Unit 5 Human Body Systems
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
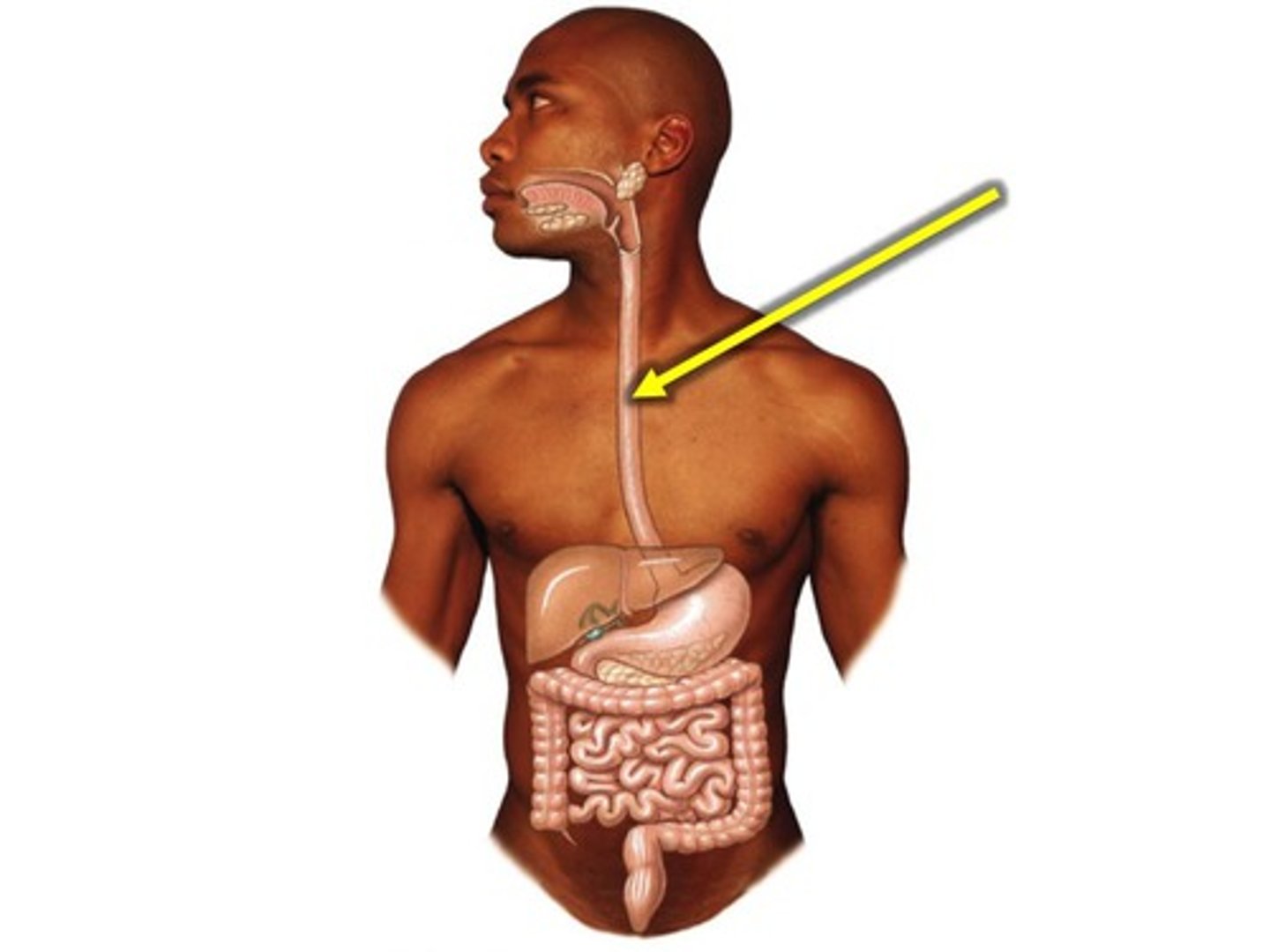
esophagus
A muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach.
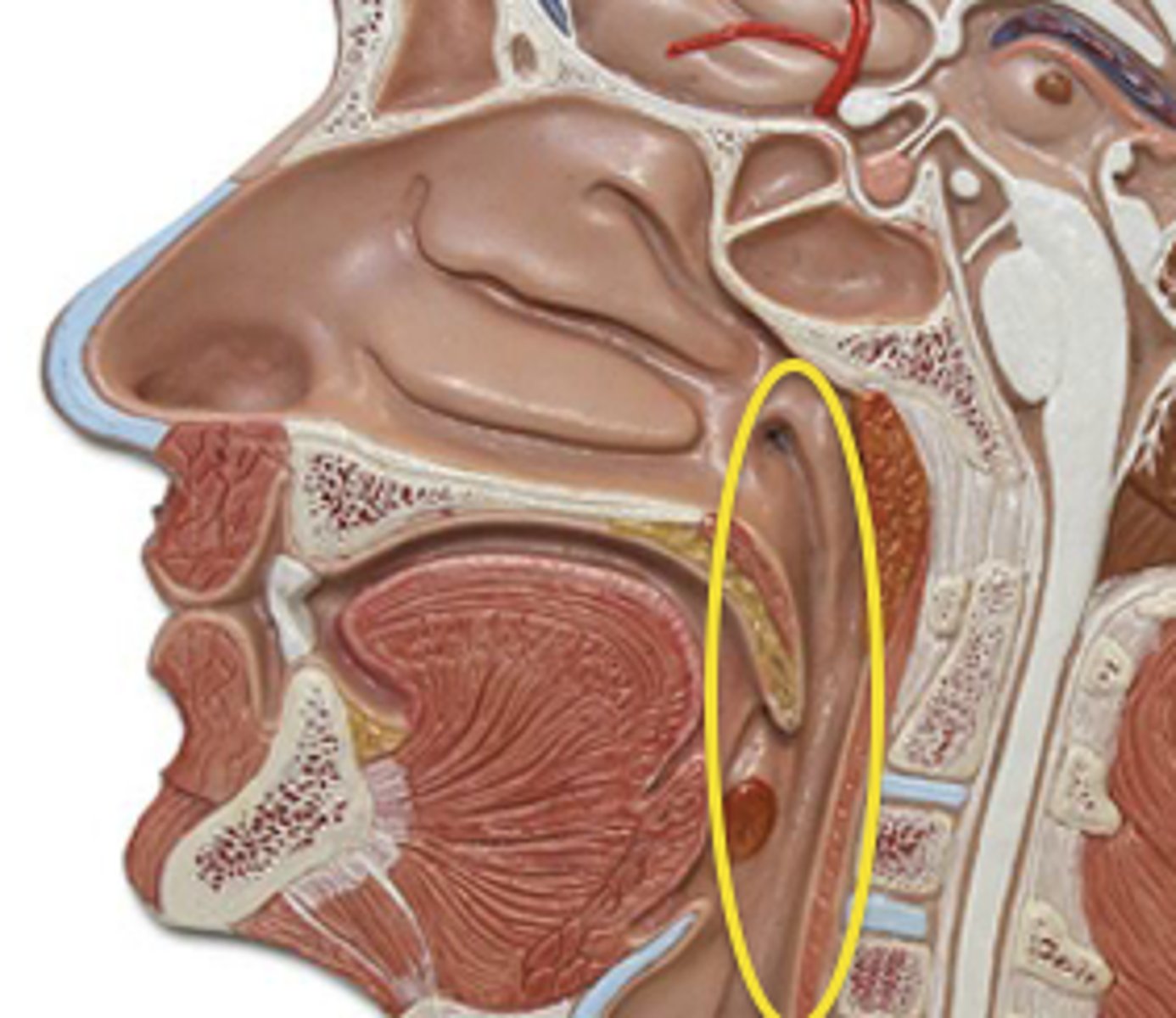
pharynx
throat; passageway for food to the esophagus and air to the larynx
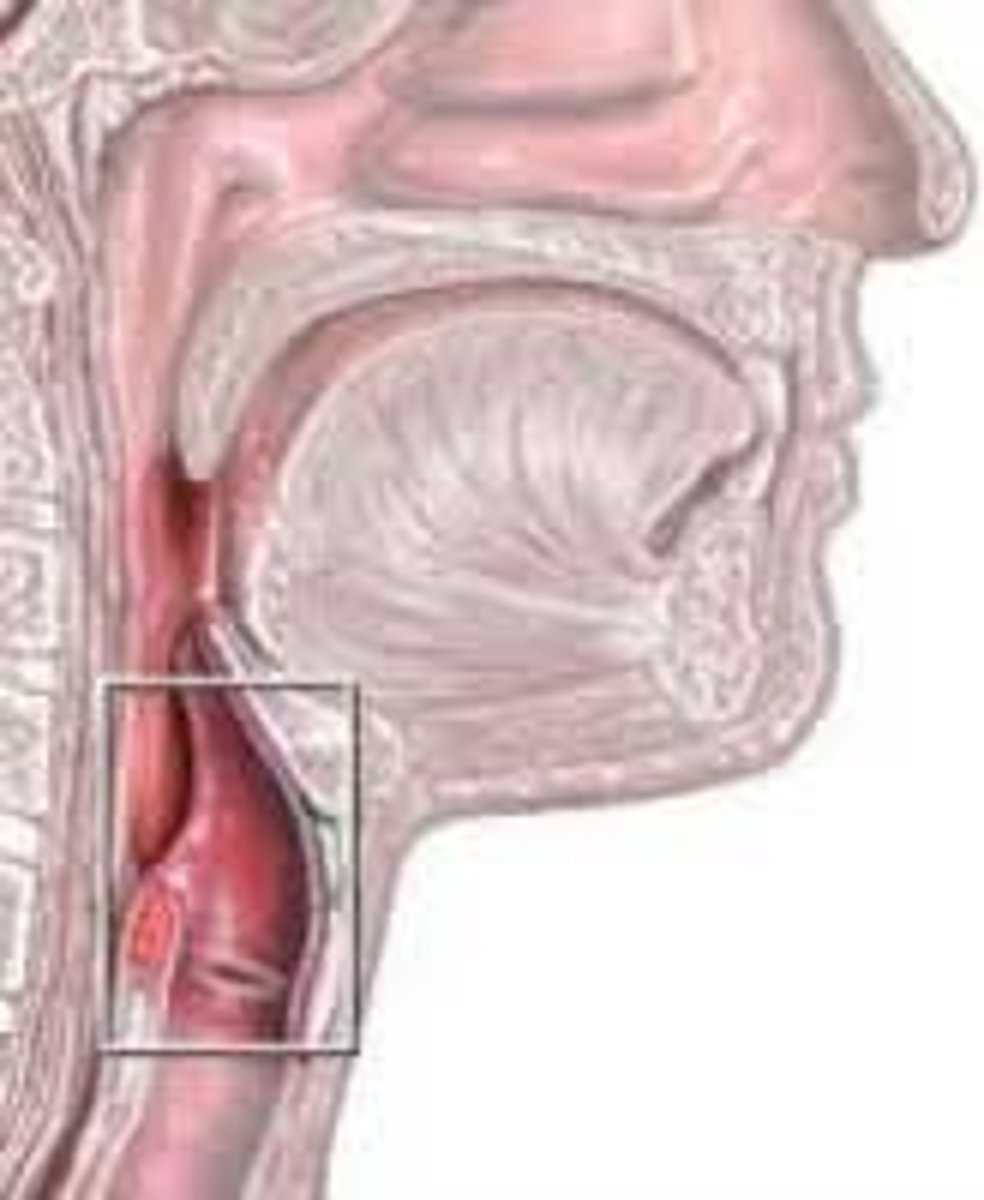
Larynx
voice box; passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea; contains vocal cords
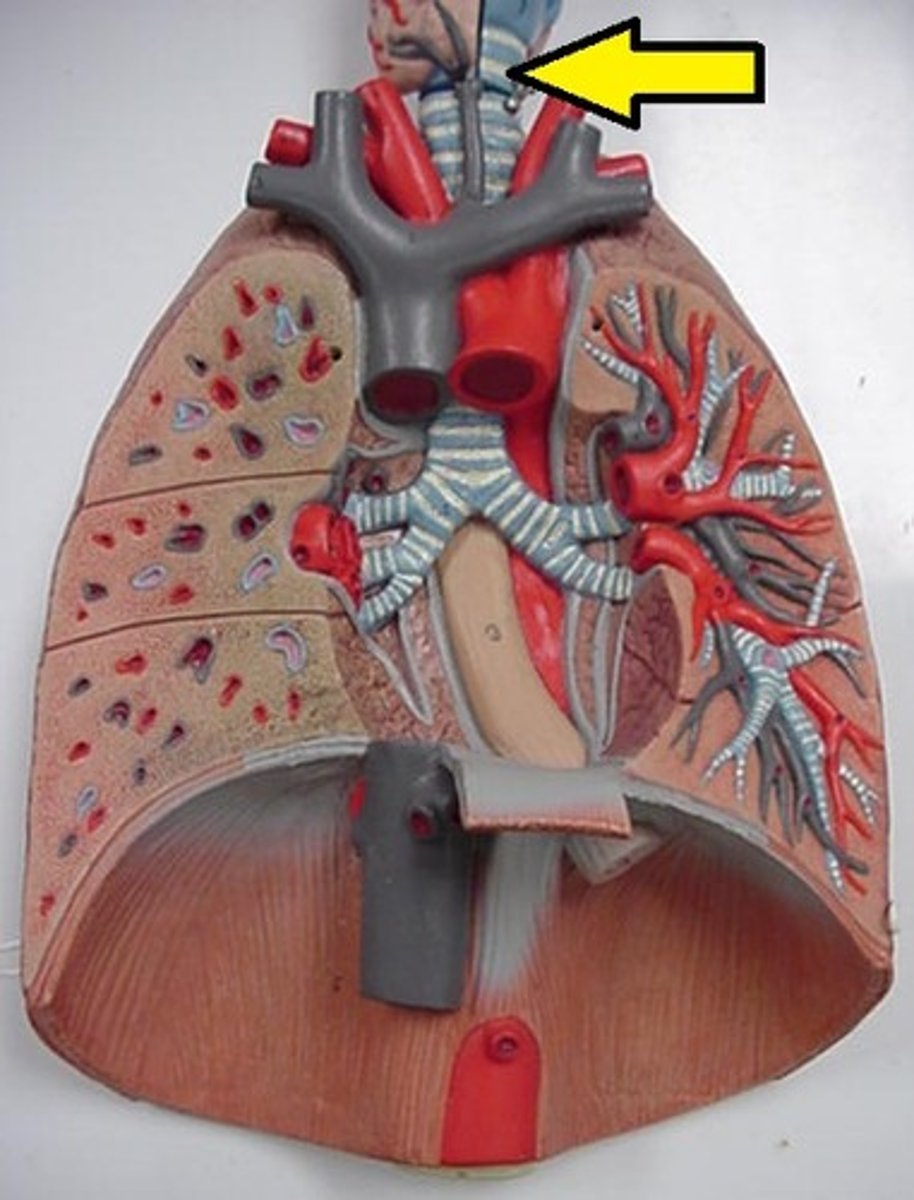
Trachea
Allows air to pass to and from lungs
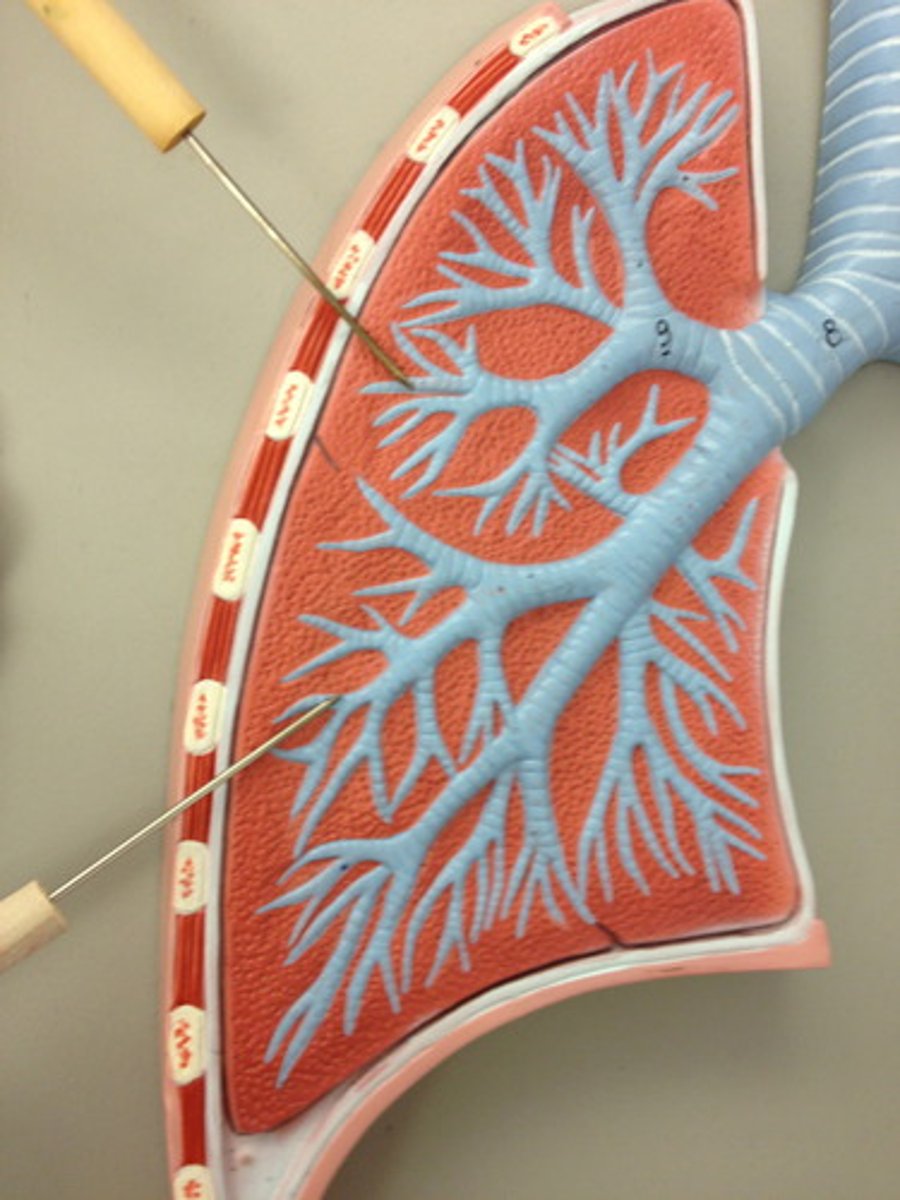
Bronchi
The passages that direct air into the lungs
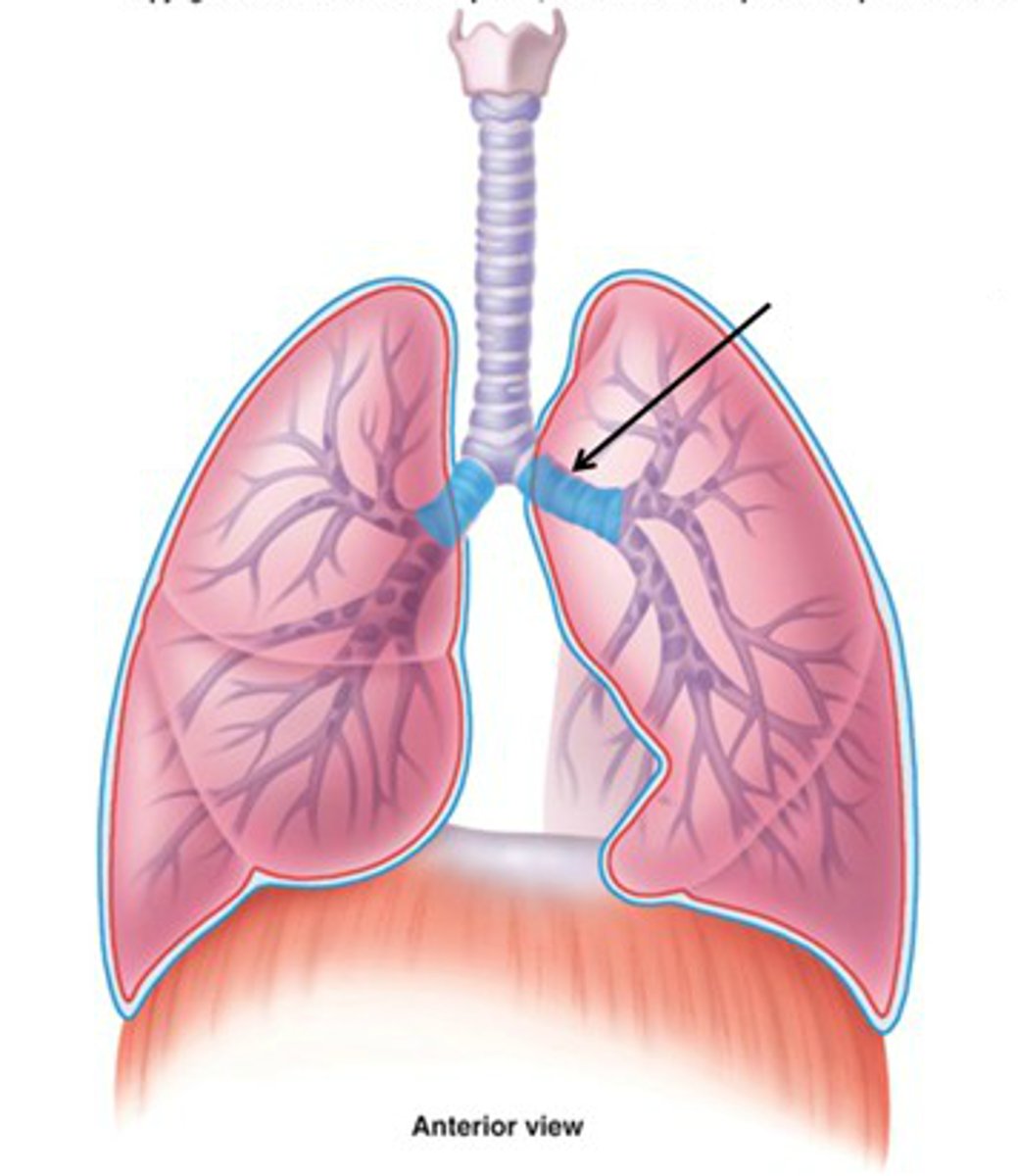
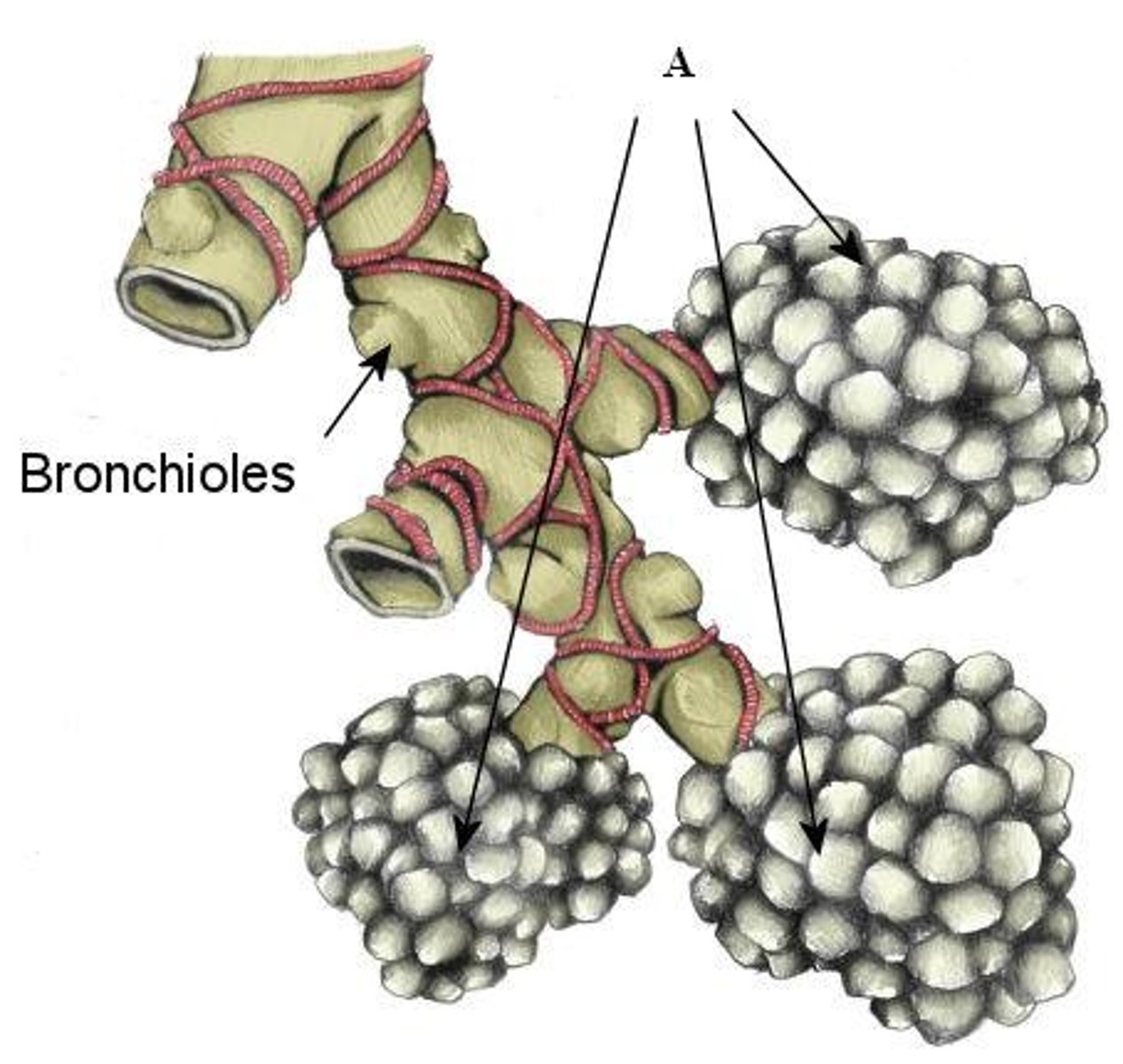
