Coral Reef Ecology, Biogeography, and Evolution: Key Concepts and Processes
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What is the scientific name of the long-spined black sea urchin?
Diadema antillarum
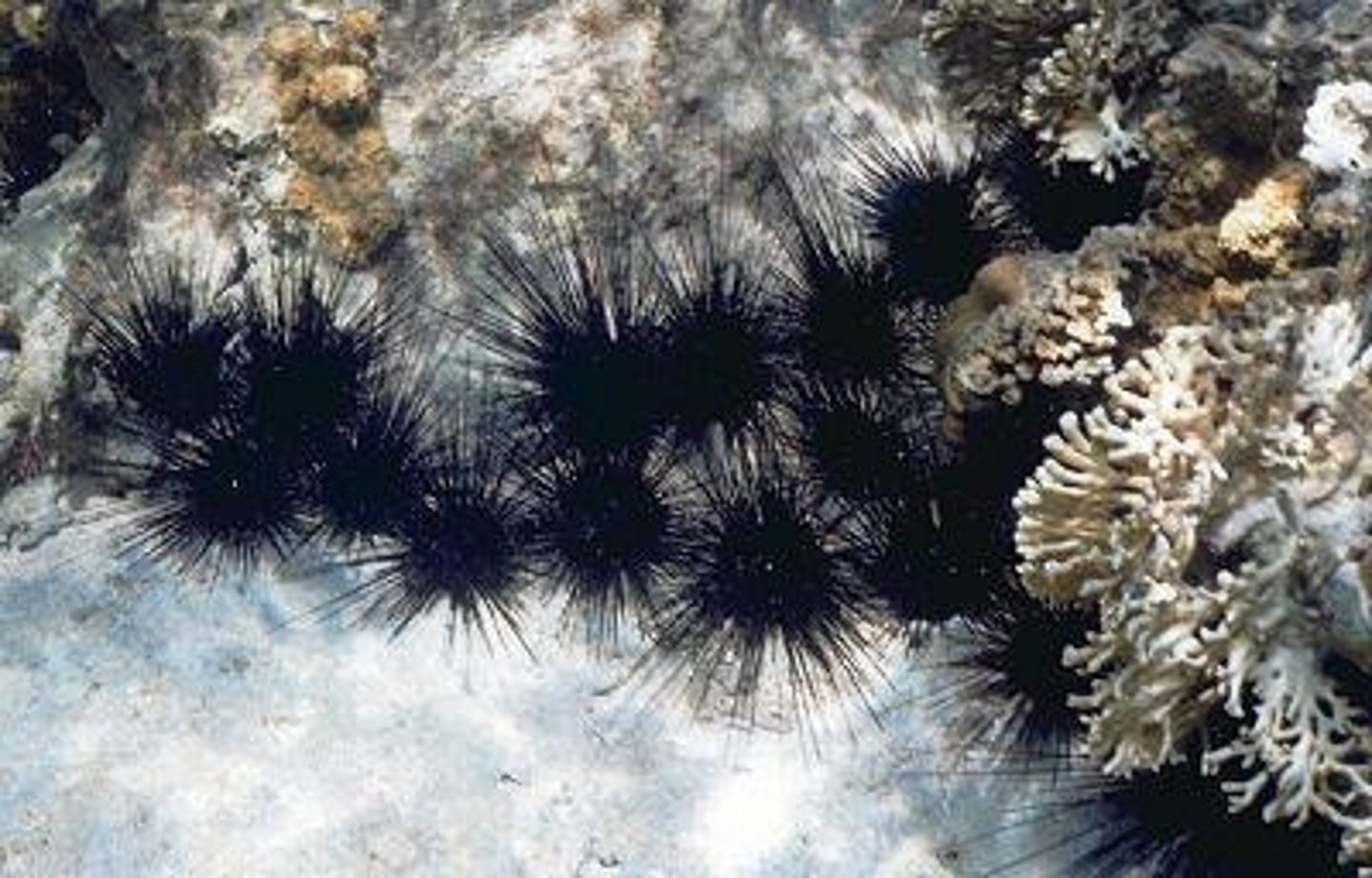

What significant event occurred to Diadema antillarum populations before 1983?
