Biology Study Guide: Taxonomy, Viruses, and Plant Anatomy
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Taxonomy
Classifies organisms based on shared characteristics and gives them names according to a hierarchical system.
Cladistics
Classifies organisms based on common ancestry and evolutionary relationships (uses cladograms).
Domains
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya.
Bacteria
Unicellular, prokaryotic, diverse metabolism.
Archaebacteria
Unicellular, prokaryotic, extreme environments.
Protista
Mostly unicellular, eukaryotic.
Fungi
Multicellular (mostly), decomposers, chitin cell walls.
Plantae
Multicellular, photosynthetic, cellulose cell walls.
Viruses
DNA or RNA, protein coat, infect all life forms.
Viroids
Small circular RNA molecules, no protein coat, infect plants.
Prions
Misfolded proteins, no nucleic acids, cause degenerative brain diseases in animals.
Prokaryotes
No nucleus, small/simple, no membrane-bound organelles, includes Bacteria and Archaea.
Eukaryotes
Have nucleus, larger/more complex, have organelles, includes Protists, Fungi, Plants, Animals.
Archaea
Extremophiles, unique membranes and genes, no peptidoglycan in cell wall.
Bacteria
Found everywhere, cell walls contain peptidoglycan.
Xylem
Transports water.
Phloem
Transports sugars.
Seeds
Protect and nourish embryo.
Fruits
Aid in seed dispersal.
Roots
Anchor plant, absorb water/nutrients.
Stems
Support plant, transport materials.
Monocots
Plants with fibrous roots, scattered vascular bundles, parallel veins, flowers in multiples of 3, and one cotyledon.
Dicots
Plants with taproot system, vascular bundles in a ring, net-like veins, flowers in multiples of 4 or 5, and two cotyledons.
Comparative Anatomy
Look for similarities and differences in structural features like leaf shape and venation, root and stem arrangement, flower anatomy, and cell types and organization.
