Classifications of Cells + Cell Organelle
1/35
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
6 kingdoms of life
bacteria, archaea, protists, plants, fungi, anamalia
random facts about cells
ndividual cells are too small to see without a microscope.
There are two main types of cells (and it is not “Plant” & “Animal” cells).
The human body is made up of approximately 30 trillion human cells… and 38 trillion bacteria cells among them.
Cells have various ways of reproducing (but not all reproduce the same ways).
Cells have a lifespan…some as short as one day and others a year or even a lifetime (like some cells in the brain).
Cells, if damaged beyond repair or if old and not as efficient anymore, will destroy themselves in a process called “Cell Apoptosis.” (Except cancer cells…)
Human body cells reproduce asexually and are made by mitosis (genetically identical offspring)
Human gamete cells (egg and sperm) use sexual reproduction and are made by meiosis. (genetically different offspring)
eukaryotic cells
Organisms that have eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes.
eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus, a nuclear envelope
The nucleus is only one of many membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotes.
Animals, plants (including algae) and fungi are all eukaryotes.
eukaryotic cells are bigger than prokaryotic cells
Some eukaryotes are single-celled organisms called protists.
the plasma membrnes of eukaryotes and made of phospholipids
eukaryotes have larger ribosomes and have microtubles in their flagella/cilia and their dna exists as many strands
prokaryotic cells
Organisms that have prokaryotic cells are called prokaryotes.
Prokaryotic cells do not have a membrane-bound nucleus.
Prokaryotes do not have any membrane bound organelles.
Bacteria and archaea are Prokaryotes.
their dna exists as a single strand
prokaryatoes are smaller
have smaller ribosomes
their plasma membrane is made out of “peptoglycans”
4 similarties between pro and euk
both have cytoplasms
both have plasma membranes
both have chromosomes
both have ribosomes
Cell membrane/plasma membrane (5)
Outer boundary of the cell.
Consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable (means some things can pass through while others can’t)
Controls what enters/exits the cell.
Gives the cell shape.
Consists mostly of phospholipids with proteins embedded throughout.
the cytoplasm (3)
Thick jelly-like substance that fills the cell interior.
The nucleus & cell organelles are suspended in it.
It is about 80% water and also contains dissolved salts, amino acids, sugars, and proteins such as enzymes
nucleus (3)
Thick jelly-like substance that fills the cell interior.
The nucleus & cell organelles are suspended in it.
It is about 80% water and also contains dissolved salts, amino acids, sugars, and proteins such as enzymes
nucleolus (4)
This is found inside the nucleus.
It is made of RNA (Ribonucleic Acid).
RNA is used to help make DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) when cells divide into new cells.
The nucleolus produces the cell’s ribosomes.
the nuclear membrane (3)
This surrounds the nucleus.
It controls what enters & exits the nucleus through channels called nuclear pores.
Gives the nucleus shape and support.
rough er (4)
a long folded membrane.
Starts at the nuclear membrane (touches it!) and works its way out towards the cell membrane.
“roadway” for materials to travel to the nucleus (including ribosomes).
The Rough ER is where proteins are made (at the site of ribosomes!)
smooth er (3)
A folded membrane that looks like the rough endoplasmic reticulum ...minus the ribosomes!
This is where lipids (fats) are made and toxins are broken down.
Detoxifies the cell ; if smooth ER is not functioning, the cell can die from toxicity.
the ribosomes (2)
These are found mostly on the rough ER but some are called “free ribosomes” if they are not attached to the Rough ER.
They help produce proteins (there are many types of proteins).
golgi bodies (2)
They package materials (ex. proteins) and transport them within and outside of the cell.
They resemble flattened stacks of pancakes.
the mitochondria (3)
the “powerhouses” of the cell… meaning they are involved in releasing energy for cells.
They are the site where cellular respiration takes place and energy is made.
The oxygen we breathe in is used by the mitochondria of your cells.
the vacuoles (1)
This is a sac which stores:
- Water
- Salts
- Minerals
- Proteins
the lysosomes (5)
Contains digestive enzymes.
They break down dead organelles and waste.
They are made by the Golgi bodies (Golgi Apparatus).
Considered “the cleaners” of the cell.
Only animal cells usually have them. … a few plants do as well though.
the centrioles (3)
These help with cell division.
Only found in animal cells.
They help the cell divide by forming “spindle fibers” that span across the dividing cell to help move duplicated chromosomes into separate cells during cell division (Like a highway of protein fibers that move chromosomes to each side of a dividing cell).
cytoskeleton (8)
Extends from the nucleus to the cell membrane
Organizes the location of organelles within the cytoplasm
Gives the cell shape
Important in cell division
Allows for movement of parts (organelles, chromosomes, etc) inside of the cell
3 parts - actin microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules
Can be assembled or disassembled in seconds!
Function: cell highway to move parts, cell skeleton to support cell
microfilaments
are pipe-like structures found in the cytoplasm that help provide shape and movement for the cells. Muscle cells have many microfilaments.
microtubules
are tiny tubelike fibres that transport materials throughout the cytoplasm.
intermediate filaments
Intertwined strands of fibrous proteins.
