21. Threats to Biodiversity
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What is the major threat to biodiversity?
Human activities
What are the multiple anthropogenic stressors?
OCCEPOC
Habitat destruction, fragmentation, modification, degradation
Change in nutrients & resource availability
Chemicals (pollution)
Eutrophication
Pathogens
Overexploitation
Invasive speices
Climate change
Different countries have different impacts because
People in industrialized countries (and the wealthy minority in the developing countries) consume a disporportionate share of the world’s energy, minerals, wood products and food, and have disporportionate impact on the enviroemnet
What is the measure for IMPACT (I) of any human population on the environment formula?
I = P A T
P = number of people
A = avg income
T = level of tech

Human ecological footprint def.
Measures the amount of land area (global hectares) and energy needed to support an average citizen of a nation

Human ecolegical foot print varries very much by the country
think of ghana vs the U.S. huge extreme
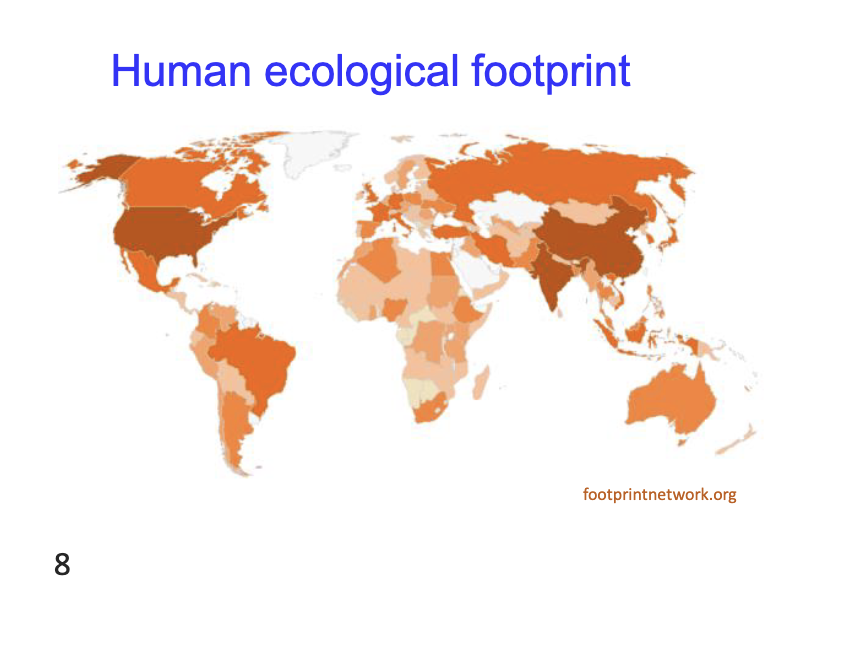
Human ecological foot priint accors the worlds
Richer and more populated conutires have a bigger impact

Ecological footprint per country rank atm
