Macroeconomics Definitions + Equations
1/364
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
365 Terms
Macroeconomics
The study of the performance of the national economy
Business cycle
The fluctuations in real GDP
Two phases of the business cycle
Expansion and recession
Recessions
Phases of persistent decline in production
Expansions
Phases of persistent increase in production
Business Cycle Peak
turning point between expansion and recession
Business Cycle Trough
turning point between recession and expansion
Sequence of Business Cycle
Expansion, peak, recession, trough
Inflation
Increases in the overall level of prices
Deflation
Decreases in the overall level of prices
Nominal GDP
the market value of all the final goods and services produced within a country in a given time period
Market value
The price for which a good or service is sold in a market
Final goods and services
A good or service that is purchased by its final user
Intermediate goods and services
Items that are produced by one firm, bought by another firm, and used as a component of a final good or service
Expenditure Approach to measure GDP
Measure total expenditures on final goods and services produced within a country in a given time period
Income Approach to measure GDP
Measure total income received by factors of production operating within a country in a given time period
Personal Consumption Expenditures
Opening by domestic households on consumer goods and services
Gross Private Domestic Investment
Spending by domestic firms on new capital goods and additions to inventories, also included expenditure on new homes by households
Capital Goods
Goods that are used to produce other goods and services, but are not completely used up in the production of these other goods and services
Additions to inventories
Goods that are produced but are not sold to their final user inside of the period we are measuring GDP
Government Expenditure on Goods and Services
Purchases of goods and services by the domestic federal, state, and local governments
Transfer Payments
Cash transfers from governments to households and firms such as social security benefits, unemployment compensation, and subsidies
Net Exports of Goods and Services
The value of exports minus the value of imports
Exports
Sales of goods and services by the domestic economy to the rest of the world
Imports
Purchases of goods and services by the domestic economy from the rest of the world
Equation for Net Exports
Exports - Imports

Trade deficit
Net exports is negative (imports>exports)
Trade surplus
Net exports is positive (Imports<exports)
Equation for Expenditure Approach
Personal Consumption Expenditures + Gross Private Domestic Investment + Net Exports of Goods and Services
Stock of Capital Goods (or Capital Stock)
The total amount of capital goods currently operating in the economy
Depreciation
The decrease in the existing stock of capital goods that results from wear and tear and obsolescence
Net Private Domestic Investment
Gross Private Domestic Investment minus Depreciation (if positive, capital stock will increase)
Nest Domestic Product
GDP minus Depreciation
Factors of production
Produce goods and services, labor, capital equipment, land, entrepreneurship
Compensation of employees
Payment for labor services
Corporate Profits
Profits earned by corporations
Proprietor’s Income
Income of the non-incorporated self-employed
Rental Income
Payment for the use of land and other rented resources
Real Gross Domestic Product (real GDP)
Measures the market value of production in all years using a fixed set of market values from some common year (base year)
Household Production
Goods and services that are produced for personal use
Underground Economy
Market transactions for goods and services where the market isn’t observed
Standard of living
A comprehensive state of economic well being, including things such as income levels, quality of housing and food, medical care, educational opportunities, transportation, communications, and other measures
Real GDP per person
Real GDP divided by the population of the nation
Equation for CPI for year Z
(Total cost of CPI basket in prices of year Z / Total cost of CPI basket in the prices of base year) x 100
Equation for GDP Deflator for year Z
(Nominal GDP for year Z / Real GDP for year Z) x 100
Equation for Inflation Rate for year Z
([Price level for year Z - Price level for year before year Z] / [Price level for year before year Z]) x 100
Equation for Real Wage for year Z
(Nominal wage for year Z / Price level for year Z) x 100
Suppose the working age population in Tiny Town is 100 people. If 25 of these people are NOT in the labor force, the _____ equals _____.
Labor force; 75
Are discouraged worked considered unemployed?
Yes
The population of Tiny Town is 100 people and the labor force is made up of 75 people. If 5 of these people are unemployed, the unemployment equation is
(5/75) x 100
What is frictional unemployment the result of?