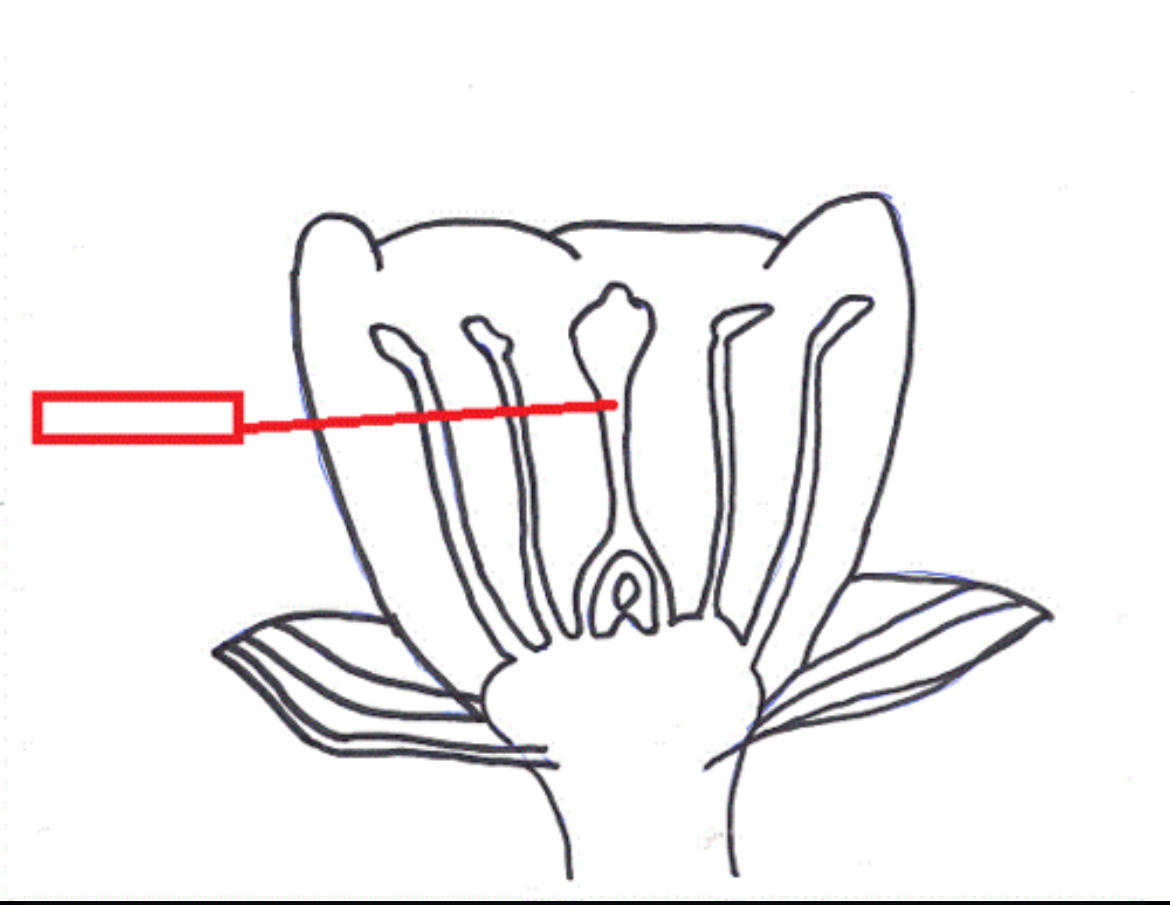
Anther
Male part of the flower where sperm (pollen) are produced by meiosis
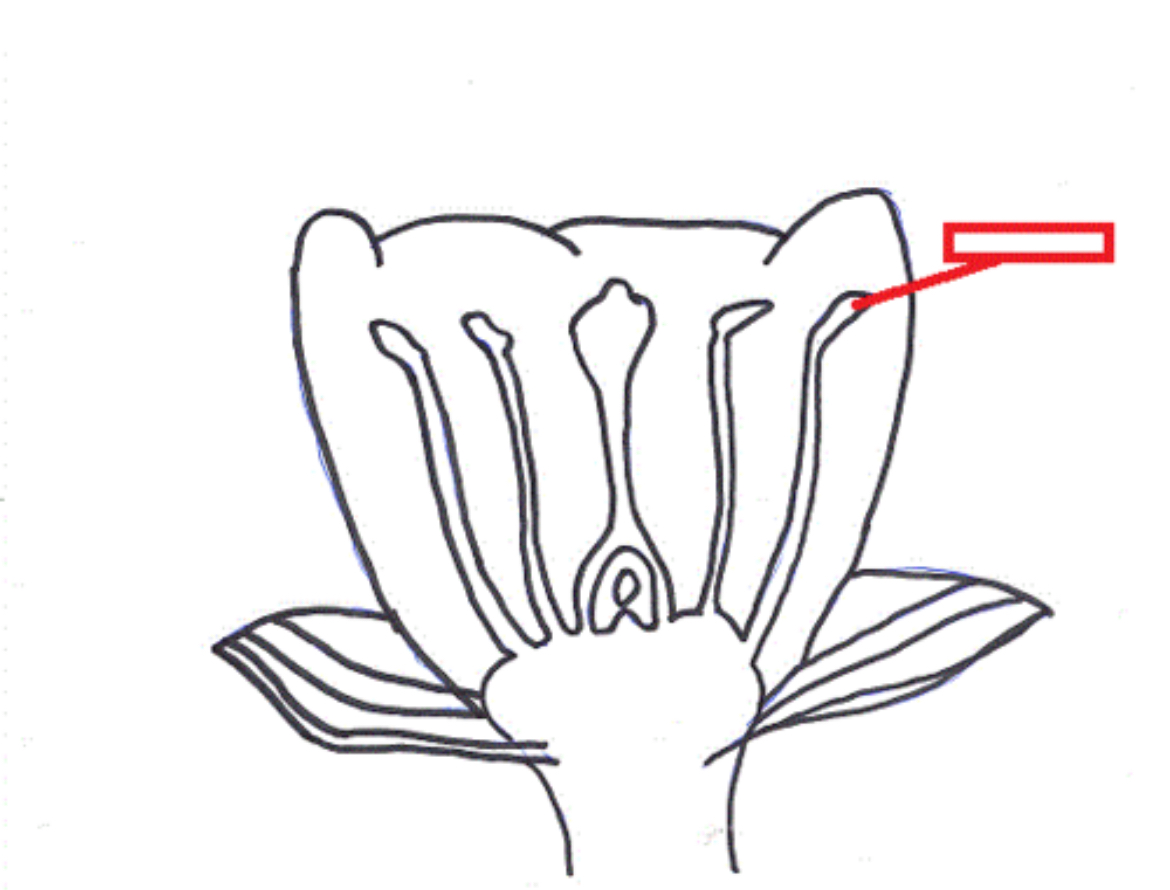
Filament
Supports the Anther
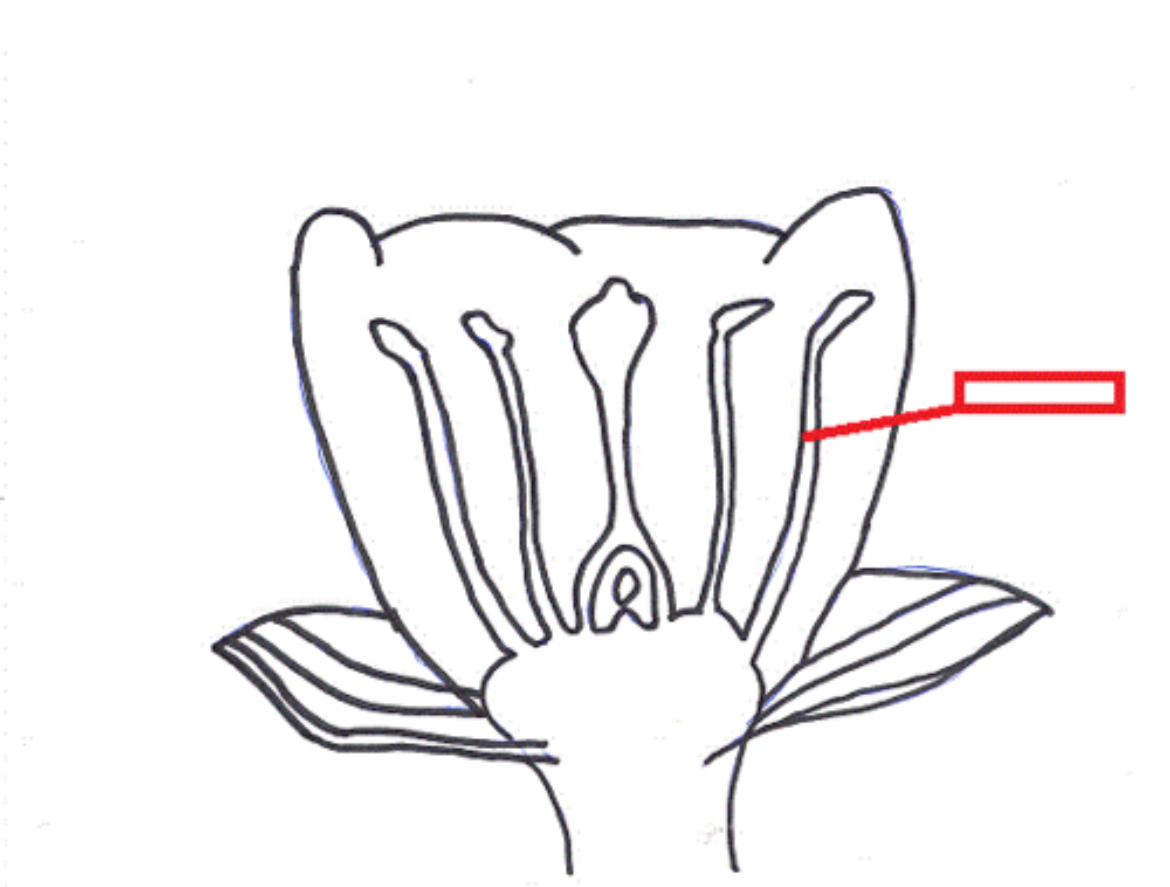
Ovary
A flower structure that encloses and protects ovules and seeds as they develop.
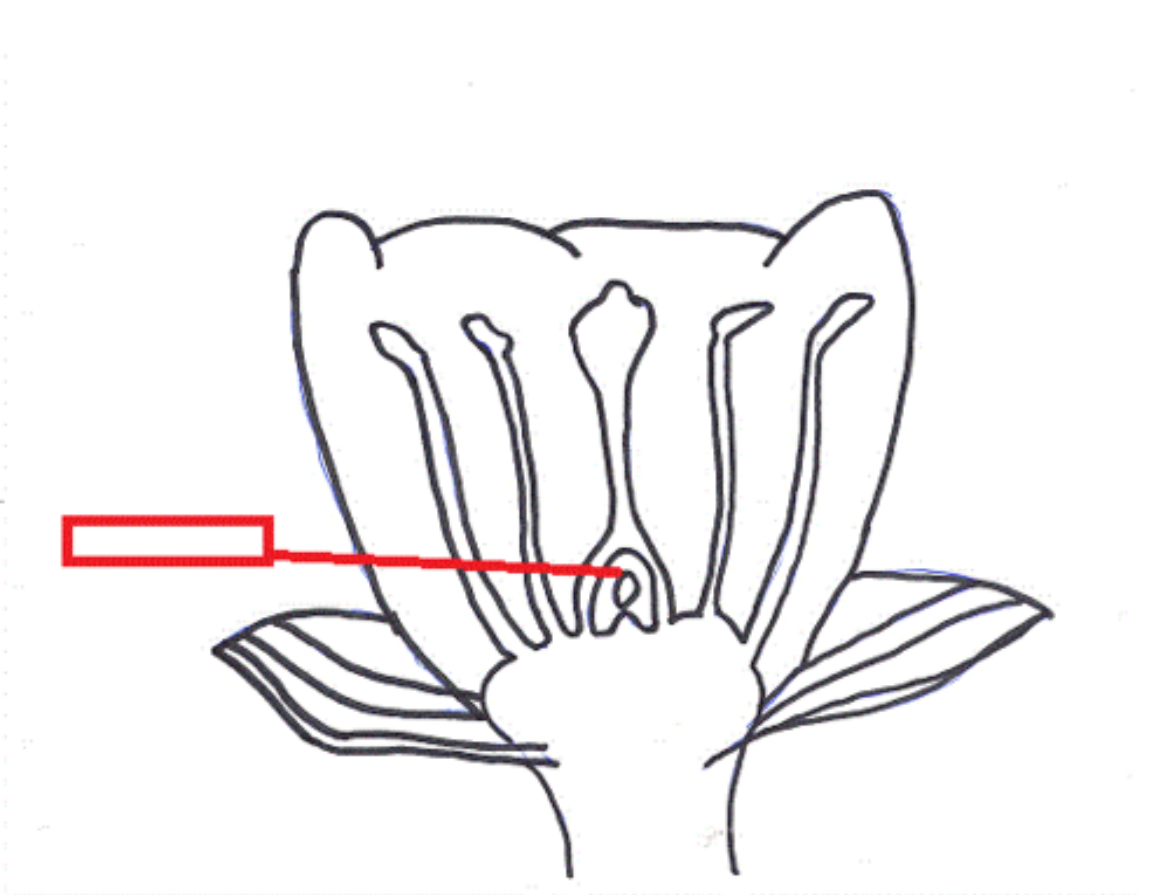
Ovule
A structure that develops within the ovary of a seed plant and contains the female gametophyte.
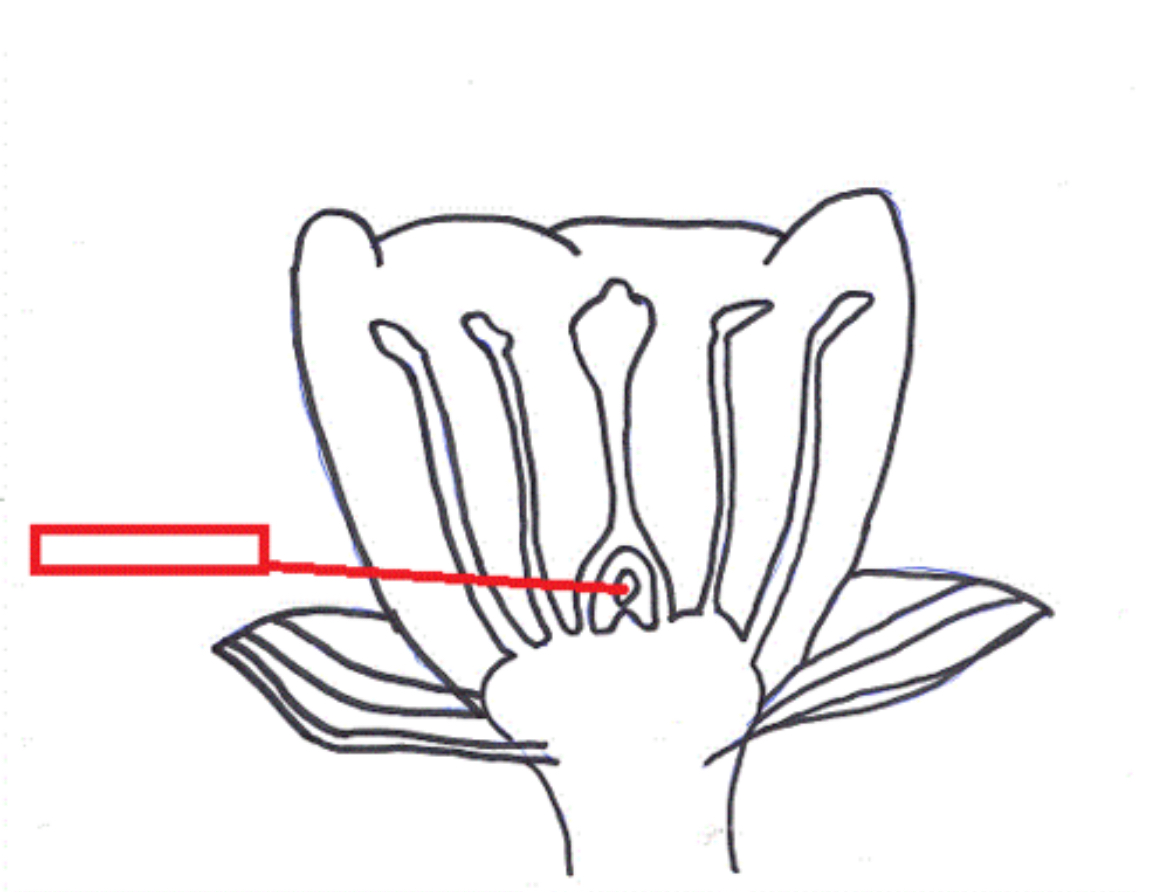
Petal
A modified leaf of a flowering plant. Petals are the often colorful parts of a flower that advertise it to insects and other pollinators.
