Electrical Currents for Pain Control
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
SUBJECTIVE, not always tissue damage
What is pain?
nociceptive, neuropathic, somatoform
the three types of pain are _____, ______, and _____
Nociceptive
______ pain is stimulation of nerve fibers that respond to stimuli approaching or exceeding harmful intensity
Thermal, Mechanical, Chemical
Nociceptive pain can be _____, _____, or ______
nociceptive
Visceral pain is a type of ______ pain described as diffuse and dull, hard to locate
nociceptive
Deep somatic pain is a type of ______ pain typically in joints, tendons, or ligaments but the patient can’t usually pinpoint
nociceptive
Superficial Somatic pain is a type of _____ pain described as easy to locate typically found with burns
Neuropathic
_______ pain is described as “Burning, tingling, electrical, stabbing, pins & needles” or phantom limb pain and neuropathy
Somatoform
______ pain, also called psychogenic, is described as pain caused, increased, or prolonged by mental, emotional, or behavioral factors
Acute Pain
________ typically needs medial, pharmacologic, and rehab care (warning system and expectation of resolution)
Chronic
______ is less defined with no biologic benefit and is often pain that persists beyond the normal time of healing
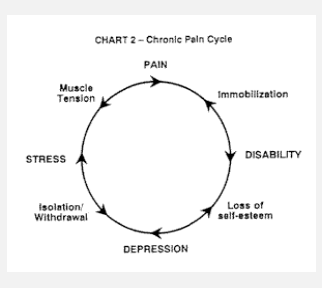
F; only takes 3 months
T/F: it takes 6 months to determine if pain has switched to chronic state
A-alpha fibers, 80-120
_______ are myelinated fibers that carry proprioception info at ______m/s with a diameter of 13-20 micrometers
A-beta fibers, 35-90
______ are myelinated fibers that carry touch info at _____m/s with a diameter of 6-12 micrometers
A-delta fibers, 5-40
______ are myelinated fibers that carry pain (mech & thermal) info at _____m/s with a diameter of 1-5 micrometers
C fibers, 0.5-2
______ are non-myelinated fibers that carry pain (mech, thermal, and chem) info at _____m/s with a diameter of 0.2-1.5 micrometers
F; A-beta are faster with conduction speed of 35-90 m/s
T/F: C fibers conduct faster than A-beta fibers
C
All of the following are myelinated fibers EXCEPT:
A-alpha
A-beta
A-delta
C
Ascending, dorsal
_____ nociceptive pathways are for sensory and afferent info through the ______ root
Descending, ventral
______ nociceptive pathways are for motor and efferent info through the _____ root
A-delta, C
the ascending nociceptive pathway includes Fast and Slow fibers: _____ fibers and _____ fibers
fast and well-localized, withdrawal reflex
Myelinated A-delta fibers assist in _______ pain or ______ like touching a hot object
slow transmission/longer lasting
Non-myelinated C fibers assist in _______ pain also described as diffuse dull pain
fun fact: this accounts for 70% of all nociceptive pain
CNS, top-down
Motor/efferent info starts in the ______ and diminishes the ascending signals via a ______ mechanism
opinion
Pain is not a reflexive response, it is an ______
Gate Control Theory
_______ of pain has 3 gates (spinal cord, brainstem, and prefrontal cortex)
one gate gets closed and makes it harder for pain signal to get through to the other two
may be ascending or descending
A-beta, inhibitory interneurons
E-Stim is the activation of ______ nerves that close a gate by activating _______ in the spinal cord
Endorphins
________ help to modulate the pain gates in the spinal cord
bind to opioid receptors
released during exercise and laughter
Black Torpedo Fish
Back in older times, the ________ was used to treat conditions like gout and headaches
1965
After _____, TENS became more popular because it was a non-pharmacalogical option for pain relief
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation
TENS stands for __________
TENS
the purpose of ______ is to reduce acute, chronic or post op
pulsed biphasic (sym or asym)
the most common waveform used with TENS is __________
conventional/high rate, low rate, burst mode, brief intense
the four types of TENS are: _________, _________, _________, and ________
Conventional, Gate Control, A-beta
_______ TENS is used for sensory level estim ONLY via the ______theory of pain which blocks pain by stimulating the ______ fibers
high, low, short