Bronchioles
smallest branches of the bronchi
alveoli
tiny sacs of lung tissue specialized for the movement of gases between air and blood
gas exchange
the process by which oxygen is transported to cells and carbon dioxide is transported from cells
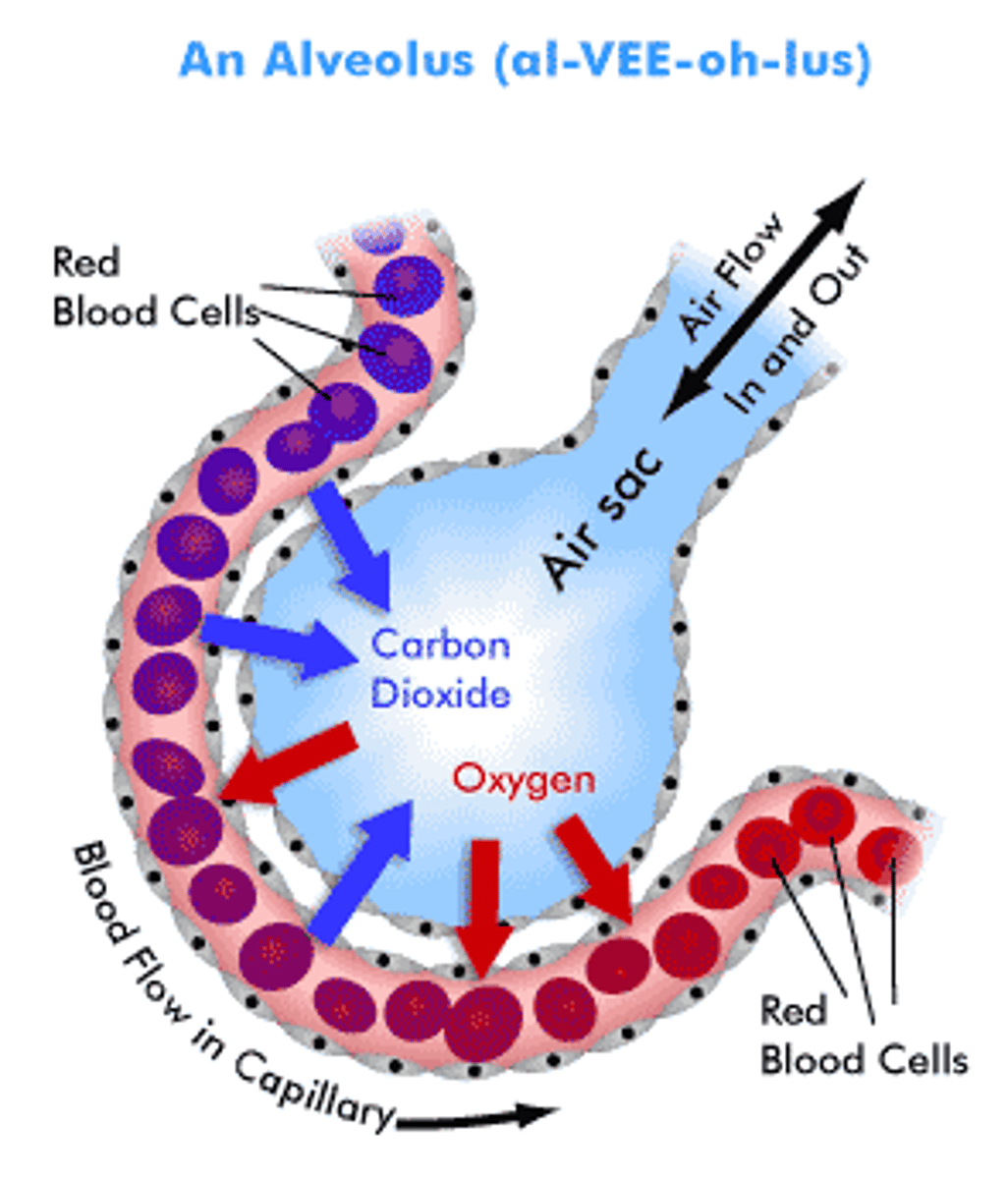
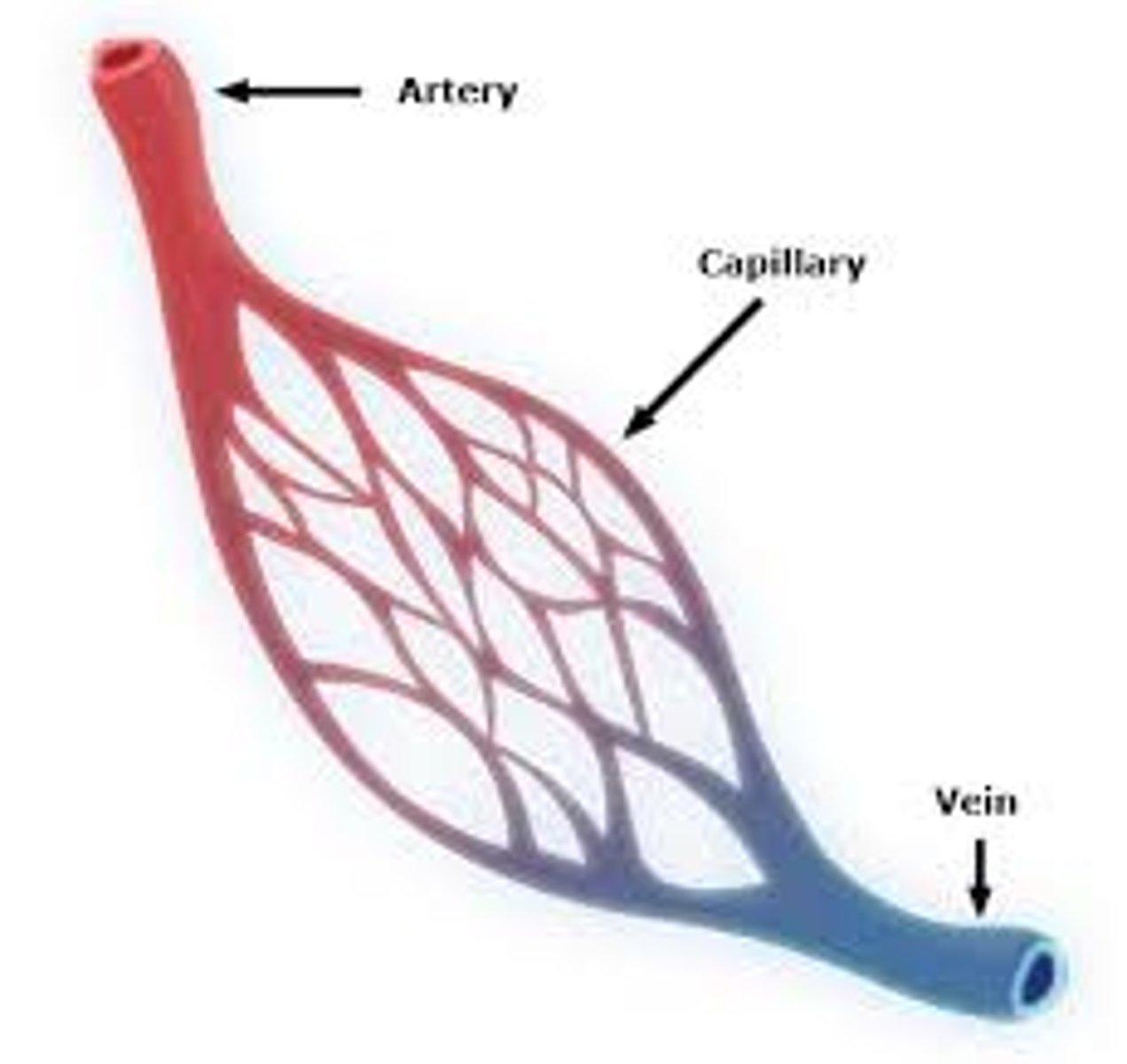
Capillaries
Microscopic vessel through which exchanges take place between the blood and cells of the body
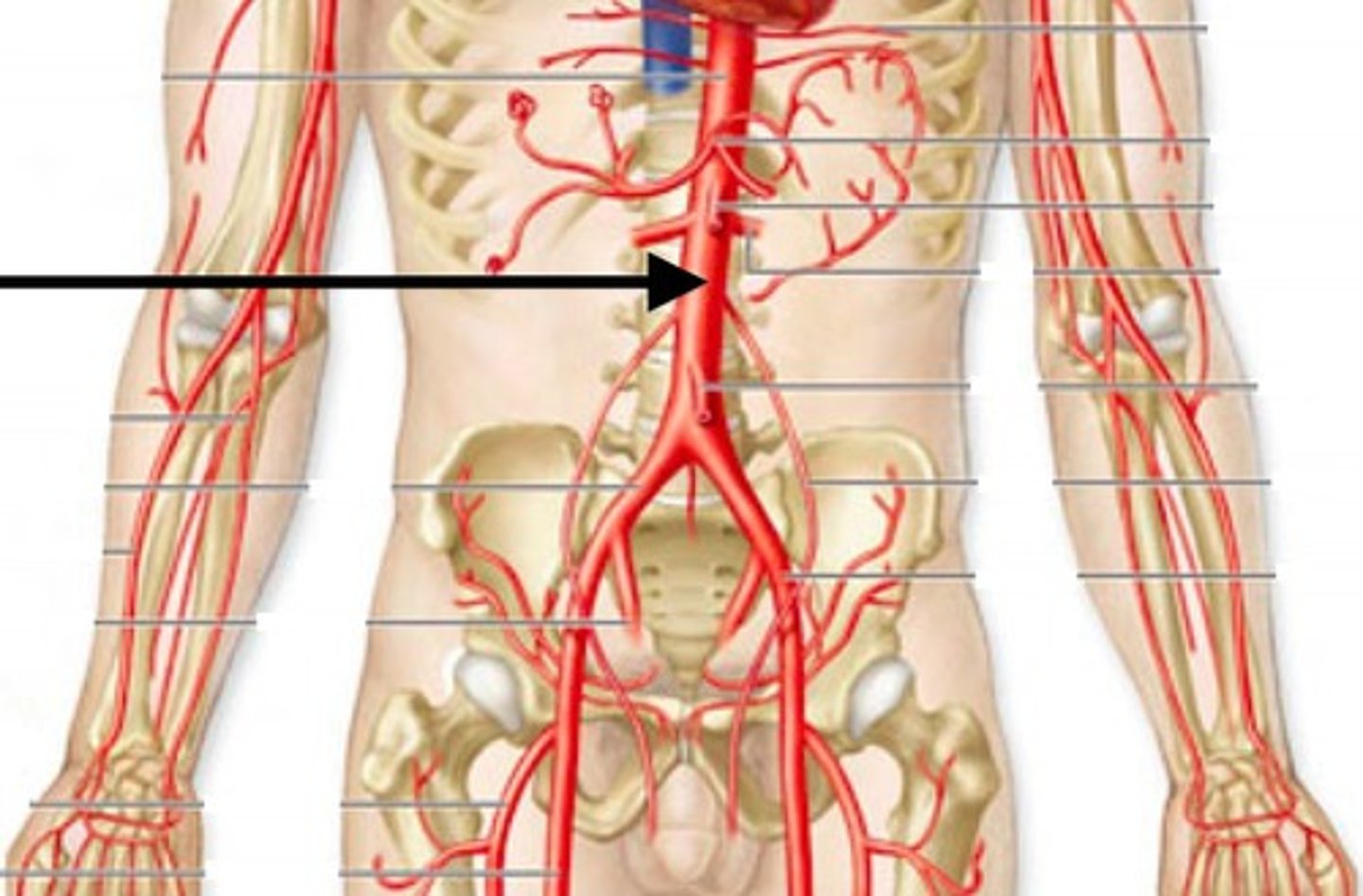
Aorta
Largest artery in the body
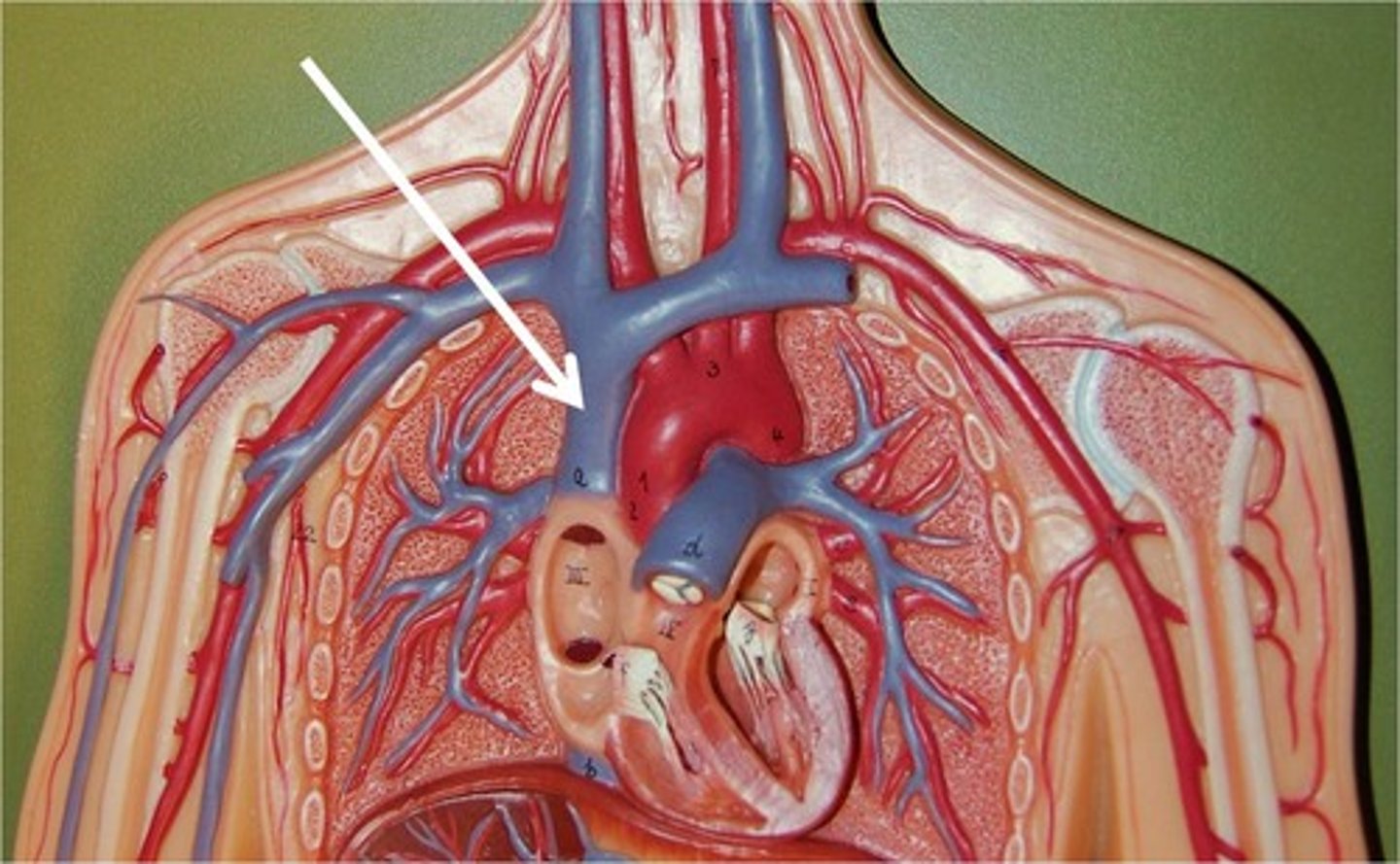
vena cava
largest vein in the body
Atria
upper chambers of the heart, where blood ENTERS
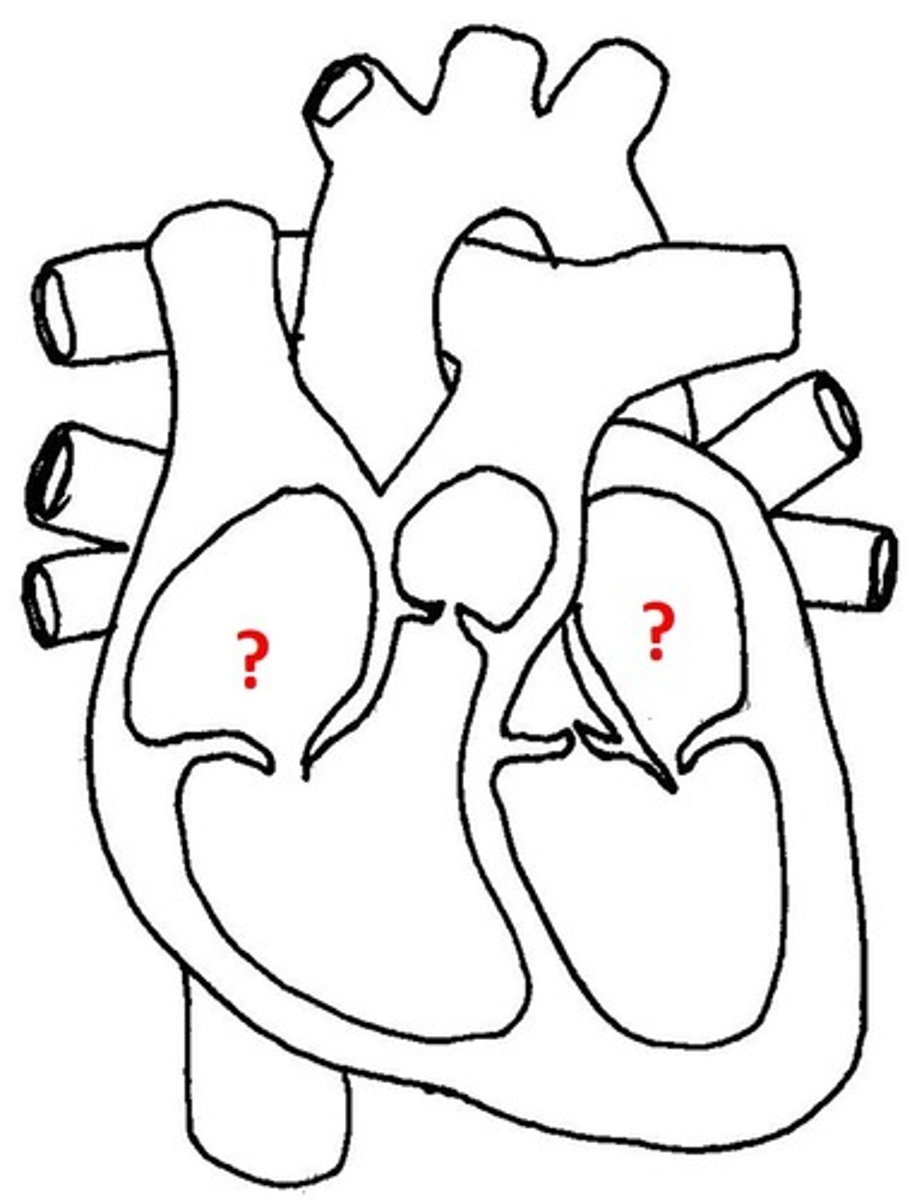
Ventricles
