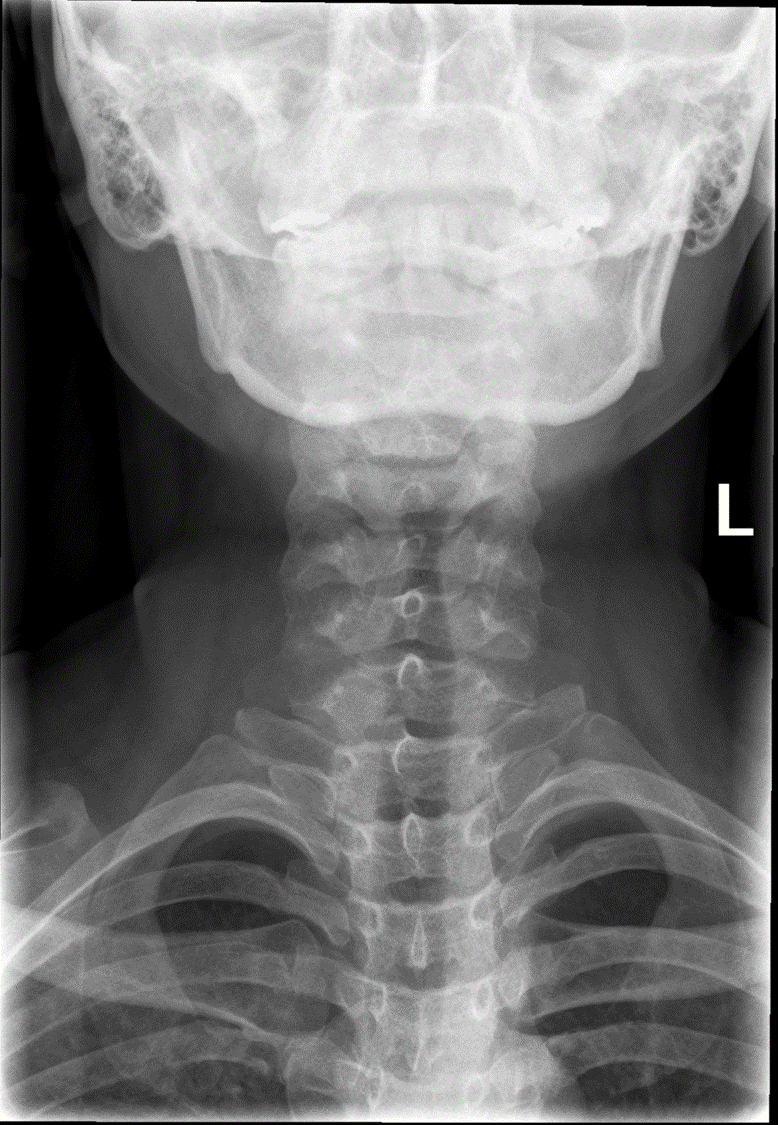
How should the mandible appear in AP soft tissue neck?
Superimposed on the base of the skull, without overlapping the pharyngeal area.
What anatomical structures must be included in AP soft tissue neck?
From C3 to T4, including soft tissue structures of the neck.
What image quality is required in AP soft tissue neck?
Throat filled with air and clear visualization of pharyngolaryngeal structures.
How do you assess for no rotation in lateral soft tissue neck?
Zygapophyseal joints should be superimposed anterior–posterior.
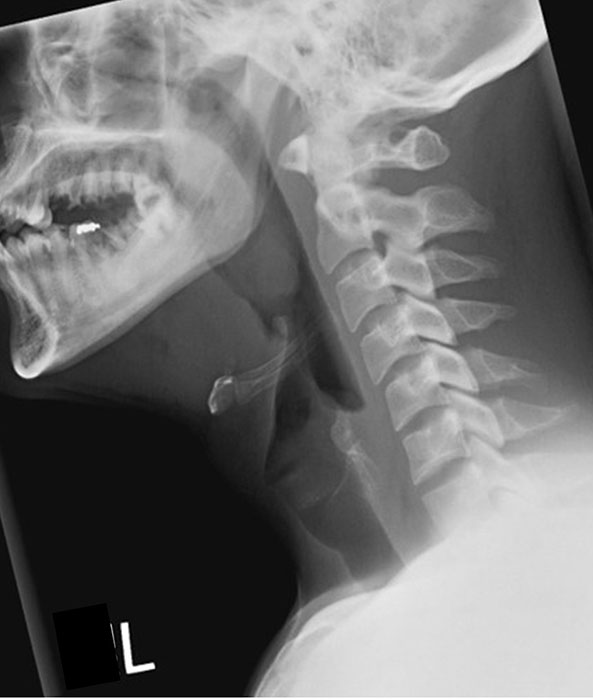
How do you assess for no tilt in lateral soft tissue neck?
