4.5.3 Public Sector Finances
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Define a budget deficit.
A budget deficit occurs when public expenditure is greater than tax revenue.
Define automatic stabilisers.
Automatic stabilisers are automatic changes to the government expenditure and revenue budget as the economy moves through stages of the business cycle which helps to stabilise the economy.
How do automatic stabilisers reduce inflationary or deflationary pressure on the economy?
In a recession, benefits increase as more people are unemployed and so the benefits are a stabiliser as it means that the overall fall in AD is reduced, preventing too much change in the economy.
On the other hand, during a boom, tax increases as people have more jobs and higher incomes, and this tax reduces disposable income so decreases consumption and AD, meaning that demand doesn’t grow too high.
Illustrate automatic stabilisers reducing inflationary pressure on the economy on a diagram.
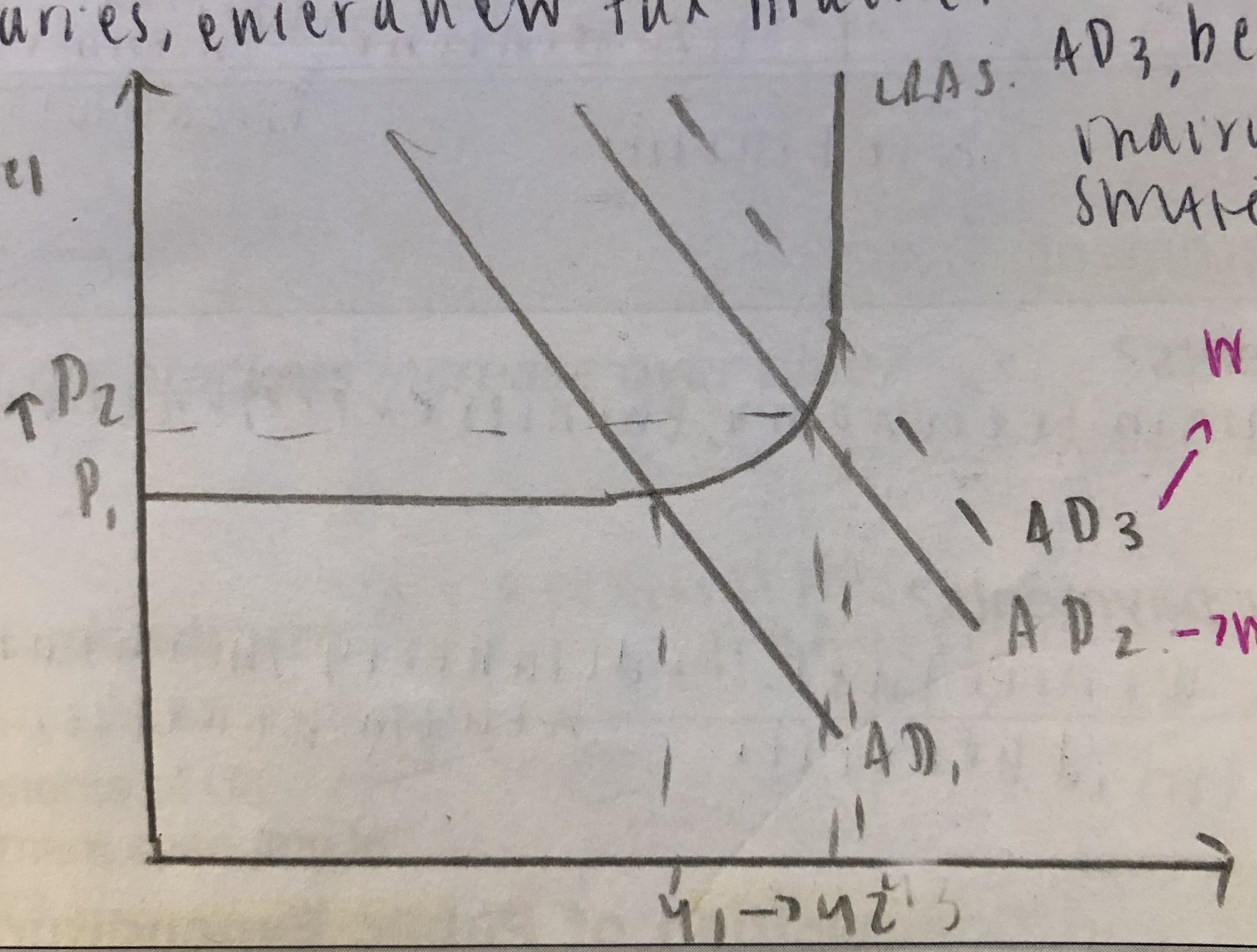
What are the downsides of automatic stabilisers?
These automatic stabilisers cannot prevent fluctuations; they simply reduce the size of these problem and there can be negative aspects to these stabilisers. Benefits may act as a disincentive to work and lead to higher unemployment whilst high levels of tax can decrease the incentive to work hard.
