Musculoskeletal System
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
Normal Anatomy & Physiology Musculoskeletal System
The musculoskeletal system comprises bones, muscles, joints, tendons, and ligaments that provide structure, support, movement, and protection.
Bones: The adult human skeleton consists of 206 bones, classified as long, short, flat, or irregular.
Muscles: The body has over 650 named skeletal muscles, responsible for voluntary movements.
Joints: Allow movement and are categorized into synovial (freely movable), cartilaginous (slightly movable), and fibrous (immovable).
Tendons: Connect muscles to bones.
Ligaments: Connect bones to other bones
Physical Examination Techniques
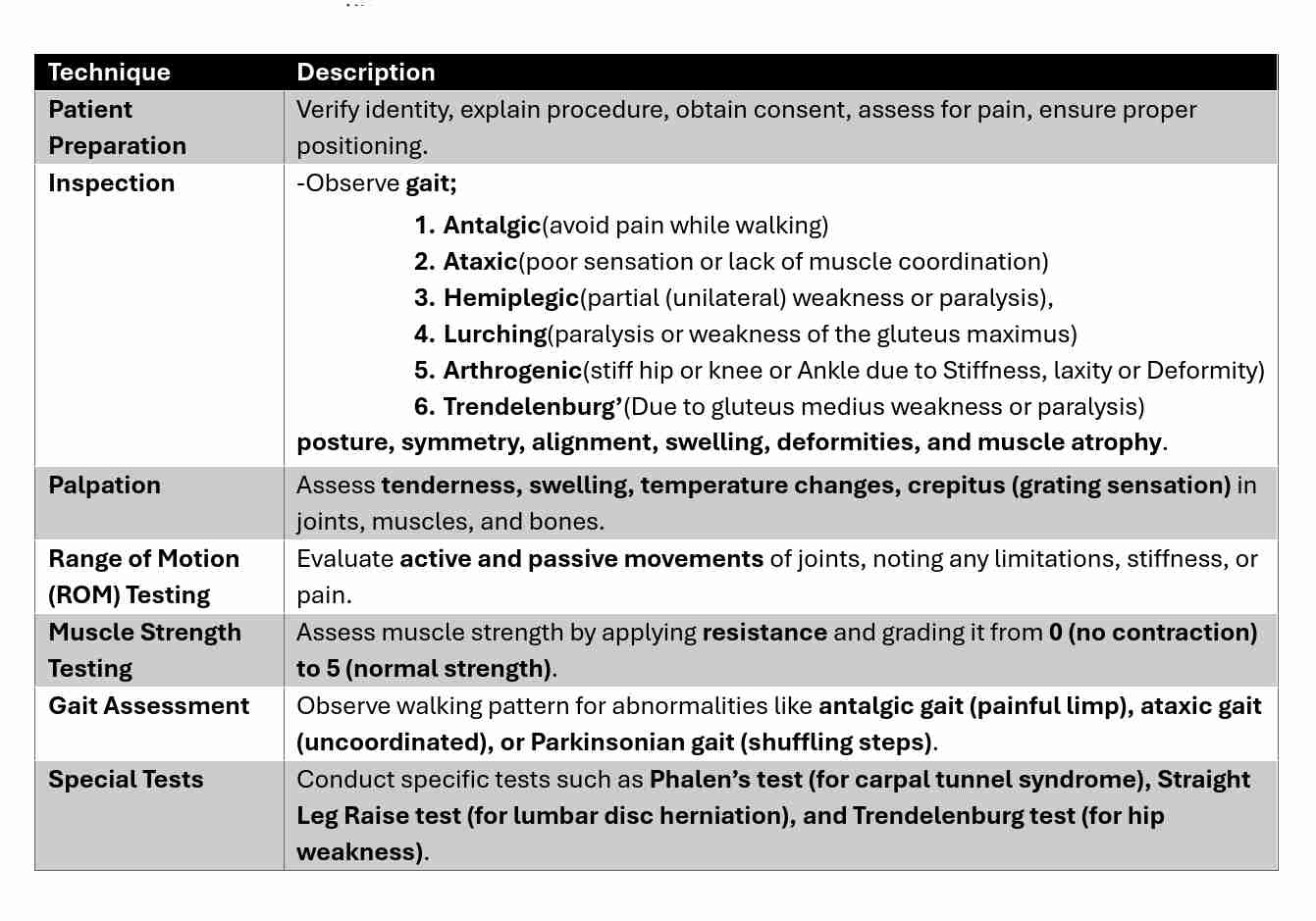
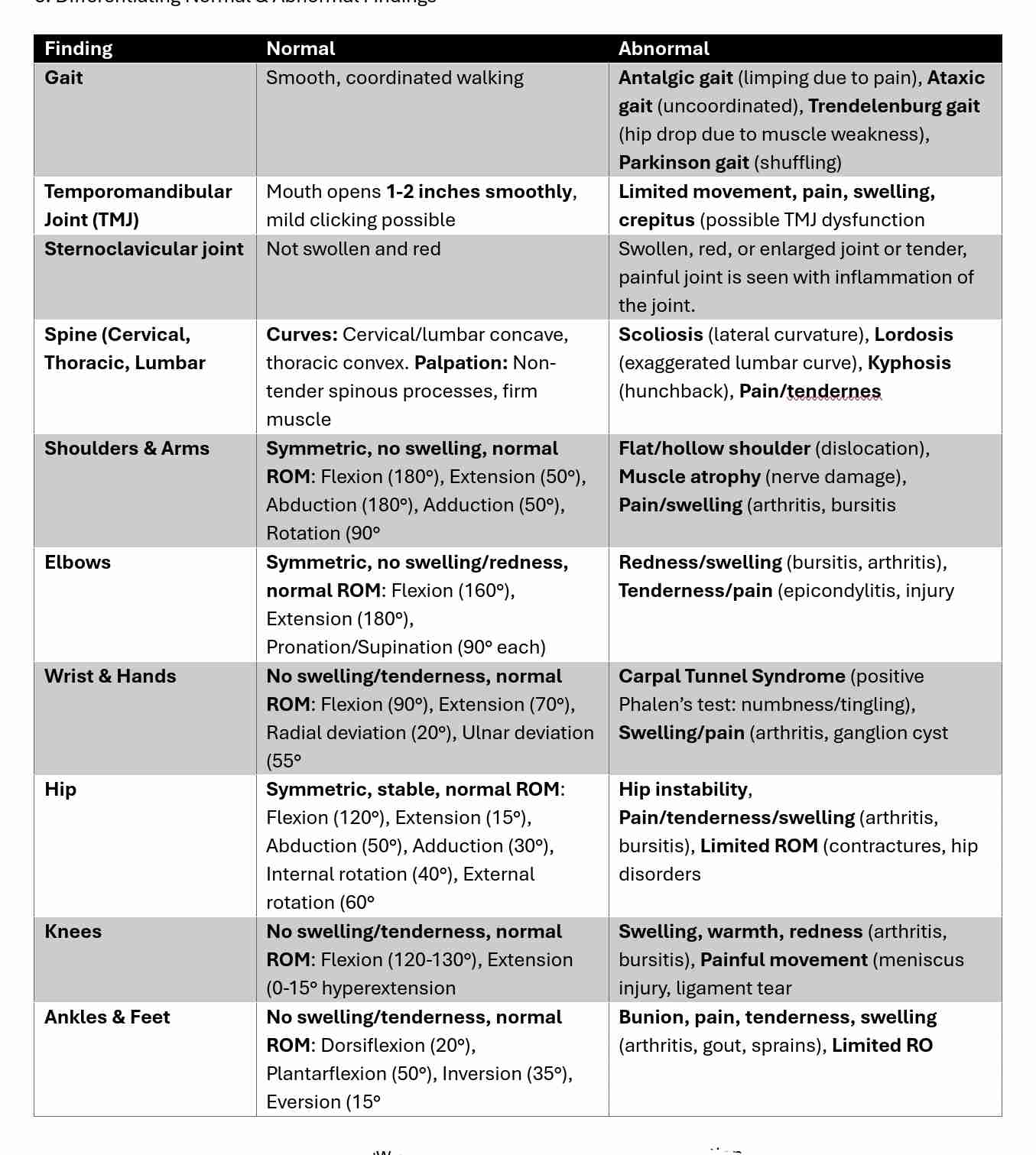
Differentiating Normal & Abnormal Findings
Analysis of Findings from Interview General survey & physical Examination
History Taking:
Pain (location, duration, severity, triggers)
Stiffness (morning vs. activity-related)
Swelling (chronic vs. acute)
Previous injuries (fractures, surgeries)
Family history (arthritis, osteoporosis)
Lifestyle factors (exercise, occupation)
General Survey:
Posture: Upright (normal), hunched (kyphosis), exaggerated curve (lordosis, scoliosis).
Gait & Mobility: Smooth (normal), limping (injury, arthritis), shuffling (neuromuscular disorder).
Muscle Symmetry: Even (normal), atrophy (disuse, nerve damage), hypertrophy (overuse).
Joint Appearance: Normal (no swelling), red/swollen (arthritis, gout).
Range of Motion (ROM): Full, pain-free (normal), limited/stiff (joint disease, contractures).
Functional Ability: Independent (normal), difficulty standing/walking (fracture, neurological disorder).
Physical Examination Findings:
Correlate observations with history (e.g., joint pain with swelling suggests arthritis).
Identify patterns of abnormality (e.g., bilateral joint pain suggests systemic disease).
Use functional assessments (e.g., gait abnormalities indicating neuromuscular issues).