the two lower chambers of the heart, and they pump blood OUT to the lungs and body.
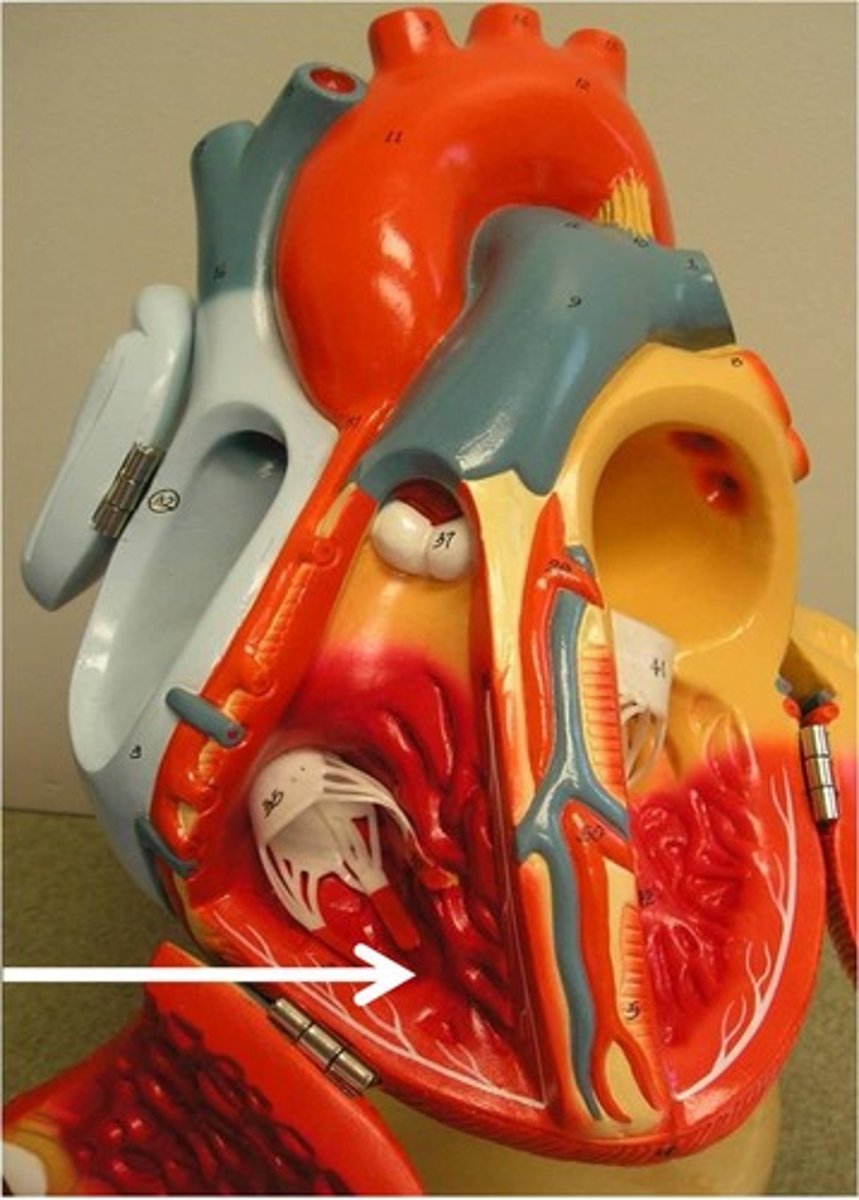
pulmonary vein
carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart
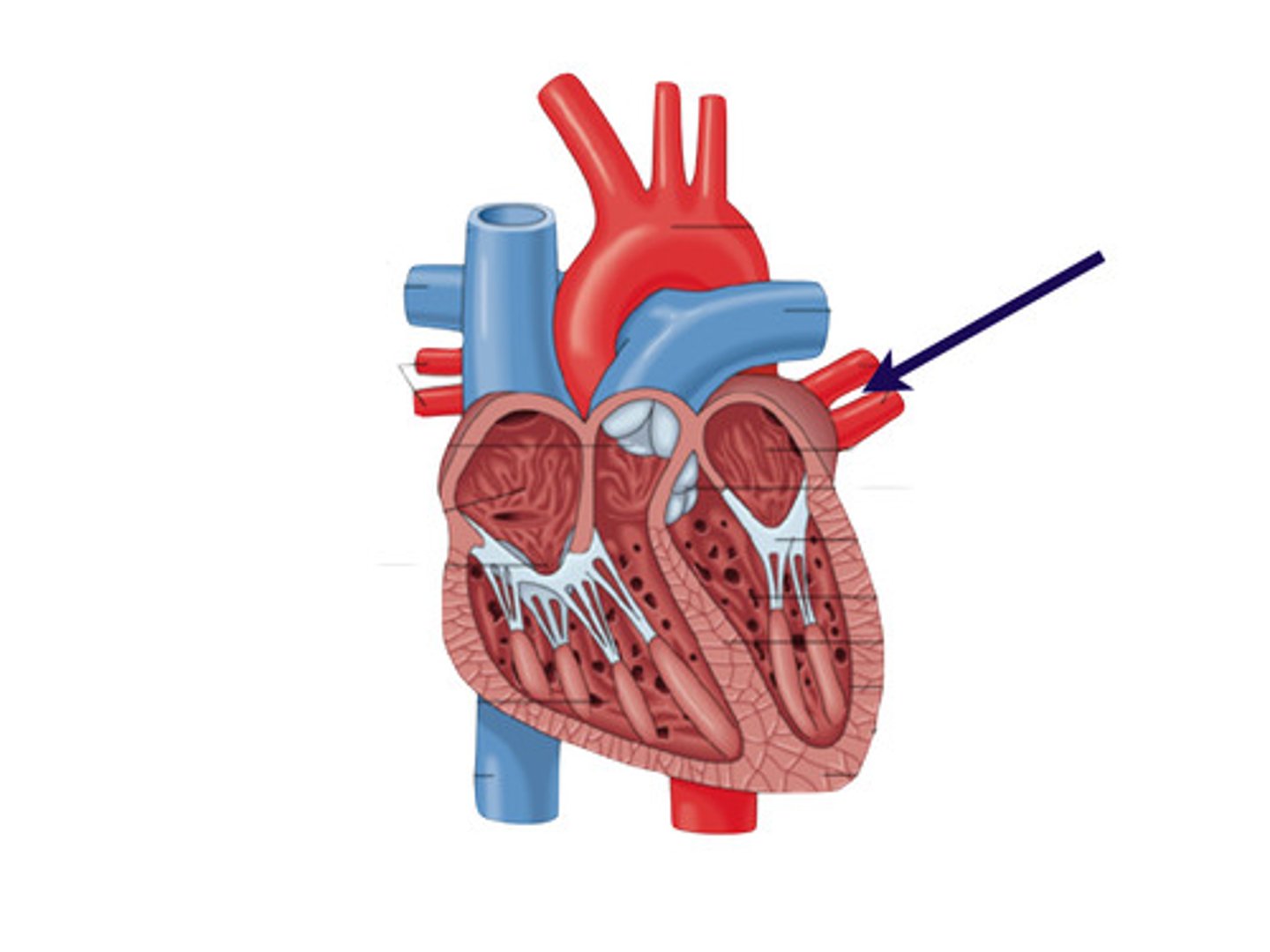
pulmonary artery
Carries deoxygentated blood from the heart to the lungs
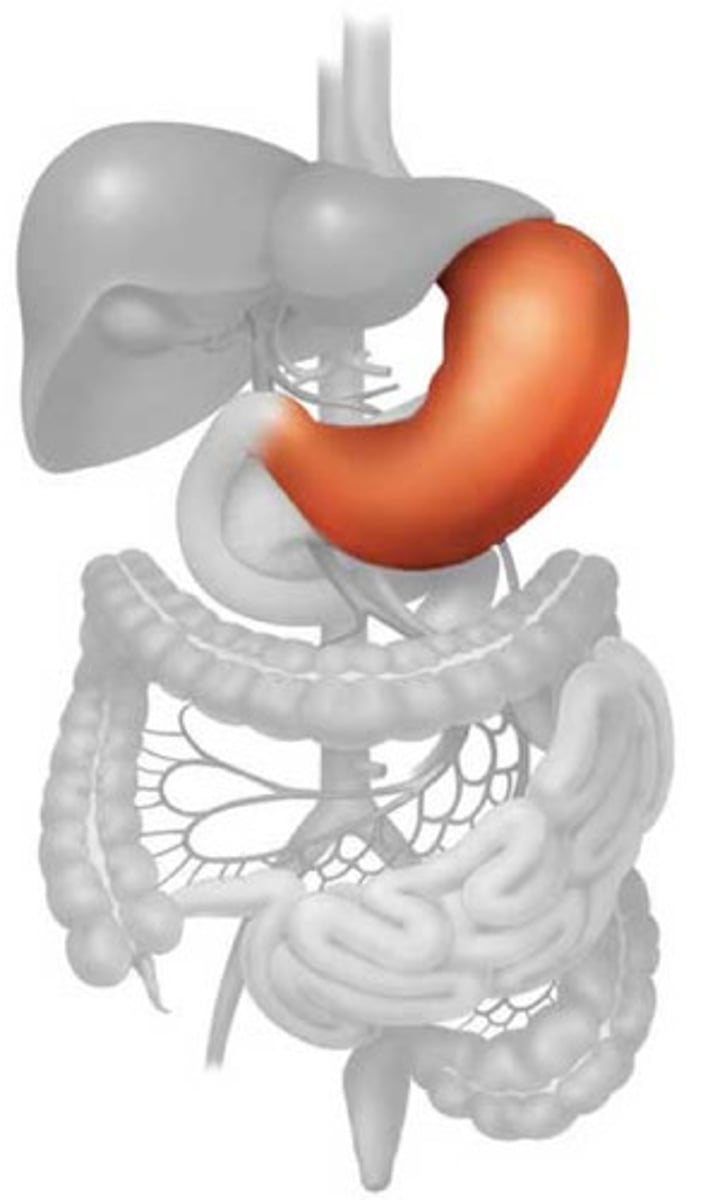
stomach
large muscular sac that continues the mechanical and chemical digestion of food
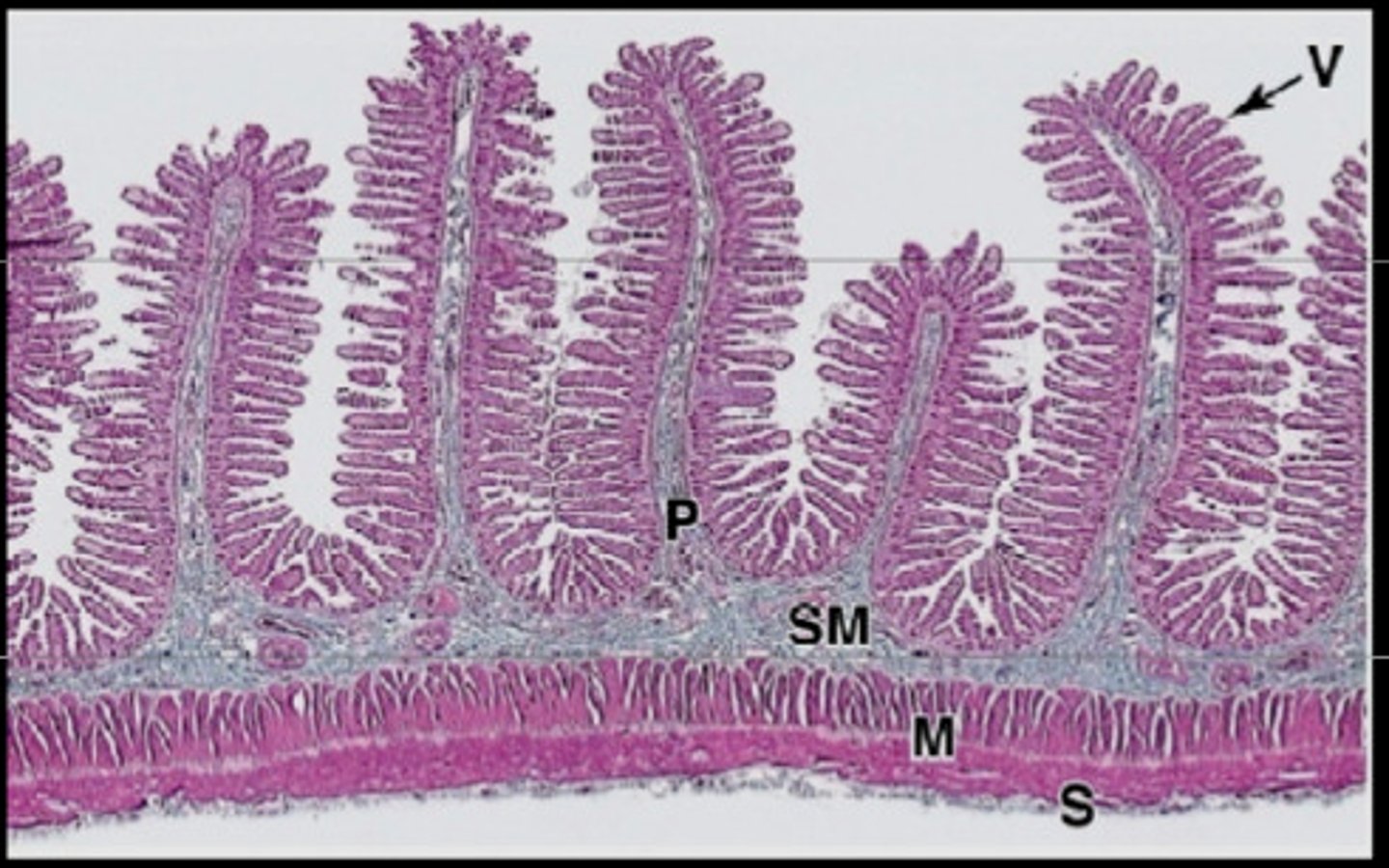
small intestine
Digestive organ where most chemical digestion and absorption of food takes place
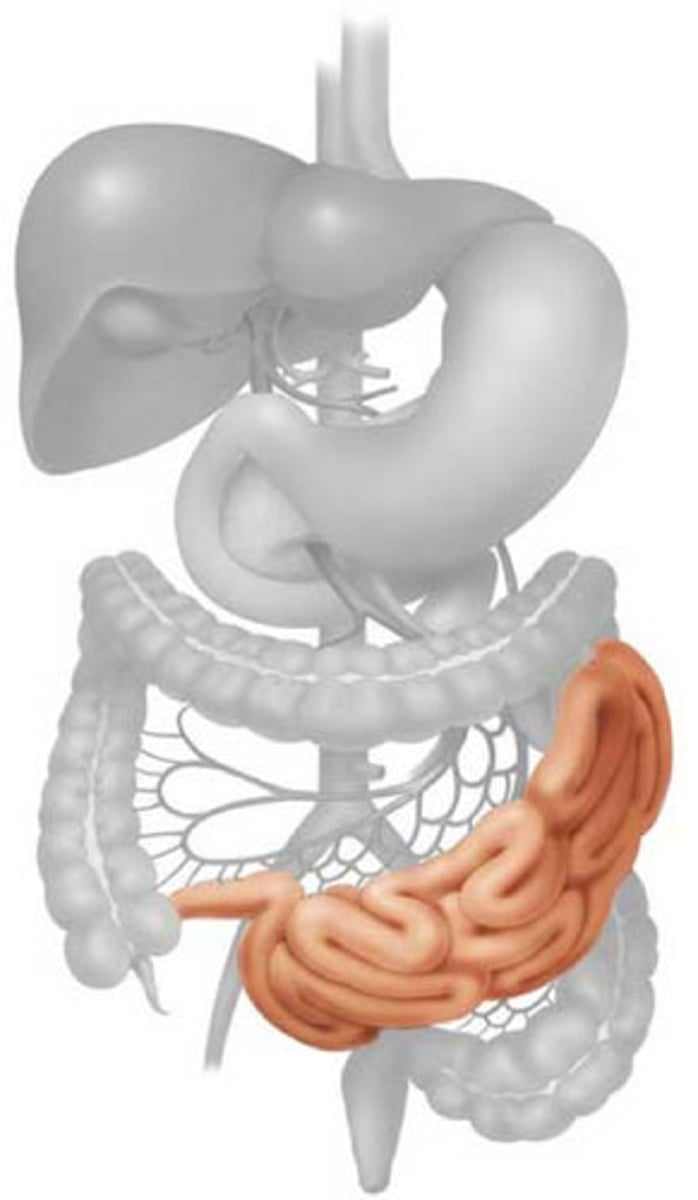
Villi
Fingerlike extensions of the intestinal mucosa that increase the surface area for absorption