Define discretionary fiscal policy.
Discretionary fiscal policy is the deliberate manipulation of government expenditure and taxes to influence the economy; expansionary and deflationary policies.
What is the difference between a fiscal deficit and national debt?
The national debt is the sum of all government debts built up over many years whilst a fiscal deficit is when the government spends more than it receives that year.
What was the UK’s budget deficit and national debt stats in 2024?
budget deficit of £86 billion
debt of 97.3% of GDP
What are the two types of fiscal deficits?
Cyclical deficits
Structural deficits
What is the business cycle?
The business cycle is based on the simple observation that virtually all economies are in a cycle where they move from negative economic growth, known as a bust, to positive economic growth, known as a boom
What is an example of an economic boom and busts?
USA during 1918-1929 saw a boom, continuous growth driving a 50% increase in output. In 1929 the economy went bust as the stock market crashed. Unemployment went up to 25%
1982 Chile hit a bust decreasing GDP by 14.3%
1991 Japan went into recession, deflationary spiral occured in the economy
Why is there an overall long run trend of increasing GDP in the business cycle?
Due to long run improvements in technology
eg AI
Define a cyclical deficit?
A cyclical deficit occurs when public expenditure increases and tax revenue decreases during a recession.
A cyclical deficit is the part of the deficit that occurs because government spending and tax fluctuates around the trade cycle. When the economy is in recession, tax revenues are low and spending is high creating a larger deficit.
Explain a cyclical deficit.
An increase in unemployment, due to low derived demand for labour, during a recession means spending on benefits will increase and income tax revenue will decrease. However, when the economy begins to recover there will be a decrease in unemployment, a decrease in public spending and an increase in tax revenue improving the budget.
Define a structural deficit,
Structural deficits are the budget deficits that remain at any stage of the business cycle. This means a country is accumulating debt at every point of the business cycle
What is argued about structural deficits?
it is argued that structural deficits need to be eliminated but this is difficult since it is impossible to know what part of the deficit is structural and what part of it is cyclical, just as it is impossible to know the size of the output gap.
What are 3 factors influencing the size of fiscal deficit?
Trade Cycle- as explained by the concept of cyclical and structural debts. During a downturn, government tax revenue decreases whilst government spending increases and so the deficit increases. In the UK, the fiscal deficit peaked in 2010 at 10.1% of GDP.
Unforseen events- such as natural disasters or recessions, lead to huge increases in spending which increase the deficit. even covid
Government aims -are important in the size of the deficit, as this will influence their fiscal policy, for example the austerity aim has helped to decrease the size of the deficit but attempting to increase AD would increase spending. The austerity policy managed to reduce the fiscal deficit by 75% since 2010
Define national debt.
The total debt built up by government borrowing over time.
What 2 factors influence the size of national debts?
Continuous fiscal deficits
Ageing population. tend to contribute to a high national debt since the government runs a structural deficit in order to fund their pensions and care and this leads to a high national debt.
What is the consensus view of fiscal deficits and its relationship with national debt?
fiscal deficits over 3% will lead to growing national debt as a proportion of GDP
What is a method of government borrowing?
Government bonds, also known as treasury bills
How do government bonds work?
Government bonds are a form of government borrowing. The government sells bonds to investors, individuals, banks and businesses. In return, the government agrees to pay back these investors with interest. This could lead to governments owing back a lot of money and increasing national debt.
What are China, USA and UK’s current national debt?
China is $1.5 trillion
US is 20 trillion
UK is 2 trillion
On what 4 aspects is budget deficits and national debt significant?
Interest rates
Financial crowding out
Future generations
Economic growth
How do budget deficits impact interest rates?
If a country has a budget deficit, the government will need to borrow money in order to fund its public expenditure. An increase in government borrowing will increase the demand for money. This will then increase the price of borrowed money, which is known as the interest rate.
How do budget deficits lead to financial crowing out?
If a country has a budget deficit, the government will need to borrow money in order to fund its public expenditure. An increase in government borrowing will increase the demand for money. This will then increase the price of borrowed money, which is known as the interest rate. This will increase the cost of borrowing for private sector firms, which means they will decrease their investment and this is called financial crowding out.
How do budget deficits and national debt impact future generations?
As the government borrows more and more money to fund a budget deficit, the national debt will increase. The government will also have to pay more interest. A high national debt will need to be paid back at some point. In order to do this, the government will either need to increase taxes or decrease public expenditure - or a combination of both.
What is one positive impact of budget deficits and national debt?
On the other hand, government borrowing can benefit growth if it used for capital spending since this will improve the supply side of the economy and thus reduce the deficit in the long term. On top of this, the budget deficit can be used as a tool for short term demand management: Keynesians argue a deficit is acceptable to use as a stimulus in demand during recessions.