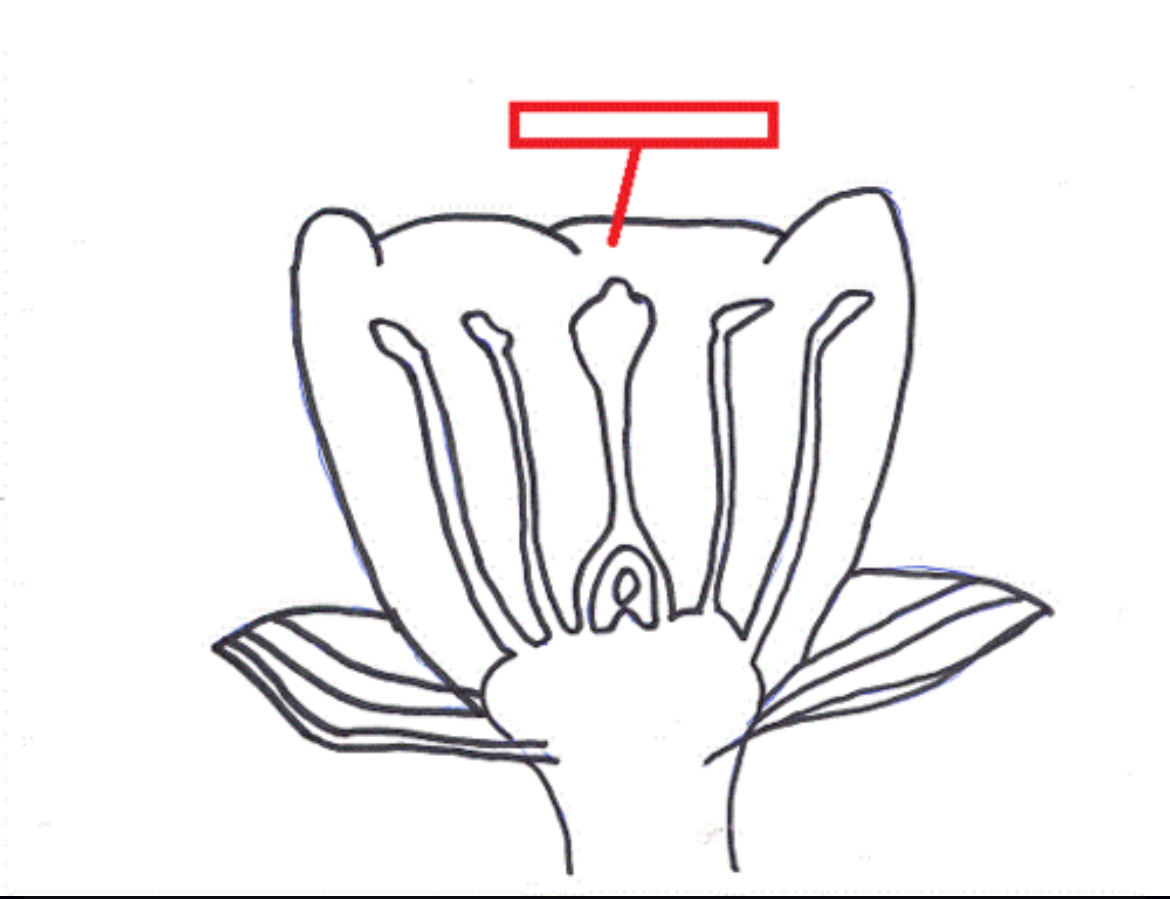
Sepal
A modified leaf in angiosperms that helps enclose and protect a flower bud before it opens.