Zygapophyseal joints should be superimposed superior–inferior.
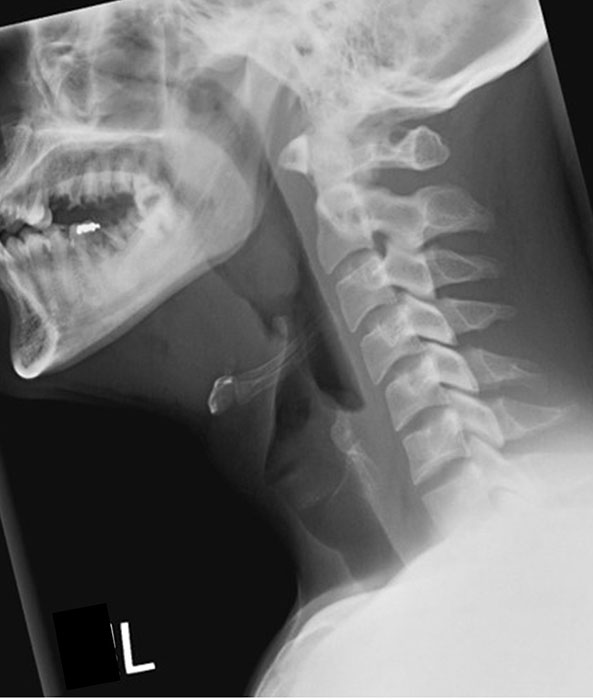
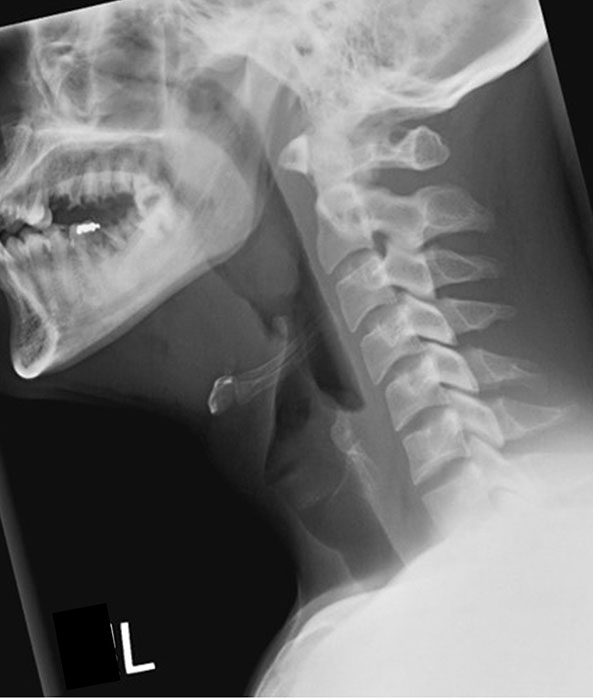
How should the mandible appear in lateral soft tissue neck?
Superimposed.
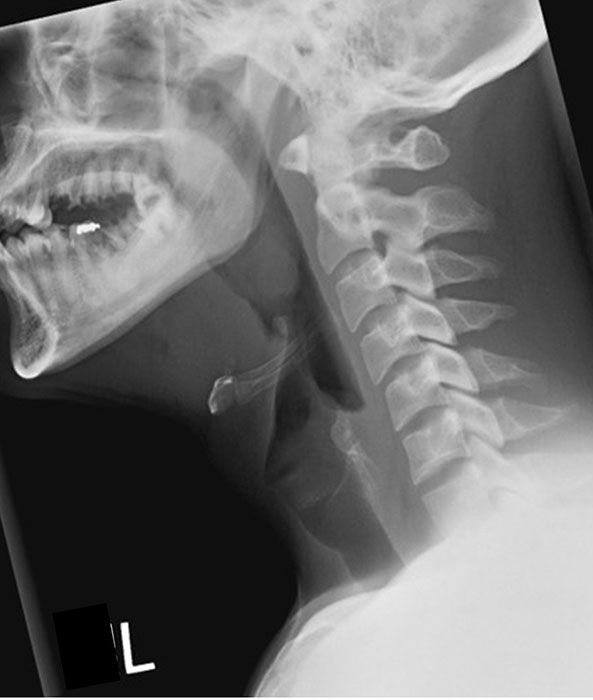
What indicates good head extension in lateral soft tissue neck?
