Immunology & Serology - Lecture - 7 - Antigen-Antibody Reactions - Part 2 - Complete
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
139 Terms
Immunodiffusion
Is the term used to describe the diffusion of antibodies and/or antigens
Agarose gel or agar
Immunodiffusion is typically done using what media?
0.3-1.5%
What concentration of agarose gel is used if used in immunodiffusion?
Agar
This support medium can be used in immunodiffusion and it provides a stable matrix against temperature and mechanical induced currents, and can still permit an unimpeded flow of proteins
Makes precipitin bands visible, Stabilizes the diffusion process
Advantages of using agarose or agar for immunodiffusion
Agar
This immunodiffusion medium is derived from red algae & seaweed
Gracilaria, Gelidium
What genus of red algae and seaweed are used for agar in immunodiffusion?
Agarose, agaropectin
Agar components in immunodiffusion
Agarose
This immunodiffusion medium is a purified form of agar and the predominant component of agar
Linear polysaccharide
Agarose composition
Agar
Agar or Agarose
Which one is cheaper?
Agarose
Agar or Agarose
Which one is more expensive?
Agar
Agar or Agarose
Production is less time-consuming
Agarose
Agar or Agarose
Production is more time-consuming
Microbiology studies, substitute for gelatin, used to make jelly
Uses of agar
Electrophoresis, immune diffusion, bacterial culture
Uses of agarose
To detect antigen-antibody interaction using precipitation as a measure of the reaction
Main goal of immunodiffusion systems
Single, Double immunodiffusion techniques
What are the different types of immunodiffusion techniques?
Single immunodiffusion techniques
In this type of immunodiffusion technique, one of the reactants (either antigen or antibody incorporated into the agar) remains gel fixed, and the other reactant is allowed to move and interact with the immobilized reagent.
Liquid
In Single immunodiffusion techniques, to make the reactant be fixed to the gel, it is a prerequisite that it has to be added to the gel medium while it is in what form?
Radial or linear
In Single immunodiffusion techniques, the free reactant (antigen) diffuses either a ________ pattern to react with the immobilized reagent (antibody).
Single linear immunodiffusion
In this type of single immunodiffusion technique, one reagent (either antigen or antibody) is gel-fixed, while the other reagent moves only in one direction.
Antibody
In Single linear immunodiffusion, what reagent is usually immobilized in a gel within a glass tube?
Antigen
In Single linear immunodiffusion, what is evenly layered into the surface, forming a thin layer, then it will diffuse downward into the gel forming a precipitin band once it can interact with the antibody in correct proportion?
Formation of precipitin band
It is the endpoint in Single linear immunodiffusion
Single radial immunodiffusion
In this type of single immunodiffusion technique, it is a method used to determine antigen concentration in a sample.
Antigen
In Single radial immunodiffusion, what is the mobile reagent?
Antibody
In Single radial immunodiffusion, what is fixed in the gel?
Radial pattern
In Single radial immunodiffusion, what pattern does the formation of the precipitin band manifest?
Formation of precipitin ring
Endpoint of Single radial immunodiffusion
Standard curve
Single radial immunodiffusion can be quantitative if this was constructed from which the antigen concentration can be extrapolated
Apoprotein determination
Clinical use for Single radial immunodiffusion
Mancini, Fahey and McKelvey method
Two techniques used for the measurement of Single radial immunodiffusion
Mancini method
In this method of measuring single radial immunodiffusion, the antigen is allowed to diffuse to completion, and when equivalence is reached, there is no further change in the ring diameter
Endpoint method
Other name for Mancini method
Fahey and McKelvey method
In this method of measuring single radial immunodiffusion, the measurements are taken before the point of equivalence is reached.
Kinetic method
Other name for Fahey and McKelvey method
Rocket immunoelectrophoresis
In this type of single immunodiffusion technique, the reagents move through the gel medium under the influence of an applied field/voltage
Voltage facilitated single immunodiffusion
Other name for Rocket immunoelectrophoresis
One
In Rocket immunoelectrophoresis, how many directions does the antigen move because it is pushed through the gel by the applied field?
Antibody
In Rocket immunoelectrophoresis, what reagent is in the gel?
Antigens
In Rocket immunoelectrophoresis, what are moved into the gel by the electrical field?