Normal labor market turnover
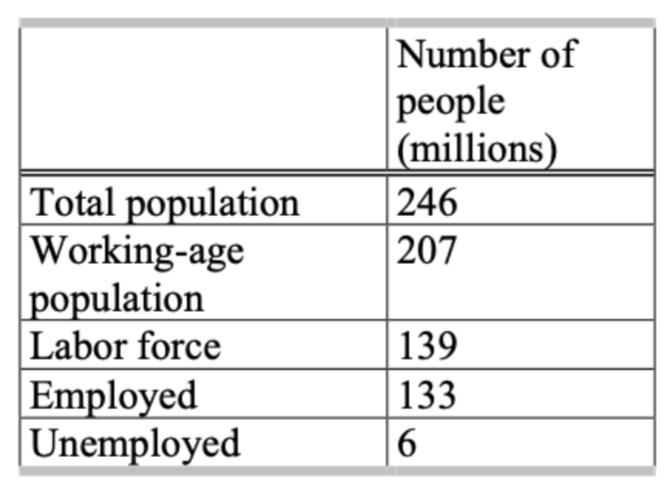
Using the information in the table, what is the unemployment rate?
4.3%
What is structural unemployment associated with?
The general decline of specific industries
What is the relationship of cyclical unemployment and the business cycle?
Cyclical unemployment fluctuates over the business cycle
What is the natural rate of unemployment?
The unemployment rate when the economy is at potential GDP, occurs when there is no cyclical unemployment present, and not a fixed percentage of the labor force.
What type of unemployment changes when a person reenters the labor force and looks for a job after spending time at home raising a child? Does it increase or decrease?
Frictional unemployment increases
Suppose the country of Tiny Town decided to open its borders to free trade. As a result, a number of its workers lost their jobs to international competition and can’t find new jobs because their skills don’t match what is required for job openings. The workers who lost their jobs would best be consider part of what type of unemployment?
Structural unemployment
The natural rate of unemployment rises with an increase in what types of unemployment?
Structural and frictional
When does full employment exist?
The economy is at the natural unemployment rate, there’s no cyclical unemployment, and there is only frictional and structural unemployment
When real GDP is _____ potential real GDP, the unemployment rate is _____ the natural unemployment rate.
Greater than; less than
What does the business cycle create a difference between?
Real GDP and potential GDP
Which of the following people would be considered unemployed by the Bureau of Labor Statistics?
I. Mrs. X returns fro, her job at the age of 55 and does not look for another job
II. Mr. Y was laid off from his job as a welder, but expects to be rehired very soon
II only
If the number of people unemployed is 100, the number of people employed is 1000, and the working-age population is 1400, then the labor force is
1100
Suppose that Matt quits a job with the XYZ Corporation in order to look for more rewarding employment. Matt would best be considered:
Frictionally unemployed
A recession causes a decrease in the demand for housing, resulting in substantial layoffs in the construction industry. The people laid off are considered:
Cyclically unemployed
When an individual who has not been working but has been looking for work decides to terminate the search process, the official unemployment rate will what?
Fall
Economic growth is measured by what?
Changes in potential real GDP
We are interested in long-term growth primarily because it brings what?
Higher incomes
If a nation’s population grows, then growth in real GDP per person will be _____ than the growth of real GDP.
Less
Suppose that in 2023, a country has a population of 1 million and real GDP of $1 billion. In 2024, the population is 1.1 million and the real GDP is $1.1 billion. The real GDP per person growth rate is:
Zero
Over the last 75 years, the average U.S. growth rate in real GDP per person was about what?
2 percent per year
Using the Rule of 70, if China’s current growth rate of real GDP per person was 7% a year, how long would it take the country’s real GDP per person to double?
10 years
If the price level falls by 5% and workers’ nominal wage rates remain constant, firms’ quantity of labor demanded will what?
Decrease
If at the prevailing real wage rate, the quantity of labor supplied exceeds the quantity demanded when?