The base of the skull should be off the cervical spine.
What structures must be included in lateral soft tissue neck?
From the EAM to jugular notch (or nasopharynx to clavicles), including anterior and posterior surfaces of the neck.
What indicates no head rotation in hyperflexion lateral C-spine?
Superimposed mandibular rami.
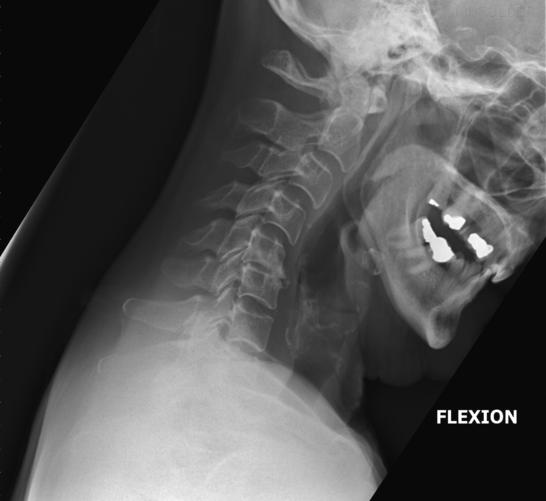
What should the spinous processes look like in hyperflexion?
Well separated.
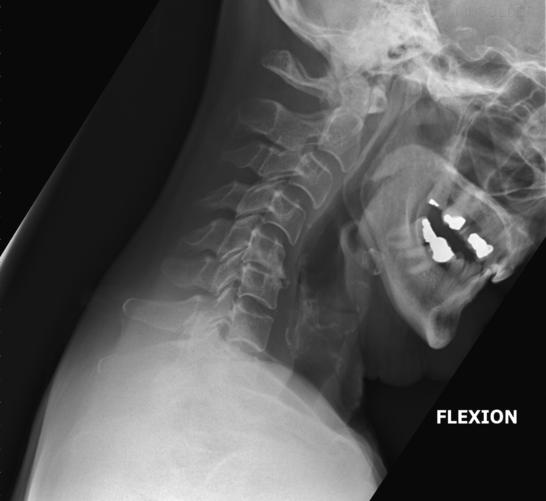
How should the mandible appear in hyperflexion?
The body of the mandible should be almost vertical.
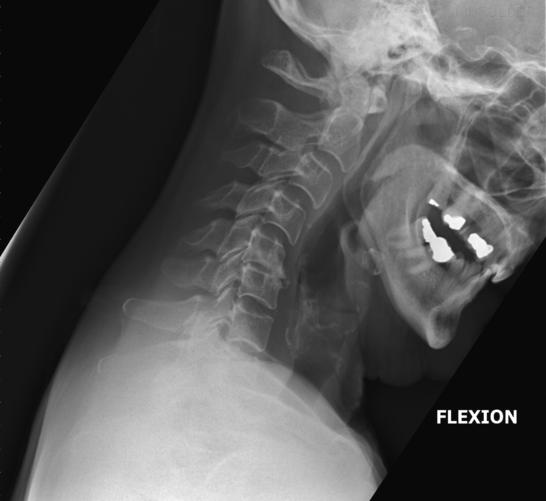
What structures must be visible in hyperflexion lateral C-spine?
C1–C7 (though C7 may not always be fully visible) and surrounding soft tissue.
