PSY 101 Chp.4-7
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
The process by which sensory receptors convert a stimulus into a neural impulse. (Specific receptors stimulate specific neurons in the CNS.)
The process of analyzing and filtering incoming sensations before sending a neural message to the cortex. (Brain-based reduction)
Attending only to important sensory info by filtering out unimportant information. (Brain-based reduction)
Decreased response to repeated or constant stimuli resulting in less sensory messages being sent to the brain. (Brain-Based reduction)
What is habituation?
A sensory-organ based decreased response to a stimulus after repeated exposure to it. Ex. Spicy foods become less spicy the more you eat them.
Where is and what is the function of the fovea?
Located in the center at the back of retina, this area contains only cones. So, it’s responsible for seeing fine detail and color.
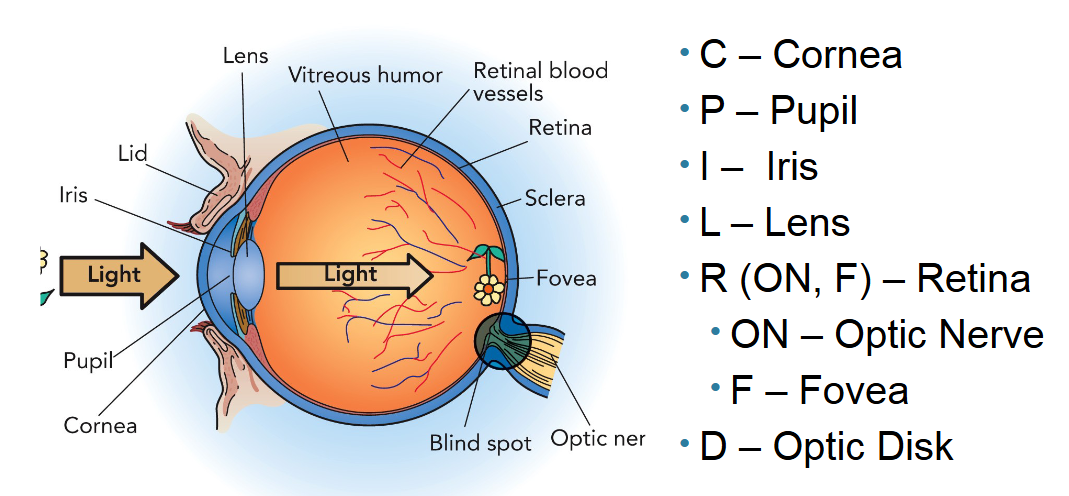
Where is and what is the function of the lens?
Located behind the iris. It’s responsible for seeing things up close and farther away by thickening and thinning respectively.
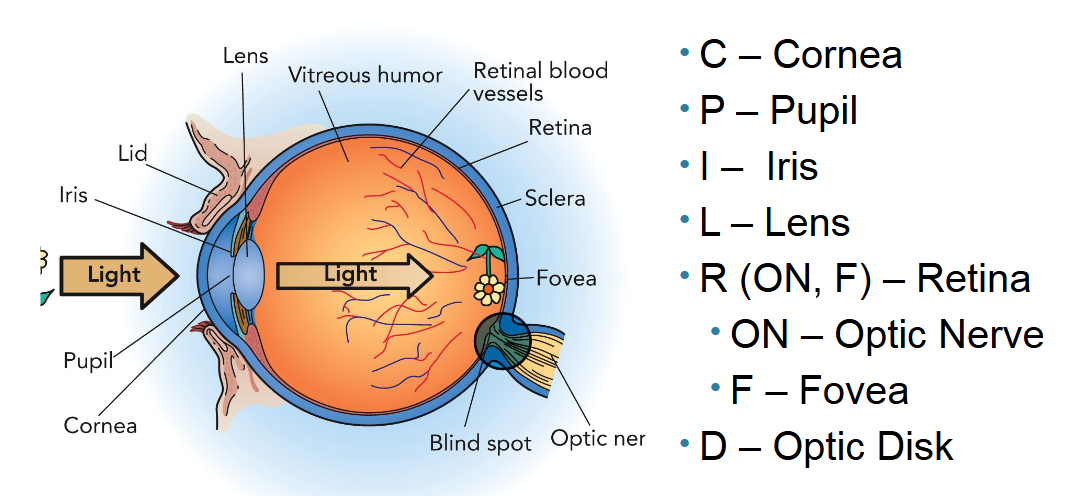
What is the function and where is the retina?