The real wage rate is greater than the equilibrium real wage rate
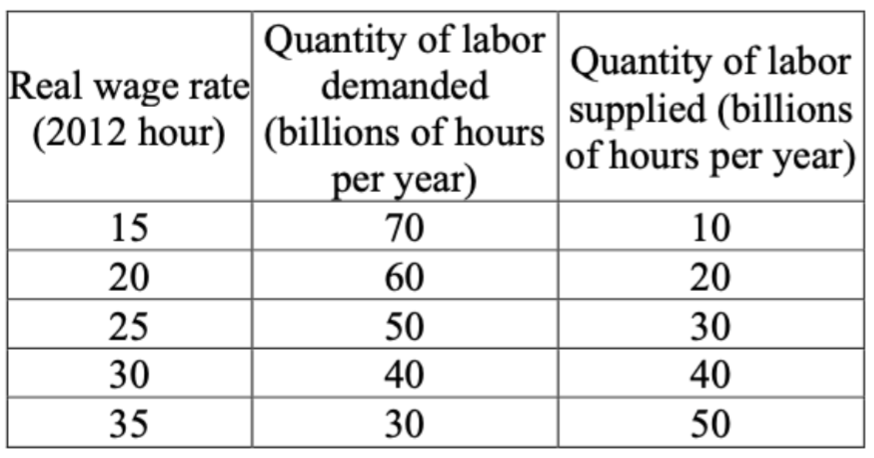
The table above shows the labor market for the country of Pickett. When the labor market is in equilibrium, the real wage rate is _____ and _____ of labor a year are employed.
$30 an hour; 40 billion hours
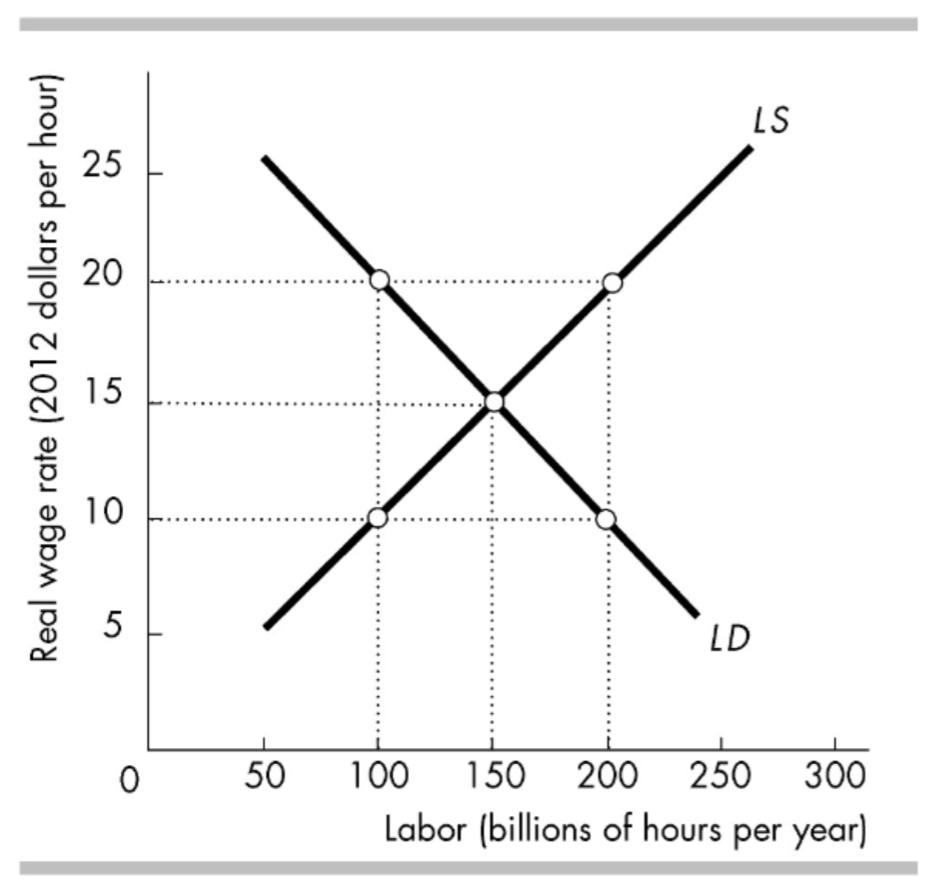
In the figure, at a wage rate of $20 per hour, there is a _____ of labor.