Ranks for total footprint can change:
China
U.S
India
Russia
Japan
Qatar and other middle east countries can have large footprinting per person
Habitat destruction is the greatest what?
The greatest threat to the world’s species, followed by overexploitation
How are tropical rain forests threatened?
Very high species richness and global importance absorbing some of the excess CO2 produced by burning fossil fuels
Habitat fragmentation meaning def.
the process whereby a large continuous area of habitat is both reduced in area and divided into two or more fragments
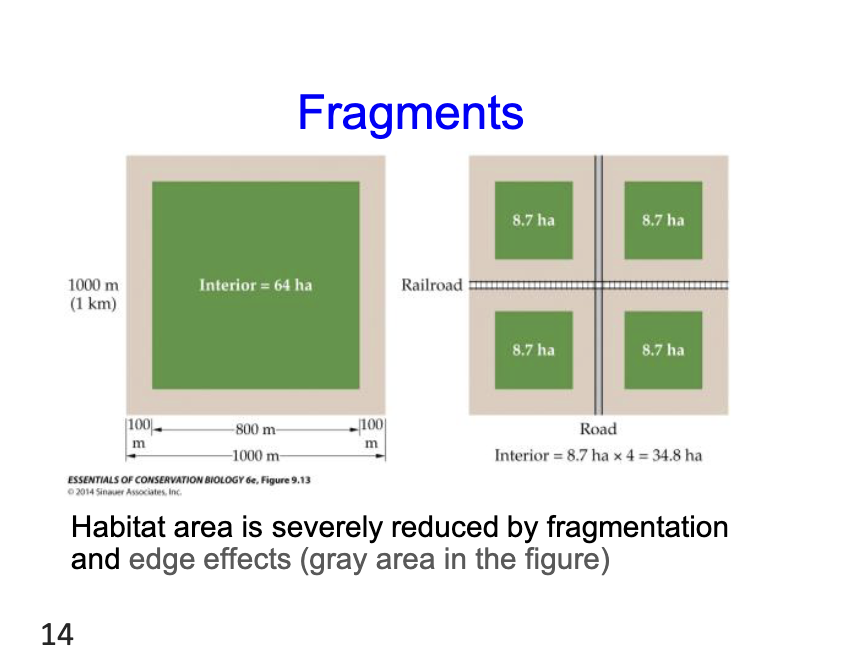
Fragments by railraods and roads
Makes the interrior areas of habitats much smaller causing them to fragmentate
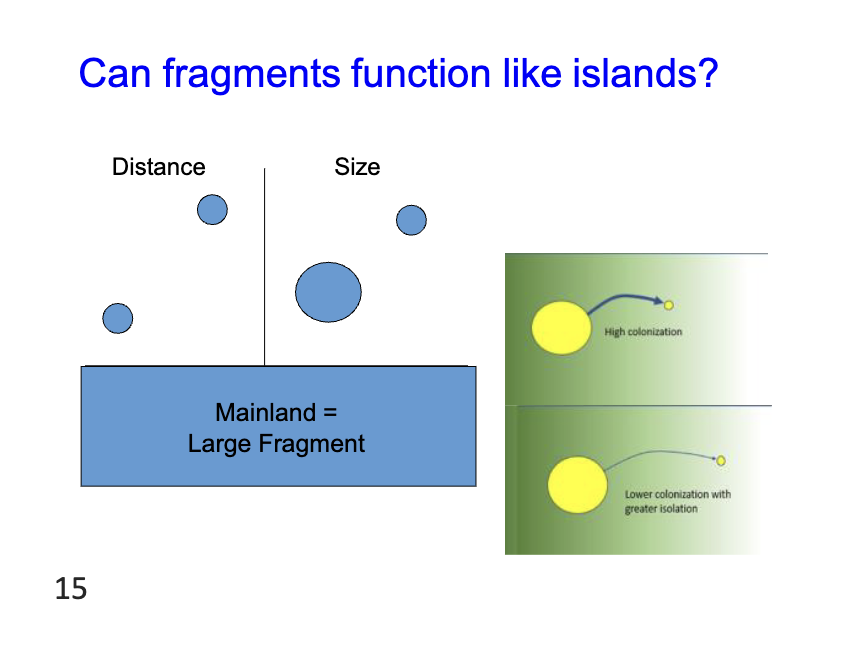
Can fragments function like islands?
No they can not due to the nature of the surrounding matrix, although there size changes based of distance and colonization
Effective population size Ne
Marine environments face multiple threats
coastline modification
sewage release chemical pollution eutrophication
fishers bycatch
Destruction of habitat by trawling
oil spoils
global climate change
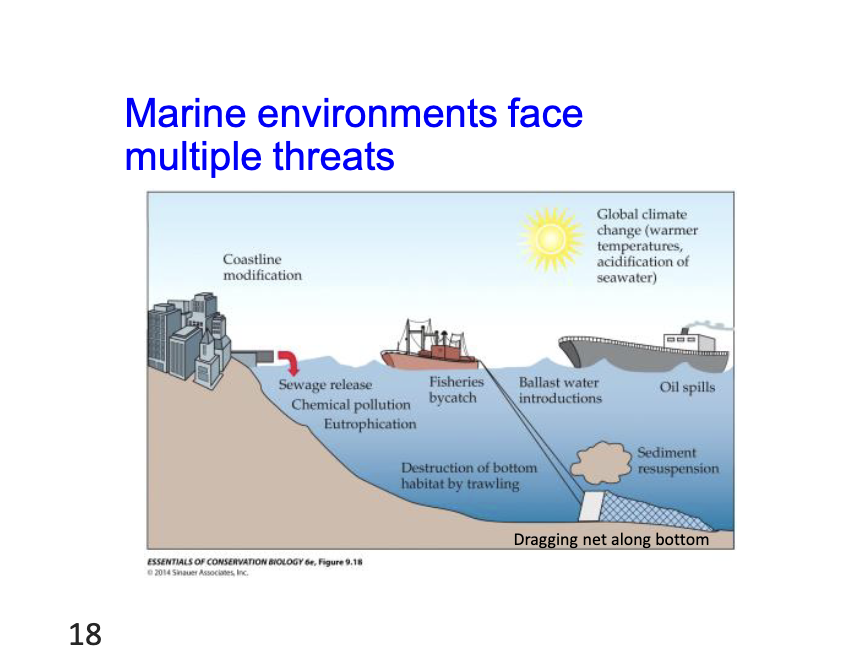
Habitat degradation and pollution def.
