10: Embedding, Microtomes & Microtomy
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Embedding is the _ of placing cells or tissue in a __ so that thin _ can be cut using a _
technique, supporting medium, sections, microtome
Types of embedding media
Paraffin wax, celloidin, resin, plastic/polyester wax (gelatine/agar)
Tools needed for embedding
Metal and plastic moulds (various sizes), tampers, forcep, knife
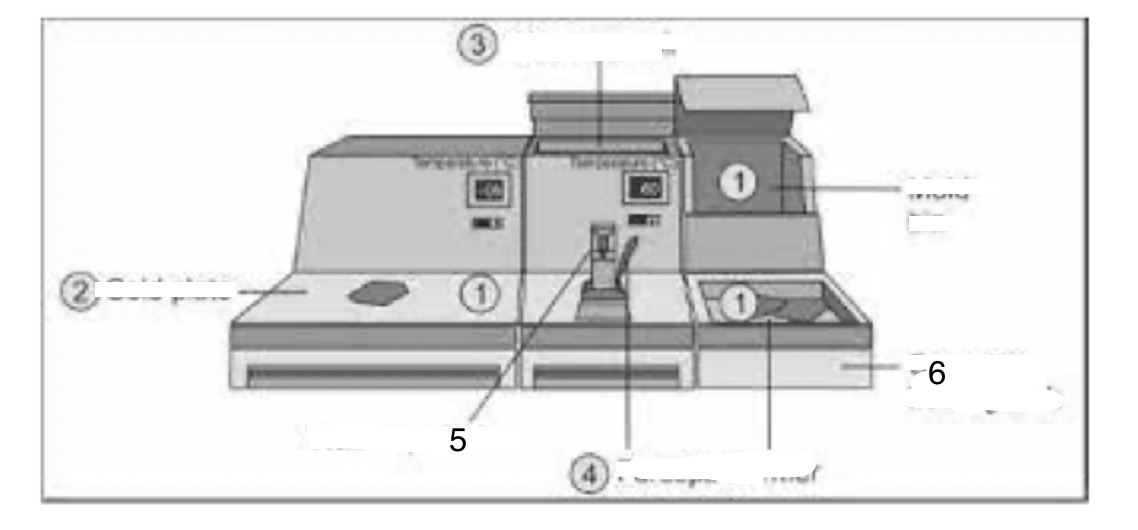
1
Mould bin
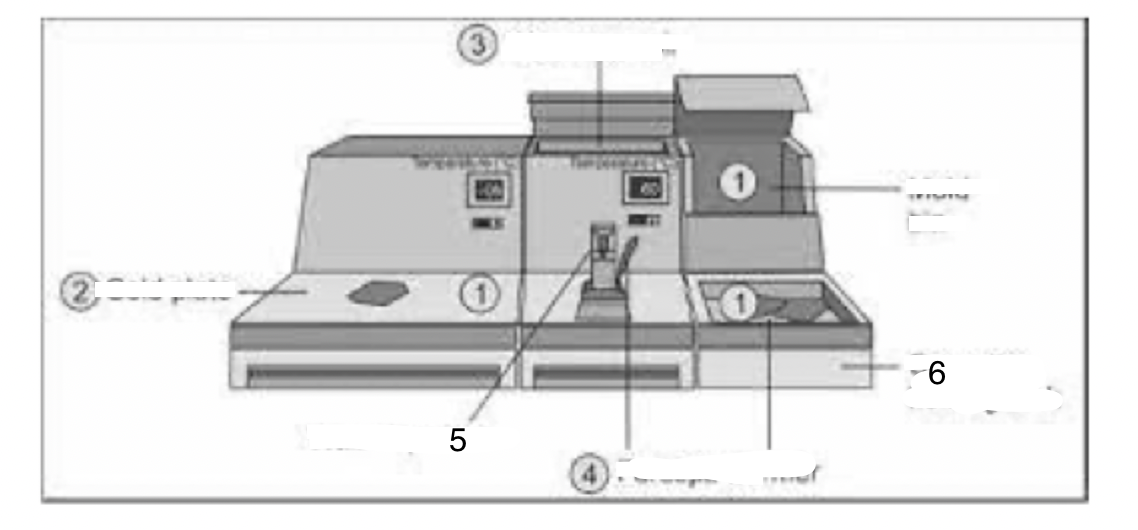
2
Cold plate
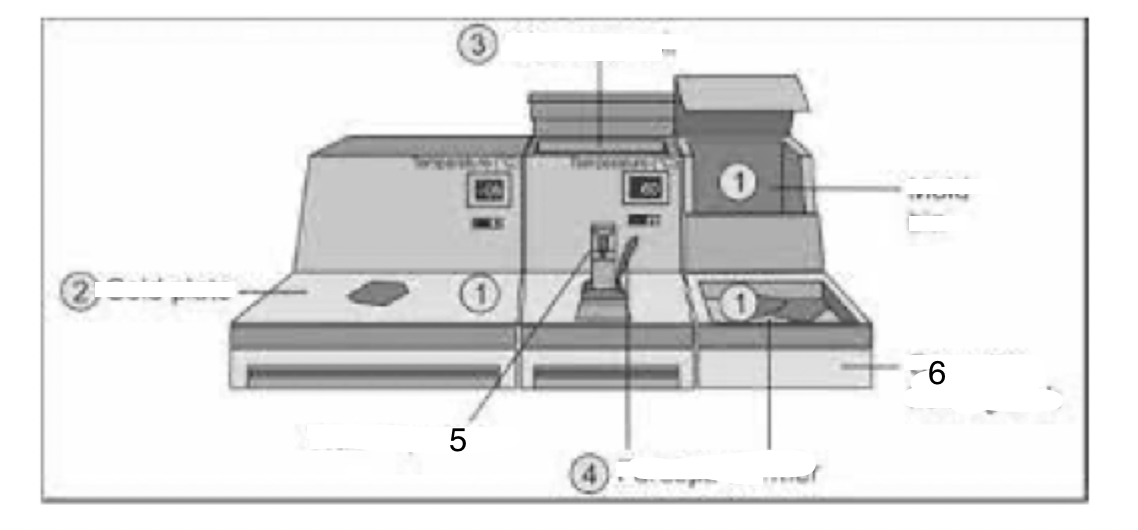
