BIOLOGY EXAM 1
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
What is descent with modification essentially?
How many broad observations did Charles Darwin have?
What are they?
Darwin proposed that existing species are…; who were different
Evolution
3
Animals perfectly suited for environment, share many characteristics with other species, & unique
Descendants of ancestral species; from present-day relatives
Evolution refers to the process by which species accumulate…
Then it was able to be measured as a change in…
Prevailing ideas of Darwin’s time were from…; Who claimed that…
a concept by which…
Consistent with…; name of concept
Differences from ancestors as they adapt to different environments
genetic composition of populations from generation to generation
Aristotle; All life on Earth was fixed
Perfect organisms could be placed from least to most complex
Bible where God created infinite life forms; Scala Naturae
Patterns of evolution is the raw…
To study these patterns, scientists draw on…; example is…
Process of evolution is mechanics of evolution that…
Includes…
These processes act upon…
Material for change observable in natural world
Knowledge from biology, chemistry & geology; fossil record
produce an observed change from one species to next
Natural selection, gene flow, genetic drift
The patterns to produce change
Darwin’s early thinking was influenced by who?
These men were actively attempting to prove what?
George Cuvier founded…; which was the …
Discovered while examining strata that …
He believed that strata represented…
Hutton, Malthus, & Lamarck
Gradualism, population dynamics, & create hypotheses on evolution
Paleontology; study of fossils
The older the strata, the more dissimilar fossils he observed
Catastrophic events such as a massive flood
Hutton proposed that Earth’s features could be explained by…
Which is when …
Example of this…
Concept that slow & graduate changes led to larger changes …
Malthus had the idea of populations…
Gradualism
Changes occur through gradual increments
Faults coming together & gradually forcing plates to form mountains
Influenced Darwin to think this could influence biological organisms
Outstripping their food supply, leading to struggle for existence
Lamarck believed that life…
His 1st hypothesis was…; where body parts…
2nd hypothesis was…; which explained an organism could pass…
This is wrong because of…; we know traits acquired by use during …
Changed along with its environment during their lifetime
Use & disuse; would grow or depreciate w/ use or lack thereof
Inheritance of acquired characteristics; modifications to offspring
Genetics; individual’s life are not inherited this way but by genes
Darwin went to Galápagos Islands where he observed a new …
He concluded that these species emerged after a,,,
He observed …; saw that each possessed traits that were…
Led Darwin to hypothesize that gradual changes over….
Yrs later, biologists have confirmed these adaptations are a …
species similar to known species but had adapted to life on islands
Common ancestor strayed from continent onto an island
Finches; suited to their environment
Evolutionary time resulted in emergence of new species w/ distinct adaptations
Result of heritable traits being passed from one generation to next
Natural selection is a process in which individuals w/…
Alternatively, traits that …
How did darwin use concept of artificial selection to help frame this?
How many observations did he make about this?
certain inherited traits tend to survive & reproduce at higher rates
Hinder individual’s success will be eliminated
Humans selectively breed plants, livestock, & pets & decide which traits are beneficial so there’s typically no natural selection pressure
2
Darwin’s first observation is that …
Which infers that traits giving an individual …
Darwin’s second observation is many species can produce…
Which infers that this unequal ability of individuals to survive…
#of key features that result in organisms adaptations to environment?
Members of a population often vary in inherited traits
fitness (ability to survive & reproduce) will be passed on
More offspring than the environment can support so many won’t survive
Will lead to the accumulation of favorable traits in a population
3
Individuals with certain heritable traits …
Natural selection increases the …
If environment changes, natural selection may …
Although natural selection occurs through…
Individuals do not…
Name the 4 types of data that document pattern of evolution
survive & reproduce at higher rate than other individuals
Frequency of adaptations that are favorable in an environment
Drive adaptation to new conditions giving rise to new species
interactions between individual organisms and their environment
Evolve, populations do
Direct observation, homology, fossil record, biogeography
Direct observation highlights that natural selection is not…
Individuals w/ heritable traits/genes which result from mutation are…
Natural selection depends on ..; & what is beneficial in …
1st example of direct observation
2nd example of direct observation
A creative process
Selected for while individuals that are ill-adapted are selected against
Time & place; generation may not be in the future
Natural selection in response to introduced species
Evolution of drug-resistant bacteria
Soapberry bugs in southern Florida use …
In central Florida, golden rain tree, replaces balloon plants & has…
Researches measured soapberry bugs beak lengths 35 yrs after…
In southern Florida, bugs have…; in central, they have…
long beak to feed on seeds embedded in balloon plant
Seeds closer to surface so they have shorter beaks
Intro of golden rain tree
Long beaks from eating balloon vines; shorter beaks after eating golden
baterium staphylococcus aureus occurs on…
1943, penicillin became 1st…
Penicillin resistant …
New antibiotic, methicillin, was introduced but then…
Next up, homology which includes…
skin or nasal passages of about 1 in 3 people
Widely used antibiotic to treat bacterial infections
Evolved in S.aureus by 1945
Methicillin resistance evolved in s.aureus by 1961
Homologous structures, comparative embryology, vestigial structures
Homologous structures are anatomical structures that are…
Examples include forearms in…
Comparative embryology is anatomical similarities during development.