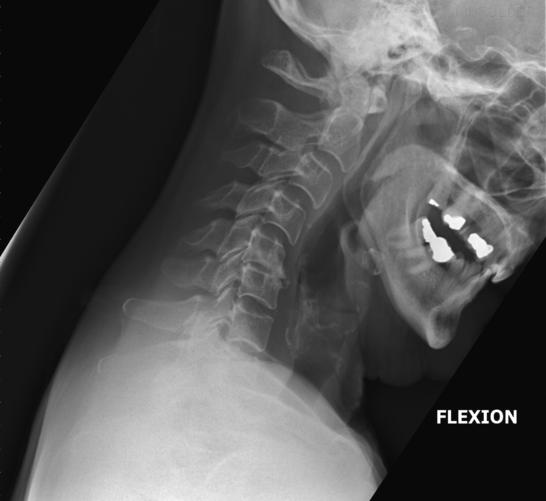
What indicates correct rotation/tilt in hyperflexion lateral C-spine?
Open intervertebral disc spaces and superimposed zygapophyseal joints.
What image quality is required for hyperflexion lateral C-spine?
Clear margins of soft tissue and trachea, and trabecular markings of vertebrae.
What marker placement is required in hyperflexion views?
Left marker plus arrow or marker showing neck movement direction within the primary beam.
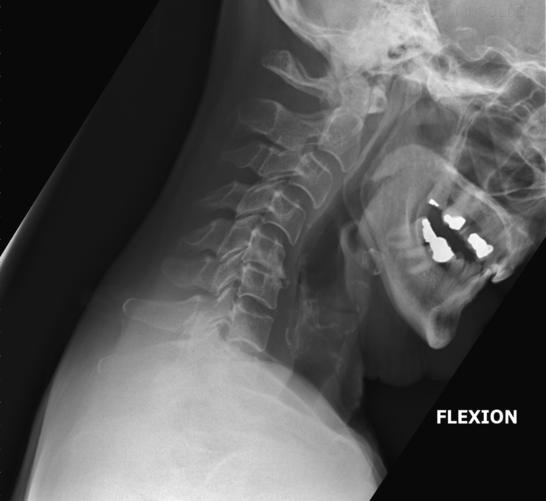
How do positioning criteria differ between hyperextension and a typical lateral C-spine?
They are almost identical, except the mandible appears almost horizontal and spinous processes are depressed/closely spaced.
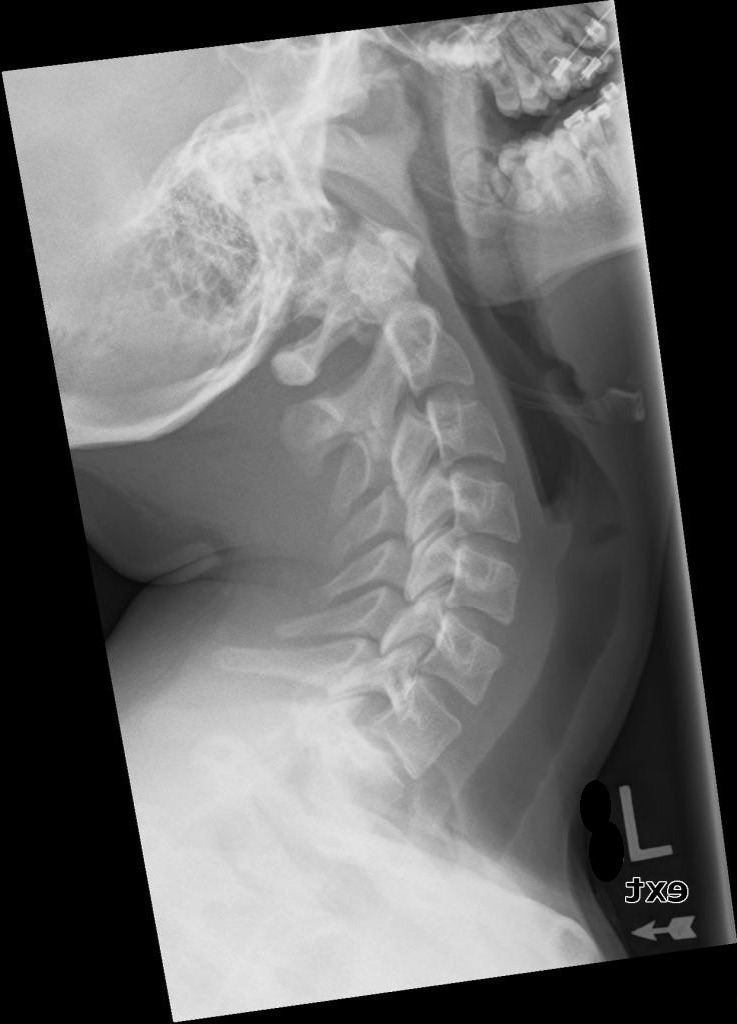
How do the mandibular rami appear in hyperextension if correctly positioned?
