Unit B: Plant Respiration and Metabolic Pathways Lecture 1 & 2
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Respiration
Process of energy release from carbon compounds.
Dark Respiration
Energy release in absence of light conditions.
Photorespiration
Process minimizing CO2 loss via RUBISCO activity.
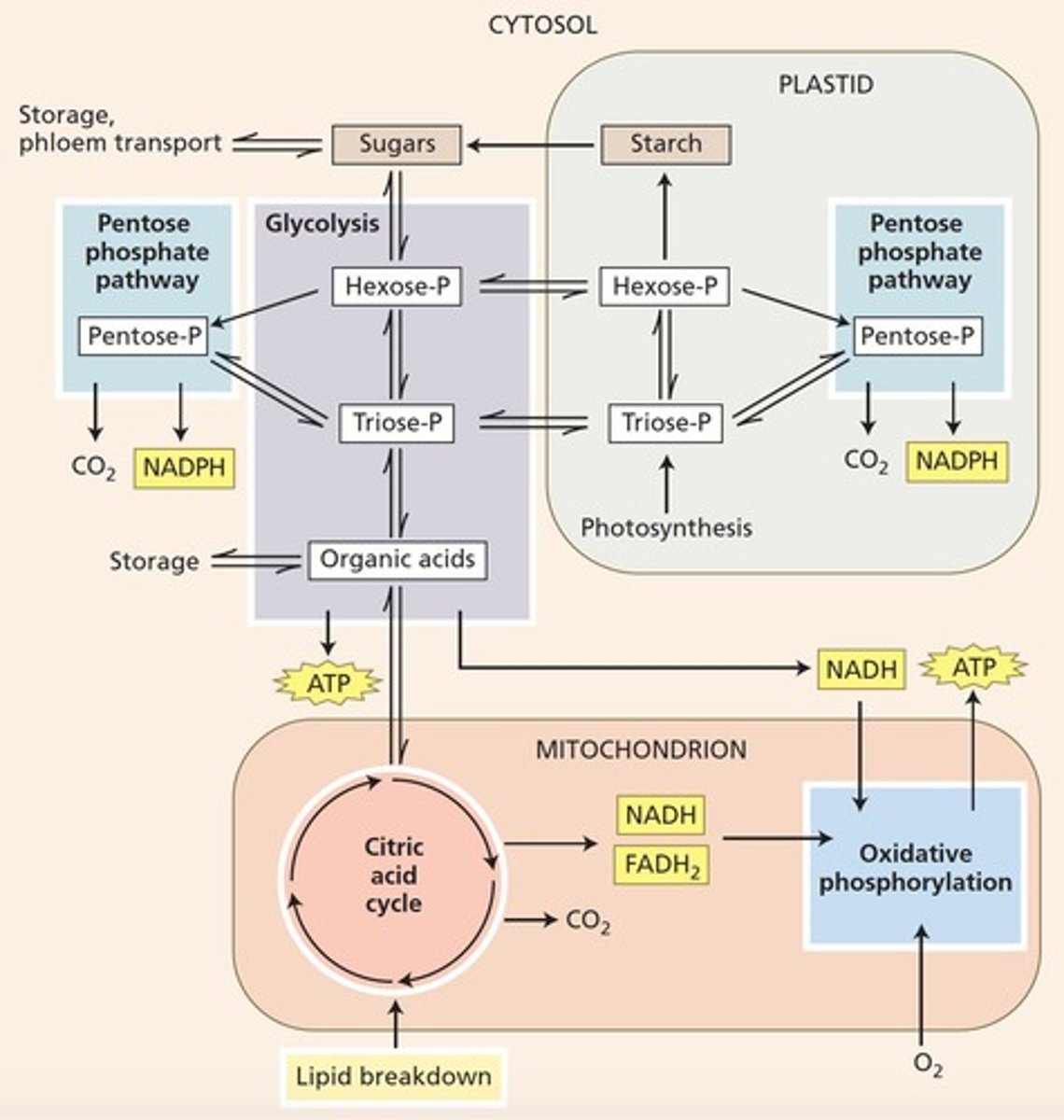
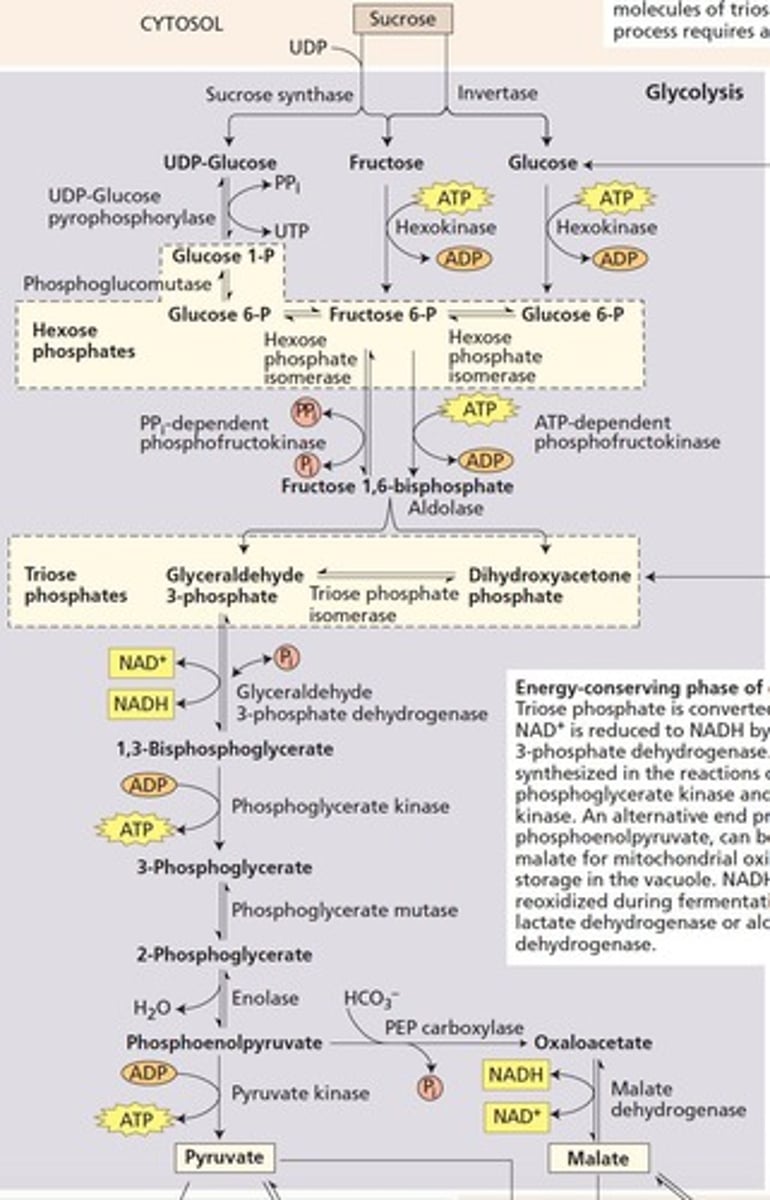
Glycolysis
First step of respiration, occurs in cytoplasm.
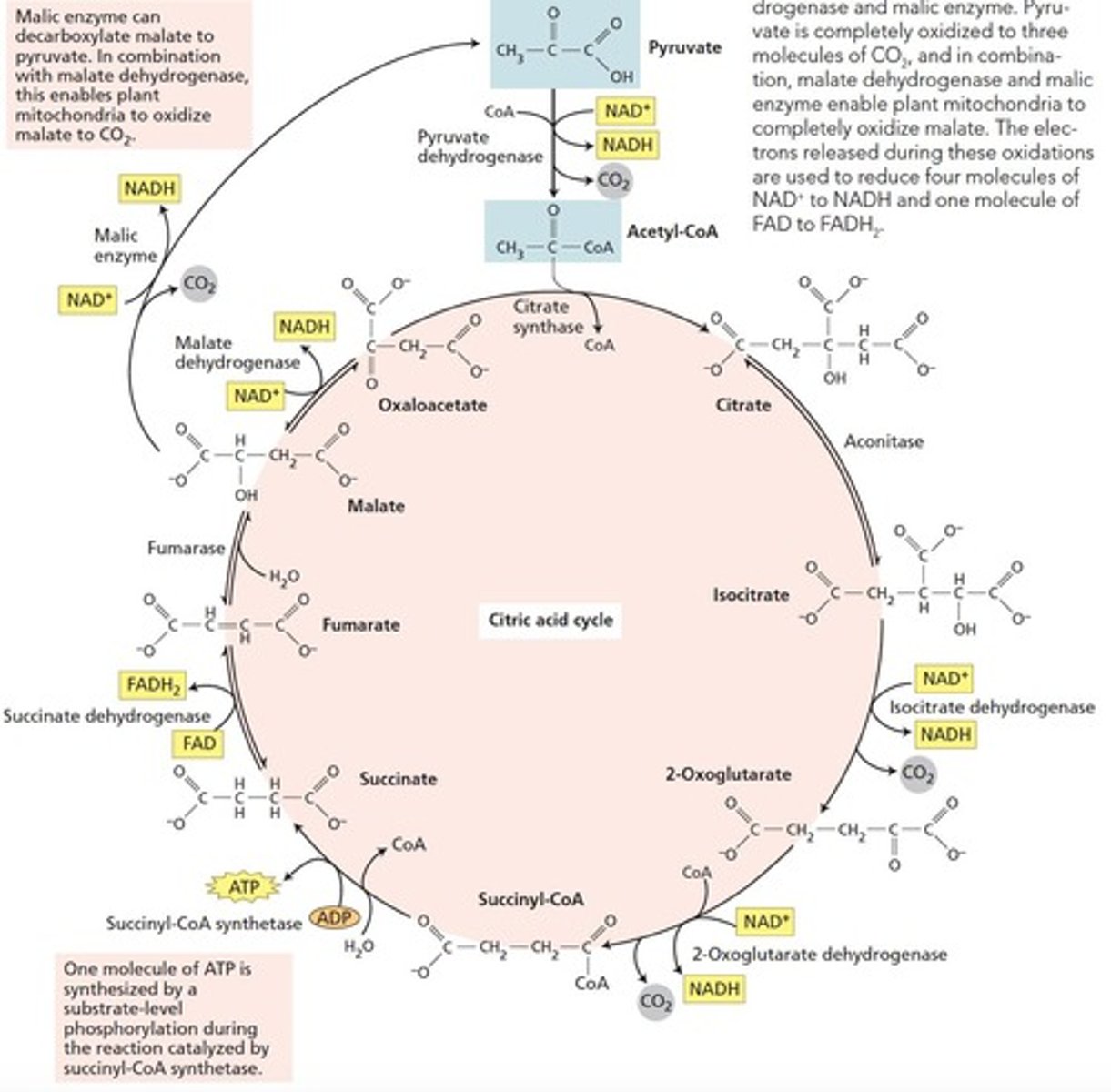
Krebs Cycle
Series of reactions generating energy in mitochondria.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
ATP production via electron transport chain.
Respiratory Quotient (RQ)
Ratio of CO2 released to O2 consumed.
Sucrose
Main sugar used in plant respiration processes.
2-Phosphoglycolate
Intermediate formed during photorespiration.
3-Phosphoglycerate
Product of converting 2-Phosphoglycolate in photorespiration.