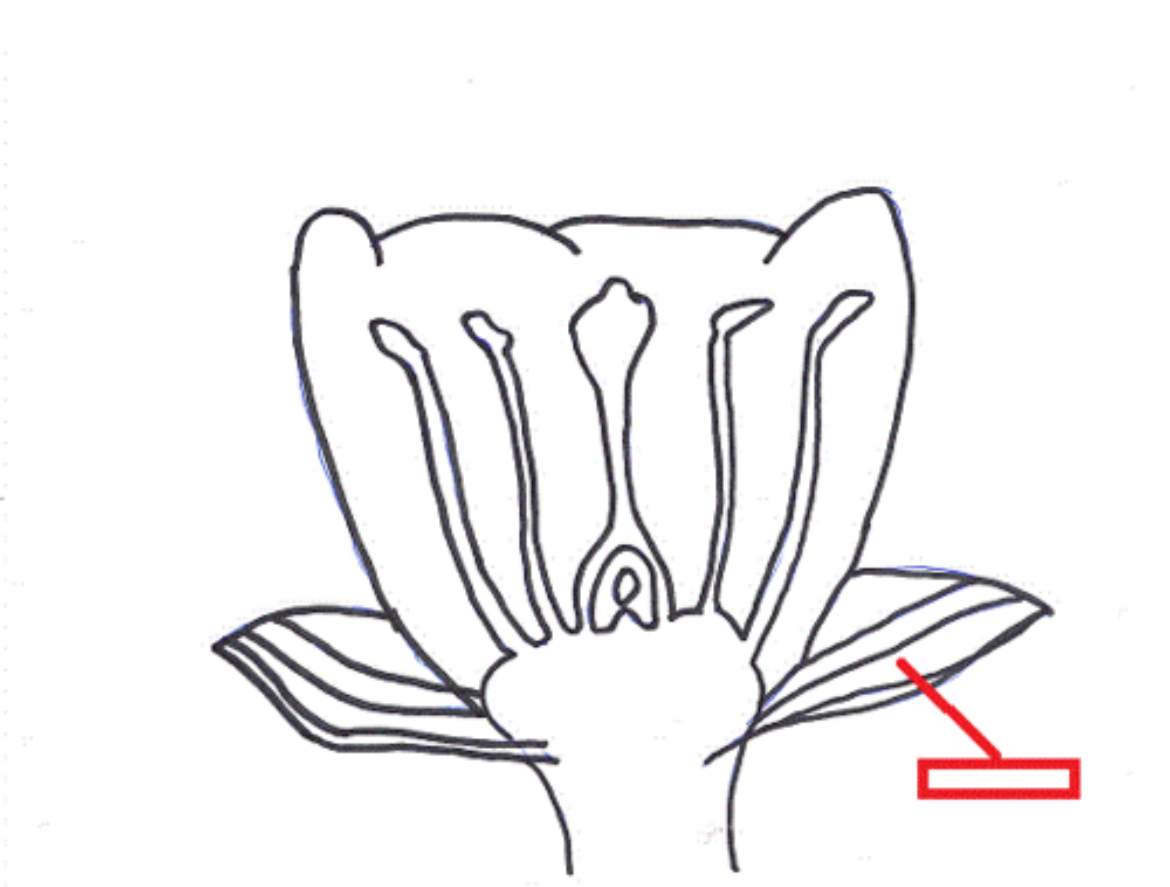
Stamen
The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower, consisting of an anther and a filament.