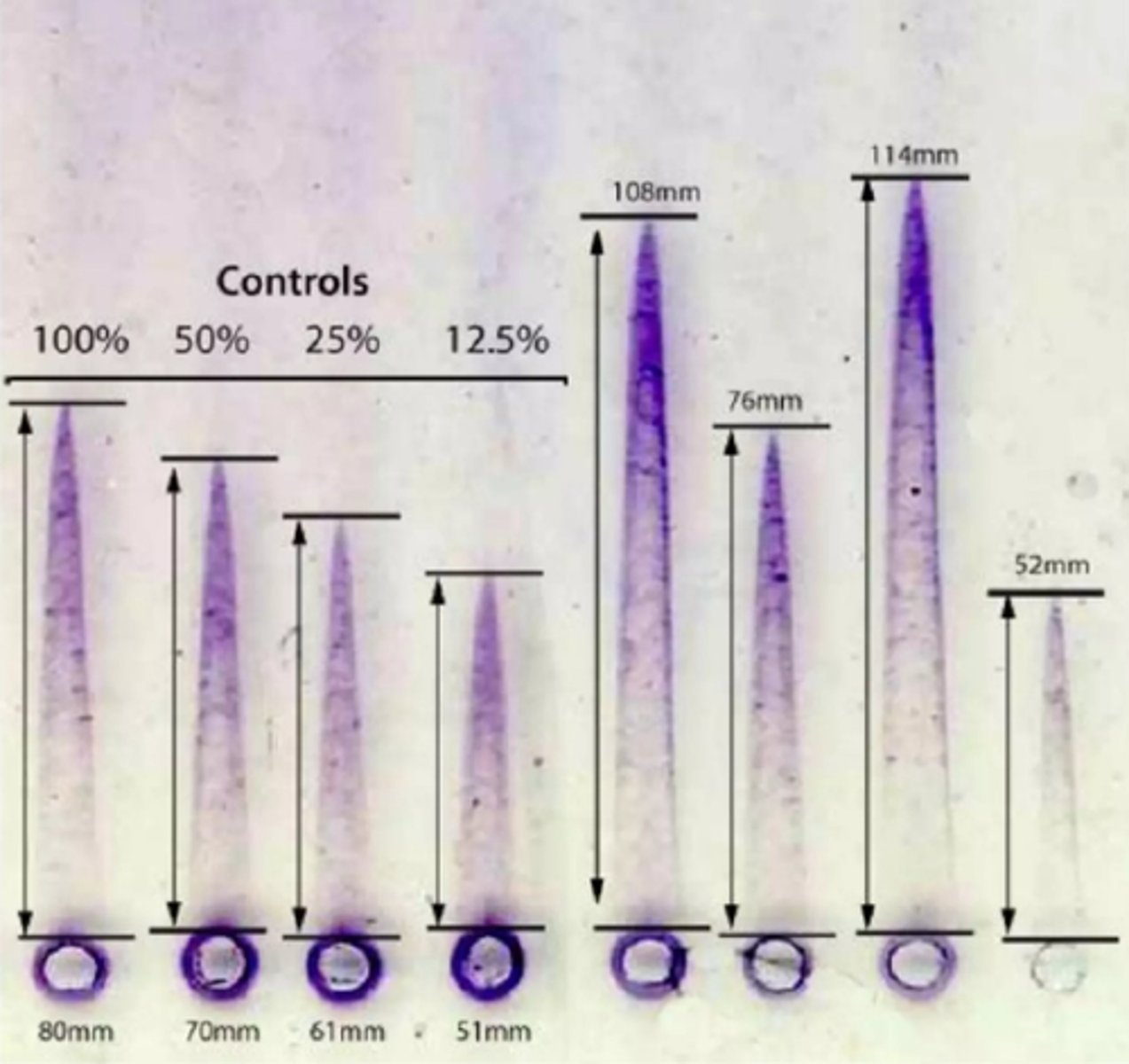
Rocket-shaped precipitation pattern
What is the endpoint for Rocket immunoelectrophoresis?
Electroimmunoassay, Electroimmunodiffusion, Luarell technique, Voltage facilitated single immunodiffusion
Other names for Rocket immunoelectrophoresis
Yes
Yes or No
Can Rocket immunoelectrophoresis be used to determine the concentration of Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen (Protein) in a mixture?
Yes
Yes or No
Can Rocket immunoelectrophoresis be used to detect abnormal monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) related to lymphocytic diseases (i.e., multiple myeloma)?
Yes
Yes or No
Can Rocket immunoelectrophoresis be used to detect allergens in food?
Charge-based separation
Electrophoresis principle
Electrophoresis
This type of single immunodiffusion technique involves the movement of charged particles like proteins, DNA, or RNA through a gel or medium under the influence of an electric field.
Size, Shape
In Electrophoresis, charge is based on what 2 factors?
Positively-charged molecules
In Electrophoresis, these molecules move toward the cathode
Negatively-charged molecules
In Electrophoresis, these molecules move toward the anode
Cathode
It is the negative electrode
Anode
It is the positively-charged electrode
Gel
The medium used in electrophoresis is often this material, such as agarose or polyacrylamide, which provides resistance that causes small molecules to move faster than larger ones.
Electrical current
In this electrical field, an ______ is applied which creates a potential difference that drives the migration of the charged molecules through the gel.