Example is all vertebrate embryos have a…; arches develop into…
Vestigial structures where whales & snakes evolved from legged …
Remarkably similar which result from a common ancestor
mammals which are same arrangement of bones but have diff functions
Not visible in adult organisms
Post-anal tail & pharyngeal arch; structures w/ diff functions in adults
ancestor & still have remnant pelvic bones w/ no anatomical function in these animals; known as left over structures
Fossil record provides evidence of…; origin of…; & changes within…
Fossils can document …; such as transition from…
Biogeography is the study of…; as Pangaea split apart, species…
extinction of species; new groups; groups over time
Important transitions; land to sea in ancestors of cetaceans
Geographic distribution of organisms; diverged into distinct species
evolutionary trees are diagrams that reflect…
Homologies form…; characteristics shared by species may…
Homology that evolved more recently are shared only within…
Example is all tetrapods have…; reptiles have an…; mammals produce…
Hypotheses about the relationship among groups
nested patterns on the tree; date to a deep ancestral past
Smaller groups
limbs w/ digits; amniotic egg; milk
Colloquial use of “theory” is what scientists refer to as…
In science, a theory accounts for ..
Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection integrates …
ongoing research by many scientists…
hypothesis
Many observations & data
Diverse areas of biological study & stimulates new research questions
Prove evolution is a fact
Microevolution is a change in…; it is evolution at its…
Things that define a population are…
Smallest unit of evolution is a…; evolution occurs over…; takes
name the 3 mechanisms that cause allele frequency change
allele frequencies in a population over generations; smallest scale
Same species, occupy same area, interbreed, produce fertile offspring
Population; evolutionary times; generations
Natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow
Below is what kind of event within a population?
Extreme drought in…; led to; how many survived …
Survivors had larger beak that…; beak length is an…
Example of …
Proportion of large-beak birds …; population…
Microevolutionary
Daphne Major Island; reduced food; 180/1200 birds
Allowed them to crack the bigger seeds available; inherited trait
Evolution by natural selection
Increased from one generation to the next; evolved, not the individual
Natural selection is adaptation to…; results in…; makes individuals…
Genetic drift is chance events that…
Gene flow is transfer of …; tends to…
environment; random, non adaptive change; better suit to environment
Alter allele frequencies
Alleles between populations; reduce genetic differences
Below is how…
Variability in heritable traits is the…; so genetic variation is a…
Gregor Mendel described…; genes are the molecular…
Genes can …; leading to…
Genetic variation arises
Foundation of evolution; prerequisite of evolution
Inheritance of traits in pea plants; units associated with traits
Mutate; leading to new versions of a gene or alleles
Genetic variation generates a …
Which allows some individuals to…
Without variation, there would be …
Evolution requires a variety of…; without it, all individuals would be…
Name the ways that genetic variation arises
pool of different alleles within a population
Have favorable inherited traits to survive & reproduce & some who dont
No differences in a population and so evolution wouldn’t occur
Traits to “select”; genetically identical & no traits could be favored
Mutations (micro), gene duplication (macro), other related processes/errors (macro)
Mutations (micro) are changes in a …
In multicellular organisms, only mutations happening in…
In animals, most mutations happen in…; in plants/fungi, multiple…
Example of mutations is…
nucleotide sequence of an organism’s DNA
Gametes gets passed on
Somatic cells & aren’t passed on; cell lines produce gametes
Point mutations
Point mutations occur when …
Example is …; where point mutation …
Results in …
Natural selection helps remove…; but many point mutations are …
Harmful alleles may be…; can stay…
single base pair is added, deleted, or changed in a gene
Sickle cell disease; GAG to GUG
altered hemoglobin structure in red blood cells
Harmful mutations; buffered in organisms bc of heterozygous protection
recessive; hidden from selection by more favorable dominant allele
Some mutations are …; many mutations at molecular level don’t…
Introns don’t…; variation in exons or…; rarely…
This is…; where most mutations will generate same
Or even if sequence changes, it …
non-coding; change phenotypic traits bc these changes occur in introns
Code for proteins; coding regions; change amino acid sequence
Redundancy; amino acid sequence
Won’t affect protein shape/function
Gene duplication (macro) is …; may be harmful by…
Some confer beneficial…
Example is ancestral …
Humans have about…
Altering gene number; altering genome and its function
Effects & play key role in evolution
Mammalian gene for detecting odors has been duplicated many times
380 functional olfactory receptor genes & mice about 1200
Other related processes/errors (macro) include…
Mutations are low in…; rates are lower in…
Sexual reproduction:much variation in pops that reproduce sexually is..