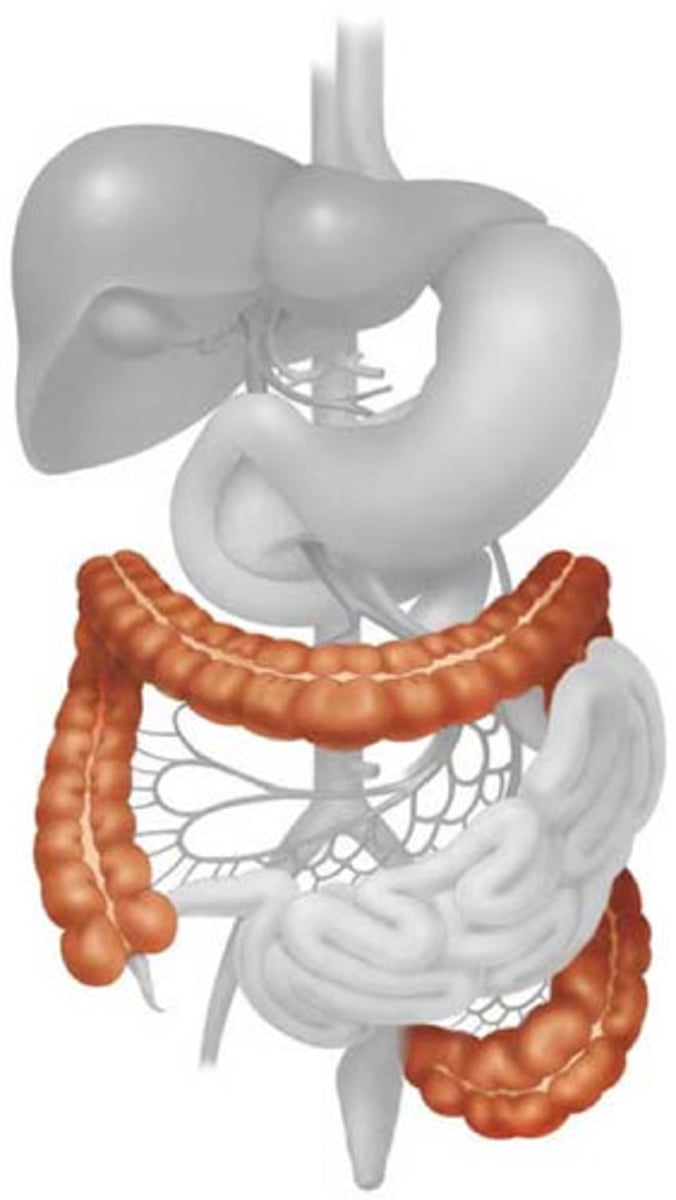
large intestine
The last section of the digestive system, where water is absorbed from food and the remaining material is eliminated from the body
Rectum
A short tube at the end of the large intestine where waste material is compressed into a solid form before being eliminated
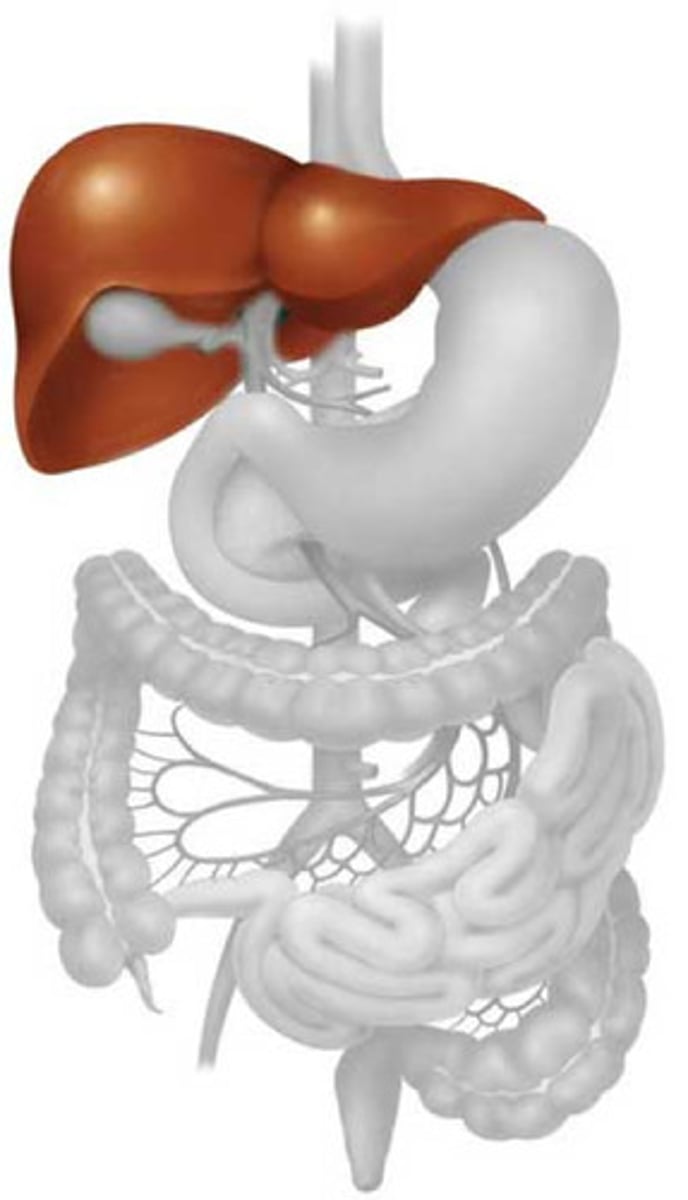
Liver
produces bile
Pancreas
Regulates the level of sugar in the blood by secreting insulin and glucagon
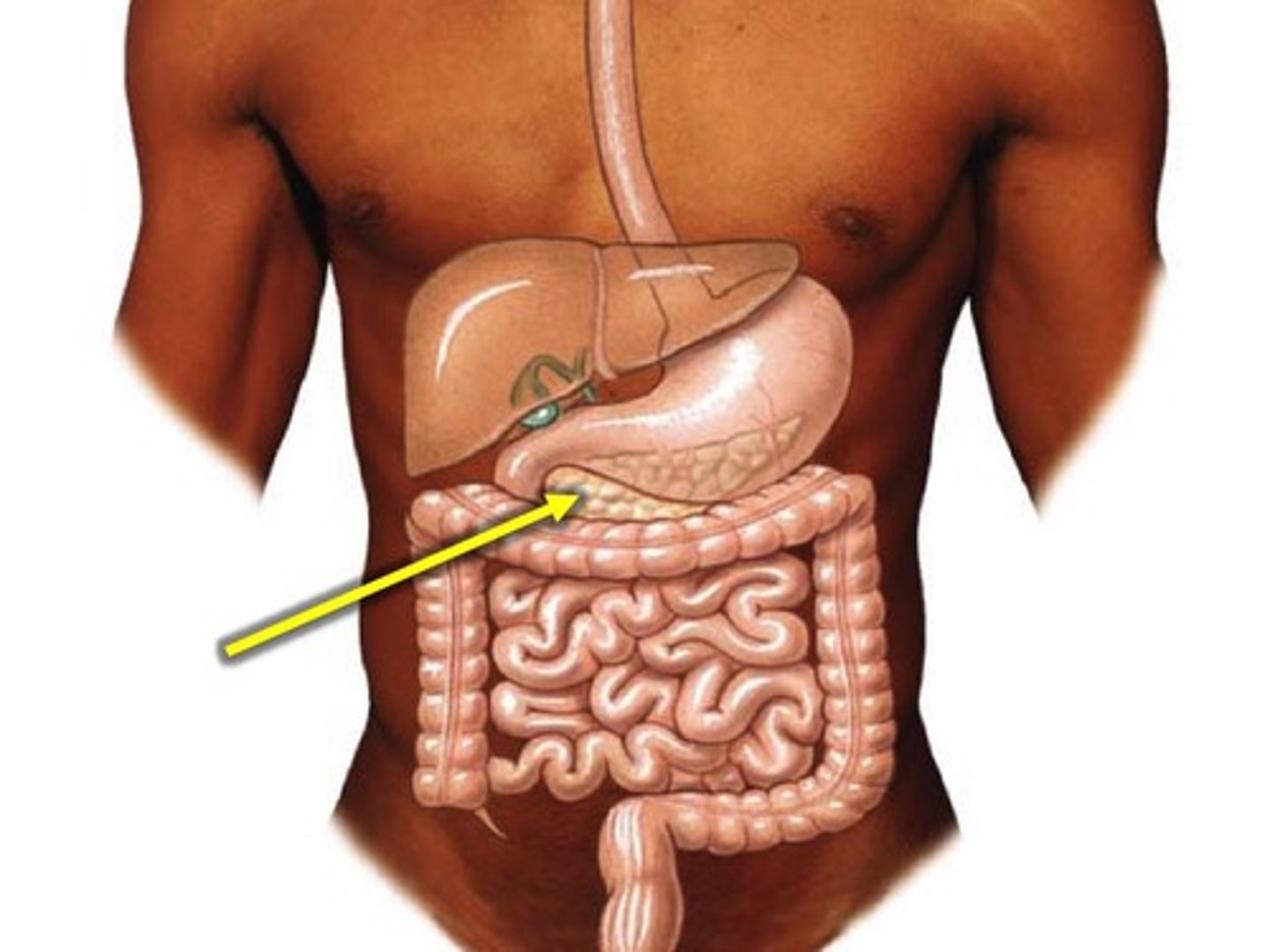
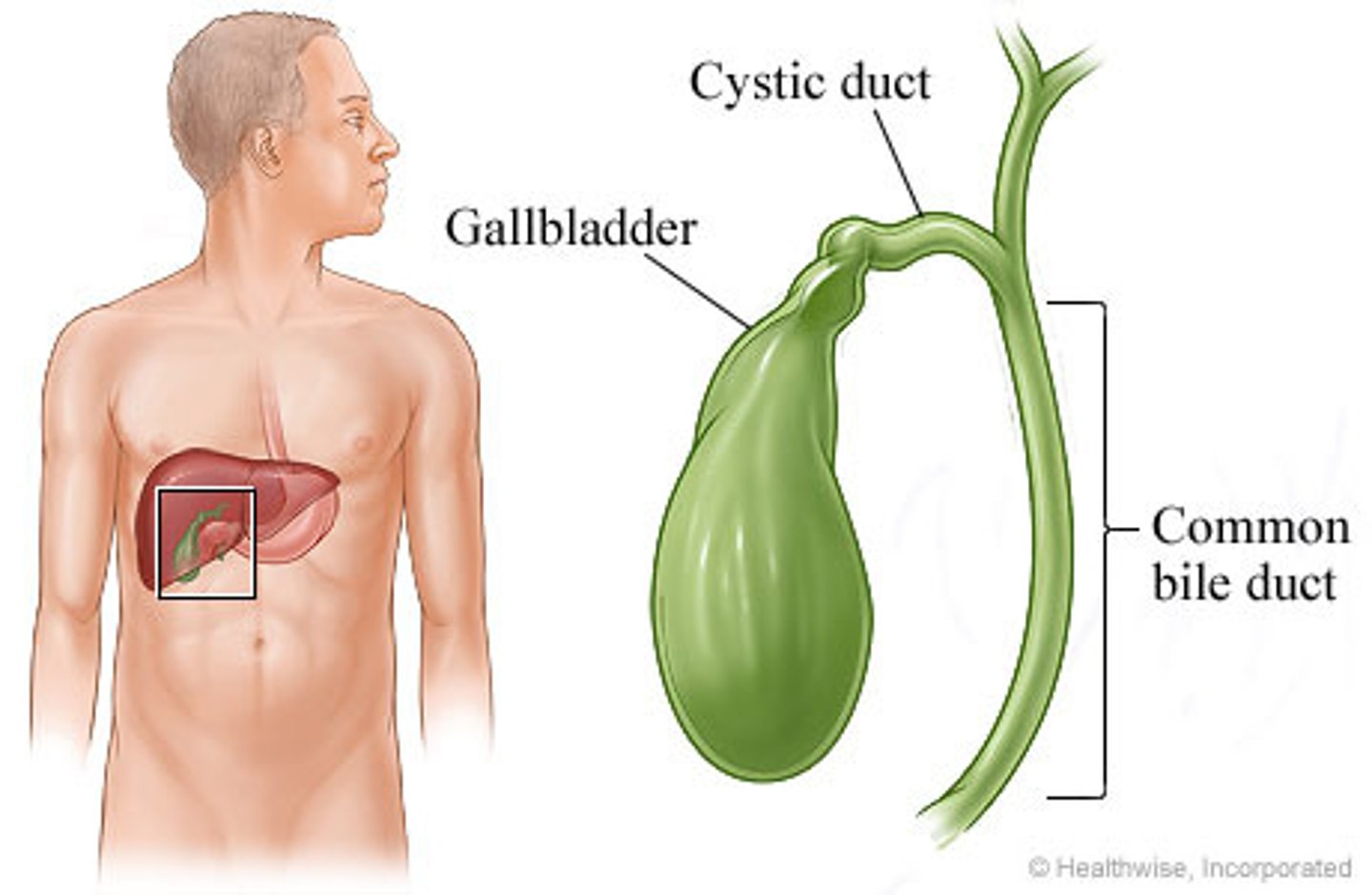
galbladder
stores bile
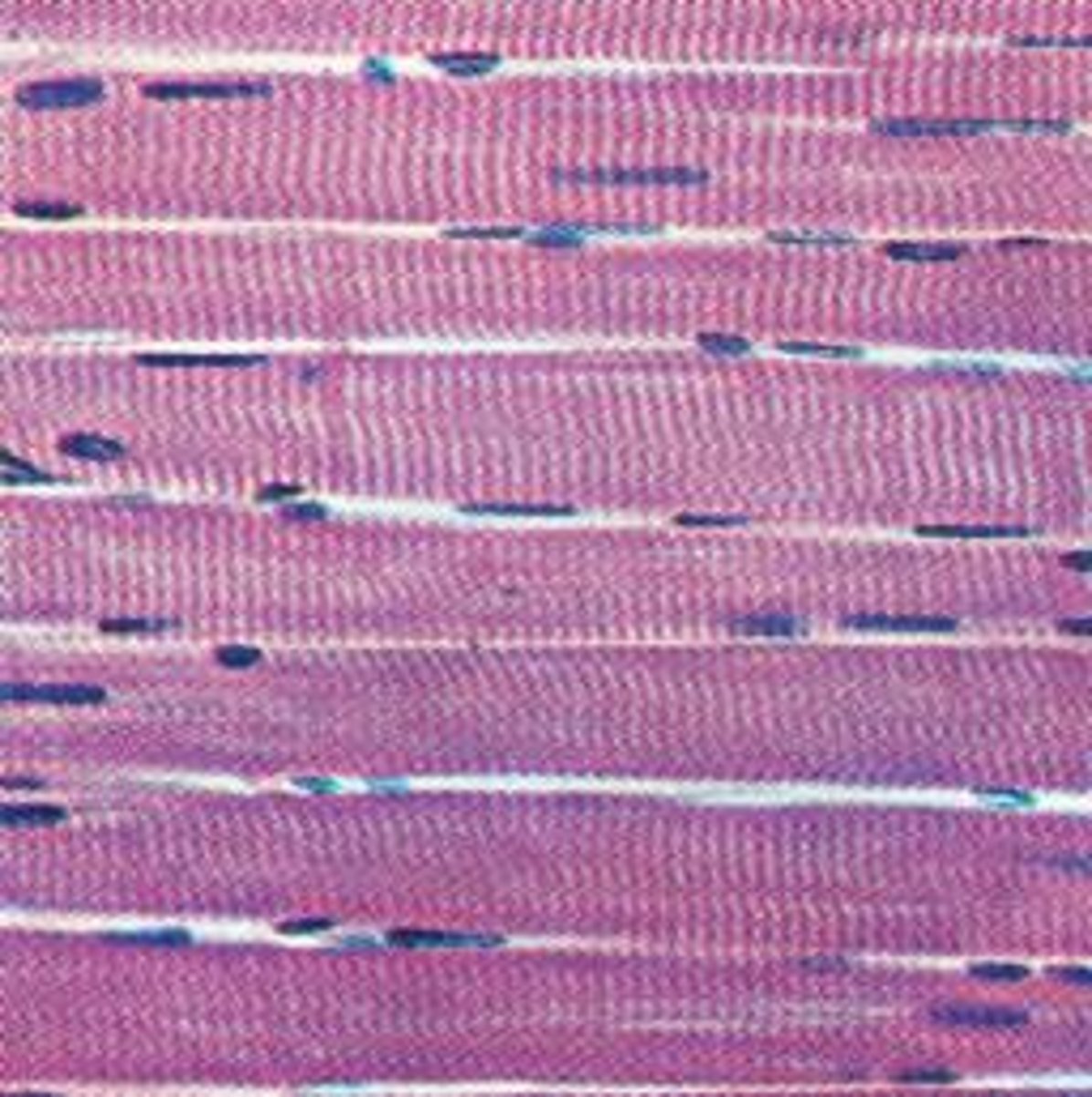
skeletal muscle
A muscle that is attached to the bones of the skeleton and provides the force that moves the bones.