with conventional TENS, use a ____ frequency, ____ intensity, and ____ pulse duration — goal is ONLY SENSORY level
Sensory-only effect — WE ARE NOT LOOKING FOR A MOTOR RESPONSE/TWITCH
the goal of conventional TENS is
F; very short term effect, maybe 2-3 hrs or during treatment
T/F: with conventional TENS, the pain relief/treatment effect occurs for 4-5 hours after
F; place electrodes on or around sites of pain or even over the nerve innervation (motor points don’t matter as much with TENS)
T/F: with TENS, you must place electrodes over motor point and avoid painful areas
A-beta
Conventional TENS works to block pain which is transported by ______ nerve fibers
Conventional
Parameters for ________ TENS:
F = 80-150 Hz/pps
PD = 50-100 microsec
On:Off Time = continuous
I/A = strongest, comfortable paresthesia (no motor response)
Tx Time = 15-20 min
Effect Time = 2-3 hrs MAX, primarily DURING tx
Modulation = maybe use it if it’s available (start with Amplitude first)
Low Rate
_____ TENS is also called acupuncture-like TENS
opioid release
Low Rate TENS is based on endogenous __________ of endorphins that bind to opioid receptors in the descending pathways
motor response (twitch NOT tetani)
Low Rate TENS requires a _______ by working with A-beta and A-alpha nerve fibers
low, high, long
For Low Rate TENS, do a _____ frequency, _____ intensity, and _____ pulse duration — this will have a longer/slower start, so give it a few minutes to take effect
True! this will help to increase the blood flow to that area and mechanically loosen the tissue —> MUST follow up with stretching new loosened tissue to use new ROM
T/F: Low Rate TENS can be used for trigger points or any area where muscle tension is present
True
T/F: for Low Rate TENS, the electrodes should be placed on trigger points or areas of muscle tension
F; give it 5-10 minutes for patient to feel it
T/F: Low rate takes a very short time to kick in
Low Rate
Parameters for ____ TENS:
F = < 10 Hz/pps
PD = 200-300 microsec
On:Off Time = continuous
I/A = Rhythmic muscle twitches (NOT tetani)
Tx Time = 20-30 min (MAX is <45)
Effect Time = 4-5 hrs
Modulation = Frequency!!
A-delta, Natural Endorphin Release
Low Rate TENS will sometimes affect _____ nerve fibers which deal with pain. This could help to amplify the _________ —> this is why the patient MIGHT feel short bouts of pain during treatment
pulse duration
If your patient cannot increase amplitude, you should change the ________ to increase the motor response
Low Rate
The goal of _______ TENS is to get patient to 20 min of motor response without making them too sore after tx
Burst Mode
if Low Rate TENS is too much for the patient, you should switch them to (conventional/burst mode/brief intense) TENS
True; still gets motor response but its more comfortable muscle contractions for patient
T/F: Burst mode is a combo of Conventional and Low Rate
Burst Mode
Parameters for ________ TENS:
F = 100 Hz/pps, delivered at 2 Hz
PD = 150-200 microsec
On:Off Time = continuous
I/A = Rhythmic muscle twitches (NOT tetani)
Tx Time = 20-30 min (MAX is <45…avoid DOMS)
Effect Time = 4-5 hrs
Modulation = not usually possible
False
T/F: Burst mode is more effective than Low Rate
high, low, long
For burst mode, use ____ frequency bursts/trains of pulses delivered at ___ frequency with ____ pulse duration — this will cause more comfortable mms contractions for the patient
wound debridement, c sections
Brief Intense TENS can be used before ______ and post ______
Brief Intense, Noxious
_________ TENS is short, local hypoalgesia for minor painful procedures at the _____ level
high, highest tolerable, long
Brief Intense TENS uses a _____ frequency, ______ amplitude, and____ pulse duration — essentially BEYOND max tolerated
superficial somatic
What type of nociceptive pain occurs when you cut yourself shaving?
endogenous opioid/endorphin release
what is the mechanism of action with Low rate tens
a-beta for sensory level NOT pain
conventional tens seeks to activate which type of nerve fibers?
a-delta
which type of nerve fiber is the fastest conductor of pain?
low rate
which type of TENS are you MOST likely to utilize for a trigger point?