Superimposed, showing no head rotation.
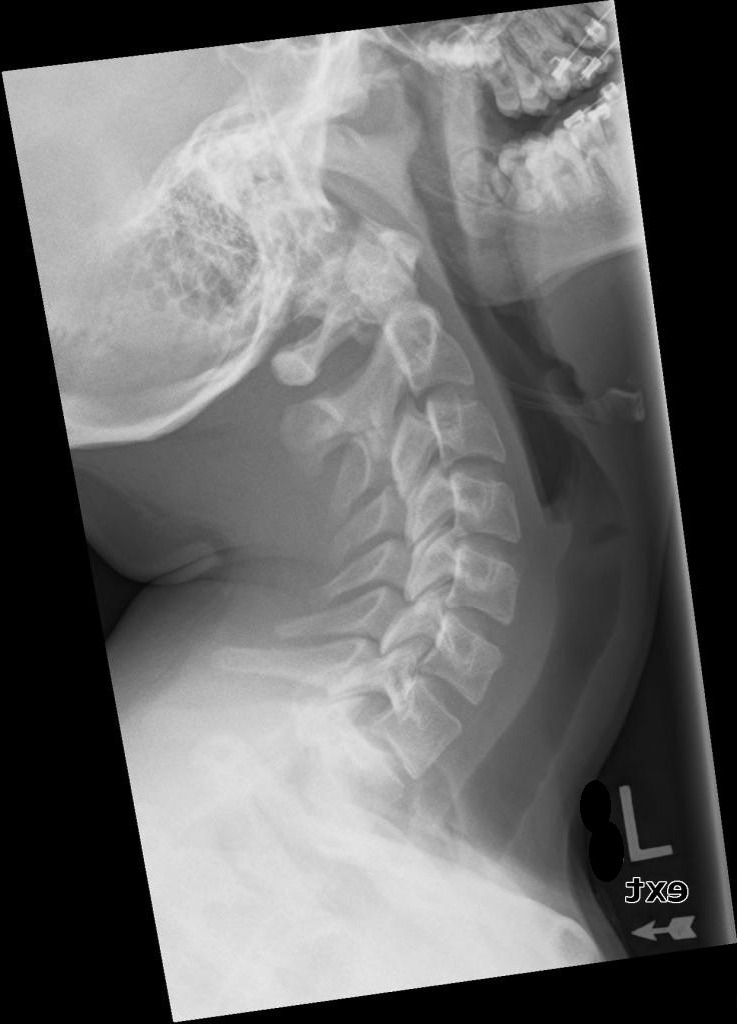
What structures must be visible in hyperextension lateral C-spine?
C1–C7 (C7 may not always be fully visible) plus surrounding soft tissue.
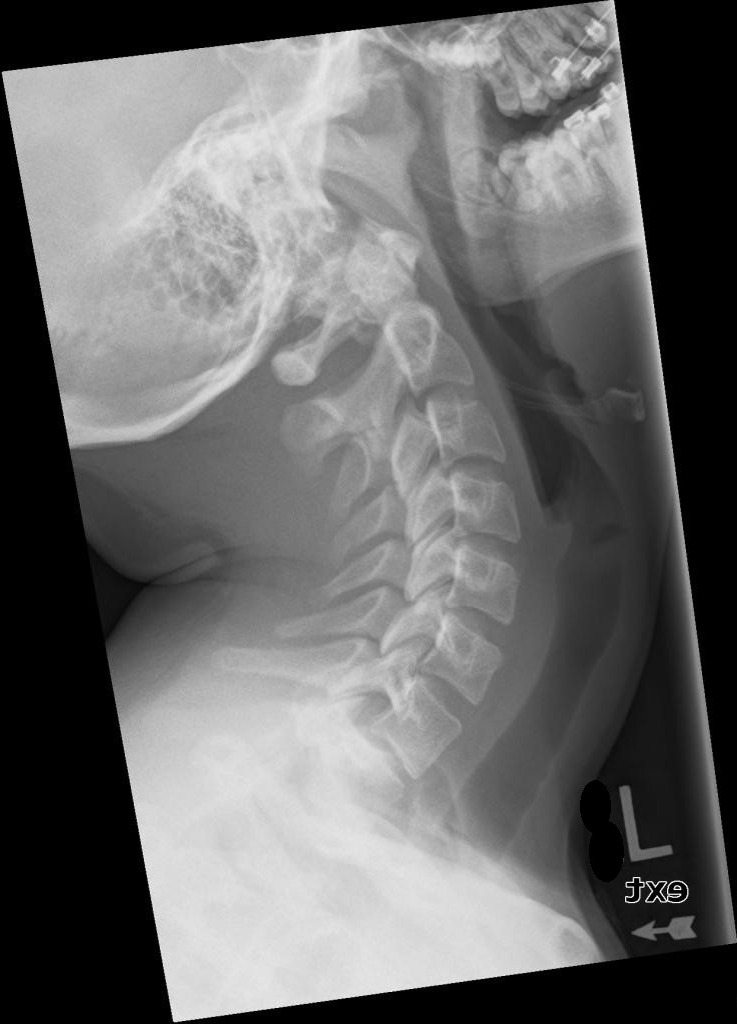
What indicates correct rotation/tilt in hyperextension lateral C-spine?