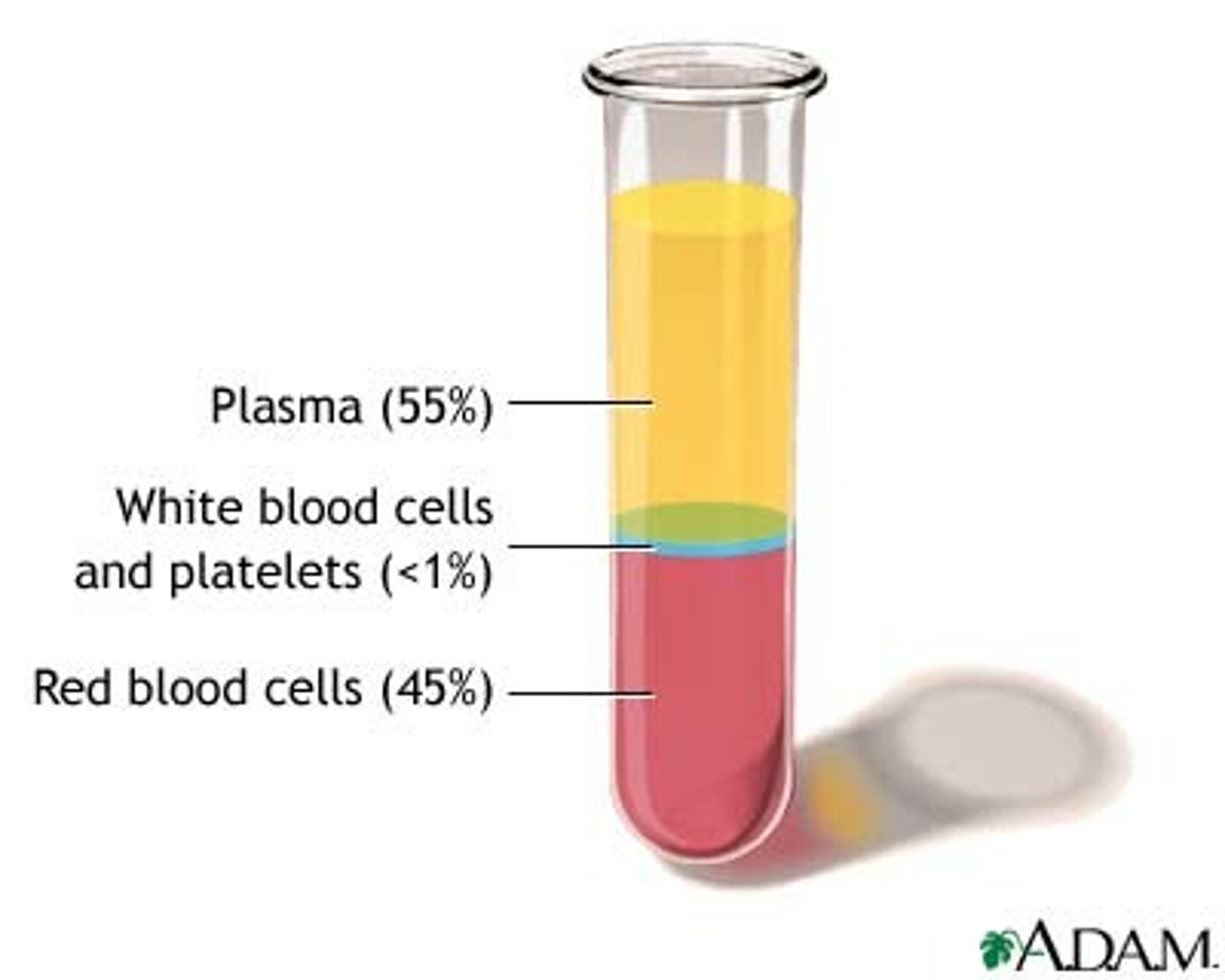
blood
Connective tissue made of plasma, erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets.
Bones
provide a resting ground for muscles and protection of vital organs
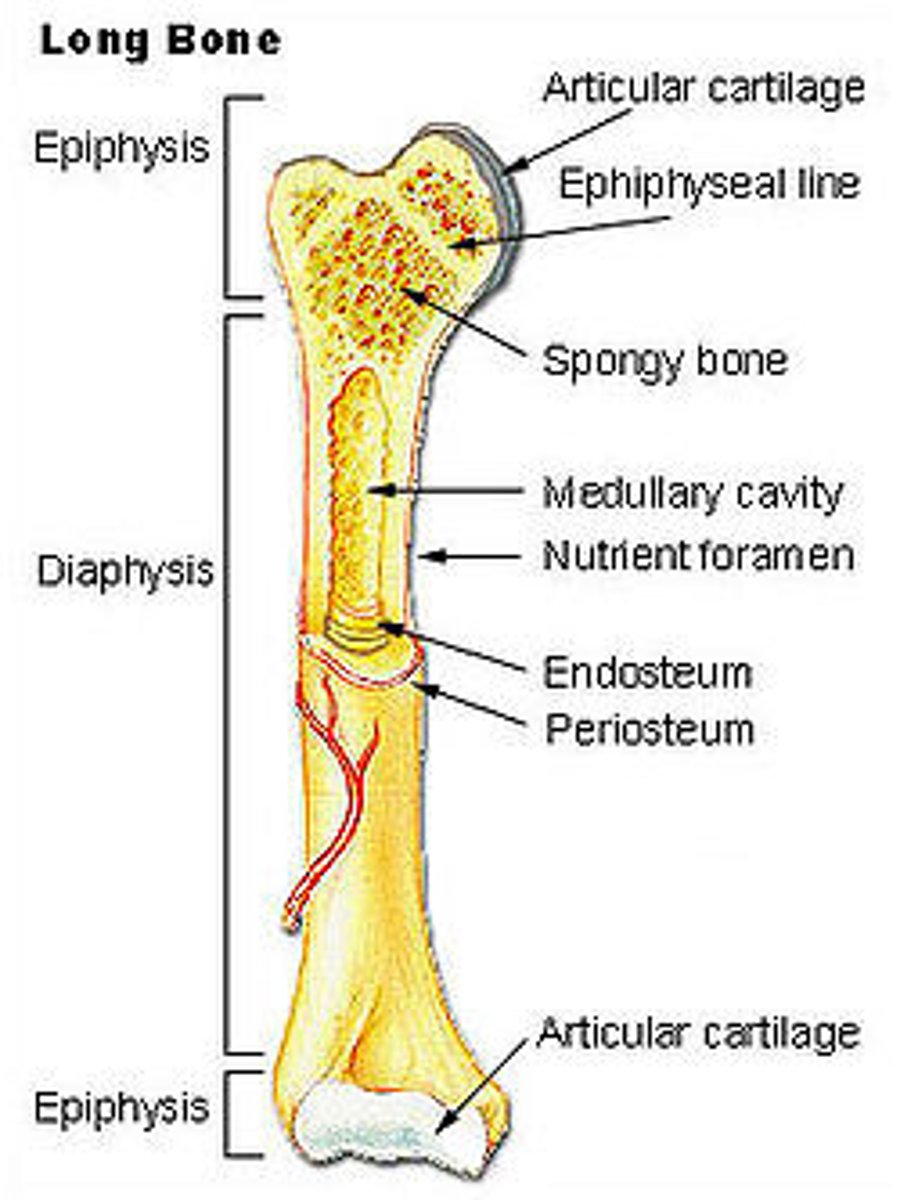
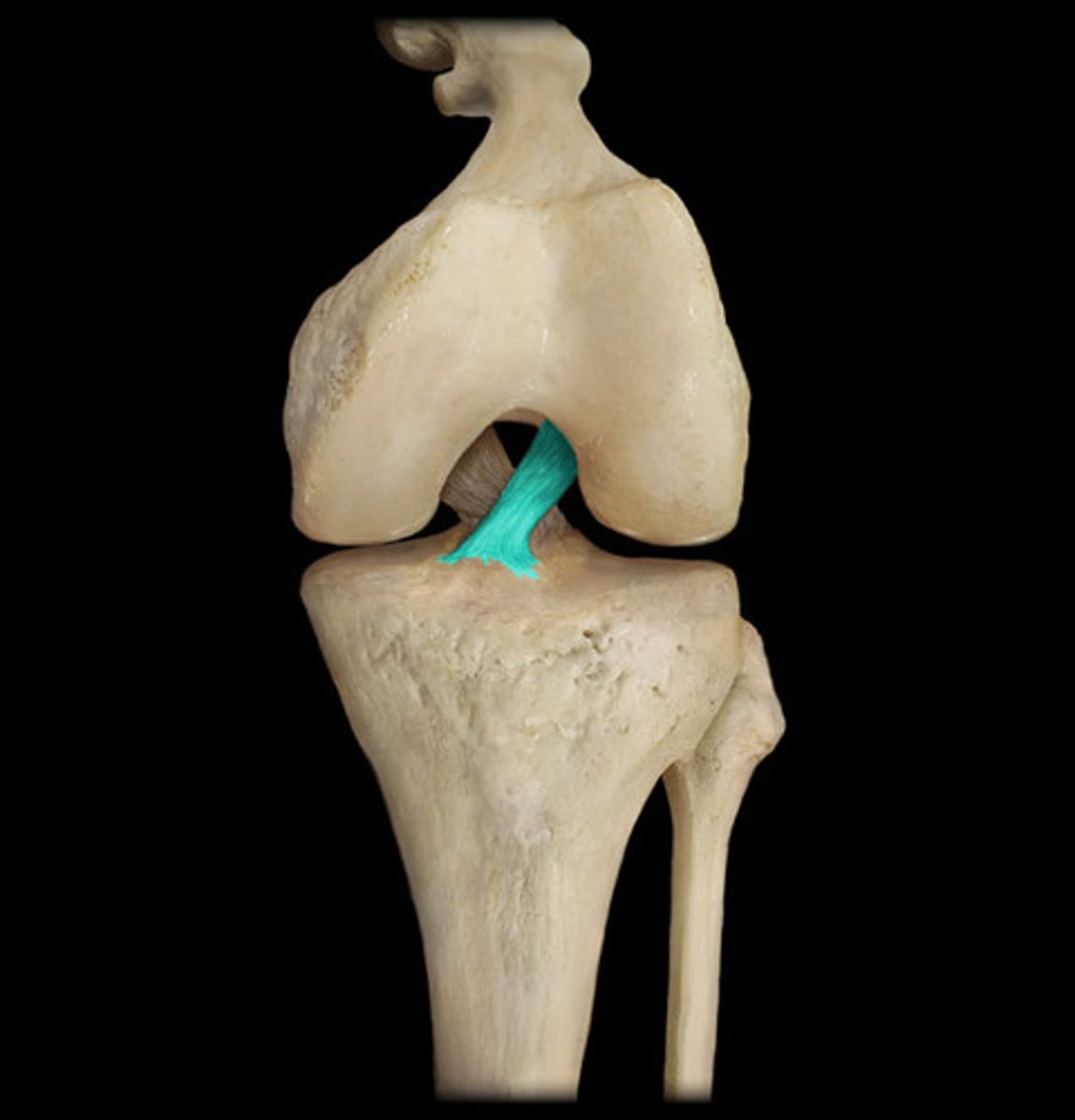
Ligaments
Connect bone to bone
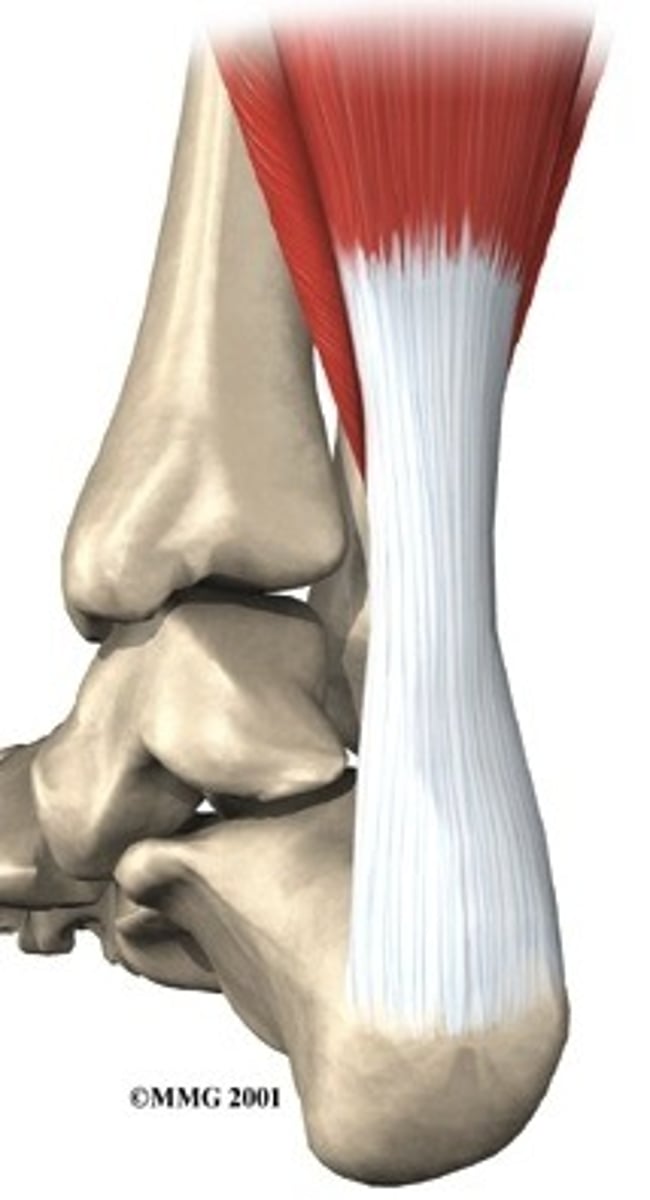
Tendons
Connect muscle to bone
Cerebrum
Area of the brain responsible for all voluntary activities of the body
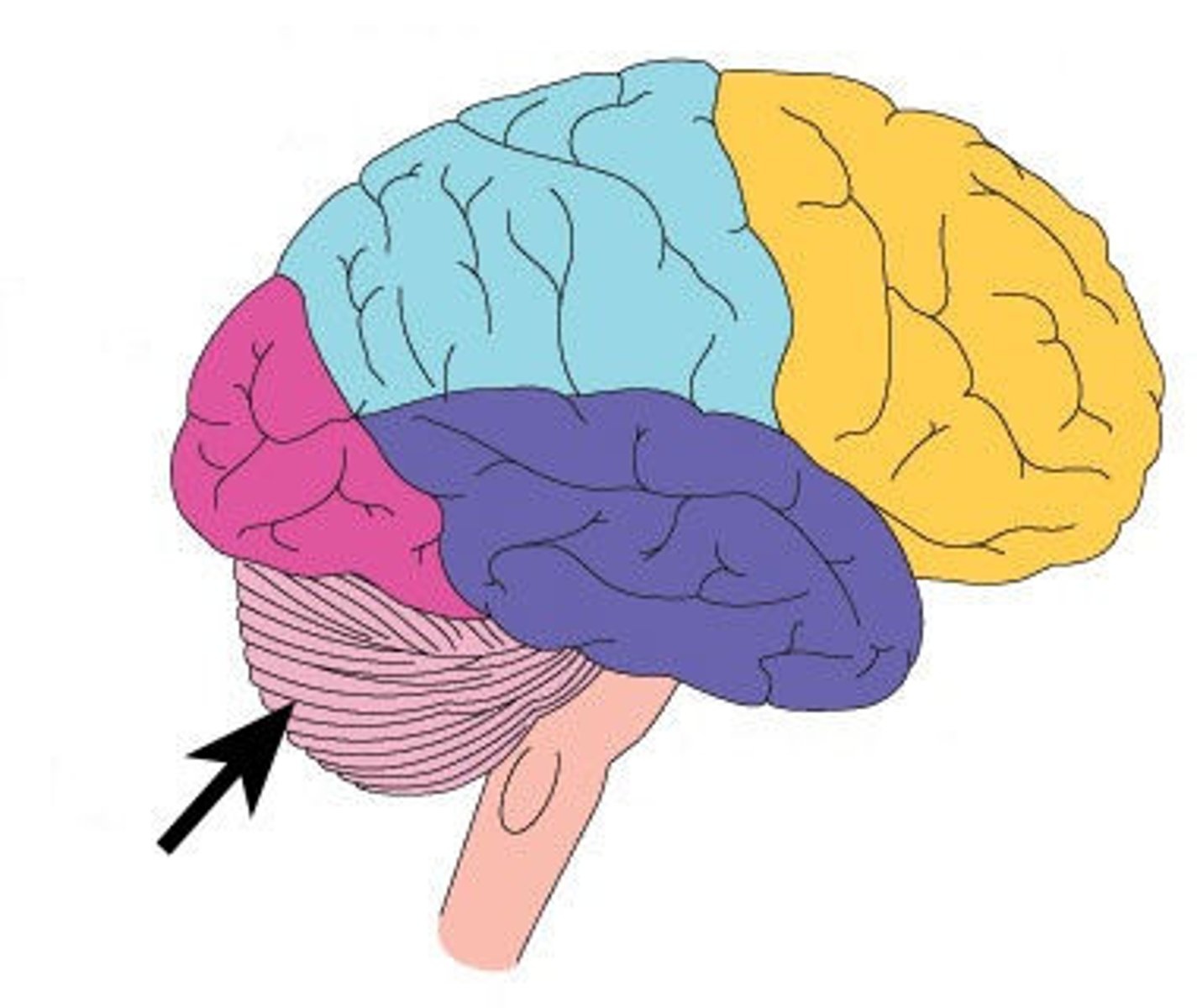
Cerebellum
A large structure of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills.