A massive die-off reduced populations by 97%.
What is a 'phase shift' in coral reef communities?
A transition from dense coral cover to dense macro-algae.
What role do parrotfish play in coral reef ecosystems?
They are grazers that help reduce macro-algae cover.
What is the impact of the crown-of-thorns starfish on coral reefs?
It feeds on hard corals and can lead to devastated reef areas.
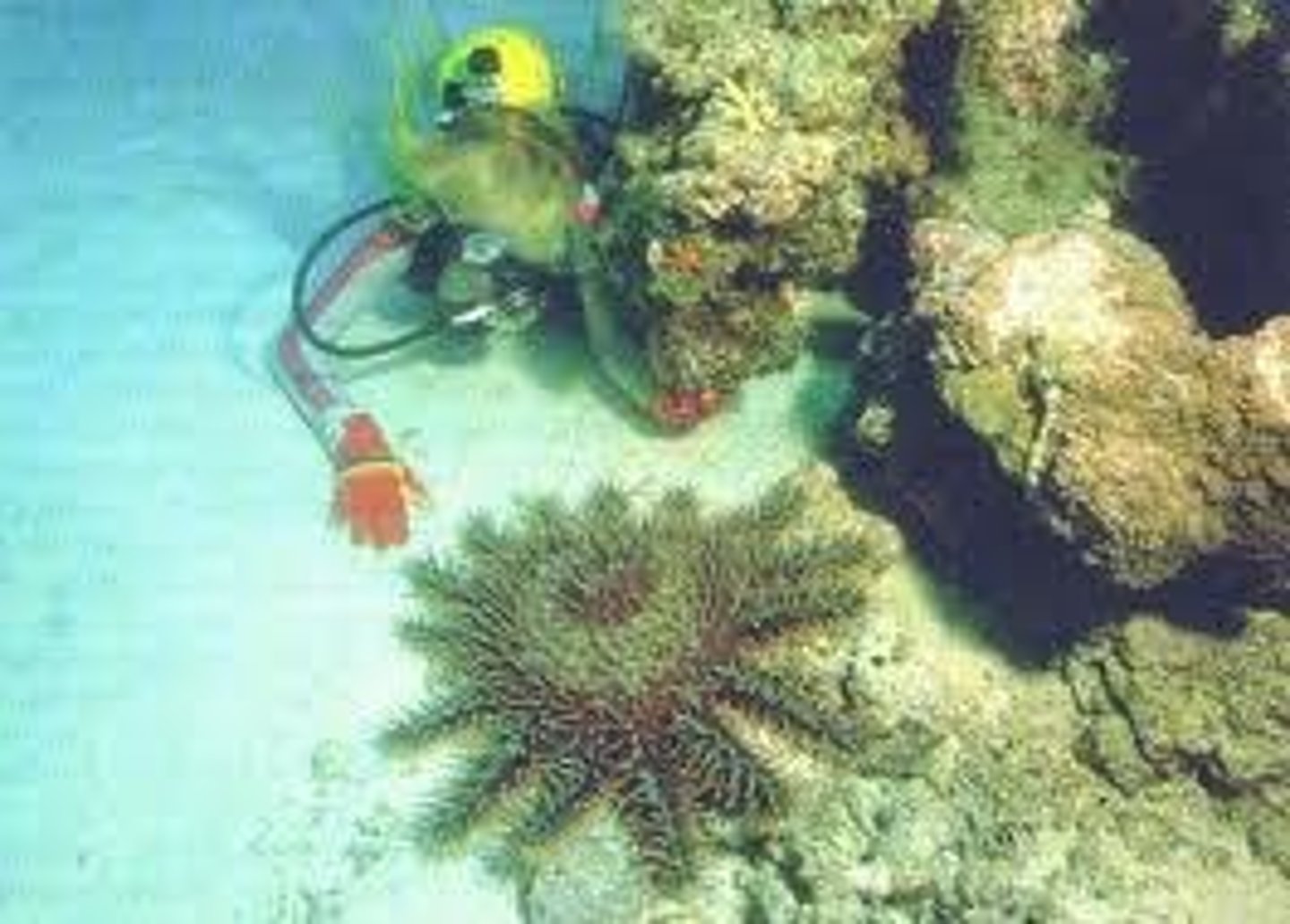

What are some hypotheses for the population explosions of crown-of-thorns starfish?