Not involved in cell movement.
Their function is purely structural.
They help the cell membrane have tension, thus maintaining the shape of the cell.
flagella
a large projection that produces whip-like motion
extension of the cytoskeleton
cilia
short, small hair like structures that cover the outer cell membrane of an organism
extension of the cytoplasm
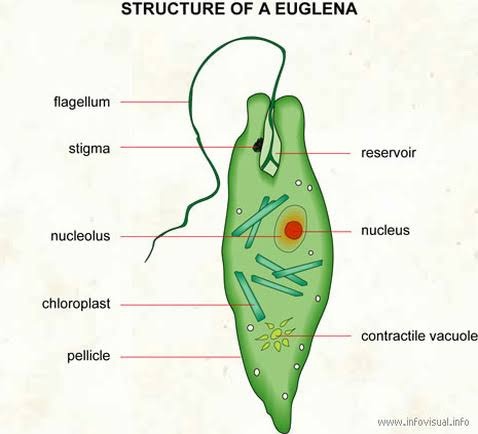
euglena
a unicellular eukaryotic protist found in water sources such as puddles, lakes and ponds, and even pools
they have chloroplasts and flagellum
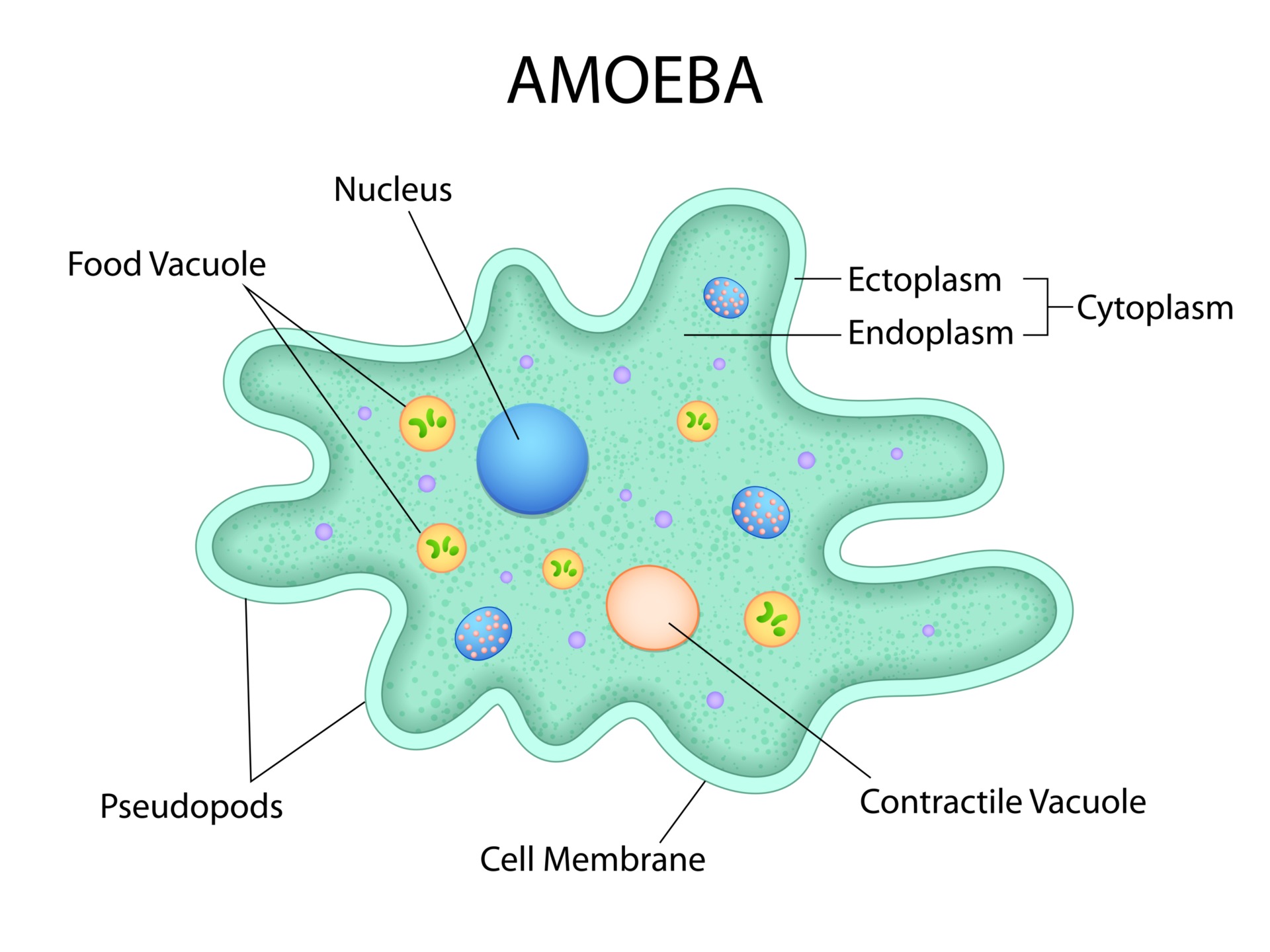
amoebas
some simple eukaryotic protists like amoebas move with psuedipodia, extensions of the cell that fill with cytoplasm
amoeba can change the shape of the pseudopodia based on the direction it moved and it can extend in a flexbile matter
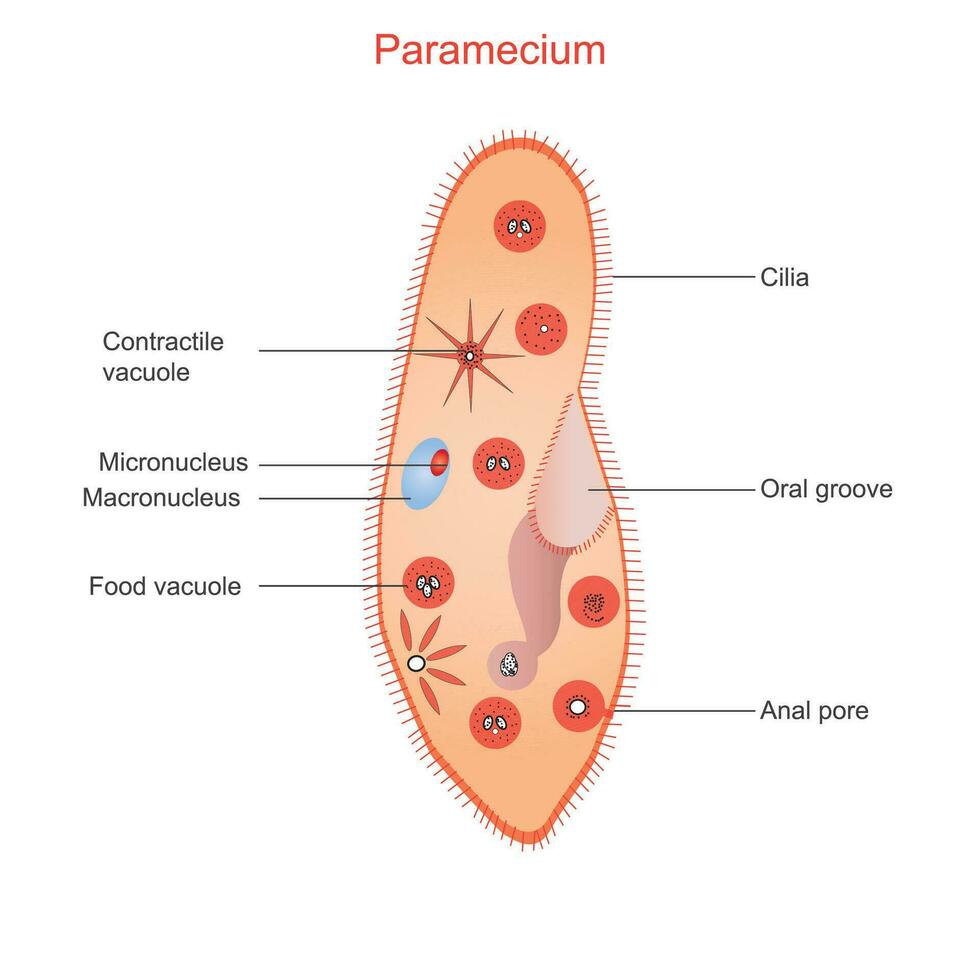
paramecium
a unicellular eukaryotic protist found in all types of water (marine, fresh , brackish)
they have hundreds of villi surrounding their outer surface
plant cell wall (5)
Around plant and fungal cells
Consists mostly of cellulose fibres and adds strength and rigidity to the cell
Spaces between the cellulose fibres allow molecules to pass to and from the cell
Plant cells have a primary and secondary cell wall
The cell wall does not control the materials that pass through it (because it has a cell membrane under the cell wall that does this!)
plant central vacuole (4)
Plant cells have a large, fluid filled central vacuole