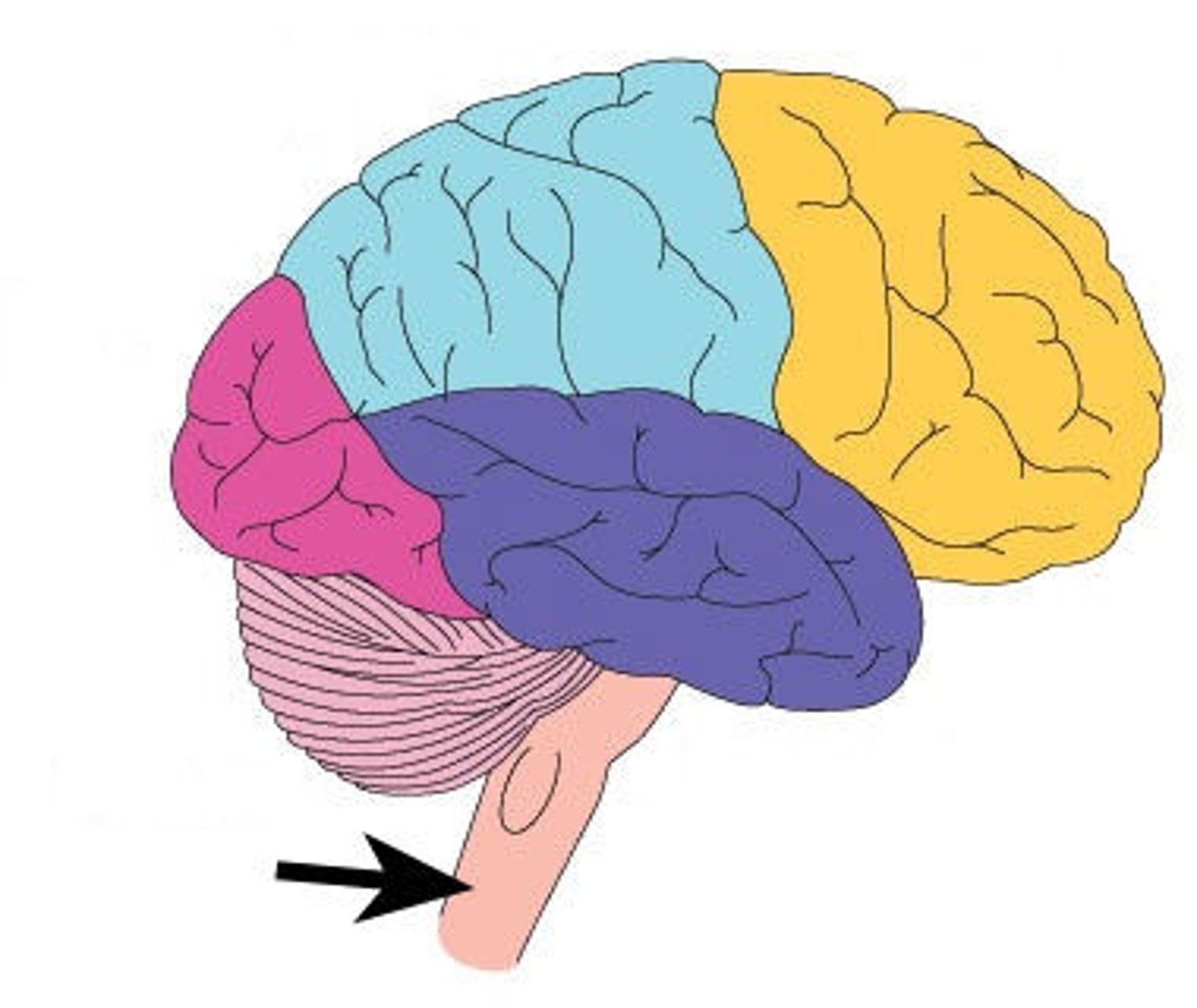
brain stem
Connection to spinal cord. Filters information flow between peripheral nervous system and the rest of the brain.
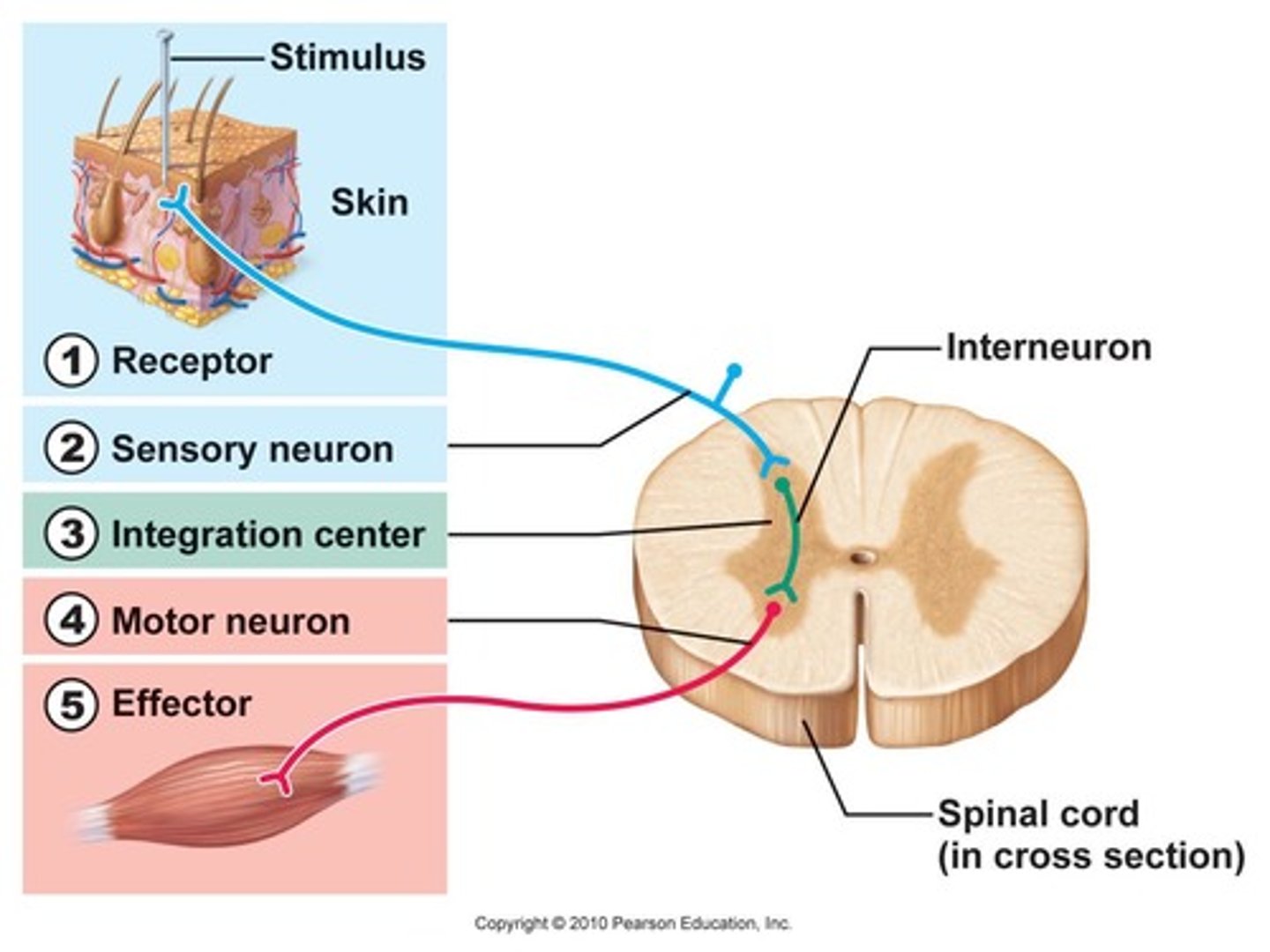
Reflex Arc
A relatively direct connection between a sensory neuron and a motor neuron that allows an extremely rapid response to a stimulus, often without conscious brain involvement.
sensory neurons
neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
Relay neurons
These connect the sensory neurons to the motor or other relay neurons. They have short dendrites and short axons.
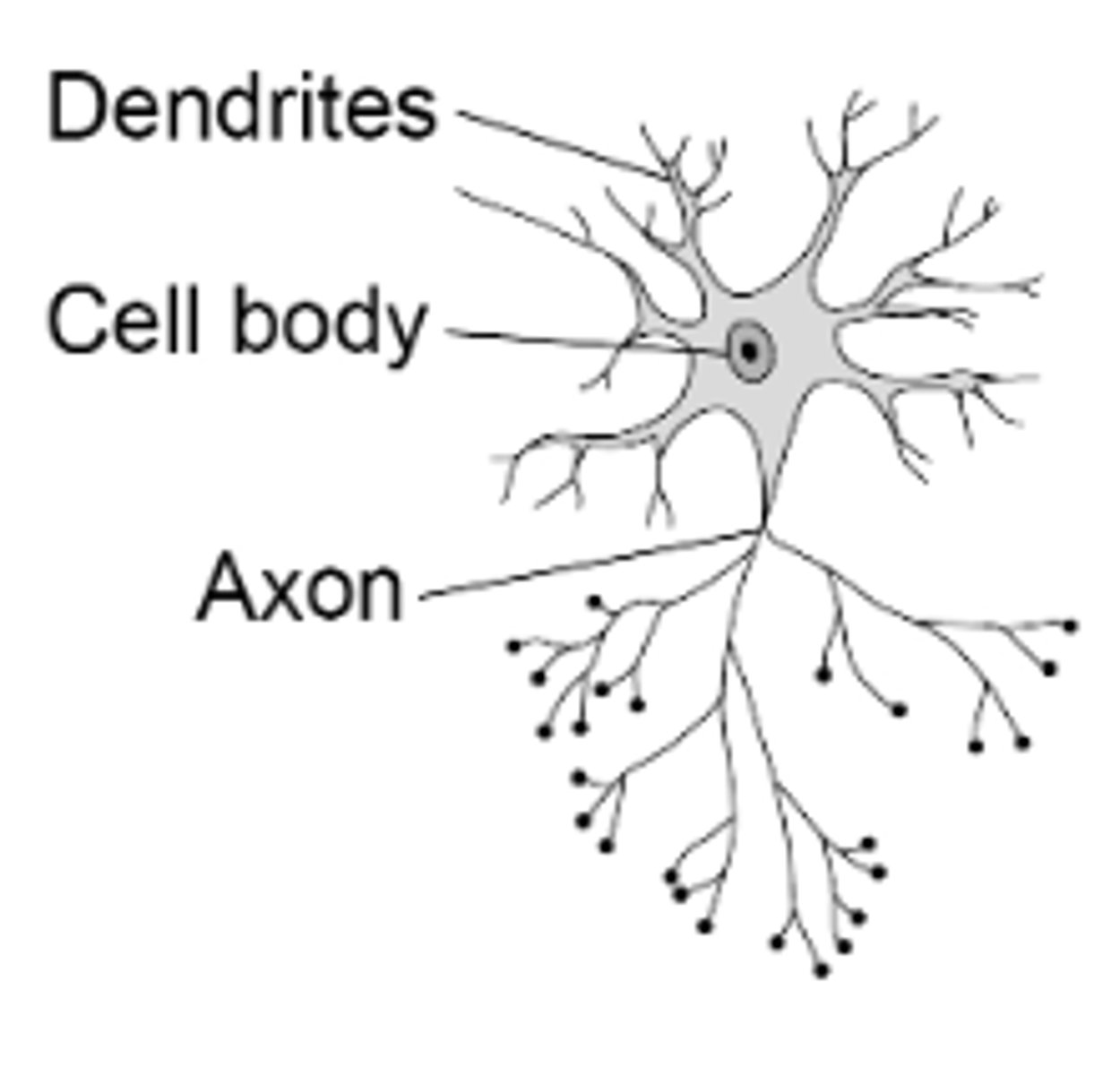
motor neurons
neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
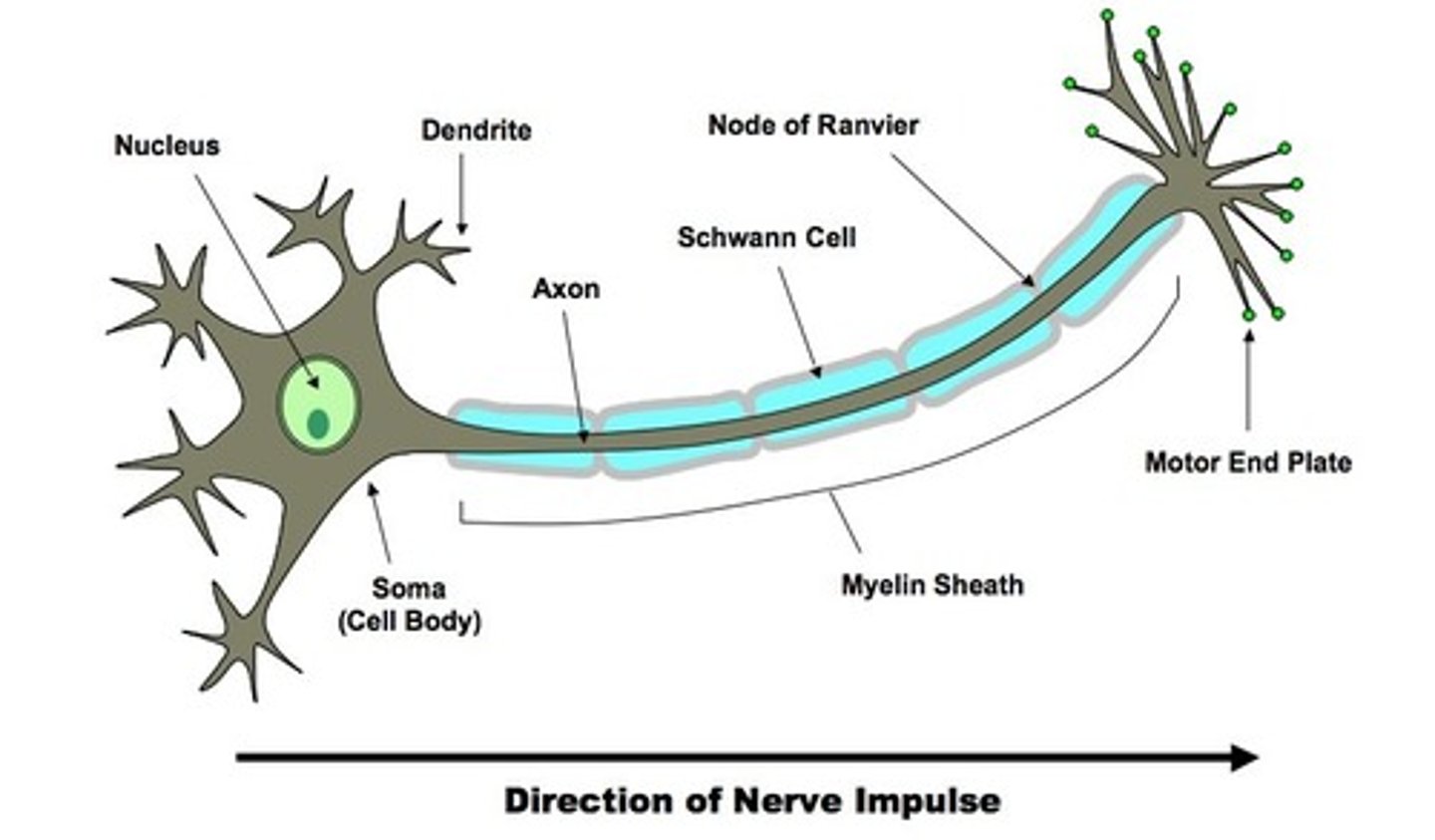
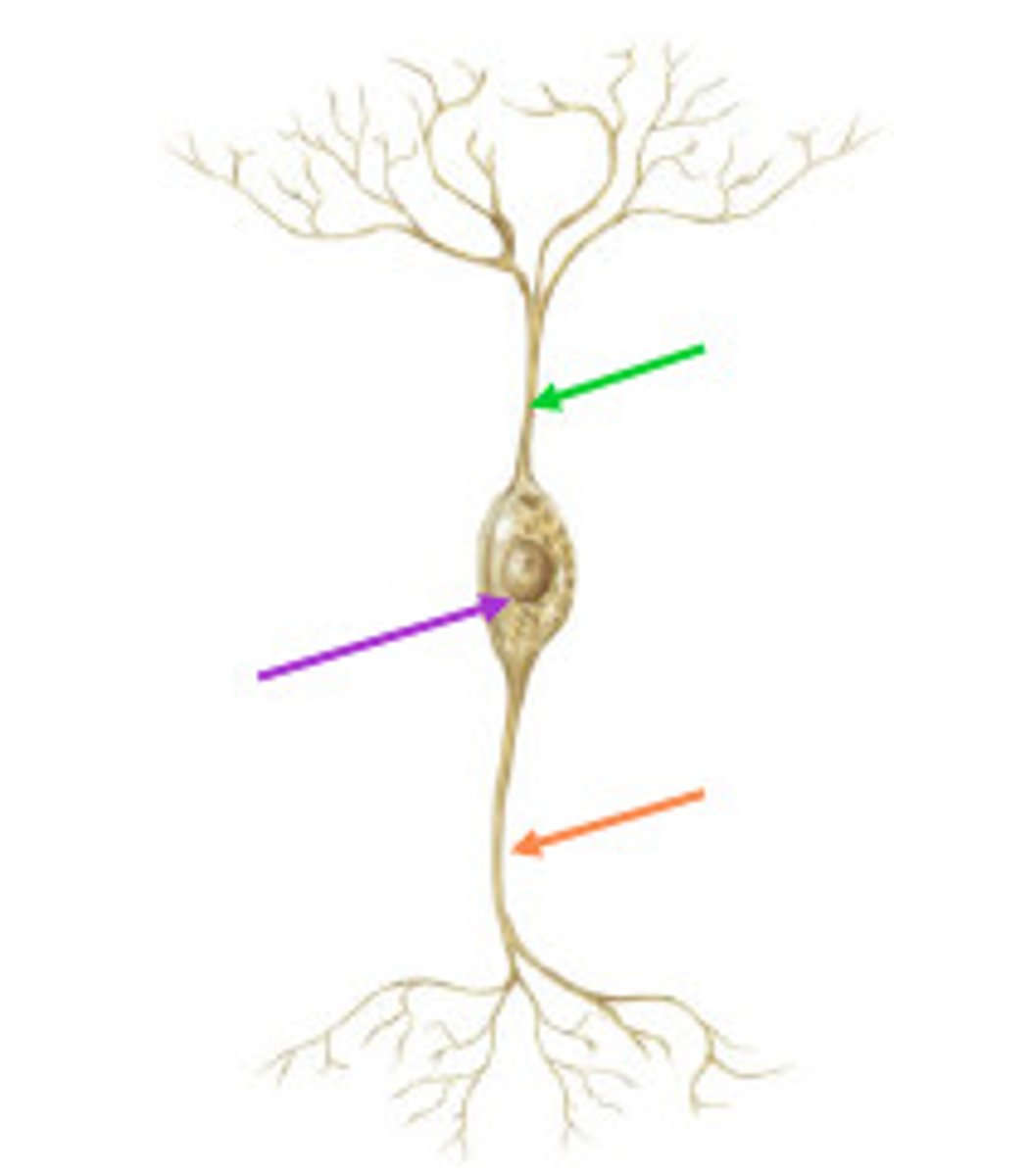