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate, energy currency of cells.
Carbon Skeletons
Molecules generated for biosynthesis during respiration.
Respiratory Capacity
Maximum rate at which a plant can respire.
Energy Demand
Amount of energy required for plant processes.
Substrate Availability
Presence of organic molecules for respiration.
Oxygen Supply
Availability of O2 affecting respiration rates.
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase
Enzyme decreasing activity in light conditions.
Basal RQ Rate
Expected RQ value around 1 for plants.
Phosphoglycolates
Compounds formed when CO2 is limited.
Electron Transfer
Process required for ATP generation in respiration.
Environmental Conditions
Factors influencing respiration rates in plants.
Energy Storage
Transient storage of energy in ATP during respiration.
RQ Value of 1.0
Indicates complete oxidation of substrates.
Oxidized Substrates
Increase RQ due to more CO2 release.
Reduced Substrates
Decrease RQ due to more O2 required.
Aerobic Respiration
Process using O2 to convert substrates into energy.
Oleic Acid Respiration
Produces RQ of 0.7 during oxidation.
Sucrose Respiration
Produces RQ of 1.0 during oxidation.
Carboxylation Reactions
Consume CO2, decreasing the RQ value.
De-carboxylation Reactions
Release CO2, increasing the RQ value.
Fermentation
Produces CO2 without O2, increasing RQ.
Nitrate Influence on RQ
More nitrates lead to increased CO2 and RQ.
Malate Utilization
Increases RQ when oxidized in roots.
Glycolysis
Breakdown of glucose to produce energy.
Krebs Cycle
Citric acid cycle in mitochondrion matrix.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Uses proton gradient in inner mitochondrial membrane.
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Pathway for glucose metabolism in plastids.