A surplus of labor
If the labor and capital grow more quickly, then real GDP will what?
Grow more quickly
If the population increases, then potential GDP _____ and employment _____.
Increases; increases
If the price level rises by 3% and workers’ nominal wages increase by 3%, then what happens to labor?
Quantity of labor demanded does not change because there is not change in the real wage rate
Potential real GDP per labor hour can increase due to what?
Increases in labor productivity
How do you calculate labor productivity?
Real GDP divided by aggregate labor hours
In addition to saving and investment in capital, making an even larger contribution to long-term economic growth in real GDP per person is what?
Technological advances
The most direct way in which money eliminates the need for a double confidence of wants is through its use as a what?
Medium of exchange
Keeping $200 on hand for an emergency is an example of using money as what?
A store of value
A $45,000 price tag on a new car is an example of money as what?
A unit of account
If an economy trued to use bananas as money, which function would bananas likely have the most difficult time fulfilling?
A store of value
In the Unites States today, money consists of what?
Currency and deposits at banks
$500 in a savings account is a good example of what type of asset?
Liquid asset
What does a depository institution pools risk, what is it doing?
Spreading loan losses across many depositors so that no one depositor faces a high degree of risk
For a commercial bank, what does the term “reserves” refer to?
The cash in its vaults and deposits at the Federal Reserve
T/F: Most commercial banks maintain cash reserves equal to a fraction of deposits.
True
T/F: The U.S. Treasury is a depository institution.
False
What is the major role of a commercial bank?
Receive deposits and make loans
T/F: Commercial banks do NOT determine what assets are money.
True
What are the riskiest assets held by commercial banks?
Loans to businesses
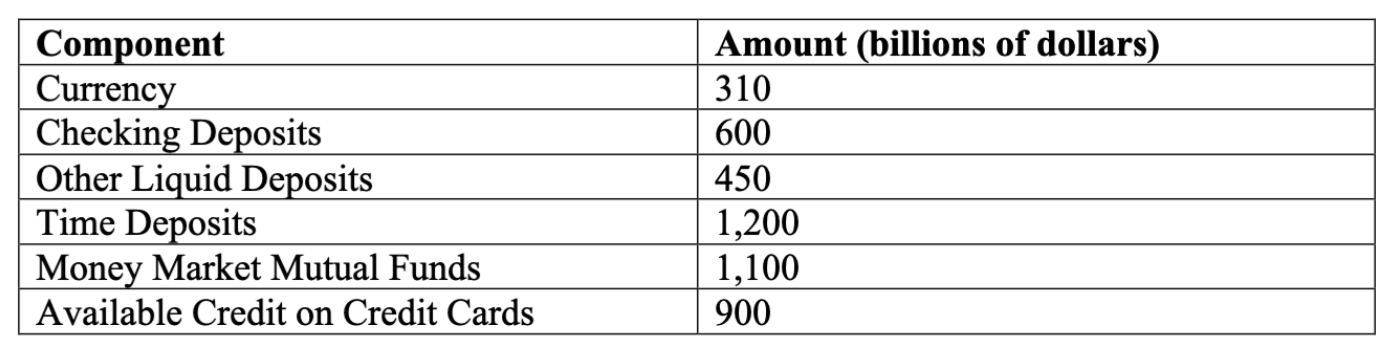
According to table above, the value of M2 is what?
$3,660 billion
The Bank of Japan is Japan’s central bank. As part of its duties, the Bank of Japan does what?
Adjust the quantity of money in circulation in Japan
The United States is divided into _____ Federal Reserve districts, each having a Federal Reserve Bank.
12
This groups consists of seven members appointed by the President of the United States for 14-year terms:
The members of the Board of Governors
Which Federal Reserve Bank president is always on the Federal Open Market Committee?
New York