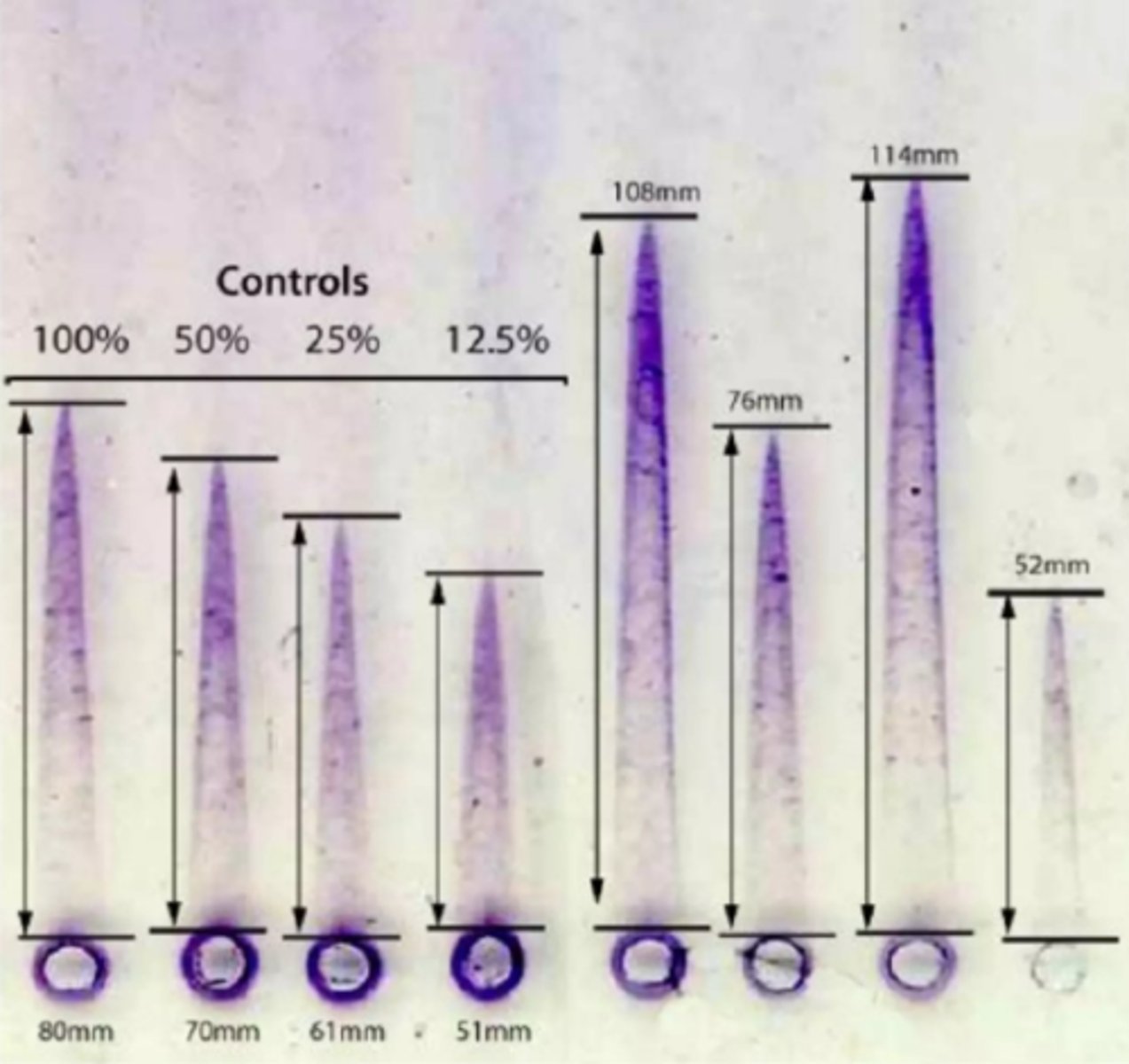
Rocket-shaped precipitates
The separation of these molecules allows for analysis as they are separated into bands based on their movement or in the case of rocket immunoelectrophoresis, we can observe ___________.