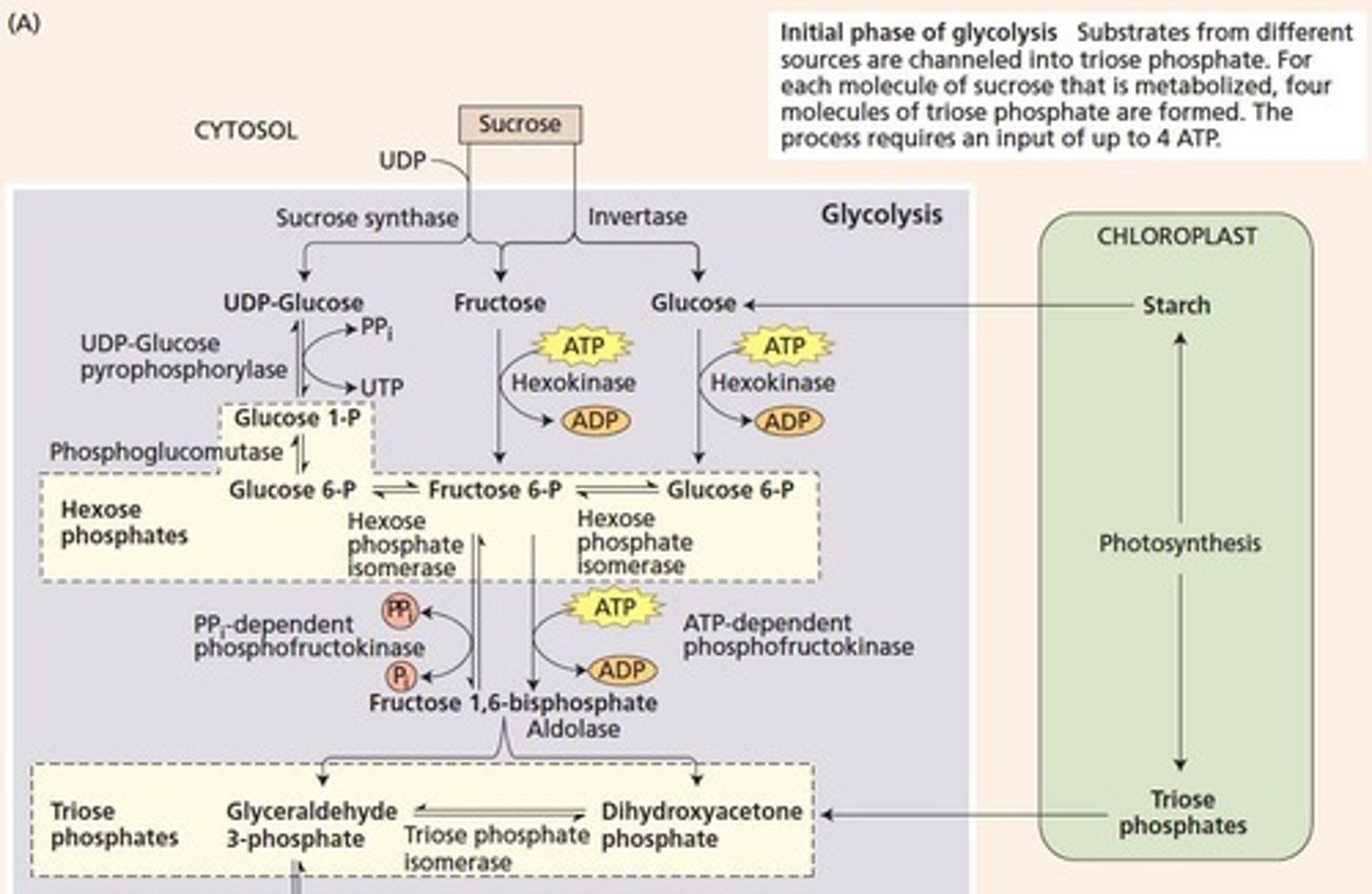
Invertase Pathway
Converts sucrose to fructose-6-P using ATP.
Energy-Conserving Phase
Produces ATP and NADH from G3P to pyruvate.
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
Direct ATP production during metabolic pathways.
ATP Cost in Glycolysis
Up to 3 ATPs used to form G3P.
Alternative End Product
PEP can convert to malate in plants.
NADH Production
Occurs during energy-conserving phase of glycolysis.
Respiration
Biochemical process converting nutrients into energy.
Glycolysis
First step in glucose metabolism, producing pyruvate.
Krebs Cycle
Cyclic series of reactions producing NADH and FADH2.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
ATP production via electron transport chain and chemiosmosis.
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase
Enzyme converting pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA.
Fermentation
Anaerobic process generating energy without oxygen.
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Pathway generating NADPH and ribose-5-phosphate.
ΔG0′
Standard Gibbs free energy change; -5,760 kJ/mol sucrose.