New combinations of existing alleles occur through 3 mechanisms…
Generation time & sexual reproduction
Many plants & animals; prokaryotes
A result of unique pairing of alleles that individual receives from parents
Crossing over, independent assortment, fertilization
crossing over is exchange of …
Independent assortment is random…
Fertilization is a random…
Genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis
Distribution of chromosomes into gametes during meiosis
Combination of gametes
chromosomes are threadlike…
Gene is a distinct sequence of…
Homologous chromsomes are chromosomes of the same…
Locus is a position…; allele are variants…
structures of nucleoid acids & proteins that carry genetic info as genes
Nucleotides forming a part of chromosome coding for a trait
Length & shape with genes in the same location
of a gene on a chromsome; of a gene that exist at same locus
molecular traits are often…; phenotypic traits are often…
Traits can reflect…; some traits are…
other traits are…; Meaning…
Some phenotypes are not…; for example..; as this phenotype isn’t…
Natural selection can only act on…
not visible between individuals; easily observed
Genetic variability among individuals; controlled by a single gene
Polygenic; they are controlled by more than one gene
Genetic; bodybuilders children wont be muscular; heritable or genetic
Variation with a genetic component
Hardy-Weinberg equation expresses principle known as…
Which states that the amount of genetic variation in a population will….
Equation is…; sum of allele frequencies for all alleles at locus must be..
P is; q is; p2 is
q2 is; 2pm is
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
Remain constant from one generation to next in absence of evolution
P2+2pm+q2=1; 1 so p+q=1
Frequency of “A” allele; frequency of “a”; frequency of homozygous AA
Frequency of homozygous aa; frequency of heterozygous genotype
If allele frequencies (of p&q) aren’t changing from…
Then the population is…; genotype frequencies will…
Population that is not evolving is in…
Equation can be used to determine whether…; and % of population…
One generation to the next
Not evolving; will stay the same
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
Population’s in hardy-Weinberg equilibrium; carrying specific allele
Hardy-Weinberg allows us to observe if…
Example is..; or a genetic disorder that prevent people from…
Recessive disorder so only impacts…
Hardy-Weinberg allows us to monitor this…; determine if there is…
Conditions of Hardy-Weinberg
genetic changes are occurring in human populations
Henylketonuria; breaking down phenylalanine leading to problems
Homozygous recessive individuals
Disease; a change in allele frequency
No mutations, random mating, natural selection, extremely large population size, & gene flow
No mutations: gene pool is modified if…
Random mating: if individuals mate within subset of populations near…
No natural selection: allele frequencies change when individuals with…
Extremely large population size: in small populations, allele frequencies
No gene flow: by moving alleles into or out of populations…
What are the mechanisms of microevolution?
mutations occur or if entire genes are deleted or duplicated
Neighbors then random mixing of gametes doesn’t occur & genotype frequencies change
Different genotypes show consistent differences in their survival
Fluctuate by chance over time (genetic drift)
Gene flow can alter allele frequencies
Natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow
Consistent selection for an allele that enhances…
Example is
enhances survival and/or reproduction results in adaptive evolution
Extreme drought which led to reduced food & large, hard seeds became more common than small, soft seed so survivors of drought had larger beaks
Genetic drift is chance events that can lead to ..
More predominant in…
Reduces …
Includes how many types? Name them
fluctuations in allele frequencies from one generation to the next
Small populations
Genetic variation through random loss of allele
4;founder effect,bottleneck effect,hurting population,rescuing population
Founder effect occurs when few …
Allele frequencies in smaller founder populations are..
Genetic drift could occur if…
Example is …; where affected woman who had 10 children…
individuals become isolated from a larger population
different from those in parent population
few individuals are indiscriminately blown to new island by a storm
High Huntington’s disease; was among first to colonize the land
Bottleneck effect is …; that can drastically…
Surviving population may be decided by chance based on …
Resulting gene pool may no longer be…
sudden environmental catastrophes; reduce size of a population
those individuals that managed to pass through bottleneck
Reflective of original population’s gene pool
Hurting a population is when greater prairie chicken habitat…
By 1993, population …; surviving birds had…
Hypothesis is that loss of ..