These bands can then be analyzed and visualized to determine their presence, size and concentration of their specific molecules
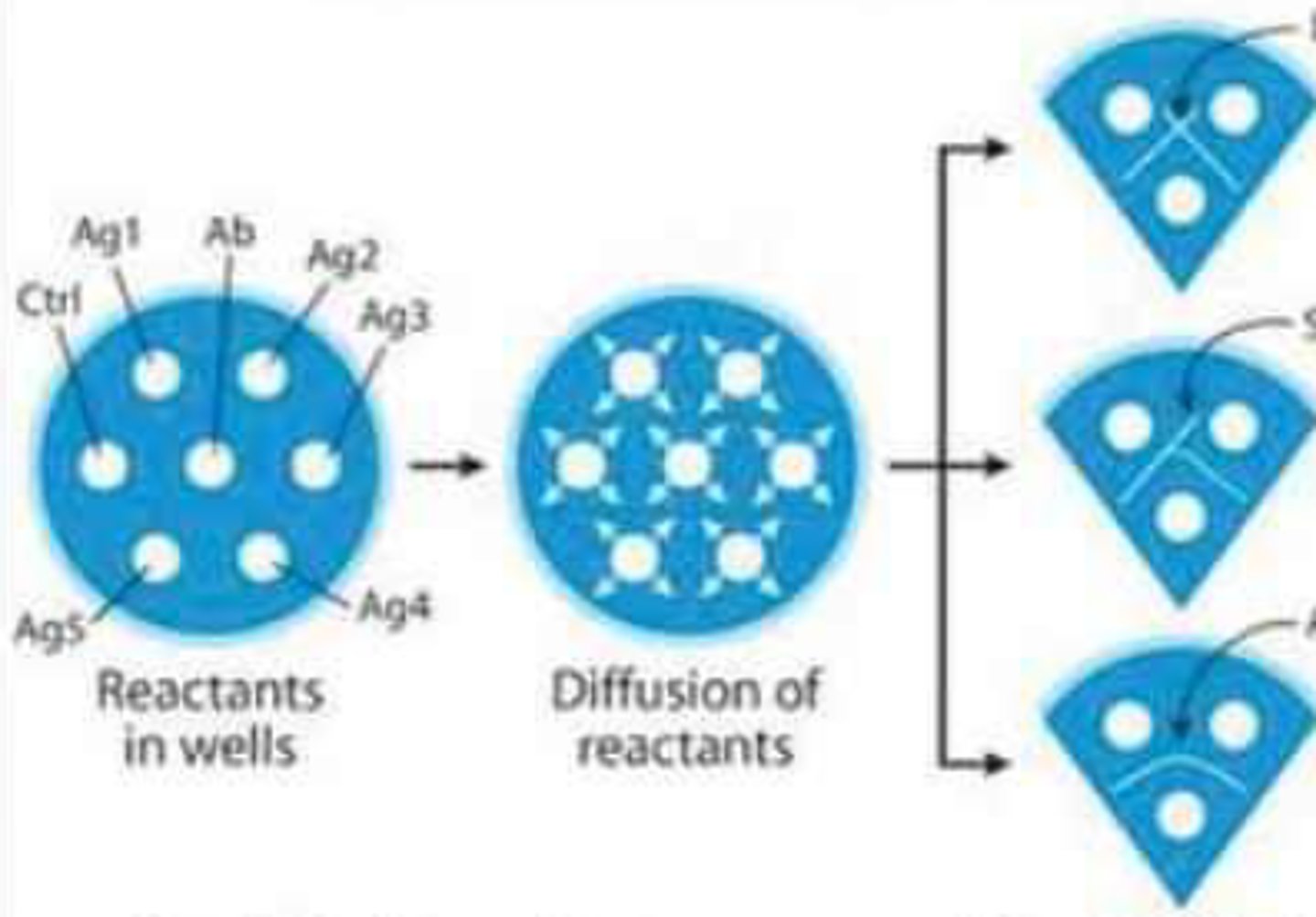
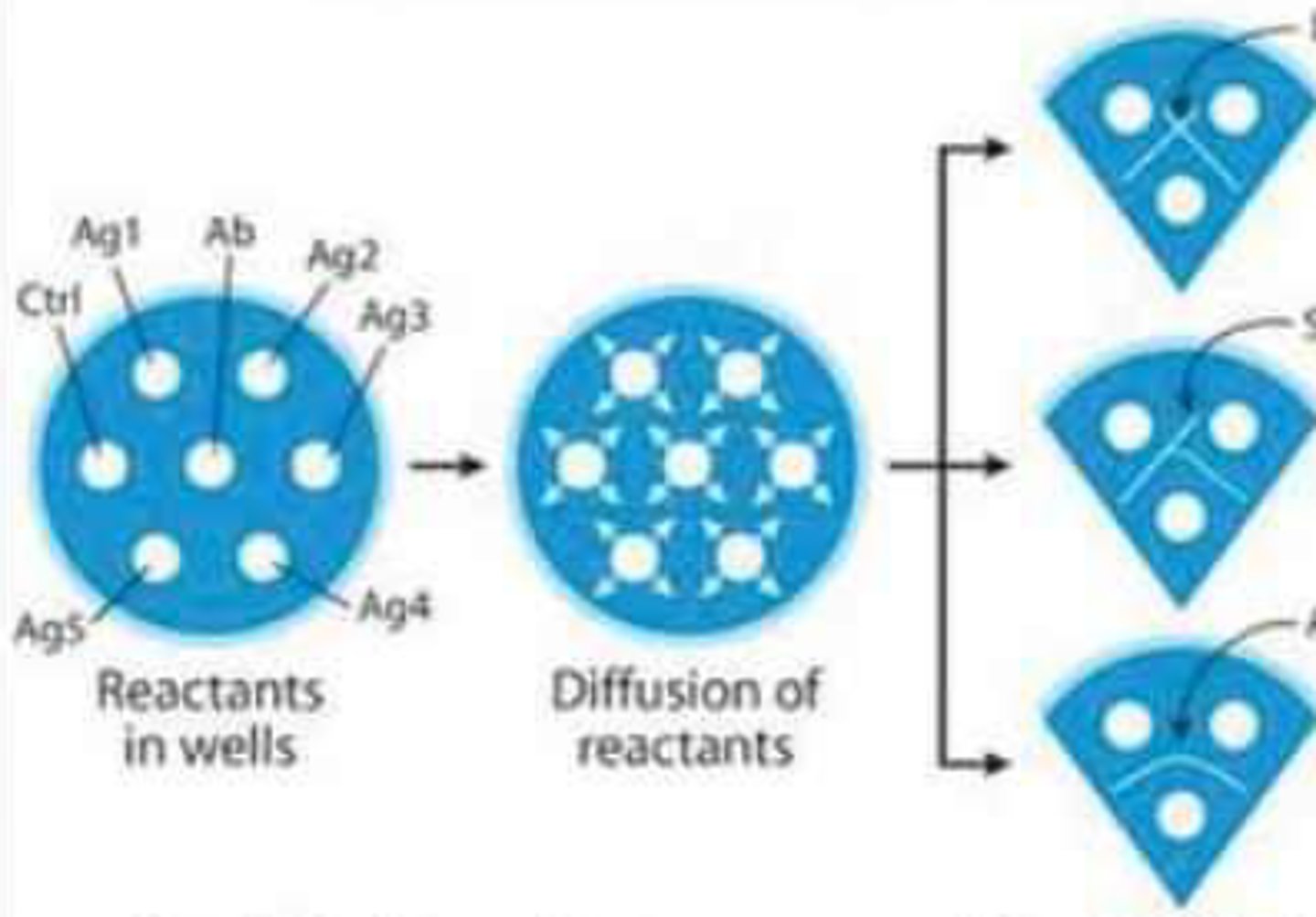
Double immunodiffusion techniques
This type of immunodiffusion technique is termed as "double" because both the reactants (antigen and antibody) are diffusing into the gel medium, forming a precipitate.
Antigen diffuses to antibody, antibody diffuses to antigen
These form the precipitate in double immunodiffusion techniques
Post-gel setting
When are the reagents in Double immunodiffusion techniques added?
Yes
Yes or No
In Double immunodiffusion techniques, both the antigen and antibody are mobile since they are both diffusing in the gel.
No
Yes or No
In Double immunodiffusion techniques, only the antigen is fixed. The antibody is not.
Yes
Yes or No
In Double immunodiffusion techniques, neither antigen or antibody is fixed.
Radial diffusion
In Double immunodiffusion techniques, each reagent is placed on a well and allowed to make a ________
Radial boundary intersection
In Double immunodiffusion techniques, it is the site when the ratio of the antibody and antigen is appropriate (zone of equivalence).
Ouchterlony, Simple immunodiffusion
These are the classic double immunodiffusion techniques
Yes
Yes or No
Are Double immunodiffusion techniques very time consuming?
No
Yes or No
Are Double immunodiffusion techniques very sensitive?
