evr 1001- key themes of environmental science
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
pop a perc and a black out
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Human Population Growth
Sustainability and Carrying Capacity
A Global Perspective
An Urban World
People and Nature
Science and Values
6 Themes of Environmental Science
1 billion; 13
We are currently increasing at a rate of ___ people every ___ years
Malthusian/Exponential Population Growth
Population growth in the absence of resource limitations; growth is proportional to population
True
T/F: Exponential population growth is equal to doubling at fixed intervals
Carrying Capacity
Exponential population growth keeps growing until they reach the ____ of their environment
Carrying Capacity (in Human Population Growth)
The number of people, other than living organisms or crops that region can support
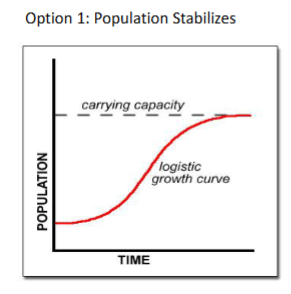
Population Stabilizes
Overshoot and Crash
Export emigrants
What 3 options can happen when a population reaches the Carrying Capacity?
Population Stabilizes; After a steady increase in population, once it reaches the Carrying Capacity, the growth stabilizes
What does this graph represent in relation to Carrying Capacity?
Overshoot and Crash; Results in degrading the environment, increase massively then decline due to lack of resources and overpopulation
What does this graph represent in relation to Carrying Capacity?
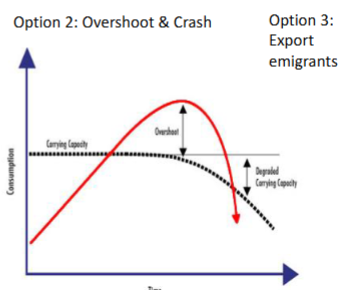
Export Emigrants; people leave
What is the third option for when the population reaches Carrying Capacity?
Carrying Capacity (in Sustainability)
The max number of plants, animals, bacteria, etc. that an environment can sustain
Depends on health of ecosystem, per capita resource utilization (how many resources each individual uses), quality of life, technology
Why is Carrying Capacity not constant?
Sustainability of a Resource
Sustainability of an Ecosystem
2 Types of Sustainability
Harvest/take no more than is replaced
Sustainability of a Resource
Human stressors
Natural disturbances/disasters
Ecosystem resilience
Biodiversity
Sustainability of an Ecosystem depends on (4)
Populations without conflict, clean energy, planned use of renewable resources, using nonrenewable resources sparingly, political system that priotizes long-term prosperity > short-term gain
Achieving sustainability would include
A Global Perspective
A recent idea that Includes climate change and how humans significantly affect the environment; remote regions are connected by atmosphere and water
Exposed the chemical “DDT“
What is the significance of “Silent Spring” by Rachel Carson (1962)?
an industrial pesticide that has a long-half life in soils and is transported by runoff and rivers where it bioaccumulates, becoming more concentrated as more animals were exposed by consuming each other, linked to declines in wildlife and is representative of human toxicity in the environment
DDT
O3 protects life from harmful UV rays
What part of the atmosphere protects life from harmful UV rays?
O3 destroyed by halogens which are common in refrigerants used by humans
What caused the Ozone hole?
The Ozone Hole is above Antarctica despite refrigerants not being used. The atmosphere current moved the refrigerant to Antarctica, supporting the issue of a global perspective
What does the ozone hole above Antarctica signify about the movement of the atmosphere currents?
An Urban World
Urbanization is both positive and negative for the environment
Positive: Reduced transportation distances and cost, less land per person
Negative: Reshapes landscape
Positive and Negatives of Urbanization
We need SUSTAINABLE cities as the middle ground
What is the common ground for urbanization?
People and Nature
Human vs Nature is a false concept, a construct of our society; humans are part of nature
Humans driving species to extinction and agriculture is still natural; the issue is the rate at which they happen
How are humans still a part of the “natural world“?
There is no single natural state of the ecosystem because change is natural; Human influence is a gradient, from heavy to less, but there is no such thing as “no human influence” and evolution is always proceeding with or without humans
Why is the concept of the “natural world“ subjective?
Values, Science
Decision-making relies on
Human equality
Economic progress
Future generations
Protection of ecosystems and species
What values does decision-making rely on?
Determine likely outcomes of different scenarios
Assess uncertainty of outcomes
What science is part of decision-making?
Always challenged by scientists
Theories can be disproven, but never proven
Rely on the scientific method
Why is scientific knowledge NOT absolute?
The Precautionary Principle
States when there is a threat of serious, irreversible environmental damage we should not wait for proof before taking precautionary actions
Prove it Before We Take Action vs Let’s be Cautious and Take Action
Burden of Proof vs The Precautionary Principle
The Utilitarian Justification
The Ecological Justification
The Aesthetic and Recreational Justifications
The Moral Justification
The Cultural Justifications
5 Justifications for Valuing the Environment
The Utilitarian Justification
The environment has quantifiable value to humans or provides necessary services (viewing what nature has to offer as equivalent to its worldly value); justification by economics
The Ecological Justification
Ecosystems are interconnected and healthy ecosystems may be required for the perseverance of many different species
The Aesthetic and Recreational Justifications
Based around the beauty of nature and joy derived from being in wilderness; spiritual, creative, emotional value of nature
The Moral Justification
Do non-humans have rights? Certain species? Ecosystems? Future generations?
The Cultural Justifications
Thousands of cultures with diverse beliefs related to the environment, nature, and treatment of animals