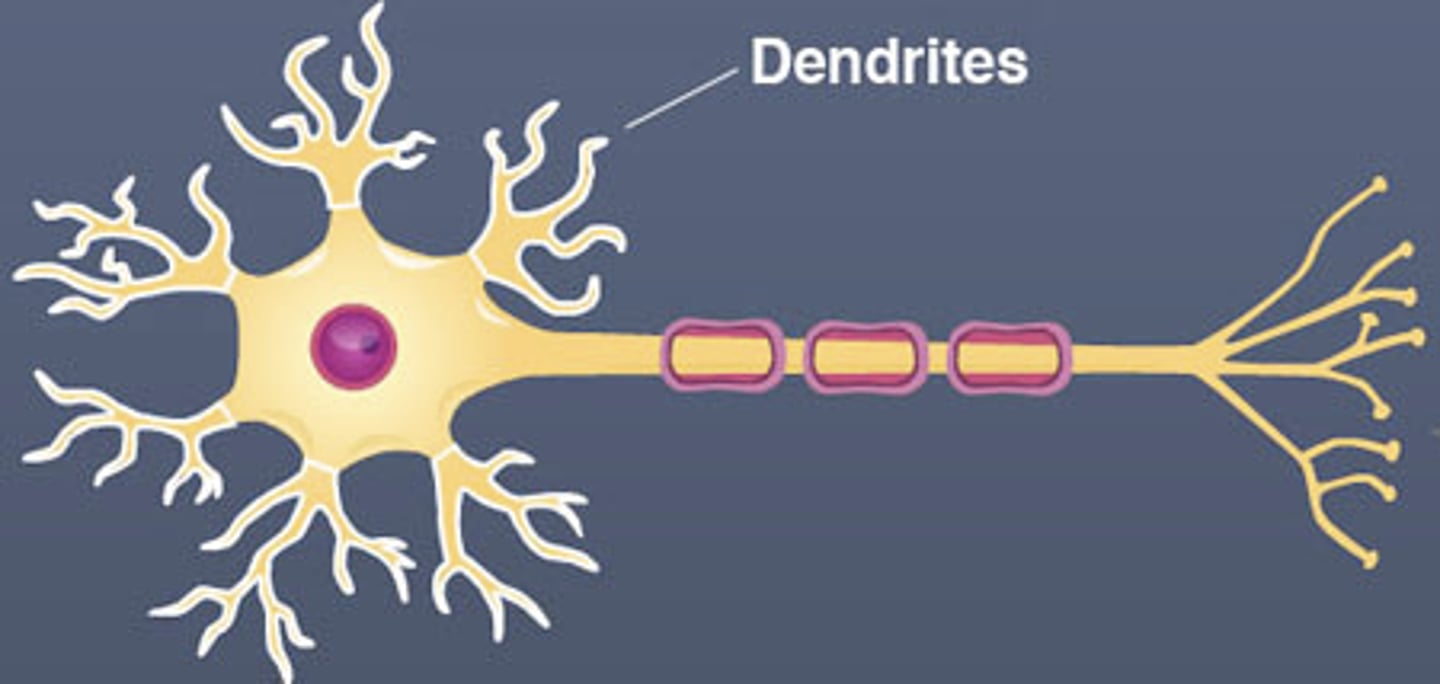
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
Axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
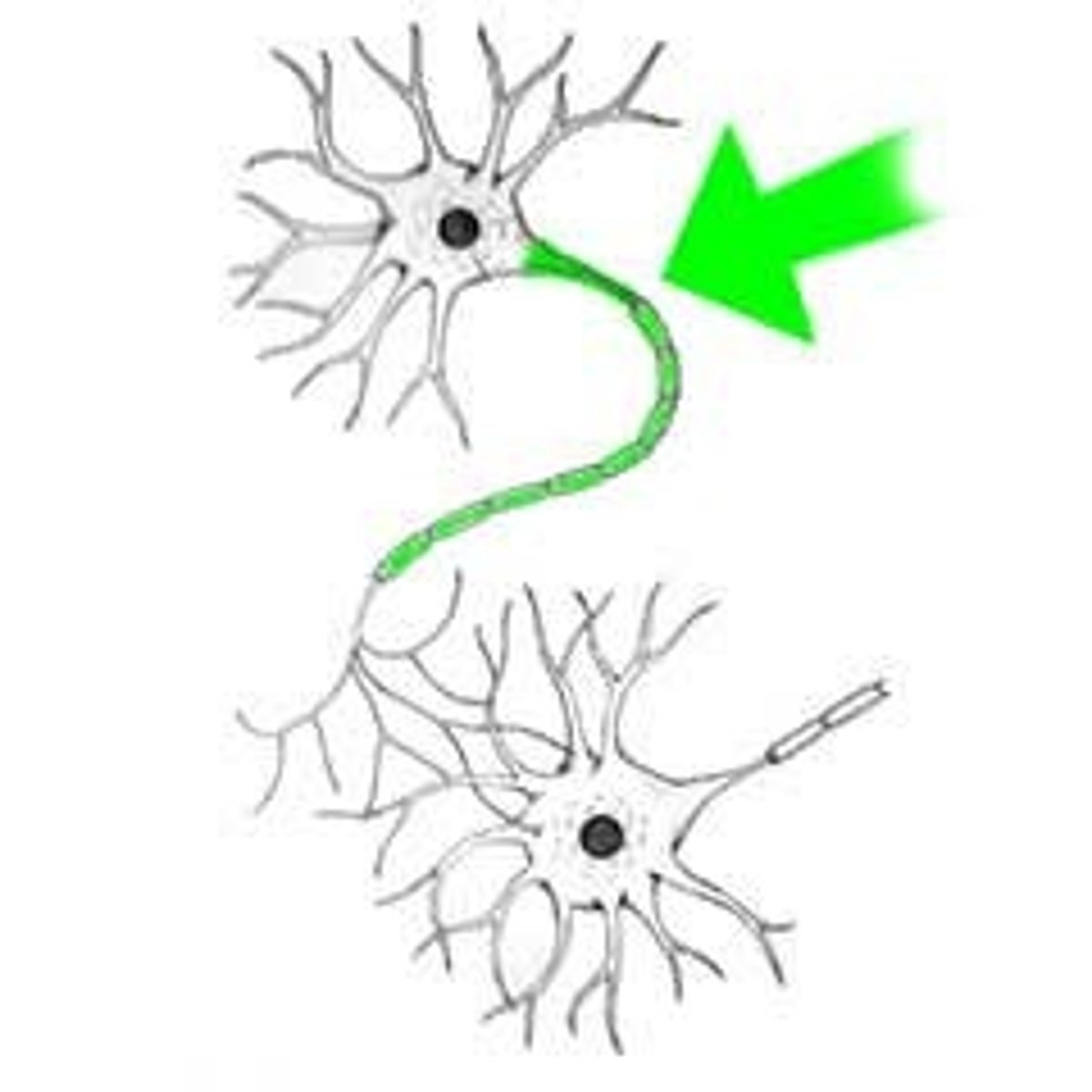
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
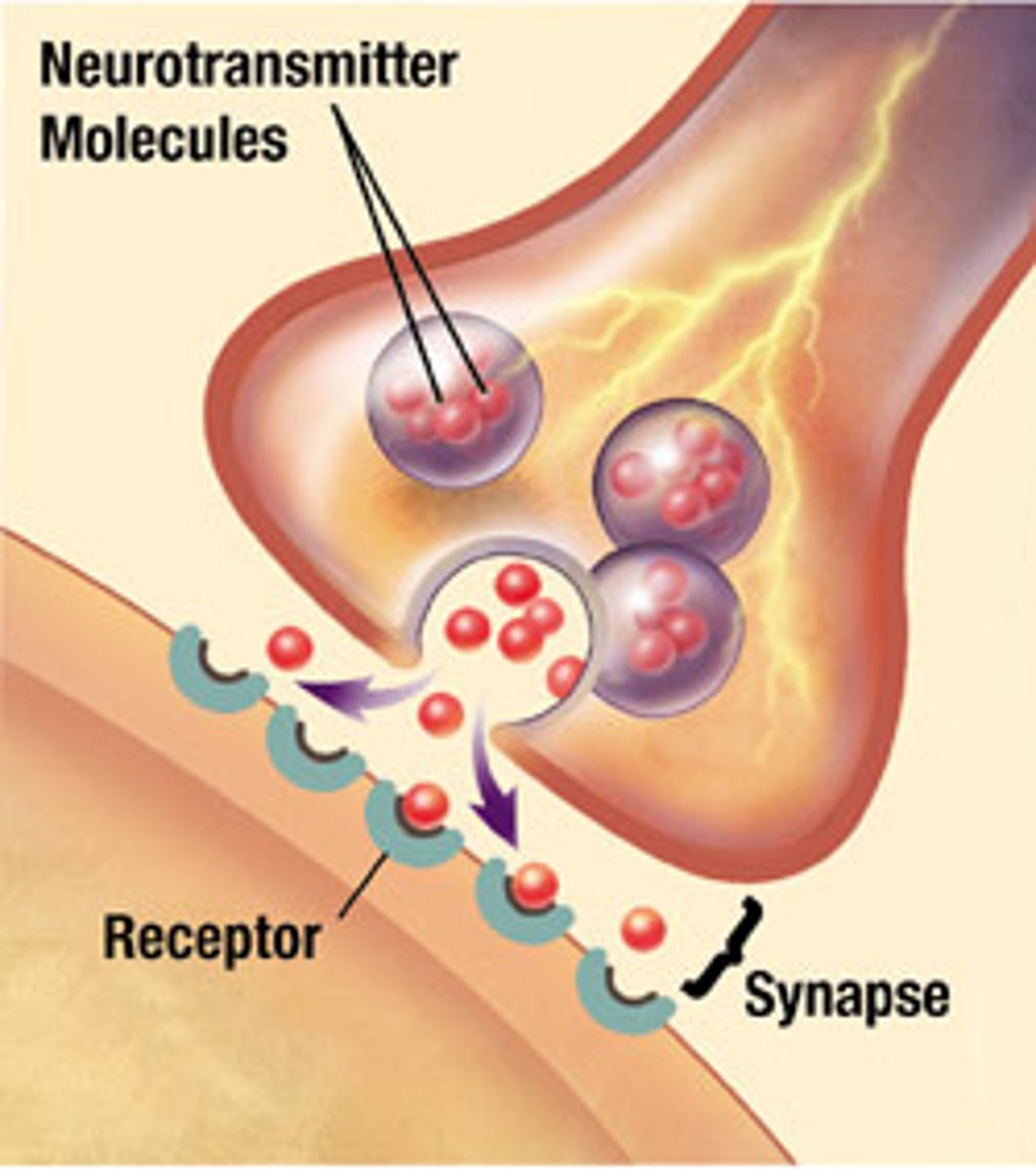
Synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
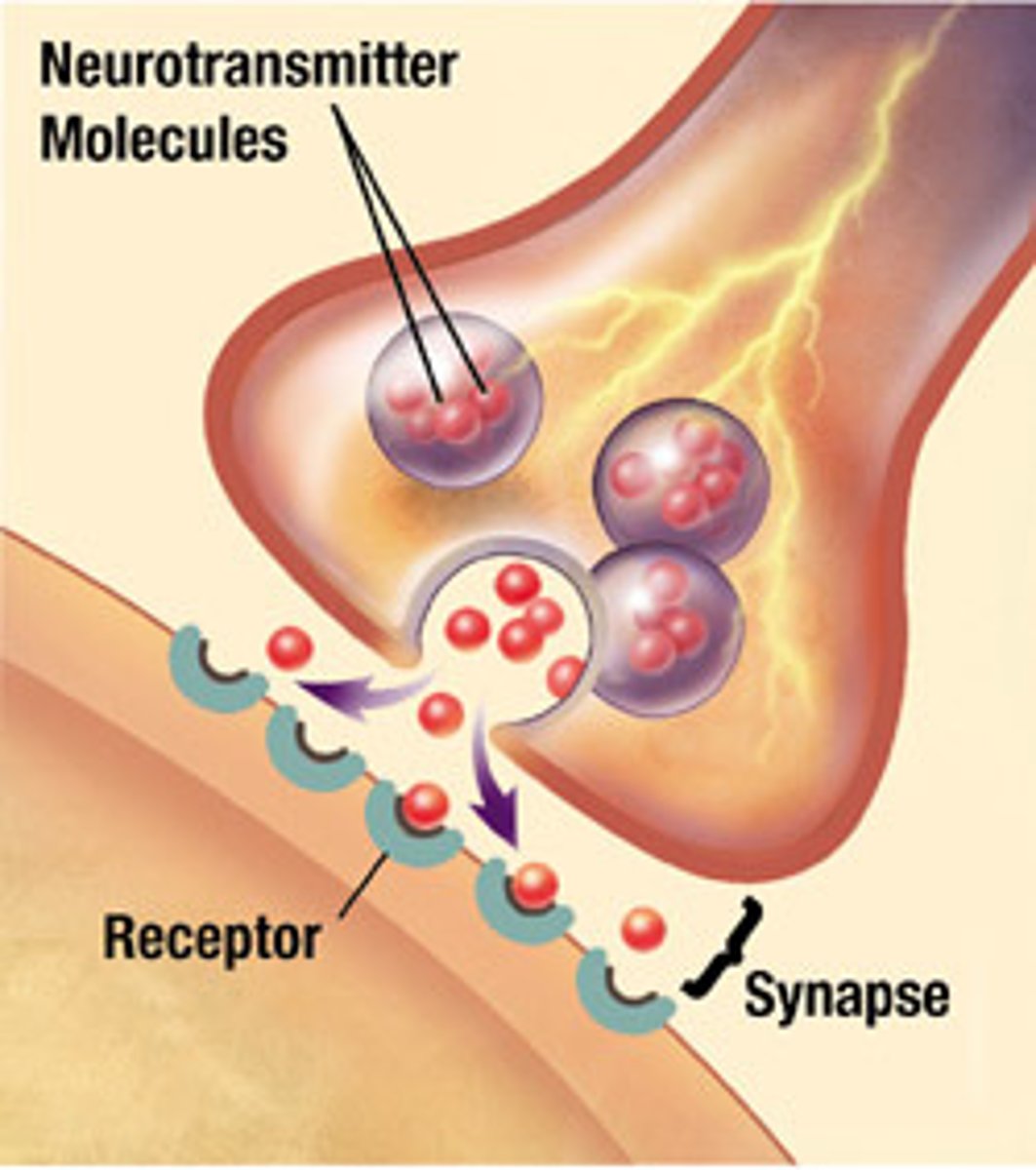
Insulin
A hormone produced by the pancreas or taken as a medication by many diabetics
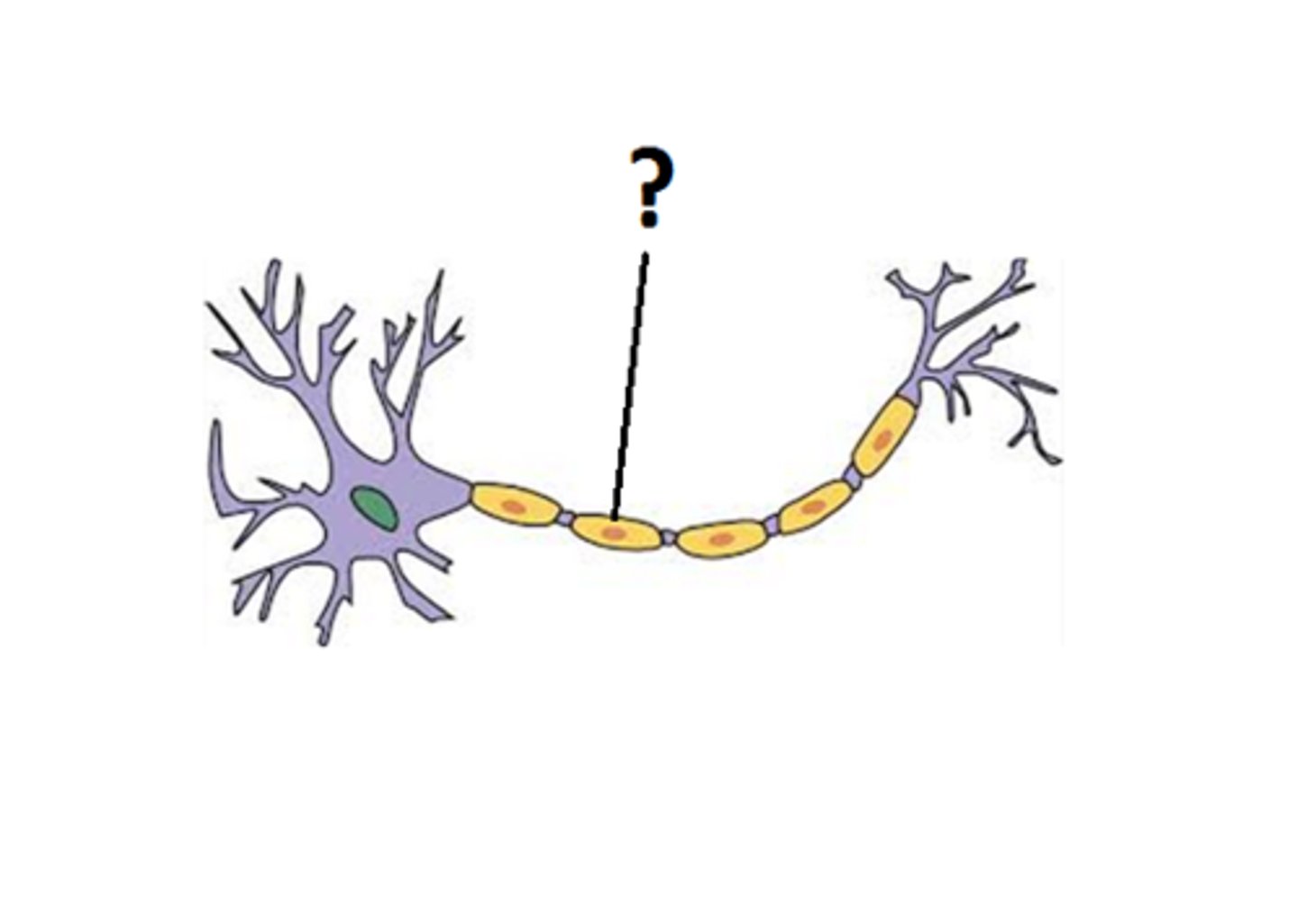
myelin sheath
A layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the next.
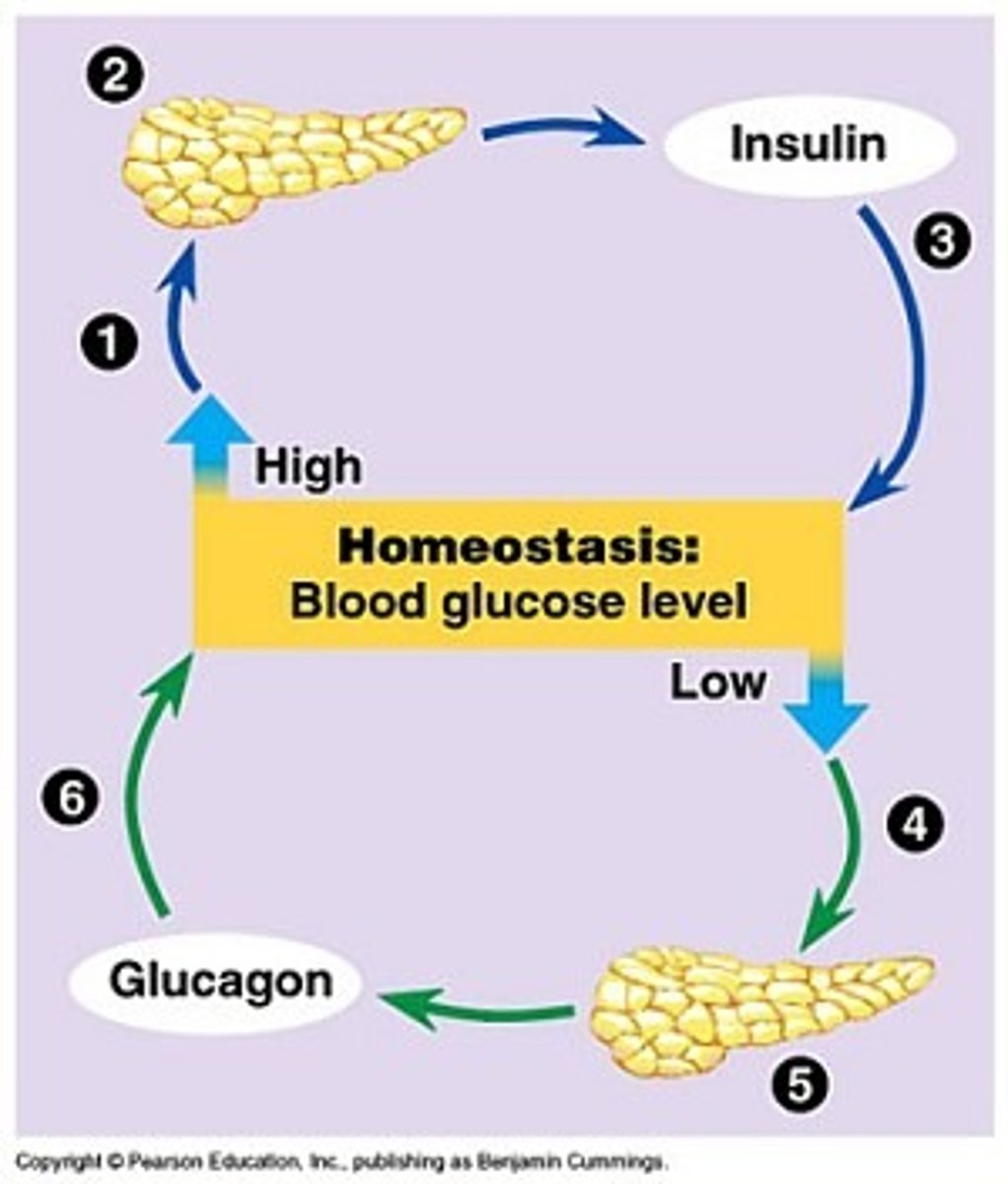
Glucagon
A protein hormone secreted by pancreatic endocrine cells that raises blood glucose levels; an antagonistic hormone to insulin.
