Biol 1210: Water and Life & Carbon and molecular diversity of life
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chp 3 - Water and Life; Chp 4 - Carbon and molecular diversity of life
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Define water
Molecule that supports life on earth and biological medium of earth and is the most requires substance by all organisms
What is the structure of a water molecule?
Contains Hydrogen and Oxygen
Polar molecule since it has uneven charges
In general, what does the polarity of water molecule allow them do? why is this important?
Forms hydrogen bonds with each other
Contributes to various properties water exhibits
What is the maximum amount of hydrogen bonds can a water molecule form?
4 Hydrogen Bonds
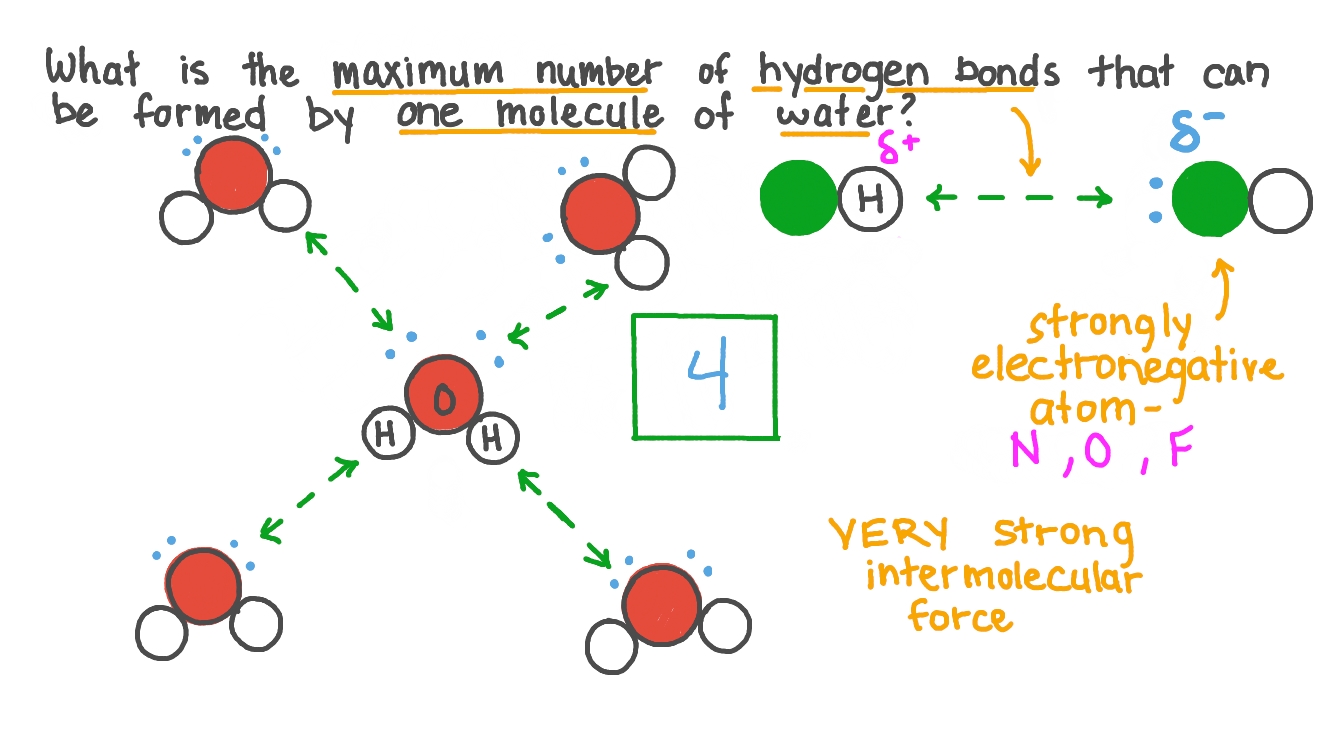
In general, What are the 6 properties of water based on Hydrogen Bonding?
Cohesive
Adhesive
Surface Tension
High specific heat
High heat of vaporization
Excellent solvent
What does it mean when water is cohesive?
It is one of the properties of water based on hydrogen bonding
It refers to the joining of many water molecules due to hydrogen bonding
What does the cohesive water property aid in?
Aids in giving water structural organization
What is the benefit of cohesiveness of a water molecule?