Rescuing a population is when scientist extracted…
drastically reduced as they were converted to farmlands in 18,1900s
Declined to <1%; <50% hatching rates
Genetic variation lef to increase in frequency of harmful genes
DNA from 15 museum specimens
Consequences of genetic drift is that it can alter…
Can randomly change …; unlike…
Can lead to loss of …; which can have…
Can cause harmful…
small populations significantly
allele frequencies; unlike natural selection
Genetic variation; detrimental consequences in population
Alleles to become fixed in a population
Gene flow is movement of…; alleles can be transferred through…
Tends to reduce variation among …
Example is …; or…
Affects…
alleles among populations; movement of fertile individuals or gametes
populations over time as alleles are transferred between populations
Migratory populations; two populations sharing geographic distribution
Adaptation to local environments
Natural selection is not…; it consistently…
Favors the relative….
Interplay bt genotype & phenotype, where selection is…
Favors individual with …; in specific…
Natural selection can alter…; depending on which …
How many types of selection are there? Name them…
random; selects for alleles & traits that confer reproductive advantage
Fitness of individual
largely acting on phenotype that is genotypically representative
Heritable traits that enhance survival & reproduction; environment
Frequency distribution of heritable traits in 3 ways; phenotypes favored
3 types; directional selection, disruptive selection, & stabilizing selection
Directional selection occurs when conditions…; common when..
Example is…
Disruptive selection occurs when conditions…
Example is mice living in…
Stabilizing selection occurs when conditions…; reduces variation by…
Example is mice has…
favor extreme range of phenotype; environment changes or migration
Light color mice living in dark rocks will be selected against
Favor both extremes of a phenotype
Patchy habitat with light & dark rocks; intermediate more susceptible
Favor the intermediate phenotype; removing extreme variants
intermediate color, light & dark mice are selected against
Key role of natural selection in adaptive evolution makes it possible for..
But they are …; and a result of…
Natural selection is the only…; that consistently..; and ultimately…
Example is …; which allows them to…
Adaptations may arise …; some more…
bottleneck or genetic drift to have a new positive effect
Inconsistent; chance
Evolutionary mechanism; confers an advantage; adaptive evolution
Jaw of snakes; swallow prey much larger than their own head
Slowly over evolutionary time; apparent than others
Sexual selection: Darwin investigated idea that reproductive success…
Sexual selection can result in…
Which is a difference in…
How many types of sexual selection are there? Name them…
Was, in part, driven by traits that attracted mates
Sexual dimorphism
Secondary sexual characteristics, bt males & females of same species
2; intrasexual (within) selection & intersexual (between)
Intrasexual selection occurs…
Often…
Intersexual selection is also known as…; it is when individuals of…
Decisions are often made on the …
More often as a form of competition between members of the same sex
Males
mate choice; one sex (often females) choose their mate
Showiness of the male’s appearance & behavior
Intersexual selection includes the …
Which proposes that females …
Example is that female gray tree frogs prefer to …
Eggs fertilized with sperm from LC & SC males 2x, the resulting…
Conclusion is that offspring fathered by an LC male…
Good genes hypothesis
Select males w/ traits that are related to genetic quality or overall health
Mate with long-calling rather than short-calling males
Offspring were raised in a common environment and survival monitored
Outperformed their half-siblings fathered by SC males
Natural selection is not…; it is..; doesn’t…
This is because it can only select from…
Example is snowhares molting to…; but population lacks …
Evolution is limited by the…; so legacy of…
planned; imperfect; produce an ideal
Existing genetic variation
White fur too early which is disadvantageous; alleles that encode delay
Existing forms & traits of a species; descent w/ modification.
Adaptation is a compromise where organisms…
Example is seals having…
Because it gives them …
Chance & environment can impact…
trade off ability to perform 1 function in order to better perform another
Flippers instead of legs
Great ability to hunt so they must trade off
Progress of natural selection
Speciation is the …
Produce the …; & helps explain its…
Microevolution is limited by…
While macroevolution is …
Ernst Mayr helped define what?