It’s the inside lining tissue of the eyeball. It contains all photoreceptors (rods and cones) to covert light/visuals into vision signals.
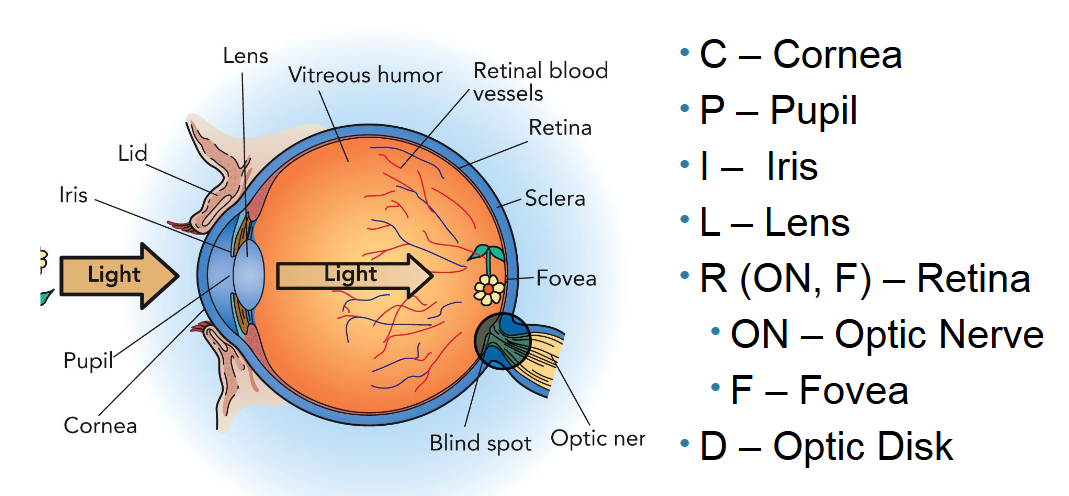
Where and what is the function of the optic nerve?
The optic nerve is located at the back of the eye, connecting the retina to the brain. Its function is to transmit visual information from the retina to the brain for processing.
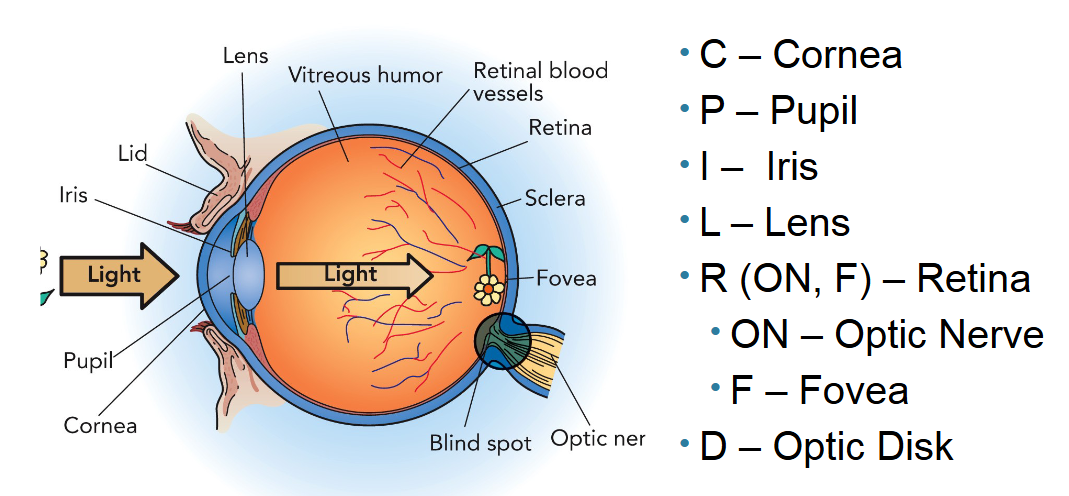
What is the optic disk?
The optic disk is the point on the retina where the optic nerve fibers exit the eye. This produces a blind spot because there are no photoreceptors at that spot.