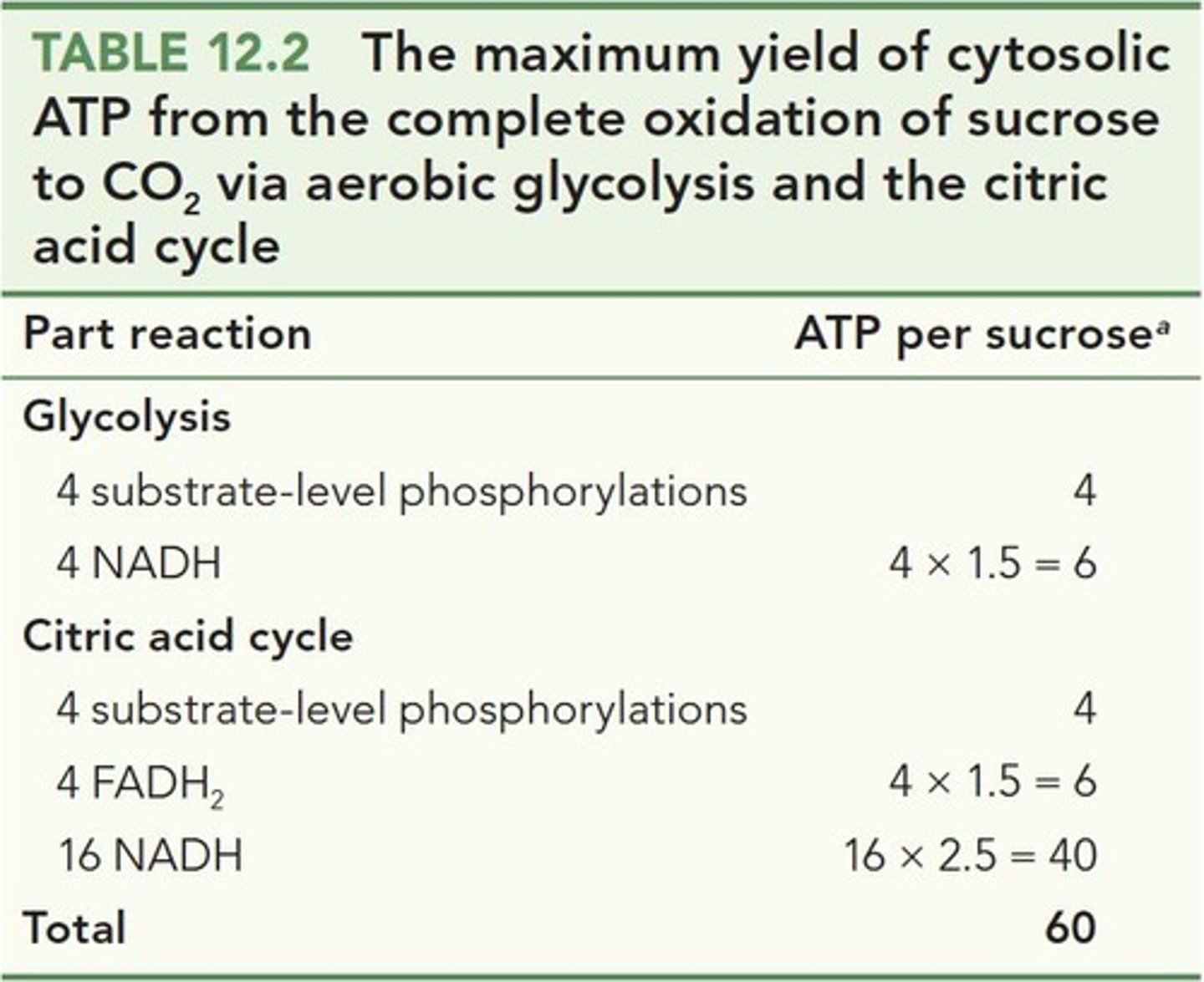
ATP Production
60 ATP generated per sucrose molecule during respiration.
NADH
Electron carrier produced in glycolysis and Krebs cycle.