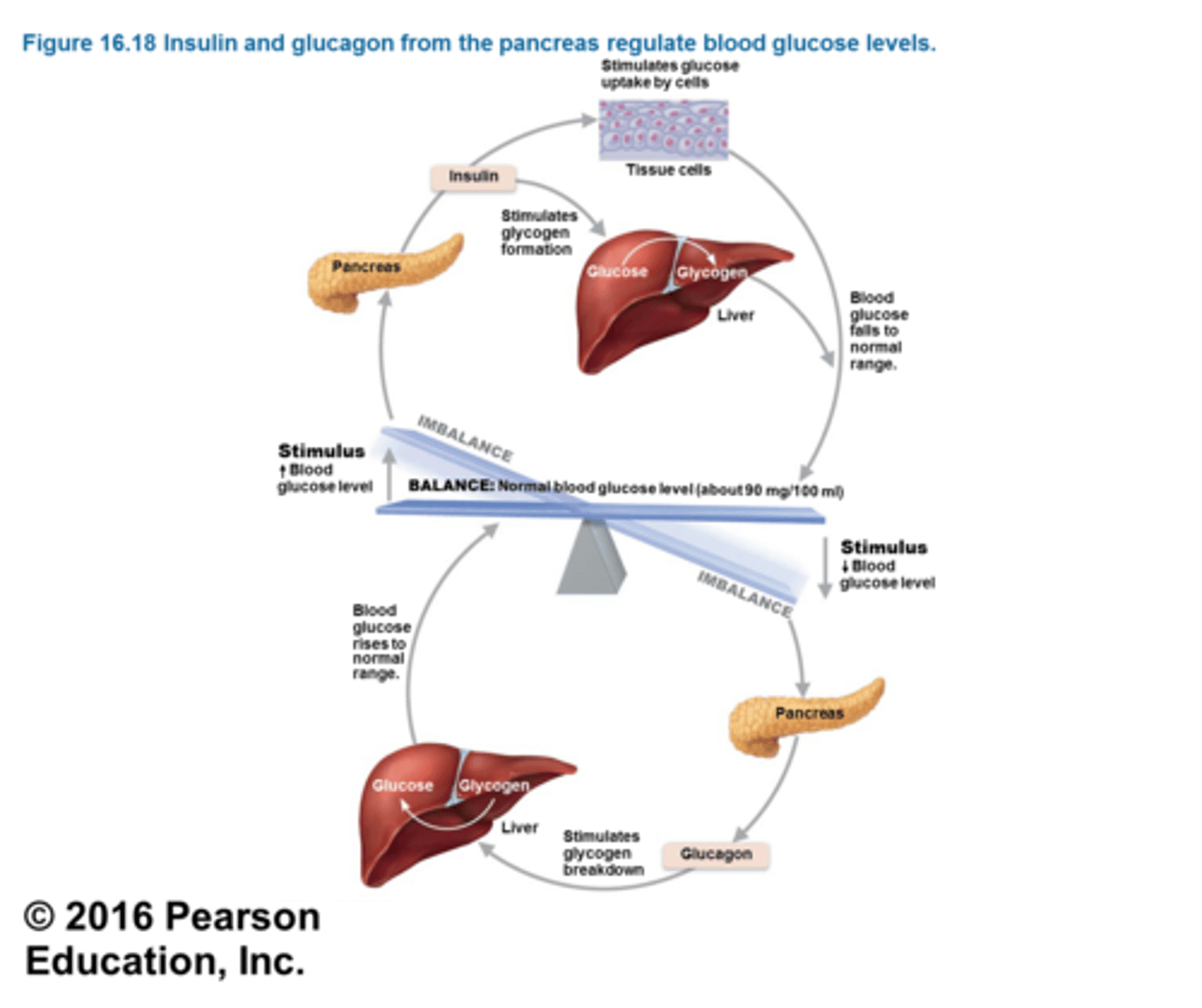
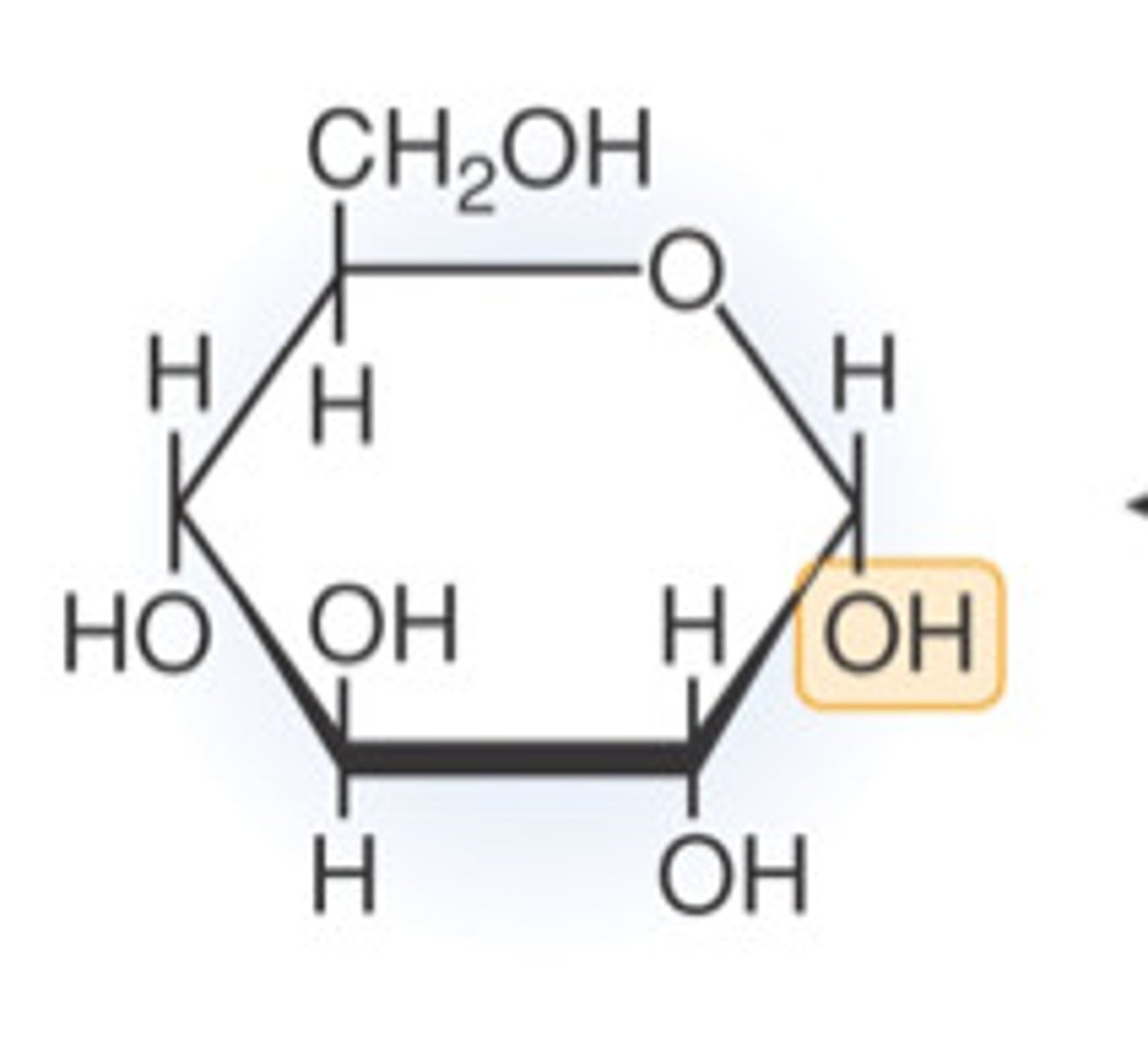
Glucose
the form of sugar that circulates in the blood and provides the major source of energy for body tissues. When its level is low, we feel hunger.
diabetes type 1
No insulin is produced. Either born with it or developed at a young age
diabetes type 2
A chronic condition where the body does not use insulin properly and becomes insulin resistant.
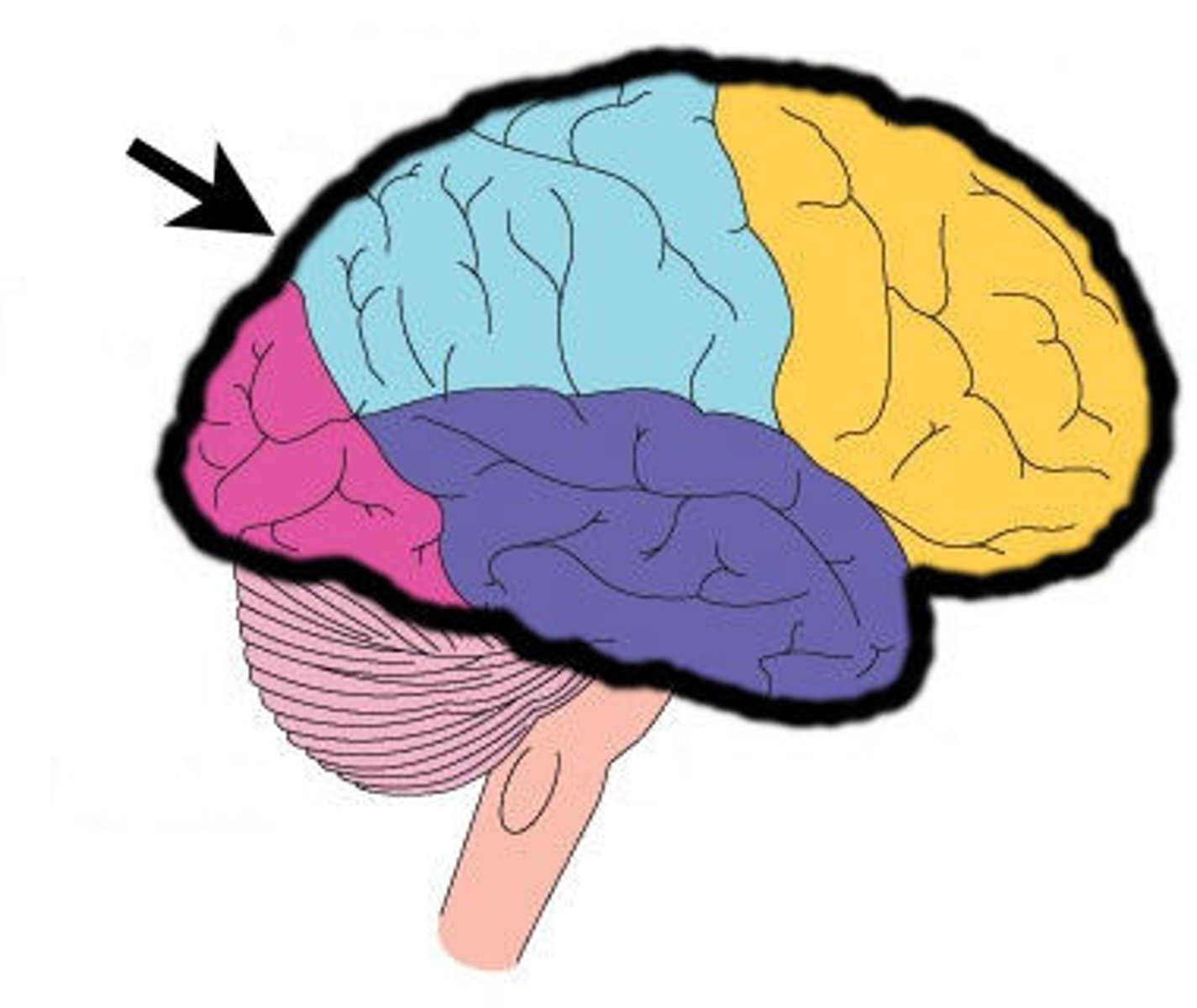
frontal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
occipital lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
parietal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch.
temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.
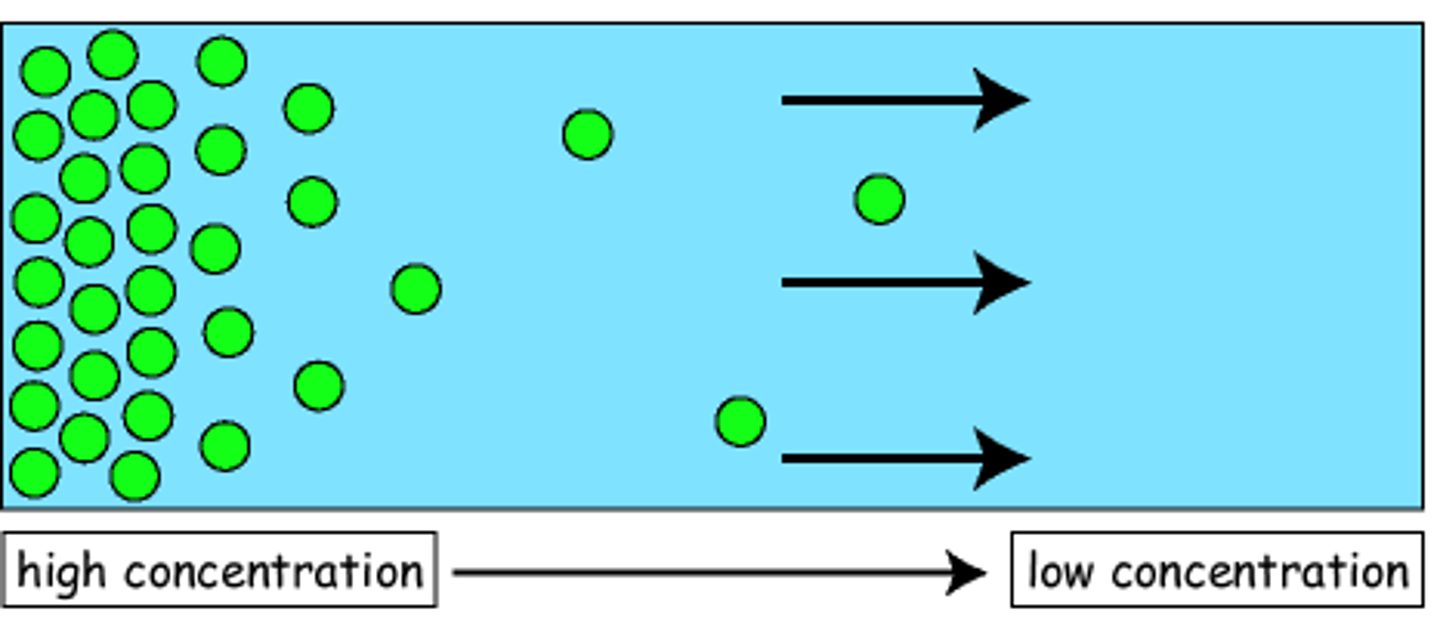
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
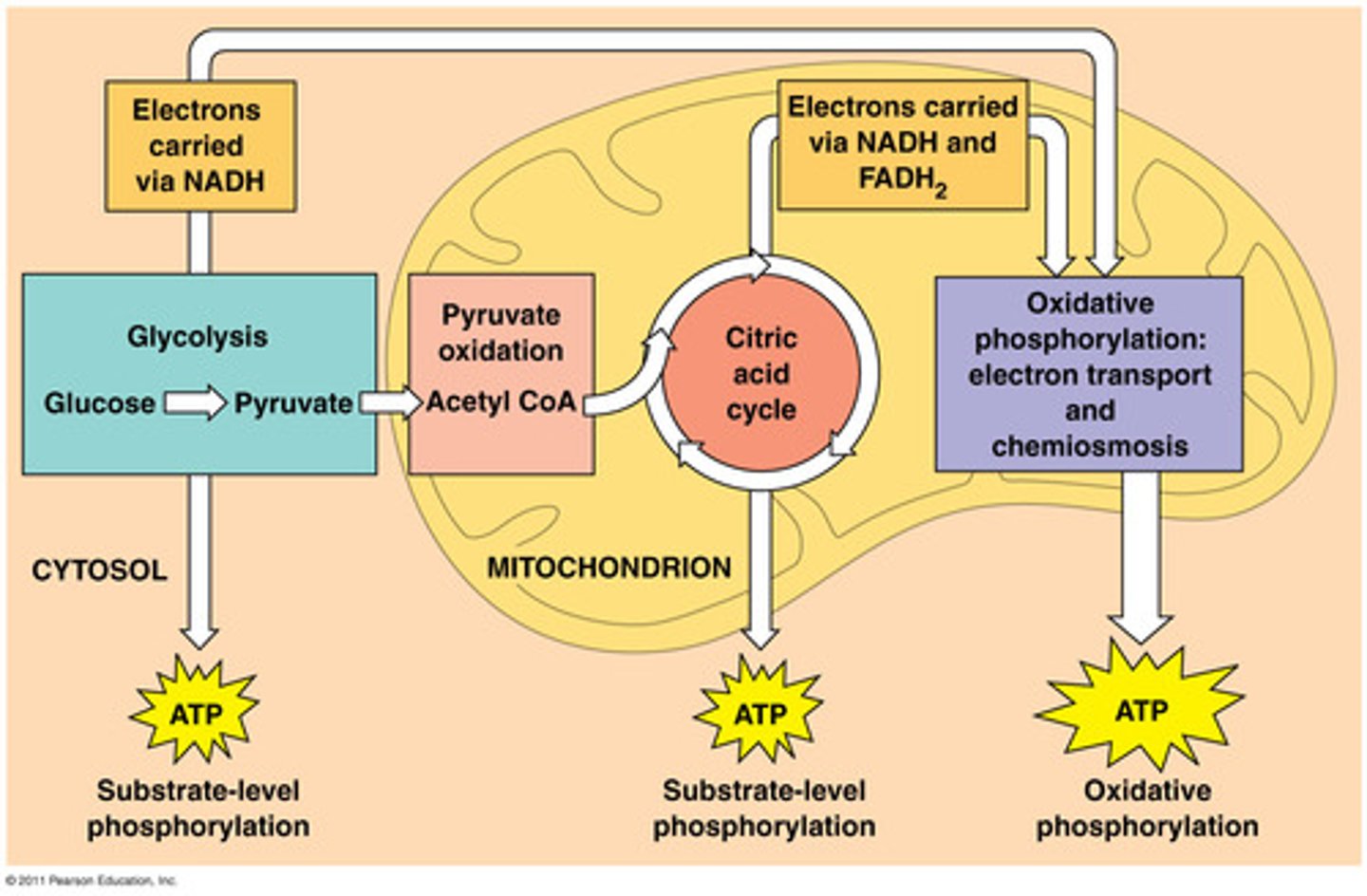
cellular respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen
Respiration
Inhalation and exhalation of air.