emergence of new species from a common ancestor
Tremendous diversity of life; unity
Changes in allele frequency in a population over time
broad patterns of evolutionary change above the species level
Biological species concept
Species is a group of populations whose…
Produce …
And do not produce…
Gene flow between populations holds a …
Diversity of a particular species may be apparent in…
members have the potential to interbreed in nature
Viable & fertile offspring
Viable & fertile offspring w/ members of other such groups
Species together genetically
Diversity of traits observed in present phenotypes
Limitations to biological species concept is species that are…
Example is …; which can…
Another limitation is species that reproduce …
Morphologically & ecologically distinct, yet can produce hybrid offspring
Polar bear & grizzly bear making grolar bear; produce viable offspring
Asexually such as prokaryotes (bacteria)
New species emerge through a loss of…
As a result of …; and can lead to the …
Once a species is formed, there are wide range of…
Name these barriers…
gene flow between two populations
Reproductive isolation; emergence of distinct species
Barriers that prevent reproduction between species
Prezygotic & postzygotic barriers
Prezygotic barriers block…
Impeding…
Preventing…
& hindering …
How many examples are there of this? Name them…
fertilization from occurring
different species from attempting to mate
successful completion of mating
Fertilization if mating is successful
5; habitat, temporal, behavioral, mechanical, gametic isolation
Habitat isolation is when two species that occupy different…
Example is when apple maggot flies …
Temporal isolation is when species that…
Example is western spotted skunks …
habitats w/in same area may encounter each other rarely, if at all
Isolated from blueberry flies bc they feed/lay eggs on different fruits
Breed at different times of day, in diff seasons can’t mix their gametes
Mate in summer & eastern spotted skunks mate in winter
Behavioral isolation is courtship …; and other…
Examples is where many species …
Mechanical isolation is where mating is…; but …
Example is where genetically openings of snails in genus bradybaena..
Gametic isolation is where sperm of one species may not …
Example is surface proteins on sperm &eggs of different sea urchin…
rituals; behaviors unique to a species are effective barriers to mating
Mate only after a unique courtship such as blue-footed boobies
Attempted; morphological different prevents its successful completion
Don’t align if their shells spiral in opposite directions
Be able to fertilize eggs of another species
Bind poorly to each other, preventing fusion & zygote formation
Postzygotic barriers prevent …
Through…
Hybrid zygotes from developing into viable, fertile adults
Reduced hybrid viability, reduced hybrid fertility, hybrid breakdown
Reduced hybrid viability is where genes of different …
Example is hybrid offspring of different subspecies of salamanders…
Reduced hybrid fertility is when meiosis may …; if parent species have.
Example is hybrid offspring of…
Hybrid breakdown is when first generation hybrids are…
Example is hybrids between certain strains of cultivated rice are…
parent species may interact in ways that impair hybrid’s development
Don’t usually complete development
Fail to produce normal gametes resulting in sterility; diff # chromosome
Male donkey & female horse (a mule) is robust but sterile
Viable & fertile but offspring in next generation are feeble or sterile
Vigorous & fertile, but members of next generation are small & sterile
Biological species concept emphasizes separateness of…
Other species definitions emphasize …
Name the other species concepts…
species because of reproductive barriers
Unity within species
Morphological, ecological, & phylogenetic species concept
Morphological species concept uses…; and …
Advantages is that it can be…
Disadvantage is that it is..
body shape; structural features to group species
Applied to sexual & asexual reproducing species
Subjective because it relies on our observations
Ecological species concept considers a…; or ways a species…
Advantage is that it can be…; and considers role of …
Disadvantages is that it doesn’t …
species niche; interacts with its abiotic & biotic environment
Applied to sexual/asexual reproducing species; disruptive selection
Consider presence or absence of gene flow/reproduction
Phylogenetic species concept defines a species as the…
Can be distinguished from other such sets by…; does not
Advantage uses…
Disadvantages often debatable as to how much …
Speciation can take place w/ or w/o …; name the two examples..
smallest group of individuals that share a common ancestor
Distinct evolutionary trajectories; require reproductive isolation
Molecular evidence (DNA) & morphology
difference is required to determine where new branch of life starts
Geographic separation; Allopatric (other country) & sympatric (same)
Allopatric speciation is a type of speciation where…
Example is mosquito fish colonized ponds which later became…
Each of the ponds could be classified as either a …
Different morphology developed & provides differential rates of…
In the lab, females prefer to mate with males of…
Geographic barriers prevent gene flow
Isolated & cut off gene flow
High or low predation environment
Escape acceleration & survival
Similar morphology
Shrimp species diverged at a …
Isolated or highly subdivided regions usually have more species than…
Reproductive isolation between populations generally…
Effect of a geographic barrier depends on ability of…
For example, a canyon may create a barrier for..; but not for…
similar time to the formation of the Isthmus
Those with fewer barriers
Increases with geographic distance
Organisms to move about
Small rodents; birds, coyotes or pollen & seeds of flowering plants
Sympatric speciation occurs in …
It is less…; because barriers don’t …
It occurs if gene flow is reduced by factors such as…
populations that live in the same geographic area
Common; separate the populations in question
Polyploidy, sexual selection, & habitat differentiation
Polyploidy is the presence of…; can be caused by…
This process can form a new species within a …
It is common in…; but rare in…; example is …
It’s estimated that around …
how many types of polyploidy; name…
extra sets of chromosomes; accidents during cell division
Single generation without geographic separation
Plants; animals; gray tree frog is a tetraploid (4n)
80% of plant life is a result of polyploidy
2; autopolyploids & allopollyploids
Autopolyploids (oneself) have more than;…; all derived from..