This property helps to pull water up through the water-conducting cells of plants called tracheid and vessel elements of the xylem tissue
What does it mean when water is adhesive?
It is one of the properties of water based on hydrogen bonding
It refers tot he clinging of one substance to another substance
How does water cling onto another substance?
Water can form hydrogen bonds with other molecules
What is the benefit of the water property based on hydrogen bonding; adhesion?
This property helps to pull water up through the water-conducting cells of plants as it clings to the cell wall of plants
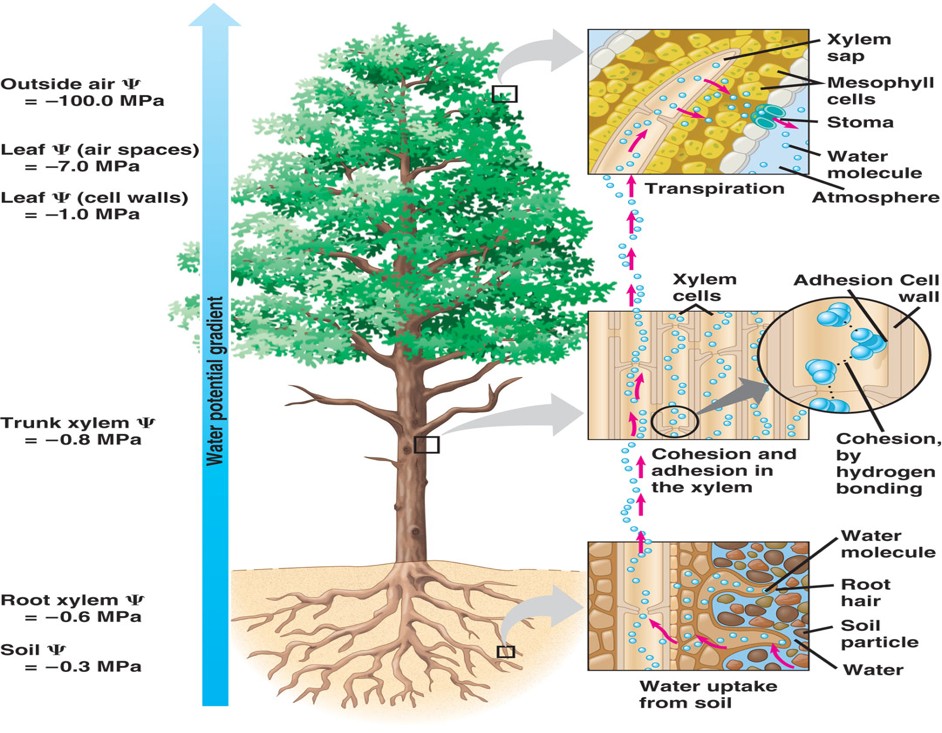
What does it mean when water has surface tension?
It is one of the properties of water based on hydrogen bonding
Measure of how hard it is to break the surface of a liquid
True or False: Surface tension property of water DOES NOT relates to cohesion
False, it does
What is the benefit of the water property due to its hydrogen bonding; surface tension?
Due to it’s surface tension it causes densely packed surface layer is strong enough to support the weight of small, lightweight insects. Insects have water striders which in turn helps in them to move across the water surface

What does it mean when water has high specific heat?
It is one of the properties of water based on hydrogen bonding
Water can absorb or lose large amounts of heat before its own temperature is changed which is due to its hydrogen bonding
True or False: High specific heat property of water mean water CANNOT moderate air temperature
False: it can
In general, what does high specific heat mean?
Amount of heat absorbed or lost when 1g of a substance changes it’s temperature by 1°C
What is the benefit of the water property due to its hydrogen bonding; high specific heat?
Provides stable water temperature which is beneficial for aquatic organisms
In general, what does high heat of vaporization mean?
Amount of energy required to change 1g of it from liquid to gas
How does high heat of vaporization relate to water property due to it’s hydron bonding?
What is the benefit of the water property due to its hydrogen bonding; high heat of vaporization?
Helps moderate earth’s climate (HOW)
Help moderate an organism’s body temperature
What does it mean when water is an excellent solvent?
It is one of the properties of water based on hydrogen bonding
Water works as a excellent solvent since any charged or polar molecule can dissolve in water
Define solvent
Dissolving agent
Define solute
What is being dissolved
How is water molecule versatile in terms of it being an excellent solvent?