3-4 days
How long can Double immunodiffusion techniques take to detect the reactants with low concentrations?
Double simple immunodiffusion
This type of Double immunodiffusion technique has both the antigen and antibody diffuse through the agarose gel or agar medium until they meet at an equivalence ratio.
Double simple immunodiffusion
This type of Double immunodiffusion technique, the antigen and antibody are placed at some distance from one another in parallel wells that have been cut out of the agarose or agar that has solidified on a petri dish or glass slide.
Precipitation of immune complexes
Endpoint of Double simple immunodiffusion
Time-consuming
It is the disadvantage Double simple immunodiffusion
Ouchterlony Double Immunodiffusion
This type of Double immunodiffusion technique is based on the diffusion of 3 reagents within an agarose or agar medium in a petri dish
Double diffusion, Double Immunodiffusion, Double angular diffusion
Other names for Ouchterlony Double Immunodiffusion
Ouchterlony Double Immunodiffusion
This type of Double immunodiffusion technique is more complicated than double simple diffusion.
3
In the Ouchterlony Double Immunodiffusion, how many wells are cut out from the gel?
At the apexes of an imaginary equilateral triangle
How are the wells arranged in the Ouchterlony Double Immunodiffusion?
All directions
In what directions are the 3 reagents in Ouchterlony Double Immunodiffusion diffusing?