In plants, mitotic errors can result in the …
Fertile offspring can be produced through…
Mating between tetraploids & diploids produces…
Two sets of chromosomes; a single species
Production of a tetraploid (4n) cell from a diploid (2n) cell
Self-fertilization or mating among tetraploids
Triploid (3n) offspring with reduced fertility
Allopolyploids (other) occurs when two different species breed & form…
Many hybrids are sterile because their chromosomes can’t…; however,
Non-disjunction errors can lead to …
Allopolyploids can successfully …; but not with…
hybrid offspring that have chromosomes derived from different species
Pair during meiosis; they may reproduce sexually
Doubling chromosome # in subsequent generation producing a diploid
Interbreed with each other; either parent species
Sympatric speciation can be…
For example, speciation of chichild in Lake Victoria was likely driven by
Sympatric speciation can also result from…; example of…
Example: apple maggot flies evolved in North America after …
Maggot flies mate on their host plant, resulting in…
driven by sexual selection
Female mate choice based on male breeding coloration
Exploitation of new habitats or resources; habitat differentiation
Switching hosts from hawthorn to apple
Habitat isolation between groups using different hosts
Hybrid zone is a region where…
It is a naturally…; hybrids are often…
They rarely serve as a …
they are often patches of…; rather than…
How many outcomes of hybrid zones are there? Name them
members of two species meet & mate
Occurring experiment of speciation; maladapted
Steppingstone toward a new species
small dots on a map; continuous bands
3; reinforcement, fusion, & stability
Reinforcement is the strengthening of…
Fusion is weakening of…
Stability is continual formation of…
Reproductive barriers & cessation of hybrid formation
Reproductive barriers leading to a single species
Hybrids of two distinct species
Rate of speciation can be studied by…
What can also be used to assess time interval bt speciation events…
Speciation can occur…
What are two kinds of speciation rates?
observing broad patterns in the fossil record
Morphological & molecular data
Rapidly or gradually
Punctuated model & gradual model
Punctuated model describes periods of apparent;where species don’t…
Gradual model described…
Fossil record shows emergence of,,; impact of..; origin of…
Earth’s environment allowed emergence of life through … events
stasis; change through several strata punctuated by sudden change
Species appear to have changed gradually over time
Terrestrial vertebrates; mass extinction; key adaptations, such as flight
4 main events
1st event is abiotic synthesis of organic molecules such as…; includes..
2nd event is joining of these molecules into…
3rd event is packaging of these molecules into membrane-bound…
4th event is origin of…
amino acids; 3 hypotheses
Larger polymers or macromolecules
Protocells that allowed 4 internal chemistry different from environment
Self-replicating molecules made inheritance possible
In abiotic synthesis of organic molecules, spontaenous abiotic …
In 2009, demonstrated that by dripping…; these bases would…
Hypothesis 1 is…; hypothesis 2 is..; hypothesis 3 is…
synthesis of all 4 RNA monomers has been demonstrated in lab
RNA monomers on hot sand & clay; bind forming polymers
Primordial soup, miller-Urey experiment, vent hypothesis
Hypothesis 1: Primordial soup is when earth formed & had…
Earliest atmosphere was thought to be …; Comprised of reducing …
Hypothesis 2: Miller-Urey experiment where experiments…; resulted in.
Hypothesis 3: Vent hypothesis where recent studies suggest early…
Replication & metabolism are…; protocells may have formed from…
hot pockets of warm water
environment; little O2, but N2,CO2,H2, methane were common
Mimicked conditions of Earth;Formation of amino acids
Organic compounds may have been locally synthesizer near volcanos
Key properties of life; fluid-filled vesicles with membrane like structure
Origin of self-replicating molecules includes that RNA was likely…
Can function like…; that can make short sections of…
Largely made possible by…; RNA could have provided template for…
First nucleic acid to form
Enzyme-catalyst called ribozymes; complimentary RNA from nucleotide
Single stranded nature of RNA; assembly of DNA nucleotides
O2 produced by…; likely 1st reacted with ..; & precipitated to form…
Once all dissolved iron had precipitated,…
When seas & lakes became saturated, O2 began to…
2.4-2.7 billion yrs ago, atmospheric O2 shot up rapidly to…
This period is referred to as…; this likely killed…; but allowed for…
Photosynthesis; dissolved iron in sea; iron oxide sediments
O2 dissolved into the water
“Gas out” and enter the atmosphere
Between 1% and 10% of its present level
Oxygen revolution; many prokaryotic organisms; rise of cellular respiration & eukaryotes
Eukaryotic cells are more …; due to their …
Endosymbiont theory highlights how…
Through a series of …
How much evidence supports this theory?