Due to its polarity
Example of Water being a solvent
NaCl in a beaker of water which results in salt dissolving in water
Water can transport molecules in blood
It interacts with proteins since it has polar molecules

What is the benefit of the water property due to its hydrogen bonding; excellent solvent?
Allows many important molecules to be dissolved in it and carried to other places
Define hydrophillic
Substances that CAN bond with water due to its being ionic or polar
Define Hydrophobic and give example
Substances that CANNOT bond with water due to it being non-ionic or polar
Ex: Veg oil
Define Acid
Substance that increases the amount of Hydrogen Ion concentration of a solution
Example of an acid
HCl is an acid. Thus when added to water:
HCl → H+ + Cl-
Define Base
Substance that decreases Hydrogen ion concentration of a solution
Example of a Base
NH3 acts as a base.
NH3 +H+ ⇌ NH4+
In pure water at 25°C, how many H+ is present?
1.0×10-7M
What determine the H+ concentration?
pH scale or pH of a solution
What is the range of the pH scale?
0-14 with 0 being the most acidic and 14 the most basic
If pH decreases, then…
Hydrogen ion concentration increases
If pH increases, then…
Hydrogen ion concentration decreases
What is the pH formula or equation?
pH = -log[H+]I
If pH is less than 7, then is the solution acidic or basic?
AcidicI
If pH is more than 7, then is the solution acidic or basic?
Basic
True or False: All living organisms do not have Carbon
False, all living organisms do have carbon
What makes compounds organic?
When compounds contain carbon
Why is carbon considered important?
Considered important for its interactions with other atoms
What kind of molecules can carbon form?
Large, complex and diverse
What makes carbon special?
Carbon has an atomic number of 6. Thus, it valence 4 allows it form 4 covalent bonds with variety of atoms
Carbon can also form covalent bonds with itself, thus how do the molecules differ by?
Length
Branching
Location of double bonds
Rings
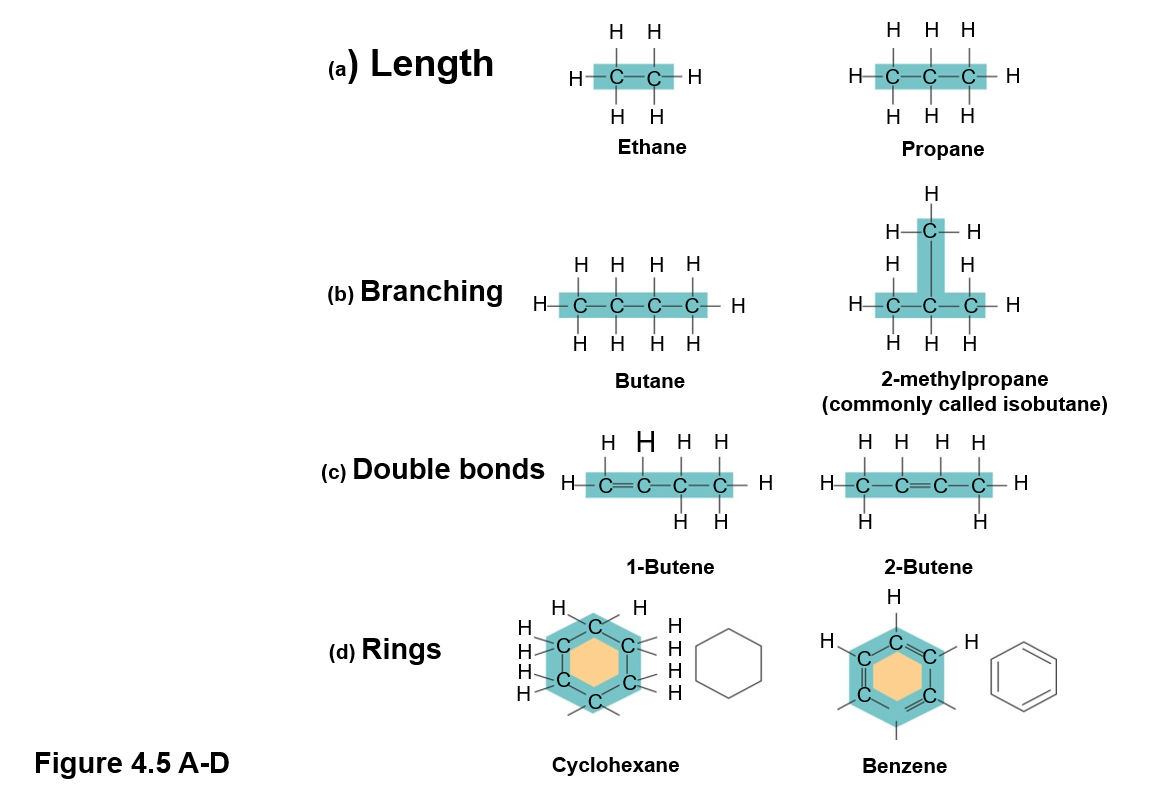
What is the simplest organic molecule?