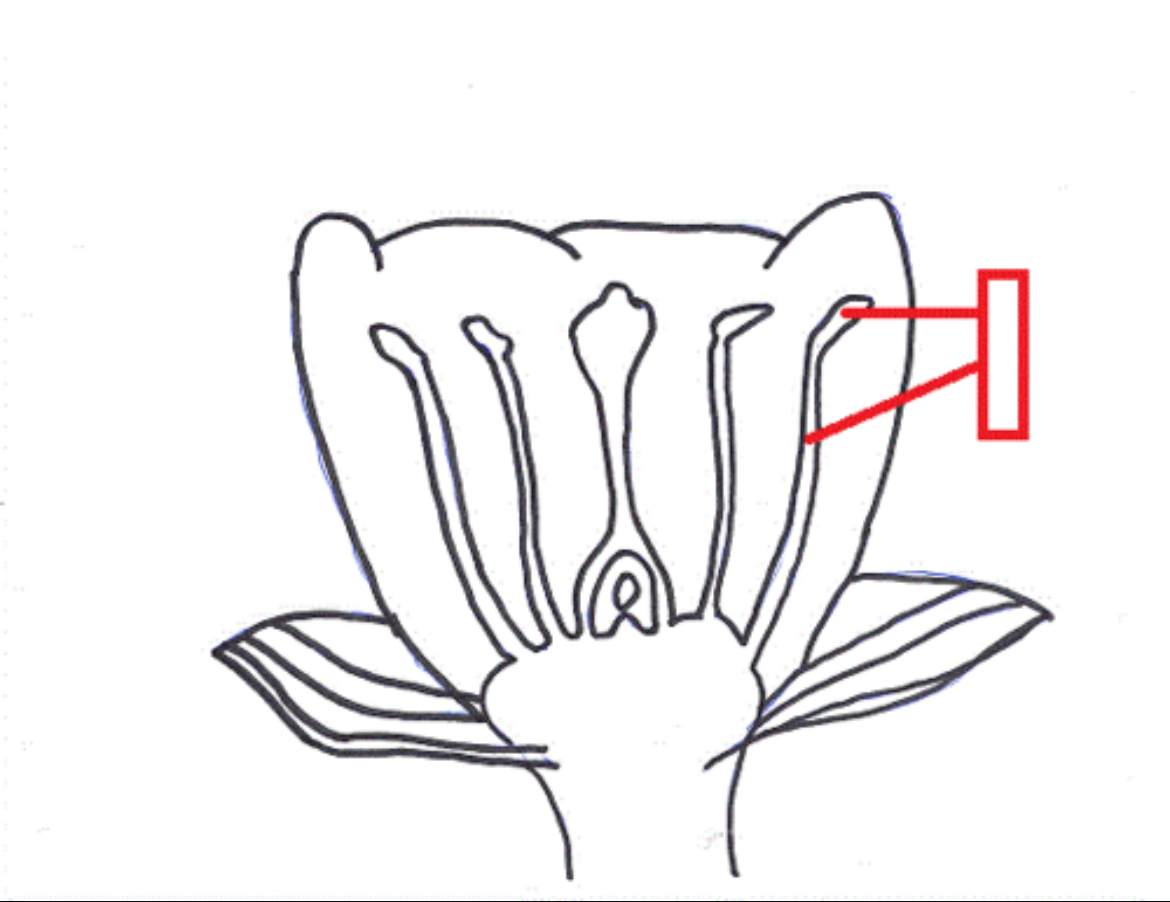
Stigma
The top of the central female part of a flower, where pollen is received.
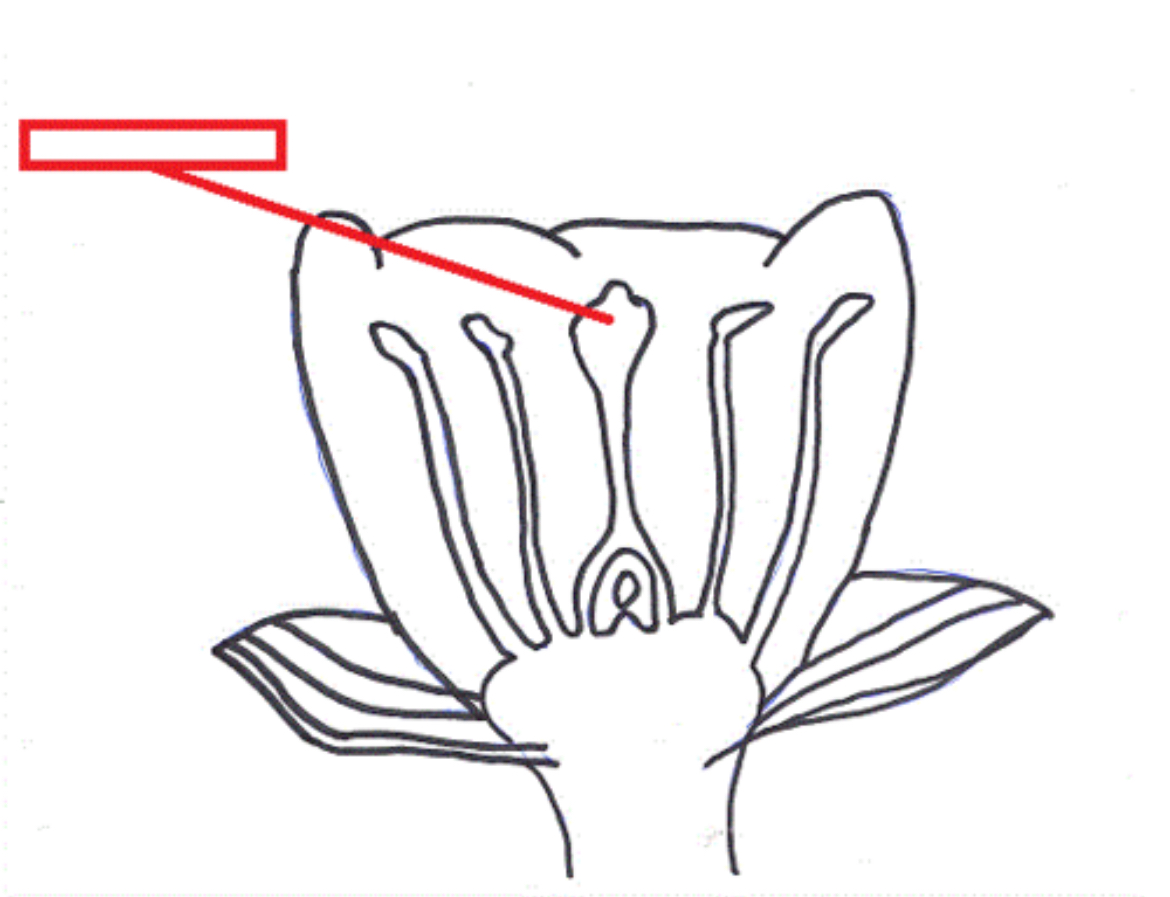
Pistil