Pattern of identity, Pattern of partial identity, Pattern of non-identity
What are the 3 basic patterns that can be observed in the Ouchterlony Double Immunodiffusion?
Pattern of identity
This pattern in the Ouchterlony Double Immunodiffusion is a continuous line.
Pattern of identity
This pattern in the Ouchterlony Double Immunodiffusion results when the unknown and known antigens into the wells are identical and specific for the antibody present in the 3rd well
Pattern of identity
In this pattern in the Ouchterlony Double Immunodiffusion, there is fusion of the lines at their junction to form an arc, representing serological identity (a common epitope is present).
Full identity, Serological Identity
Other names for Pattern of identity
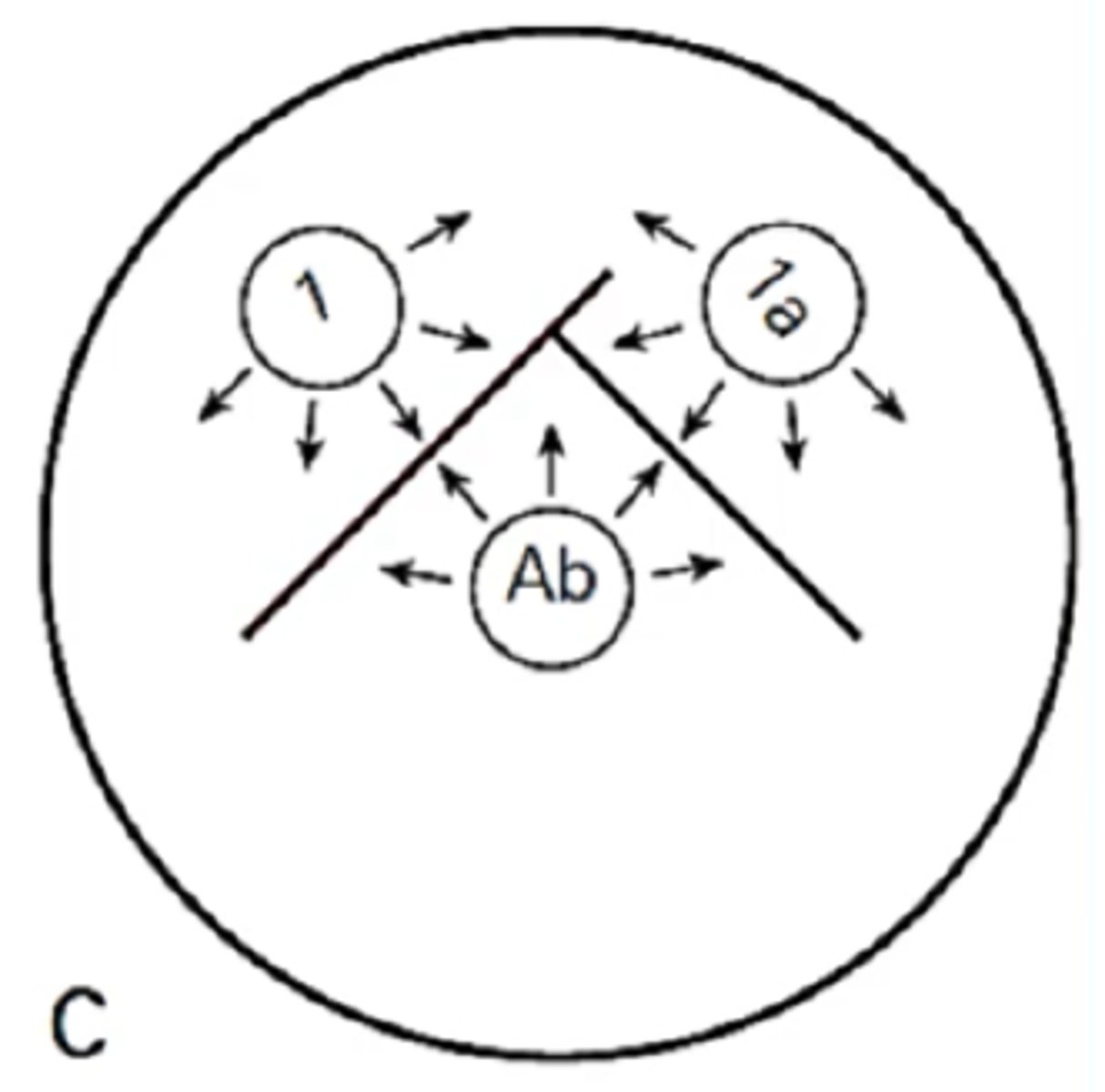
Pattern of partial identity
This pattern in the Ouchterlony Double Immunodiffusion is a continuous line with a spur at one end.