Hydrocarbon
Define Hydrocarbon
Molecule made up of only Carbon and Hydrogen
Give examples of Hydrocarbon?
Methane
Ethane
Ethene
True or False: Hydrocarbon is NOT soluble in water
True, its not {WHY}
Define Chemical groups
These groups give each molecule it unique function
Define functional groups
Chemical groups that may determine how the molecule participates in chemical reactions
List the 7 chemical groups that are most important in biological processes.
Hydroxyl Group
Carbonyl Group
Amino Group
Carboxyl Group
Sulfhydryl Group
Phosphate Group
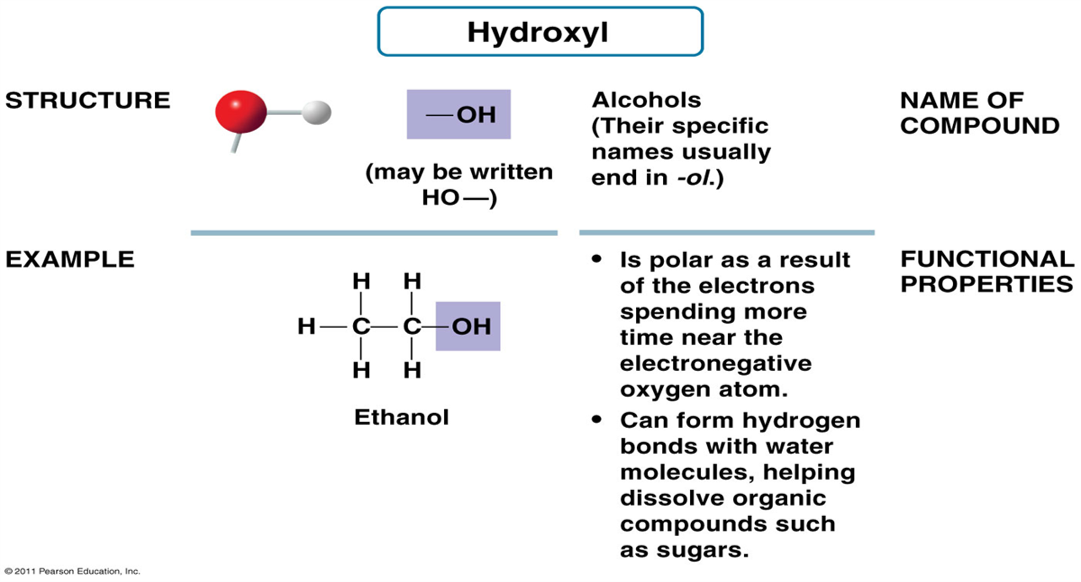
What is the structure of the Hydroxyl Group?
What is the structure of the Carbonyl Group?