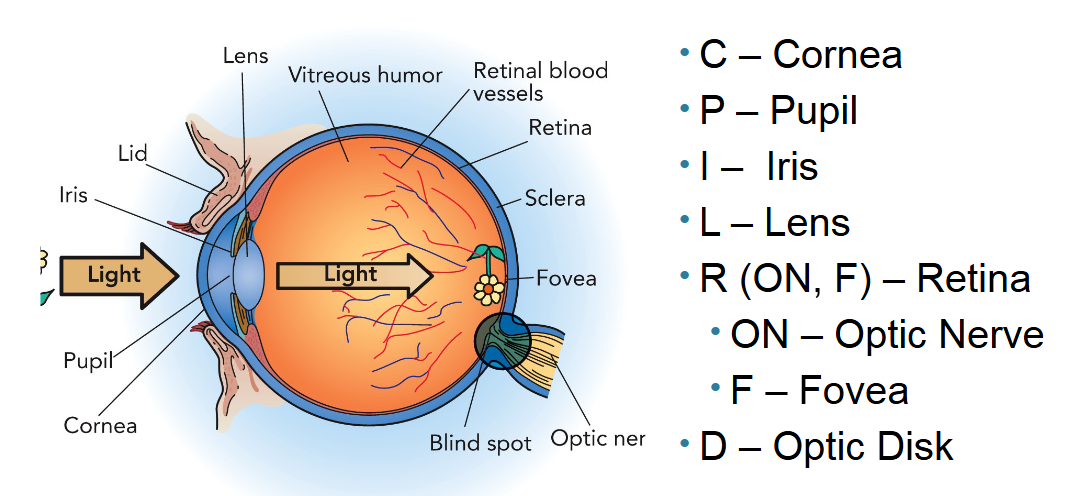
What are cones?
Photoreceptor cells that transduce info about fine detail and color.
What are rods?
Photoreceptor cells that transduce info about black, white, and grey. They surround the outside of the fovea.
What is trichromatic theory?
States that there are three types of cones (red, green, and blue) in the retina that are sensitive to different but overlapping wavelengths of light.
What makes up the outer ear?
The pinna, ear canal, and tympanic membrane.
All are responsible for funneling soundwaves from the outside and amplifying it to the middle ear.
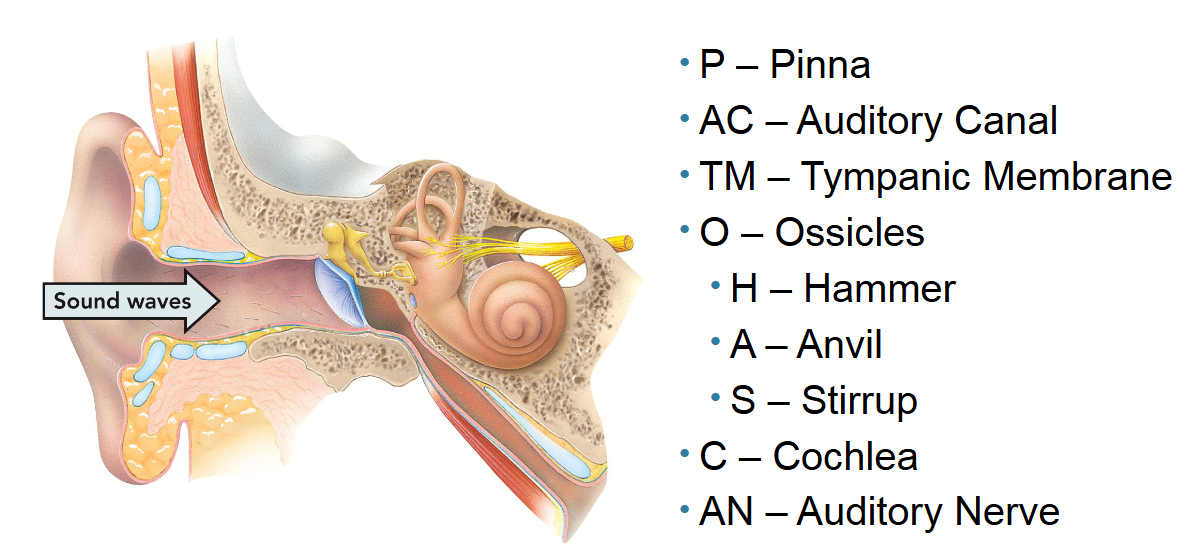
What makes up the middle ear?
The ossicle bones (anvil, hammer, and stirrup). They further amplify the sound waves to the inner ear.