FADH2
Electron carrier produced in Krebs cycle.
CO2 Release
Carbon dioxide produced during Krebs cycle per pyruvate.
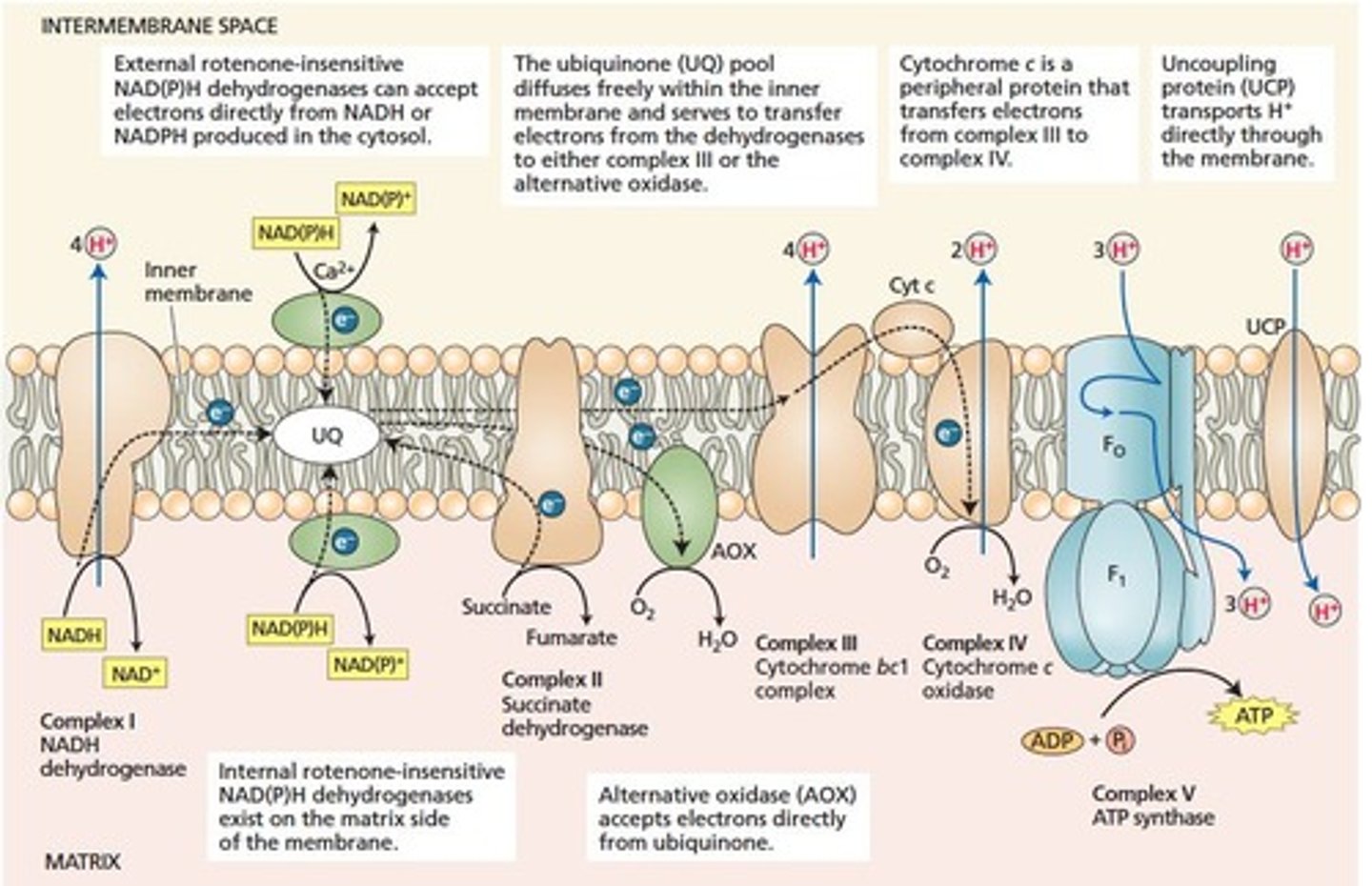
