AP Chemistry - Chapter 10
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What are the properties of gases? (5 properties) (CCELF)
Compressible
Can diffuse and effuse
Expand to fill their containers
Low density
Fluid - they flow
What are ideal gases?
theoretical gases that perfectly fit all the assumptions of kinetic molecular theory
ideal gas properties (5 properties) (TANCE)
tiny particles + far apart compared to each other
average kinetic energy depends on temperature
no forces of attraction between gas particles
gas particles are in constant rapid motion (contains kinetic energy)
elastic collisions (no kinetic energy is lost in collisions)
what is pressure?
the force created by the collisions of molecules with the walls of a container per unit area
Standard Pressure
1 atm
101.3 kPa
760 mmHg/torr
Celsius to Kelvin formula and temperature of absolute zero
C + 273 = K
Absolute zero: -273C/0K
Standard Temperature and Pressure
Temperature: 273K/0C
Pressure: 1 atm | 101.3kPa | 760 mmHg/torr
Gas Laws Formulas
NOTE: Temperature must be in Kelvin and Volume must be in Liters
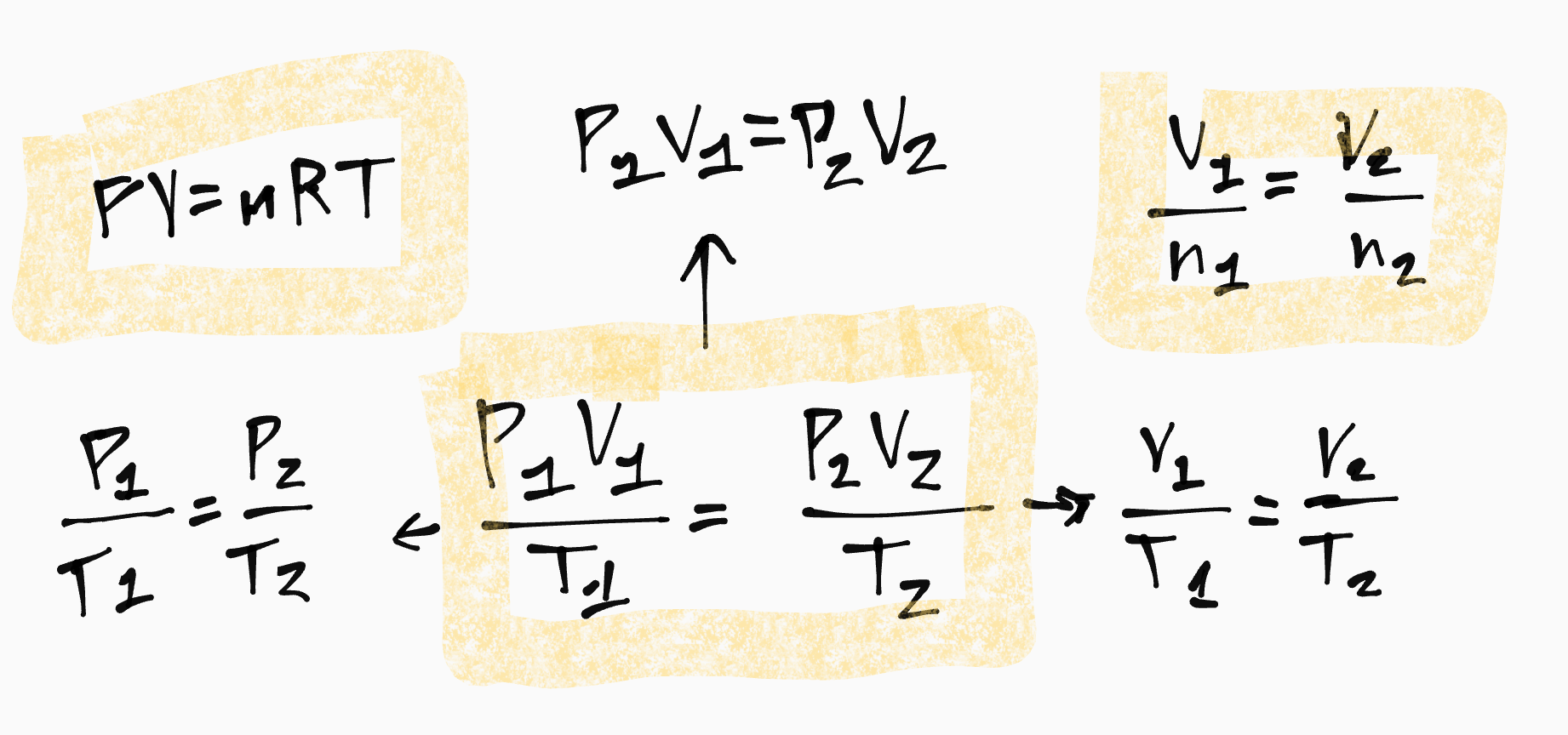
Relationship between pressure, volume and temperature:
Pressure and Volume are inversely related
Volume and Temperature are proportionally related
Temperature and Pressure are proportionally related
When do real gases behave like an ideal gas?
At higher temperature and lower pressure.
Formula for Density
d=MMP/RT
Value of R Constant
0.08206 L*atm/mol*K
What is the molar volume of a gas at STP?