Birds, marine mammals, and many other ocean animals sicken and die when they are covered by curde oil following spills
Bioaccumulation and biomagnification def.
toxic chemiclas in water become sucessivley concetrated at higher trophic levels
Eutrophication in freshwater habitats
increase in nutrient levels in a water body with important effects on the aquatic communities
Abudnace of phytoplankton: increases. these photosynthesizing organims cover the upper sunlit layer of the water bodies
Euthrophication examples
algal blooms creates high growth and biomass of various types of photosynthetic organisms

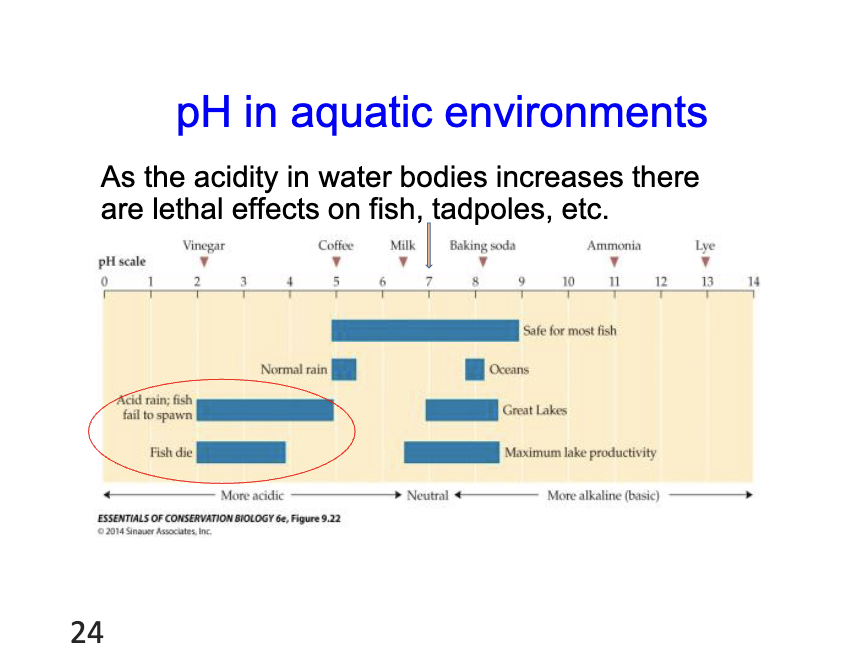
pH scale
strength of hydrogen ions, the lower the pH the more acidic, less then 7 is acidic, and mroe is basic/alkaline
pH is aquatic enviroments
as the acidity in water bodies increase there are lethal affects on fish, tadpoles, etc.
Air pollution def.
Contaminants in air can damage and weaken tree speices and make them more susceptiable to attacks by insects, fungi and disease
Acid rain def.
Produced when industires release huge quantites of nitrogen and sulfur oxides into the air, where these ehcmical combine with mositures in the atmoshpere to proudce nitric and sulfuric acids.
Overexploitation & overharvesting
Harvest that exceeds the productive capacity of a species and causes populations and conseqeuntly the yield to decline over time. The terms can also be applied to ecosystems and resoruces (e.g. water, aquifers)
Extraction exceeds sustanabile harvest levels
Logging def.
A net forest loss of 7 million hectares per year takes place in tropical countires, particular in low income countires, usally consumer demand is the reason
Broad leaf mahogany aka caoba
African cherry
Fishing
Intensive harvesting has reached crisis levels in many of the worlds fisheries
Overhunted terrestrial mammals def.
hunted by native americans, later by colonizers, almost to extinction like the maerican biosn-buffalo
Bushmeat criss and llegal wildlife trade
people buy wild animals dead or allive
GMO crops
High crop demand in the worlds → hope to acheive higher yields
Arround 25 years since GMO crops have been commericlaized
Invassive speices def.
they are everywhere espcially in these highlghted regions tha tdeal with trade
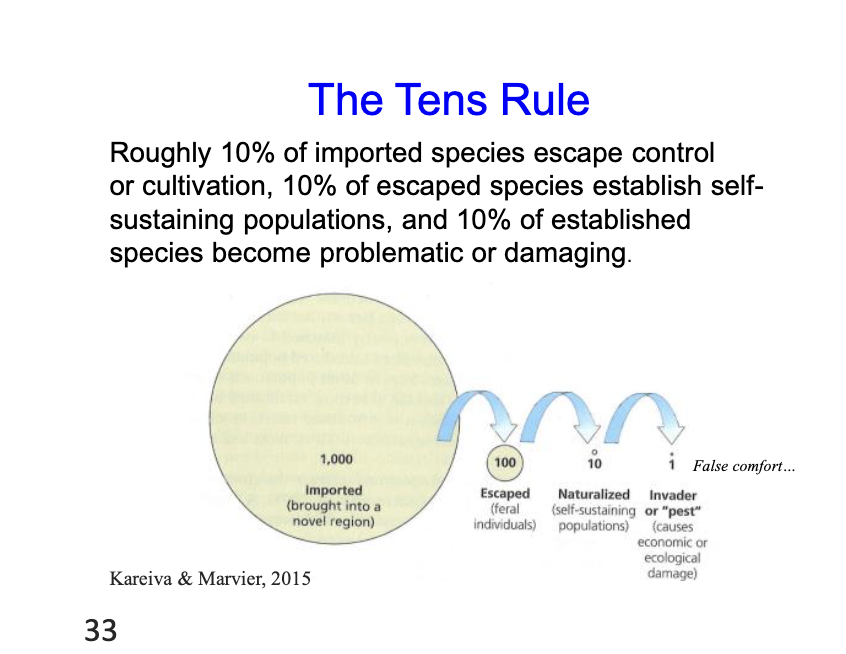
The tens rule
roughly 10% of imported speices escape controll or culitvation, 10% escaped speices estbalish self sustaiging populations and 10% estbalish d=speice beocome problemtic if 1,000 impoted, 100 secape, 10 establish, and only 1 is an invader.