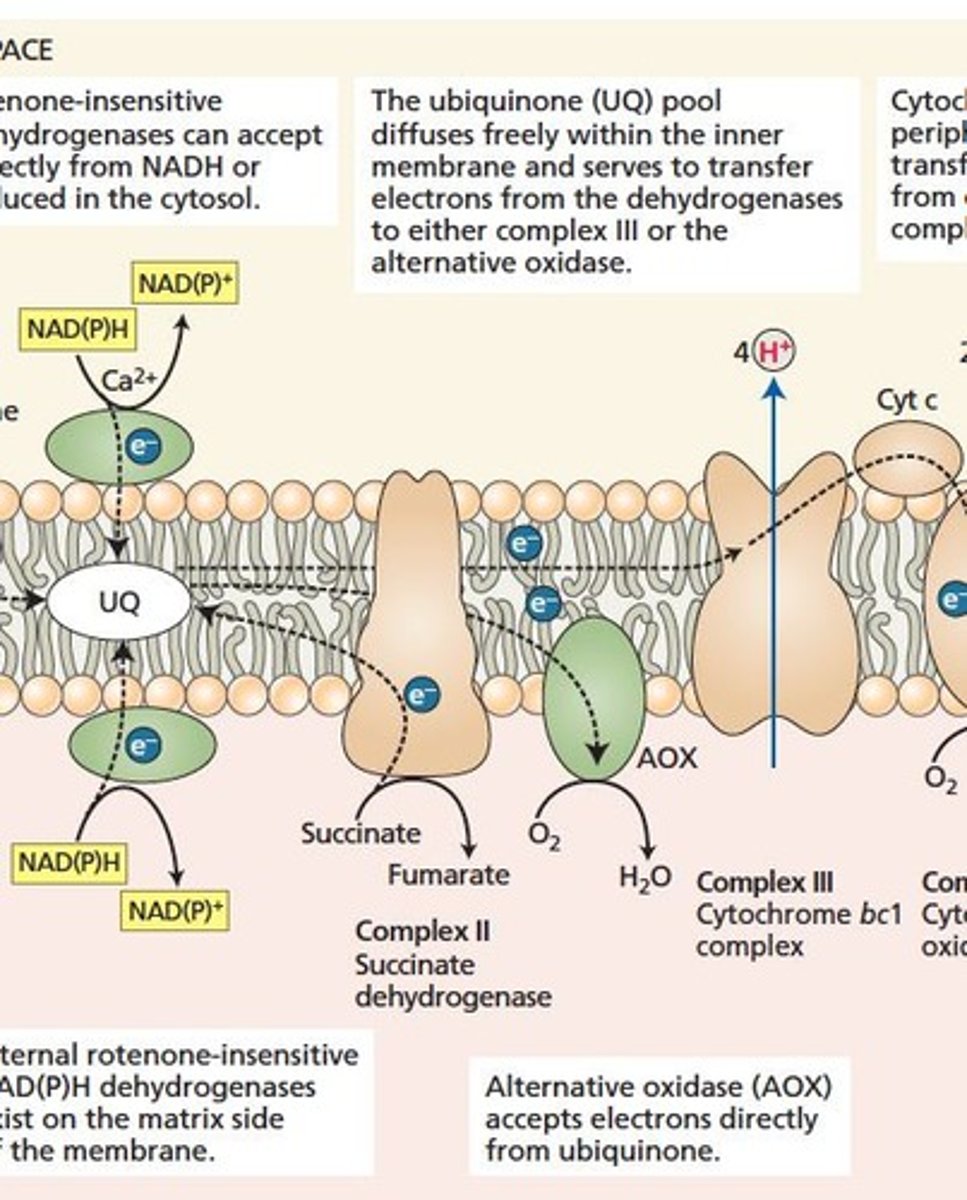
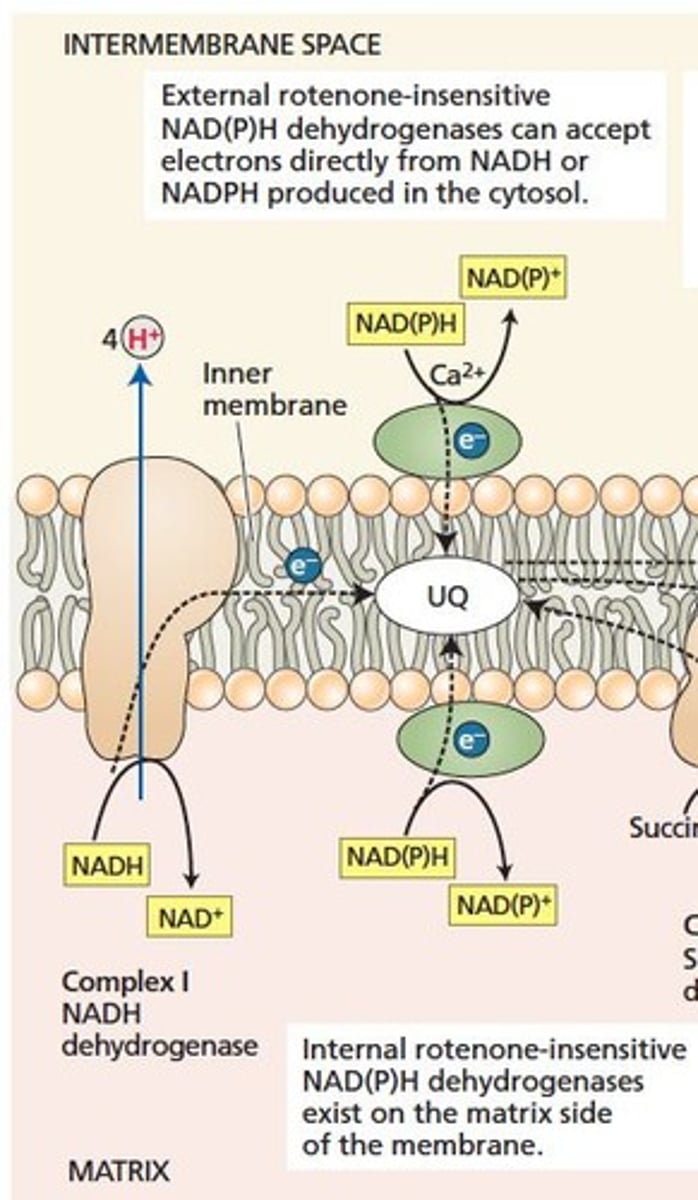
Complex I
NADH dehydrogenase transferring electrons to ubiquinone.