Presses outwards on the cell wall to help support it
Storage space for water and other substances
May contain toxins that make the cell taste bad to animals
plastids
Chemical factories and storehouses for food and color pigments in plants.
The sacs are surrounded by a double membrane
Only found in plant cells
Overall function: chemical factories for sugars and storehouses for starch and color pigment to plant structures such as flowers and fruit.
3 plastids
chloroplasts, leucoplasts, chromaplast
chloroplast
An oval shaped organelle with a double membrane surrounding a fluid filled interior.
Like the mitochondria, chloroplasts
have their own DNA and ribosomes,
allowing them to replicate themselves during cell division.
Chloroplasts are only found in plant cells that perform photosynthesis
Contain a green pigment called chlorophyll
Function:
Photosynthesis occurs inside the chloroplast
Chloroplasts specialize in photosynthesis, a process in which plants combine carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air, with water (H2O) from the roots, in the presence of sunlight.
chromoplast
Another type of plastid, chromoplasts store the orange and yellow pigments found in numerous plant parts, including fruits, flowers and fall leaves.
The bright colors chromoplasts produce attract insects to various plants and help people identify food ripeness.
leucoplasts/amyloplasts
Non-pigment plastid
Function: a storehouse for starch, these colorless plastids can be found in seeds and potato roots