75 microseconds
which pulse duration are you MOST likely to use with conventional tens?
frequency
which parameter is BEST to modulate with low rate tens?
conventional/high rate
which type of tens is BEST for pain control after a recent injury?
F; use high rate
T/F: use low rate and burst mode TENS with inflammation
conventional/high rate
You should use ____ TENS with your “touchy” patients, aka those who ALWAYS rate their pain 12/10 — they will be able to tolerate sensation but NOT mms contraction
conventional aka high rate
with a recent injury, you should use (conventional/low rate/burst mode/brief intense) TENS
FALSE »» use for chronic injuries where there is a longer tx effect and longer duration of pain control
T/F: low rate tens is used with acute injuries
smaller pads
With TENS on paraspinals, use _____ when there is a specific area of pain or trigger point
larger pads
with TENS on paraspinals, use _____ when there is more diffuse pain
smaller pads
for tens around the knee, use _____ for specified pain like medial compartment
larger pads
for tens around the knee, use _____ for general pain
bony prominences
ALWAYS AVOID _______ but tens is more forgiving about this compared to NMES as tens doesn’t really require motor points
False!!! TENS only requires rhythmic muscle twitches NOT tetani
T/F: both NMES and TENS focus on max muscle contraction
Modulation
_______ options include:
M: decrease pulse width 40% for 2”, returns for 3.5” (conventional)
SD1: decreases pulse rate 50% for 2”, returns for 7” (low rate, frequency)
SD2: decrease pulse width 60% for 2”, returns for 3.5”
DO NOT
For portable TENS and chattanooga machines, you (do/do not) cross the channels when placing electrodes around the area of pain
is pt appropriate for tx
clean skin and remove excess hair
connect leads to unit and electrodes
securely place electrodes
adjust parameters
slowly increase amplitude (take till pt feels sensation, then keep going till pt says too painful, then back down a little)
gently remove electrodes and assess skin condition
pt education (if home unit, wear times/parameters/placement and care of electrodes/skin care/batteries)
APPLICATION OF TENS (just read thru…its a lot and you know this)
120 pps, 75 microsec
which of the following settings is the MOST appropriate for conventional tens?
4 pps, 200 microsec
120 pps, 75 microsec
4 pps, 75 microsec
120 pps, 200 microsec
thought to relieve pain based on the gate control theory (endogenous opioid release!!!)
which of the following statements is MOST true about low rate TENS?
pulse frequency should be between 10 and 20 pps
thought to relieve pain based on the gate control theory
treatment time should be no longer than 45-60 minutes
amplitude should be increased until mms contraction occurs
IT DEPENDS :) hehe
think about goal, amt. of pain, schedule for rest of day
when is it MOST appropriate to use TENS application, before or after tx?
Interferential Current
what does IFC stand for
medium frequency
IFC is interference of 2 _________ alternating currents with slightly different frequencies (but same intensities)
1000, 4-5k
IFC can range anywhere from ____ to 10,000 Hz with a midrange at _________ Hz
IFC
______ (aka Amplitude Modulated AC) is delivered through 2 sets of electrodes from separate channels in the same machine
FALSE: currents intersect ON the skin
T/F: with IFC, the alternating currents interfere WITHIN the machine before they’re in contact with the skin
In Sync/Phase
When IFC currents are ______ there is constructive interference, meaning they line up with each other
Out of Sync/Phase
When IFC currents are ______ there is destructive interference, meaning they are opposite of each other
beats
IFC produces “envelopes”/bursts of pulses known as _____
beat frequency
_________ is the difference between the 2 frequencies also known as the therapeutic effect
ex: #1 @ 5000 Hz // #2 @ 5100 Hz
difference of 100 Hz
sensory level, motor level
the MOA for IFC is mainly _____ but can be _____ via gate control theory and opioid mechanism
True-ish, some research supports this as IFC might reach deeper tissues compared to TENS
T/F: IFC can improve circulation
80-130
IFC using the gate control theory should be at ______ Hz
2-5
IFC using opioid mechanisms should be at _____ Hz
Sweep, Vector Scan
Two types of modulation for IFC is _____ and ____
Sweep
_____ is when the machine varies the beat frequency usually in a shape
preset or user sets ranges
not much evidence
Vector Scan
______ alters the amplitude on one or both currents
like the agitator of the washer (turns one way then turns other way)
might be better for larger areas