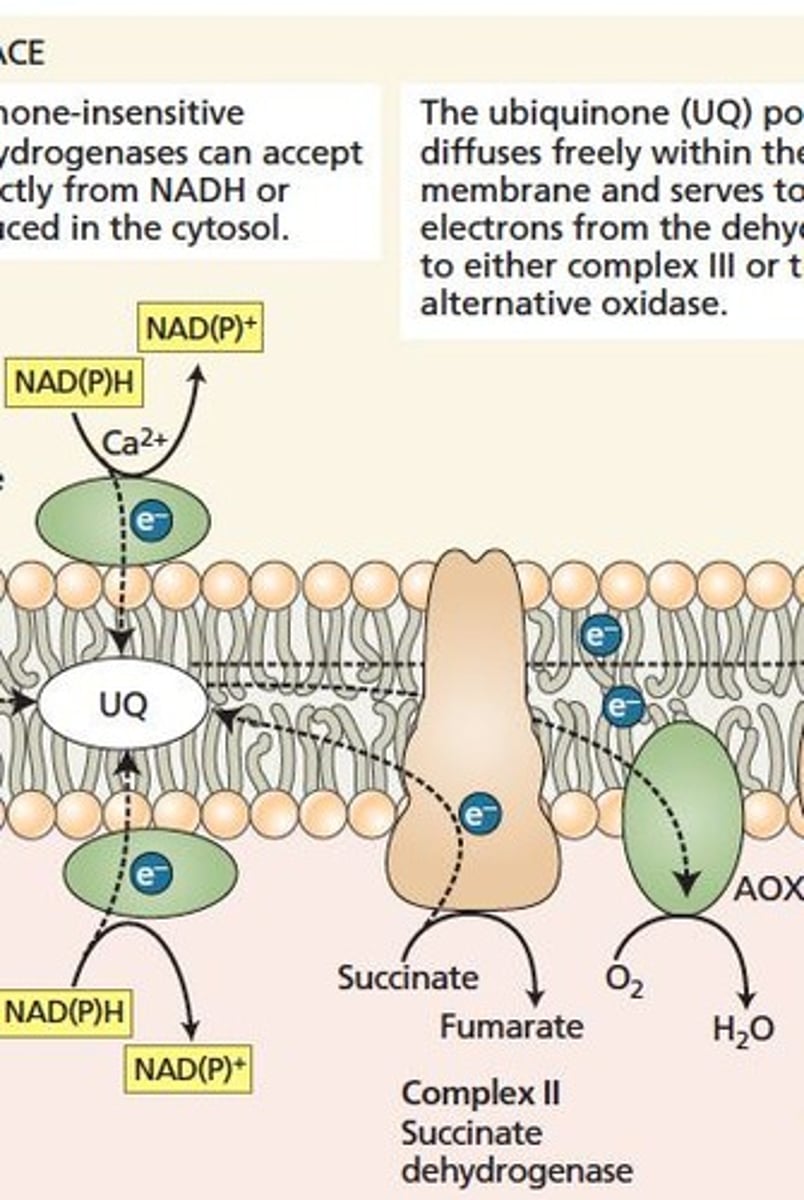
Complex II
Succinate dehydrogenase oxidizing succinate, no protons pumped.
Complex III
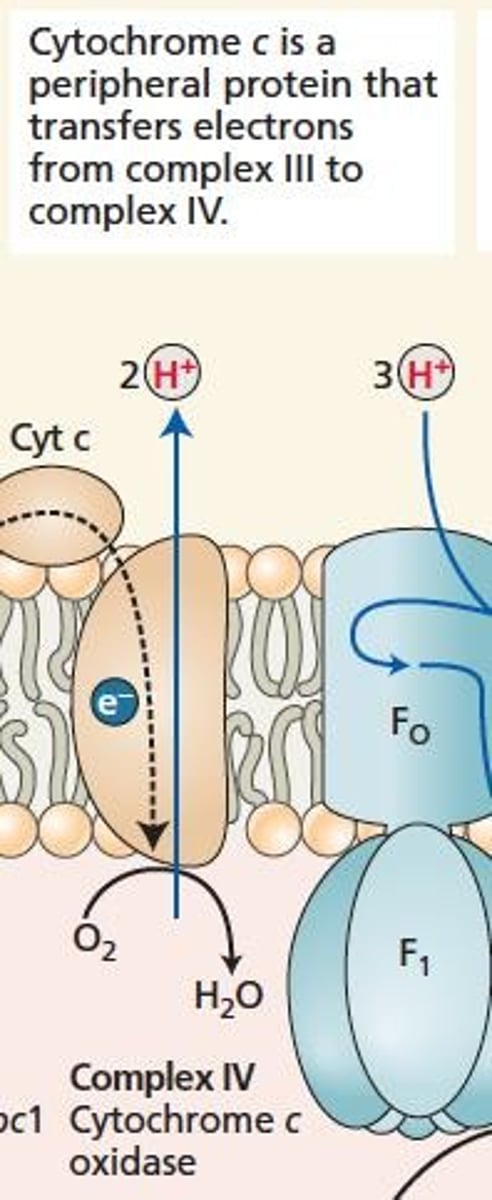
Cytochrome bc1 complex oxidizing ubiquinone, pumping protons.
Complex IV
Cytochrome c oxidase, terminal oxidase in electron transport.
Complex V
ATP synthase generating ATP from proton gradient.
Uncoupling Protein
Protein reducing ATP synthesis by dissipating proton gradient.
Alternative Oxidase
Plant-specific enzyme bypassing Complexes I and II.
Electron Transport Chain
Series of complexes transferring electrons to produce ATP.
Energy Loss
48% of energy lost as heat during respiration.
Mitochondrial Matrix
Site of Krebs cycle and pyruvate conversion.
Intermembrane Space
Region where protons are pumped during oxidative phosphorylation.
Acetyl-CoA
Key substrate entering the Krebs cycle from pyruvate.