Open intervertebral disc spaces and superimposed zygapophyseal joints.
What image quality is required in hyperextension views?
Clear margins of soft tissue and trachea, and trabecular bone markings.
What marker placement is mandatory in hyperextension?
Left marker plus arrow/marker indicating neck movement direction within the primary beam.
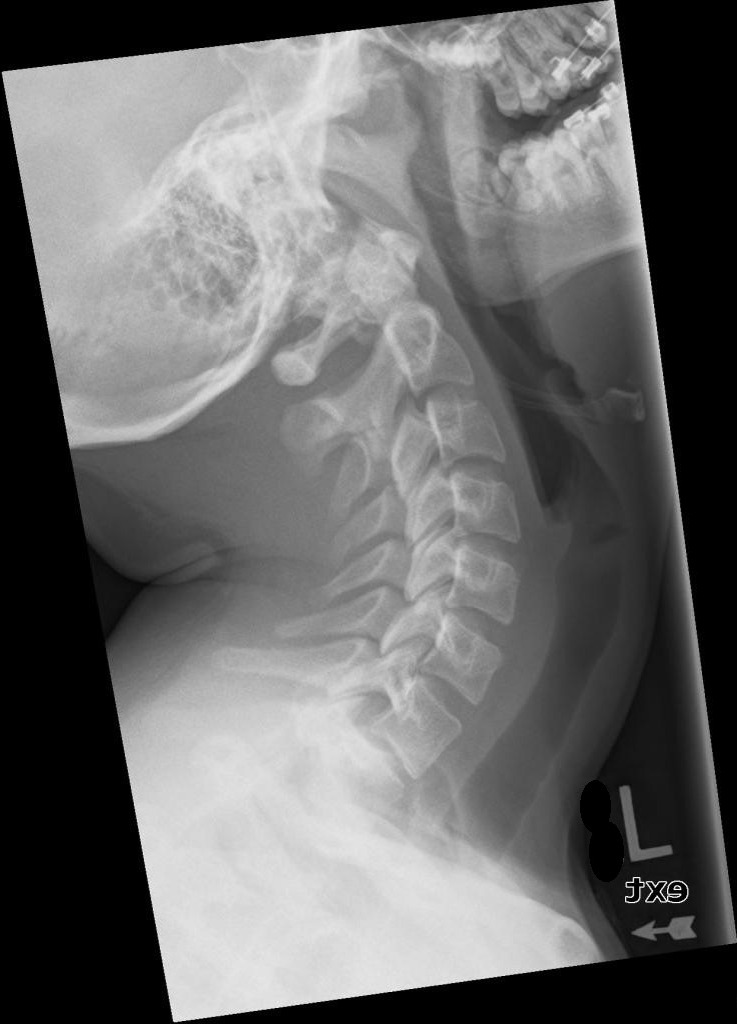
What projection title should be used for AC joint imaging without weights?
AP left AC joint (without weights).
What structures must be included in AC joint imaging?
AC joint of interest, lateral clavicle, acromion process, and superior scapular angle.