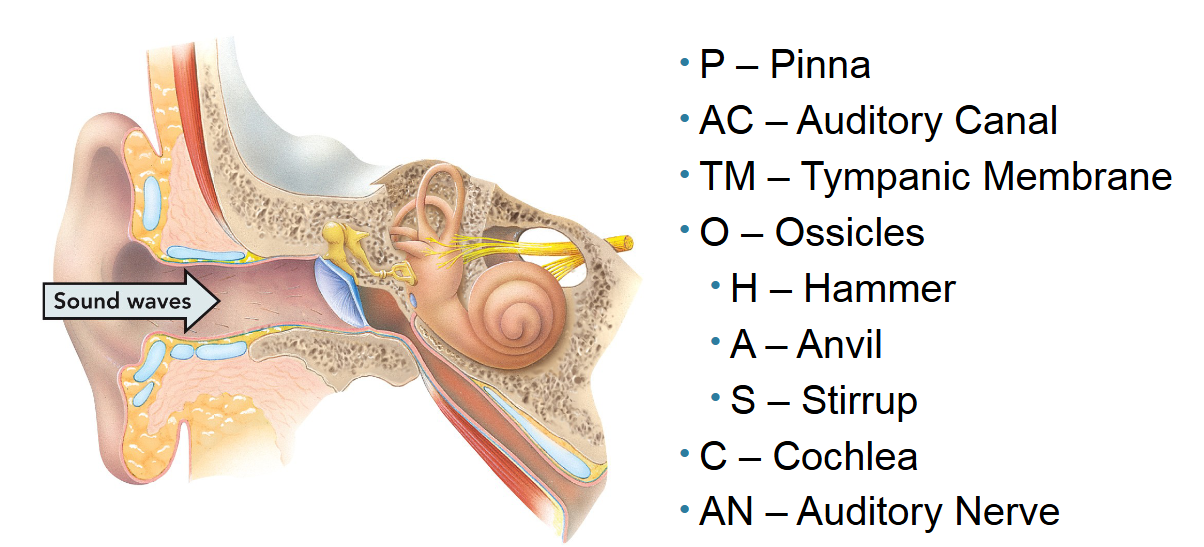
What makes up the inner ear?
The cochlea and auditory nerve. The cochlea are hair-like cells that are receptors for vibrations. The auditory nerve relays that stimulus to thalamus and then auditory cortex in the temporal lobe. Together they sense sound and where our head is positioned in space.
Different locations on the cochlea are stimulated by different pitches. (True for higher pitch sounds.)
Pitch is sensed based on the firing rate of the auditory nerve. (True for lower pitch/low frequency sounds).
What is perceptual parsing?
What are the critical features for perception?
Depth perception, constancy, and motion.
What is no awareness?
Unconscious processes such as associative learning. Freud believes we have unconscious thoughts that direct our behavior.
What is subconcious awareness?
Occurs when people are awake, sleeping, dreaming, incubation, and parallel processing. Basically processes that occur that don’t interfere with our awareness
What are altered states of consciousness?
Produced by drugs, trauma, fatigue. sensory deprivation, and possibly hypnosis. Basically a mental state that is not typical.
What is lower-level conciousness?
Automatic processing that requires little attention. Such as watching a sunset.
What is high-level consiousness?
When individuals actively focus their efforts on attaining a goal. Such as doing a math problem.
What are procedural memories?
Motor skills. Ex. riding a bike or driving a car.
What explicit memories?
Memories that involve conscious recall.
What is semantic memory?
Memories about general facts or knowledge. Ex. bananas are yellow.
What is episodic memory?
Memories about personal experiences/life events. Ex. when you graduated highschool.
The process of getting information out of storage and bringing it to awareness. It can be done by recall, recognition, or relearning.
A biological mechanism for learning and memory involving a long-lasting increase in neural excitability. Either through repeated stimulation or
Examples of neurotransmitters involved in memory
Epinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine.
Difference between fixed and variable interval reinforcement?
Fixed: Given after a fixed amount of time since last response.
Variable: Given after a variable amount of time since the last response,
Difference between fixed and variable ratio reinforcement?
Fixed: Reinforcement given after a fixed number of responses.
Variable: Reinforcement given after a variable number of correct responses. Usually centered around an average.
What is the basal ganglia’s and cerebellum’s role in memory?
Creation and storage of implicit and basic memory.
What is the hippocampus and surrounding area’s role in memory?
Holds explicit and implicit LTM and the sequences of events. It activates the areas of the brain associated with a memory.
What is the thalamus’ role in memory?
Formation of new, spatial, working, explicit, and implicit memory.
What is the cerebral cortex’s role in memory?
Responsible for the encoding, storage, and retrieval of explicit and implicit memories.