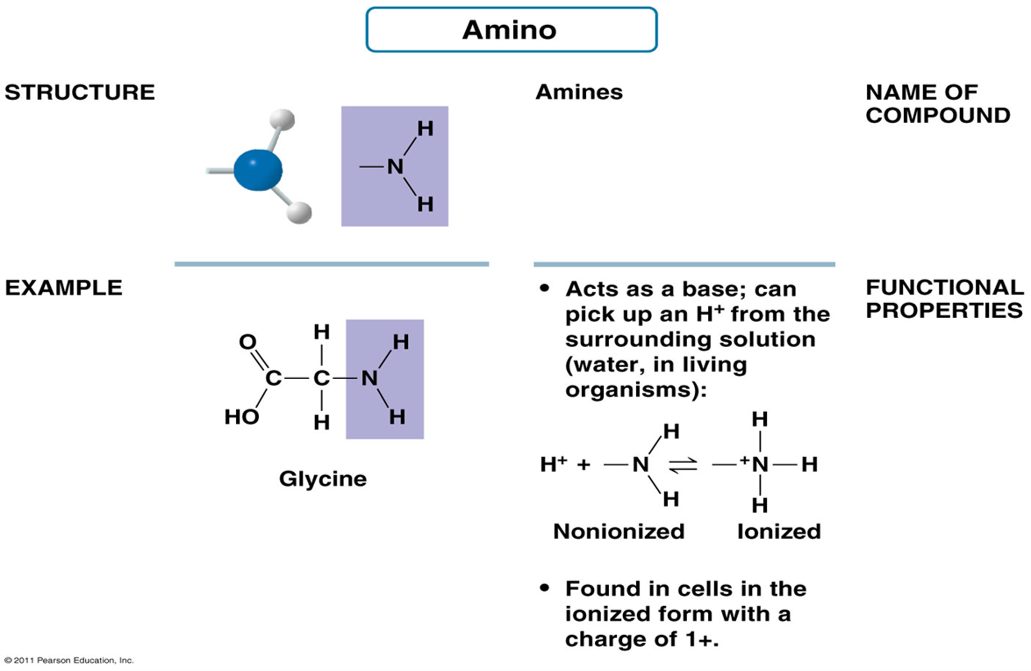
What is the structure of Amino group?
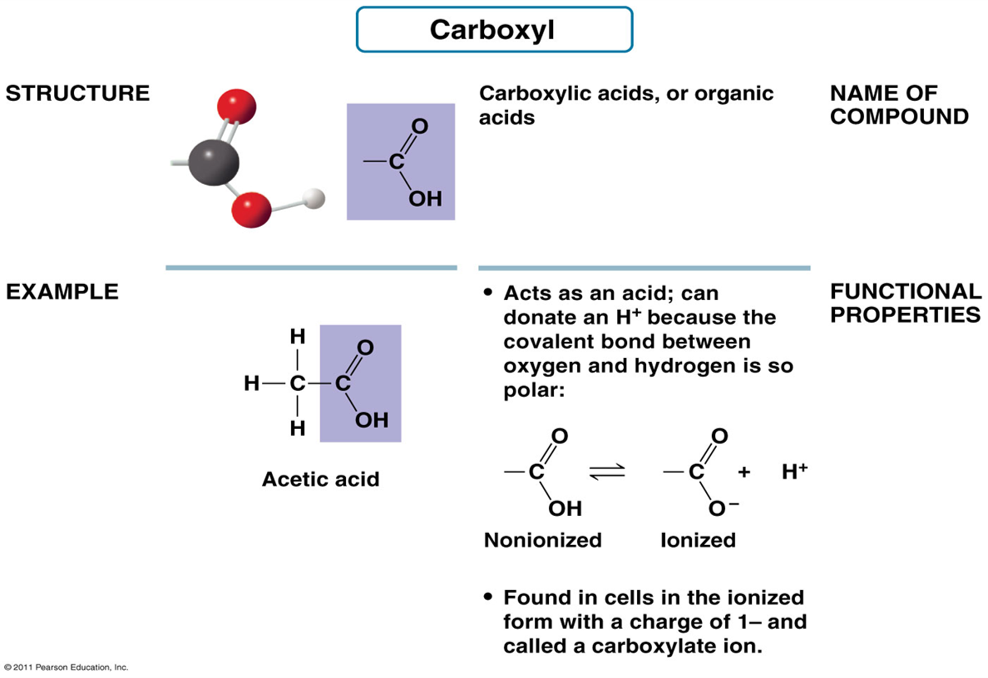
What is the structure of Carboxyl Group?