Pattern of partial identity
In this pattern in the Ouchterlony Double Immunodiffusion, there is fusion of 2 lines with a spur signifying partial identity
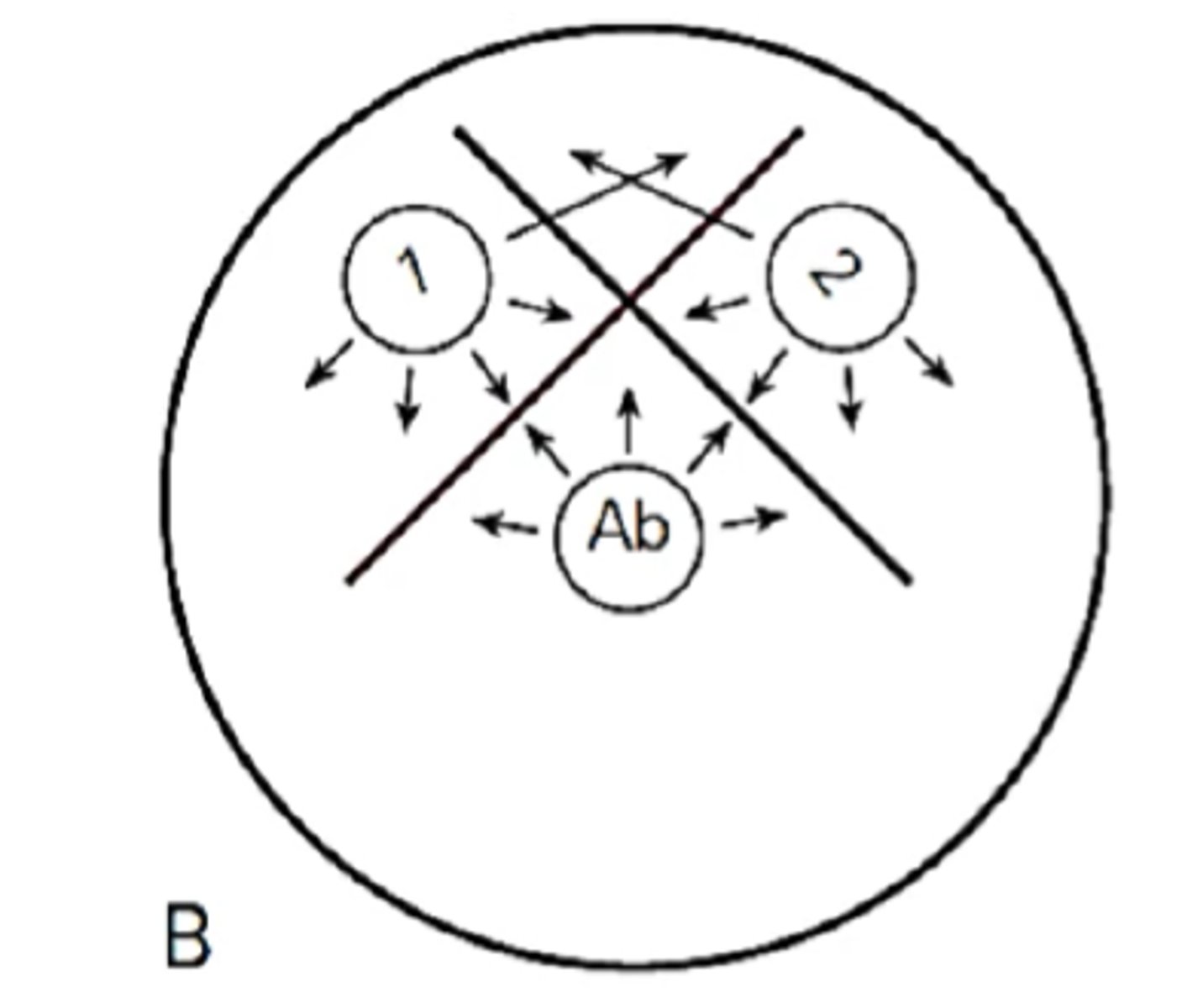
Pattern of non-identity
This pattern in the Ouchterlony Double Immunodiffusion has the 2 lines crossed completely.