1mol = 22.4L
How many liters of ammonia can be produced when 12 liters of hydrogen react with an excess of nitrogen? (At STP 1 mole of GASES = 1 liter)
3H2(g) + N2(g) → 2NH3(g)
12L H2 * (2L NH3/3L H2) = 8.0L NH3
2KClO3(s) →2KCl(s) + 3O2(g)
a) How many liters of oxygen gas, at STP, can be collected from the complete decomposition of 50.0 grams of potassium chlorate? (1 mole = 22.4L ONLY AT STP)
b) How many liters of oxygen gas, at 37.0C and 0.930 atmospheres, can be collected from the complete decomposition of 50.0grams of potassium chlorate?
a) 13.7L O2
b) 16.7L O2
Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures
Ptotal = Px + Py + . . .
Mole Fraction Formula
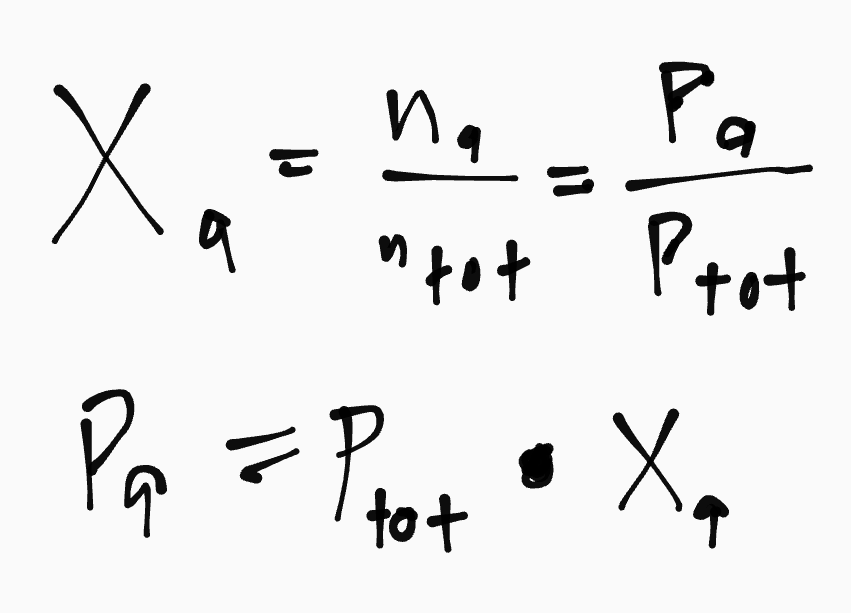

When these valves are opened, what is each partial pressure, the total pressure, and the mole fraction of each gas?
a) Partial Pressure of EACH gas AFTER opening the valves (Use P1V1=P2V2)
b) Total Pressure of Gases AFTER
c) Mole Fraction of Gases AFTER
a) CH4: 1.20atm | N2: 0.763atm | O2: 0.292atm
b) 2.255atm
c) CH4: 0.532atm | N2: 0.338atm | O2: 0.129atm
Fluorine gas is in a 5.0L container that is at 25C and 2 atm. A certain amount of hydrogen gas with a partial pressure of 0.5atm is added to the container. What is the mole ratio of hydrogen gas?
0.2
At a temperature of 560C and a pressure 90 atm, Venus’ atmosphere consist of about 96% CO2 and 3% N2, with trace amounts of other gases including water, sulfur dioxide, and sulfuric acid. Calculate the partial pressures of CO2 and N2.
CO2: 86.4 atm
N2: 27 atm
Kinetic Molecular Theory (5 properties) (VAACE)
volume of individual particles is around 0
particles of matter are always in motion
average kinetic energy is proportional to Kelvin temperature of a gas
collisions of particles with container walls cause the pressure exerted by gas
particles exert no forces on each other
What factors effect the kinetic energy of gas particles?
At the same conditions of temperature, all gases have the same average kinetic energy.
Therefore at the same temperature, small molecules move FASTER than large molecules.
Average Kinetic Energy Formula
KEavg=(3/2)RT
R = 8.314 J/K*mol
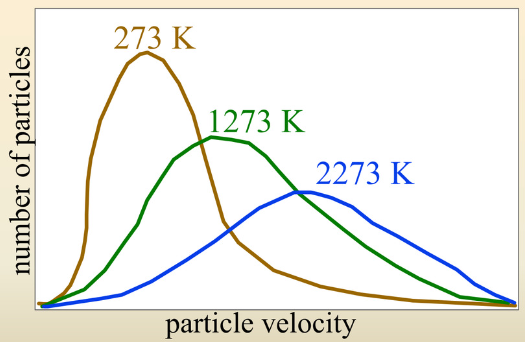
Interpret the Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution Graph
Average increases as temperature increases
Spread increases as temperature increases
diffusion
described spontaneous mixing of gases; the rate of diffusion is the rate of gas mixing
diffusion is the result of random movement of gas molecules
rate of diffusion increases with temperature
small molecules diffuse faster than large molecules
effusion
describes the passage of gas into an evacuated chamber through a small opening
Graham’s Law of Effusion
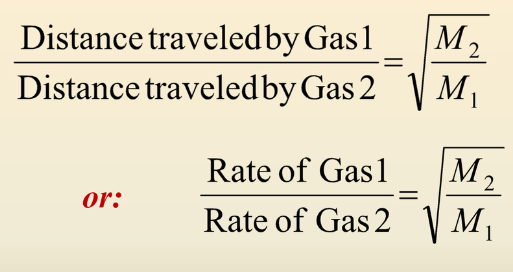
How much faster does helium, He, diffuse than argon, Ar?
Helium diffuses 3.16 times more faster than argon.