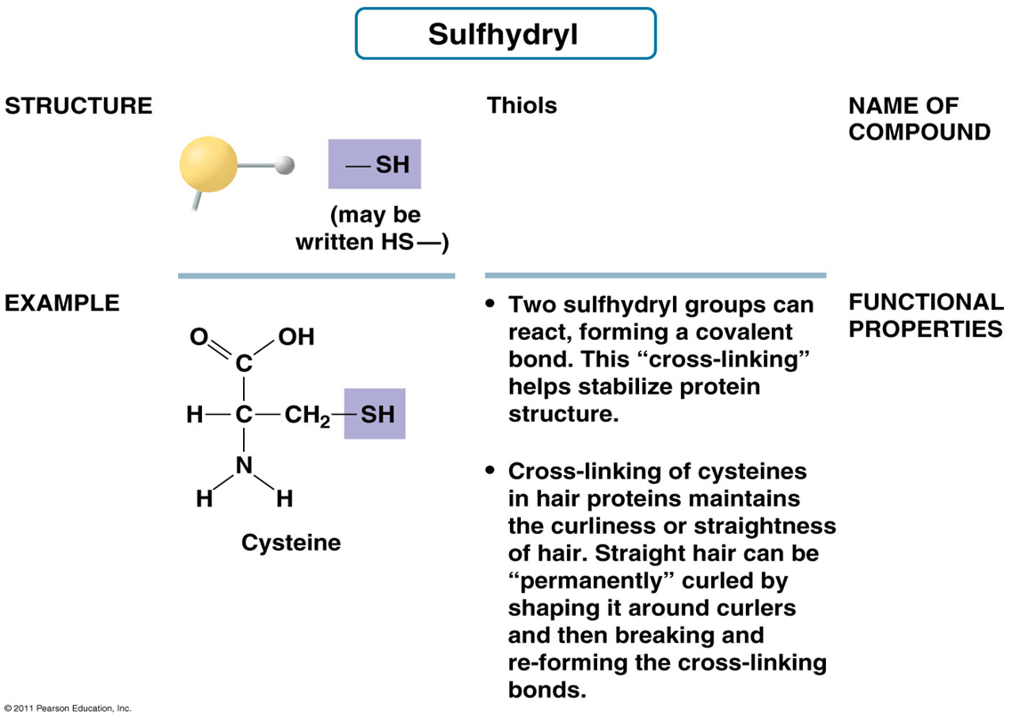
What is the structure of Sulfhydryl Group?
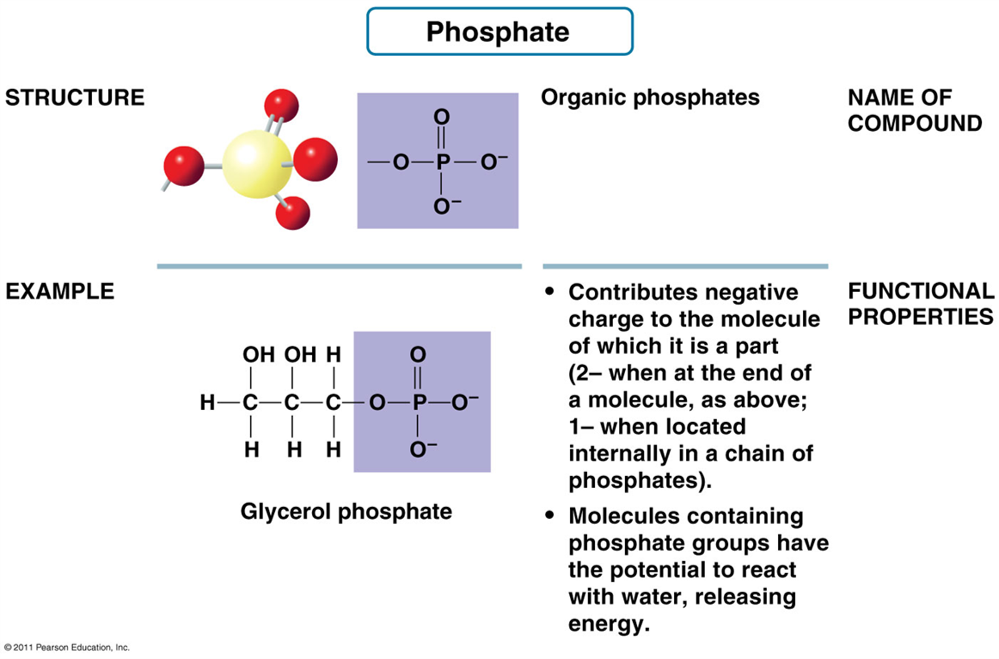
What is the structure of Phosphate Group?
What is structure of Methyl Group?