complex than prokaryotes; structure & composition
Eukaryotic cells emerged from prokaryotic cells
Symbiotic & evolutionary steps
3
Evidence 1: inner membranes of both organelles have…; that are…
To those found in…
Evidence 2: mitochondria & plastids replicate by…
Evidence 3: each organelles contain a single…; that, like chromosomes…
enzymes & transport systems; homologous
Plasma membranes of living prokaryotes
Splitting process that’s similar to that of certain prokaryotes
circular DNA molecule; of bacteria isn’t associated w/ histone or other proteins
Fossil record is based on …
shows that many past organisms…; many are…; new groups…
Fossil record is an…
Because few organisms were…; many were…; only fraction have…
accumulation of fossils in sedimentary rock layers, called strata
were unlike those today; extinct; arose from previous existing ones
Incomplete chronicle
Preserved as fossils; destroyed; yet been discovered
Known fossil record is…; in favor of species that …
Were…; had…; such as…
Fossils in fossil record are dated using…; this uses the…
That are incorporated into a …
Biased; existed for a long time
Abundant & widespread; hard parts; shells or skeletons
Radiometric dating; known half-life of radioisotopes
Specimen while it is living in the atmosphere
Study of fossils is used to establish the…; which is a standard…
Geologic record is divided into how many eons? Name them…
What is the most recent eon?
How many eras are in the most recent eon? Name them…
Boundaries between these eras correspond to …
Geologic record; time scale dividing Earth’s history
4 eons; Hadean, Archaean, Proterozoic, & Phanerozoic
Phanerozoic
3; Paleozoic, Mesozoic, & Cenozoic
Major extinction events in fossil record
During Cambrian period, first signs of …
Plants & fungi …; by developing critical…
Biological diversity is a balance between…
Balance is displayed …
These changes are affected processes including…
fungi, plants, & animals inhabiting land appear
Co-evolved & adapted together on land; symbiotic relationships
Speciation & extinction
Conceptually in this evolutionary tree
Plate tectonics, mass extinction, & adaptive radiation
Plate tectonics are continents that are the…
1.1 billion years ago, all the plates…;Each time they broke apart, a …
When plates collide, they…; when they create friction, this results in…
When they move apart, they result in…
Earth crust floating in the underlaying mantle
Came together; new configuration of continents was formed
Can form mountains; earthquakes
Formation of oceans
Continental drift is…
During Pangaea, the seas went from …
Places like Canada have moved from…
Species unique to Australia are found in…
Allopatric speciation on a grand scale
Shallow to deep altering marine habitats
The tropics to the far north
The fossil record of Asia & South America
Fossil record shows that most species that have ever lived are…
Extinction can be caused by changes to a..
Mass extinctions occur when large …
5 mass extinctions have been documented in the fossil record over…
now extinct
Species’ biotic or abiotic environment
Numbers of species rapidly become extinct worldwide
The past 500 million years
Permian extinction divides the …
About …
Occurred during an …
Eruptions resulted in increase in…; acidification of…
Global climate …; nutrient enrichment of oceans caused…
Paleozoic from the Mesozoic era
96% of marine species became extinct
Extreme episode of volcanism
Atmospheric CO2; oceans that reduced calcium carbonate
Warmed by about 6 degrees Celsius; microbial blooms
Cretaceous extinction is where more than…; examples
Presence of iridium in sedimentary rocks from the time suggests…
Debris clouds from the impact would…; causing a rapid, enduring…
Impact occurred off…
Mass extinctions can change the…; they also facilitate
50% of marine species; terrestrial plants, animals, & all dinosaurs
A massive meteorite collision
Block the sun; drop in global temperature
mexican coast 66 million years ago
Types of organisms in ecological communities; adaptive radiation
Adaptive radiation is …
And adapt to..