Natural phenomena, reduced predators, nutrient enrichment.
What types of symbiotic relationships are common in coral reef communities?
Mutualisms and commensalisms, such as cleaning stations for large reef fish.
What are hermatypic corals?
Stony, reef-building corals that contain zooxanthellae.
What is the primary function of zooxanthellae in hermatypic corals?
They provide corals with sugar and oxygen through photosynthesis.
What is calcification in corals?
The deposition of CaCO3, secreted as aragonite, requiring significant energy.
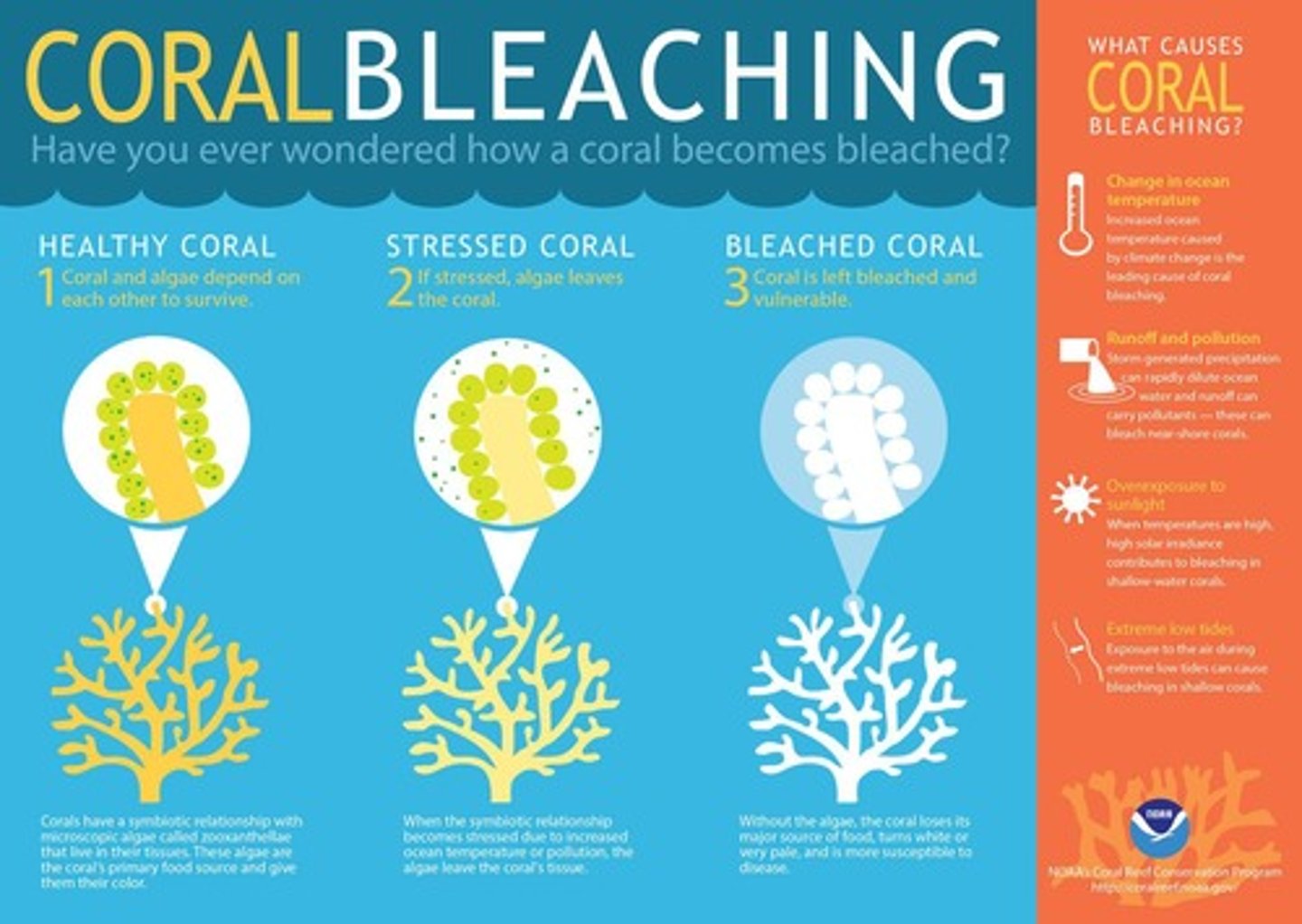
What causes coral bleaching?