Invasice speices are…
notnative
established
abudnacent
spreading
with effets on local speices/impacts on ecoelgical processes in the ecosystem
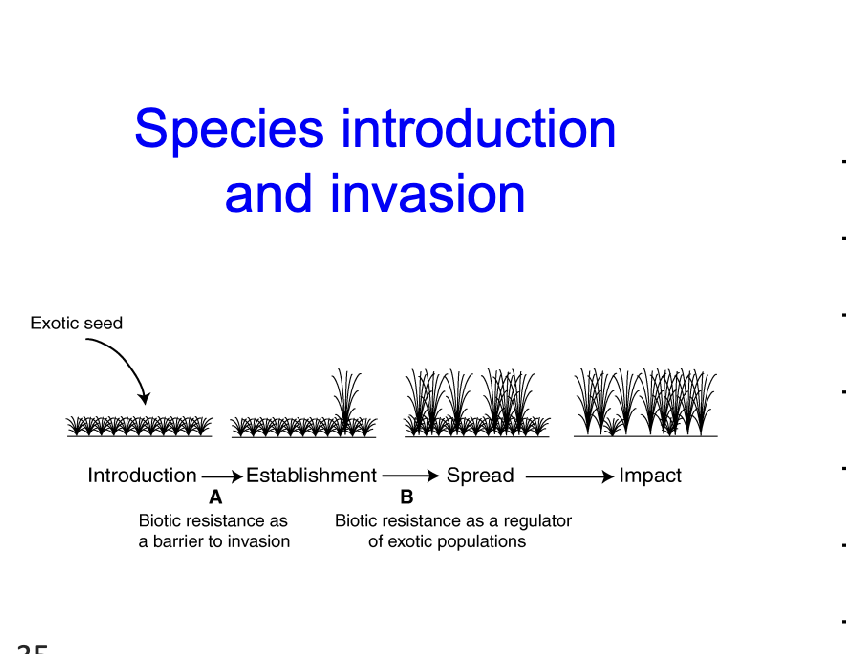
Speices introduction and invasion
the introuced, establish, spread, and then impact like this exotic seed
How introduced species becomes a succesufl invasive sp?
high reproductive rate and high dispersal rate
Cane toad in Australia
a devastating invasive species in Australia, introduced in 1935 to control sugarcane beetles but instead becoming a major pest due to their rapid spread, voracious appetite, and highly toxic bodies that poison native wildlife like quolls and goannas
Anthropogenic interactions and infecttiosu diseases
significantly drive infectious diseases by altering ecosystems, increasing close contact between humans, livestock, and wildlife, and facilitating pathogen spread through climate change, deforestation, urbanization, global trade, and intensive agriculture, leading to more zoonotic spillover events (like Ebola, SARS-CoV-2) and the emergence of novel threats.
Pandemics
like the black death killed more than 1/3 of the pop in europe in the 14th century, caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis, spread primarily by fleas on rats, but also directly between humans (pneumonic form) and through contaminated trade goods
Covid 19, Sars-CoV-2 has had neveiormental imparcs
a huge ton
zoonosis and emerging diseases def.
disease producting pathogens that move fron an animal speices to humans of the emergnic pathognes 75% are zoonontic
lands use change and vectors
deforestationand mining create more spots that collect rainwater offering enviroemtns sutiable for larve of disease tranmitng mosquites
Movement of pathogens and hosts def.
pathogen pollution; human intorudcing of pathogens or hosts into new areas

humans affect populations of vulutres which can impact human helath def.
vulutres play ciritcal rol in the dipserao of catttle carcasses, whchih reudces disease trnasmion amogn domestic wild ungulates
delcieng opoulation of culutres cretes less dieretrya itnake in idnia, pakistan, and nepal