The female ovule-bearing part of a flower composed of ovary and style and stigma
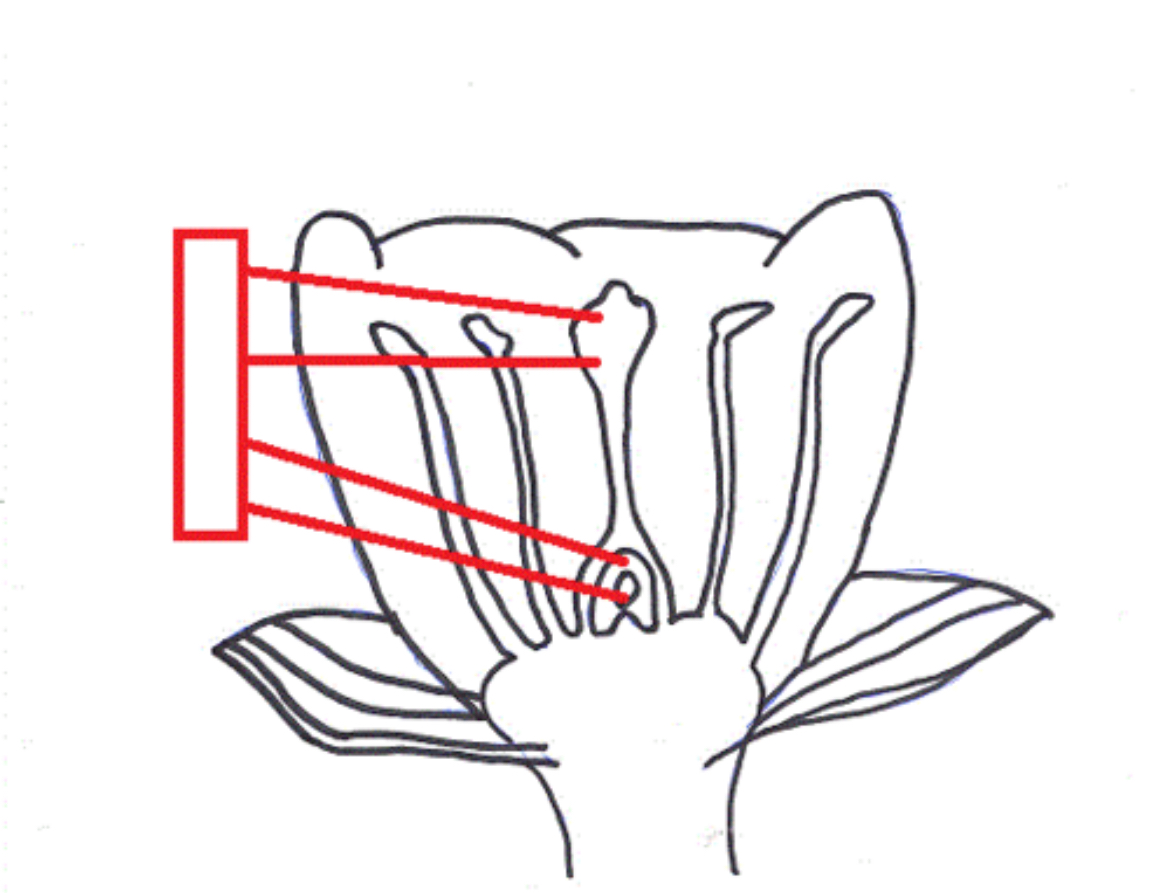
Style
The narrow elongated part of the pistil between the ovary and the stigma