The expulsion of zooxanthellae due to environmental stress, leading to loss of color.
What are the two main reproductive strategies of corals?
Asexual reproduction via colony expansion and sexual reproduction via egg and sperm production.
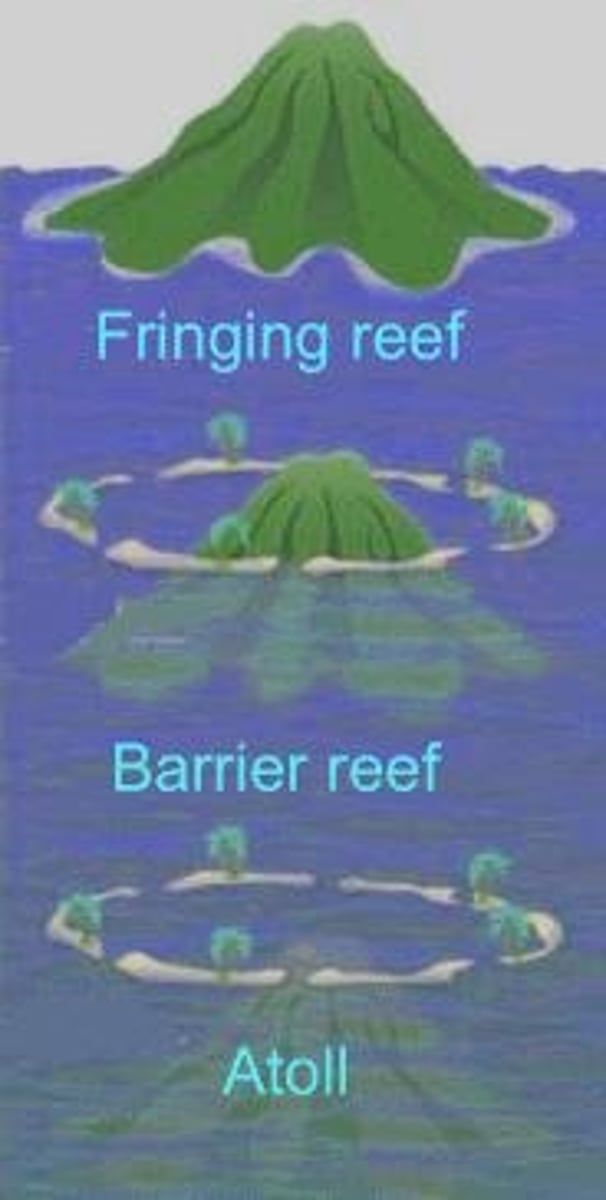
What are the three types of coral reefs?
Fringing reefs, barrier reefs, and atolls.

What are the four forms of coral reef algae?
Phytoplankton, micro-filamentous algae, coralline algae, and macro-algae.
What role do herbivores play in coral reef ecosystems?