Pattern of non-identity
This pattern in the Ouchterlony Double Immunodiffusion has a pattern of crossed lines meaning 2 separate reactions and indicate that no common epitopes are shared by the compared antigens
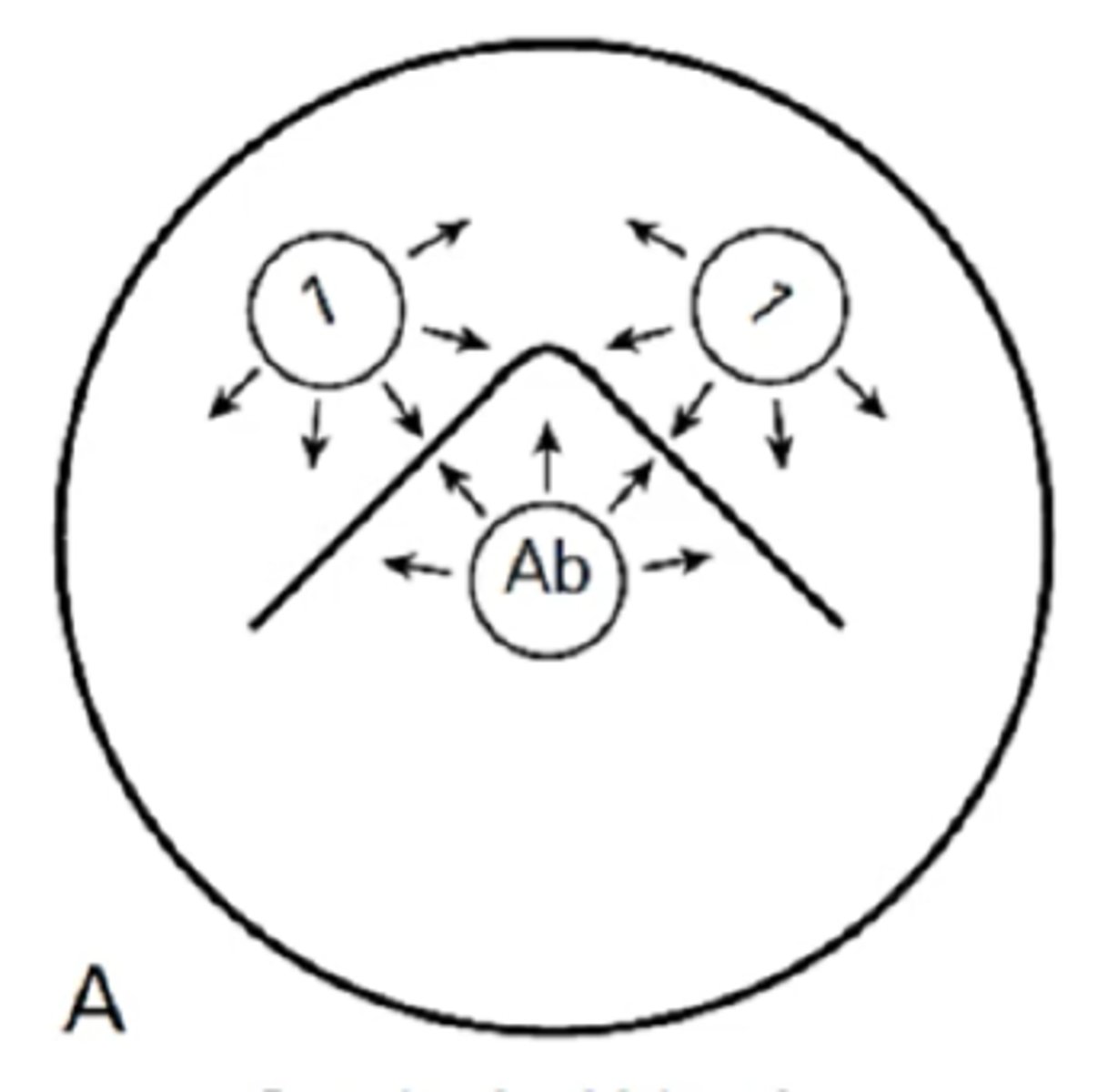
Pattern of identity
Identify Ouchterlony diffusion pattern
Pattern of partial identity
Identify Ouchterlony diffusion pattern
Pattern of non-identity
Identify Ouchterlony diffusion pattern
Antibody
In the Ouchterlony Double Immunodiffusion, it is a mixture of anti-1 and anti-2 and is placed in the central well.
Unknown antigens
In the Ouchterlony Double Immunodiffusion, these are placed in the outside wells.
Pattern of identity
This pattern in the Ouchterlony Double Immunodiffusion, the arc indicates that the 2 antigens are identical
Pattern of non-identity
This pattern in the Ouchterlony Double Immunodiffusion shows crossed lines representing 2 different precipitation reactions; Antigens share no identical determinants
Pattern of partial identity
In this pattern in the Ouchterlony Double Immunodiffusion, antigen 1a shares a determinant that is part of Antigen 1 but is not as complex. The spur formed always points to the simpler antigen.
Counter Immunoelectrophoresis
In this type of Double immunodiffusion technique, in the agarose gel, the movement of the antigen and antibody is due to the applied voltage rather than diffusion (application of an electric field).
Counter Immunoelectrophoresis
In this type of Double immunodiffusion technique, the antigen and antibody are placed in parallel wells and move toward one another under the influence of an electric field.
Counter current electrophoresis, Voltage facilitated double immunodiffusion
Other names for Counter Immunoelectrophoresis
Formation of precipitin band
In Counter Immunoelectrophoresis, what is the result once the antigen and antibody meet in the proper ration?