Adaptive radiations can occur in: 1. the opening of…
2: The evolution of novel characteristics that…
3: The colonization of new regions with…
Rapid periods of evolutionary change where many new species arise
Adapt to different ecological niches
Niches following mass extinctions
Enable the exploitation of new resources or habitats
Few or weak competitors
Opening of niches where size & diversity of mammals was…
After the extinction of terrestrial dinosaurs, mammals underwent…
evolution of novel characteristics where several adaptive radiation have
Adaptive radiations by plants, insects, & tetrapods followed the …
Some groups diversified as adaptive radiations in…
Restricted by predation & competition from dinosaurs
Adaptive radiation by filling ecological niches left open
Occurred in response to the evolution of major innovations
Evolution of key adaptations for survival on land
Other groups provided new food sources
Colonization of new region were common in…; where after, a lineage…
Different evolutionary processes act in these environments…
Reason why islands …
islands; colonization; quickly diversifies to occupy diff ecological niche
Leading to evolution of different species
Have a higher prevalence of endemic species
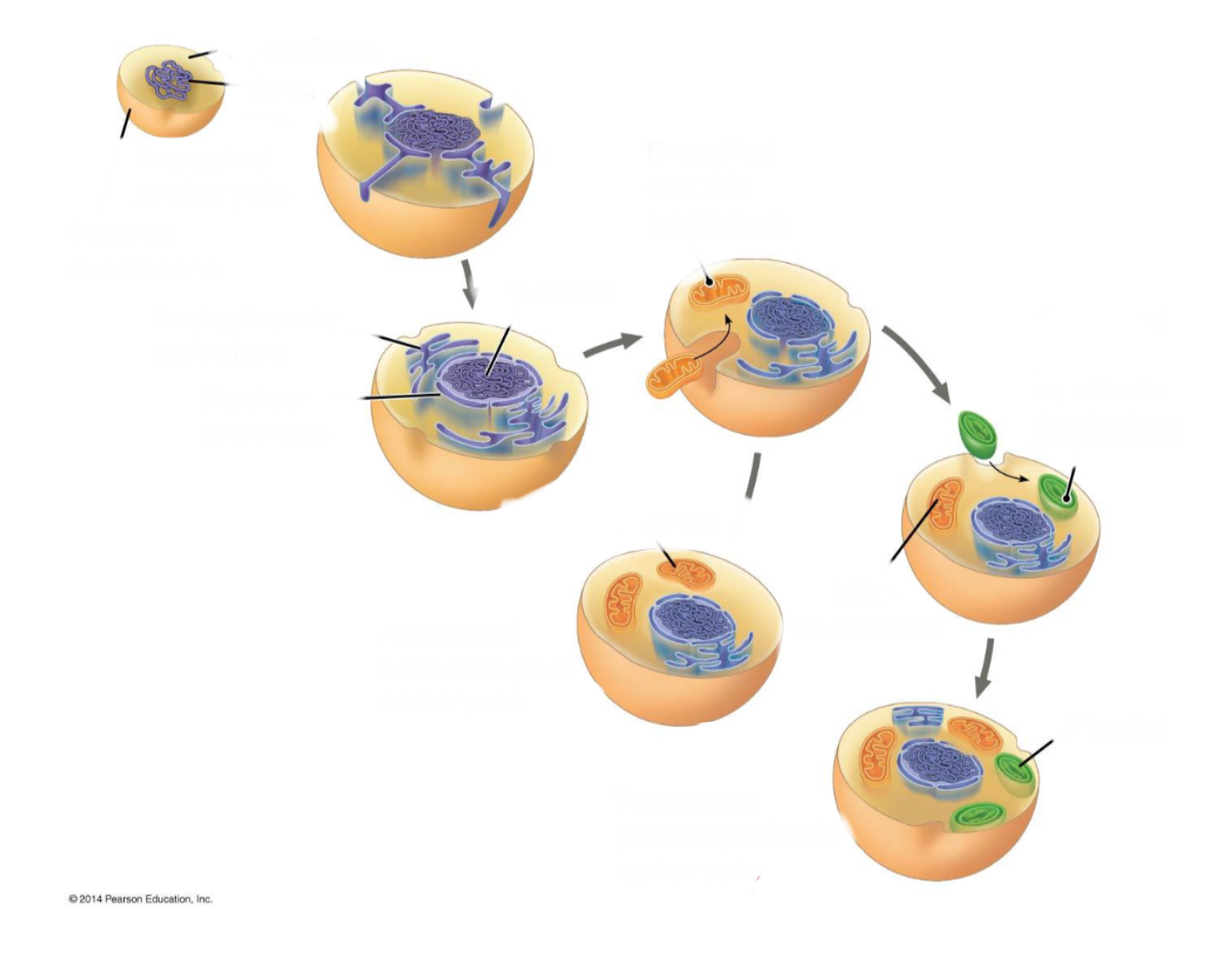
Label following image
Labeled