They prevent algae from smothering corals and maintain reef health.
What is the significance of biodiversity in coral reef biogeography?
Biodiversity varies with time and space, influenced by environmental factors.
What is the ecological niche concept?
It links species abundance to competition for limited resources.
What is competitive exclusion?
When two species compete for the same resource, one will outcompete the other.
What is the difference between a fundamental niche and a realized niche?
Fundamental niche is without interference; realized niche is reduced due to species interactions.
What is character displacement?
When two similar species diverge over time to reduce competition for resources.
What are some major threats to coral reefs?
Overfishing, ocean acidification, coral bleaching, sedimentation, nutrient enrichment, pollution, invasive species, and recreation.
What is the role of cyanobacteria in coral reef ecosystems?
They fix nitrogen, providing essential nutrients for coral reef algae.
What is the optimum temperature for coral calcification?
26-27°C; calcification ceases above 31°C.
What is the significance of mass spawning in corals?
It involves synchronous release of eggs and sperm for fertilization in the sea.
What factors influence coral reef diversity?
Temperature and light are dominant factors controlling growth and distribution.
How does coral reef diversity change with latitude?
Diversity decreases with increasing latitude.
What is the Adaptive Bleaching Hypothesis?
It suggests that corals may switch symbionts to obtain more temperature-tolerant zooxanthellae.
What is biogeography?
The study of past and present geographical distribution of organisms.
What does evolution refer to?
Change in heritable characteristics of organisms.
What significant event occurred on Krakatau Island in 1883?
The greatest volcanic explosion ever recorded.
What was the impact of the Krakatau eruption on Earth's temperature?
It caused Earth's average annual temperature to be 0.5° C colder.
What is dispersal in the context of biogeography?
The movement of organisms from their birthplace or area of high density.
What types of seed dispersal were observed on Krakatau after the eruption?
Wind-dispersed seeds and water-dispersed seeds.
What is the difference between extinction and extirpation?
Extinction is the complete elimination of a taxon; extirpation is the loss of a species from a particular part of its range.
What is the Equilibrium Theory of Island Biogeography?
A conceptual model explaining immigration, colonization, and persistence of species on islands.
Who proposed the Equilibrium Theory of Island Biogeography?
Robert H. MacArthur and Edward O. Wilson in 1967.
What factors influence species richness on islands according to the Equilibrium Theory?
Distance to the nearest landmass and size of the island.
What is the species-area relationship?
The relationship described by the equation logS = logc + zlogA, where S is the number of species, A is the area.
What is natural selection?
The process where individuals that are better adapted to their environment survive and reproduce.
What are the five principles of natural selection proposed by Darwin?
1) Individuals within a population vary, 2) Variation is heritable, 3) Too many offspring lead to competition, 4) Limited resources create competition, 5) Individuals that survive and reproduce are better adapted.
What is the difference between micro-evolution and macro-evolution?
Micro-evolution involves changes within populations, while macro-evolution involves changes above the species level.
What is speciation?
The process of a population undergoing sufficient genetic divergence to become a new species.
What is the Biological Species Concept?
A group of interbreeding natural populations that are reproductively isolated from other groups.
What is the Phylogenetic Species Concept?
Species as the smallest diagnosable cluster of organisms with a parental pattern of descent.
What is the Hawaiian Archipelago known for in terms of biodiversity?
It has 98 endemic bird species, with half extinct by 1778 due to various factors.
What are the main causes of extinction on islands?
Habitat destruction, hunting, competition with non-native species, and introduced predators.
What is the significance of the Galapagos Archipelago in evolutionary studies?
It serves as a natural laboratory for observing speciation and micro-evolution.
What is the role of ecological interactions in evolution?
They influence both micro-evolution and macro-evolution processes.
What is the rescue effect in biogeography?
Repeated immigration by species already on an island may save species from extirpation.
What is the significance of Wallace's line?
It represents a boundary that separates distinct biogeographic provinces in Southeast Asia.