3
Wax reservoir
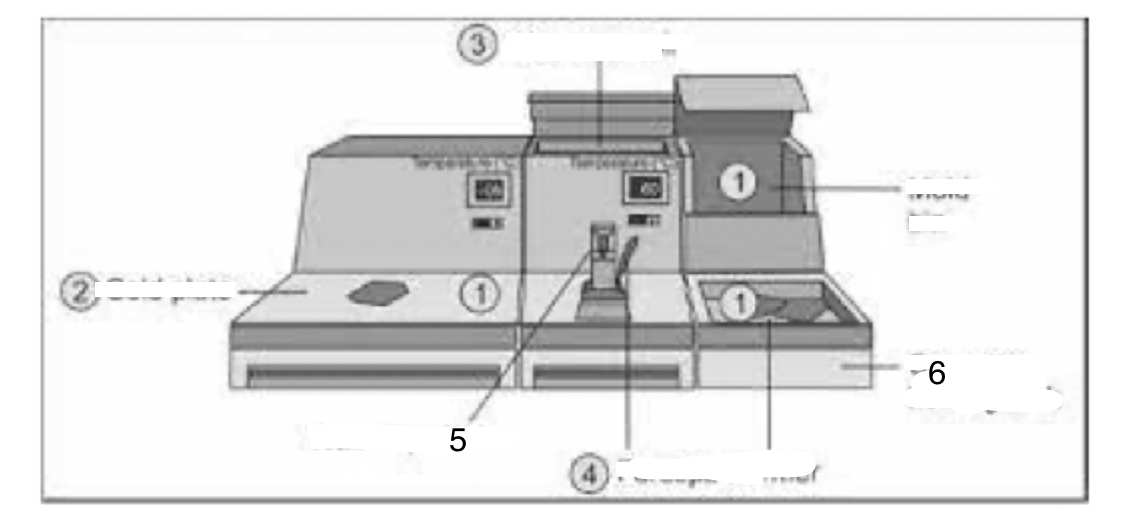
4
Forceps warmer
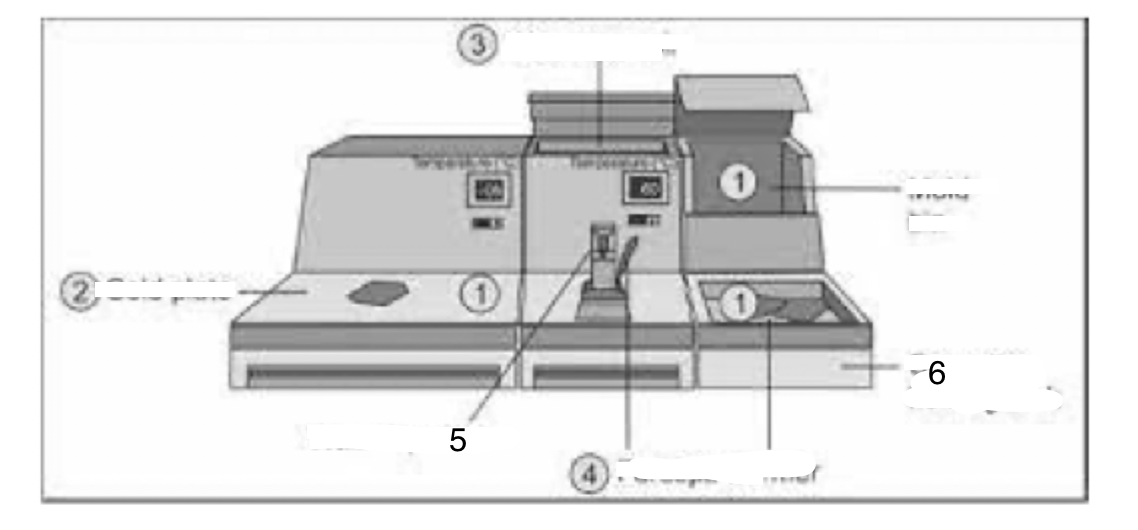
5
Wax dispenser
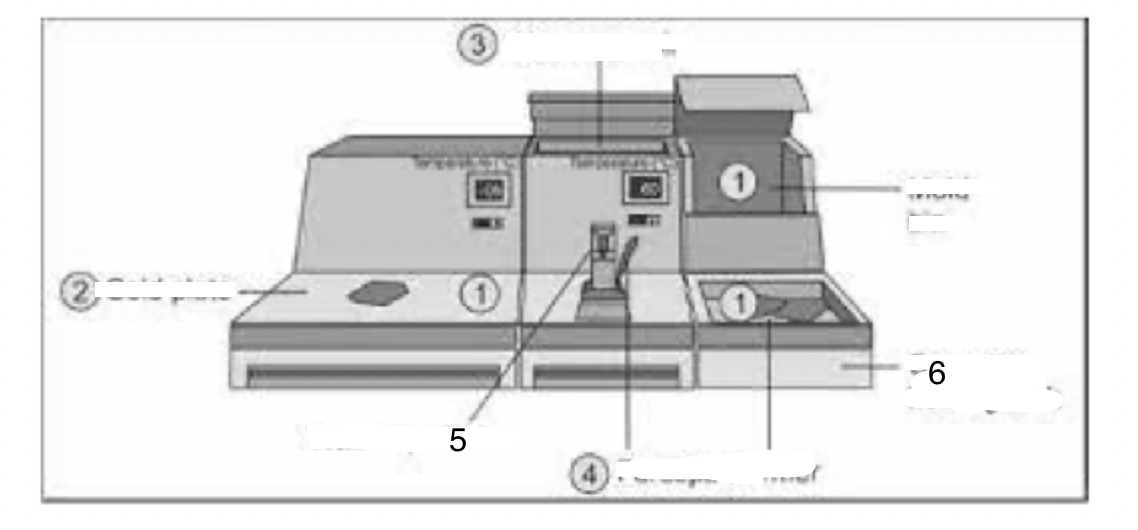
6
Cassette-holding tank
Early form microtomoy
Free hand sectioning of fixed or fresh tissue
Types of microtomes
Rocking, base sledge, sliding, ultra, freezing (cryostat), rotary (manual or automated)
Oldest type of microtome
Rocking microtome
Base sledge microtome used for…
Large blocks, botanical histology technique for hard material, neuropatholofy and opthalmic pathology, cutting resin section
Sliding microtome used for…
cutting celloidin (embedded tissue blocks, large paraffin blocks)
Ultra microtome used for…
cutting very thin sections for use in EM studies, to look at ultra cellular structures
Ultra microtome knives
Glass (thick sections), diamond (thin sections)
Freezing microtome (cryostat) used for…
Section prepared on unfixed tissue (urgent diagnosis), rotary microtome housed in deep freezer cabinet, temp maintained -30°C to -15°C
Rotary microtome types
Manual, semi-automated, fully automated
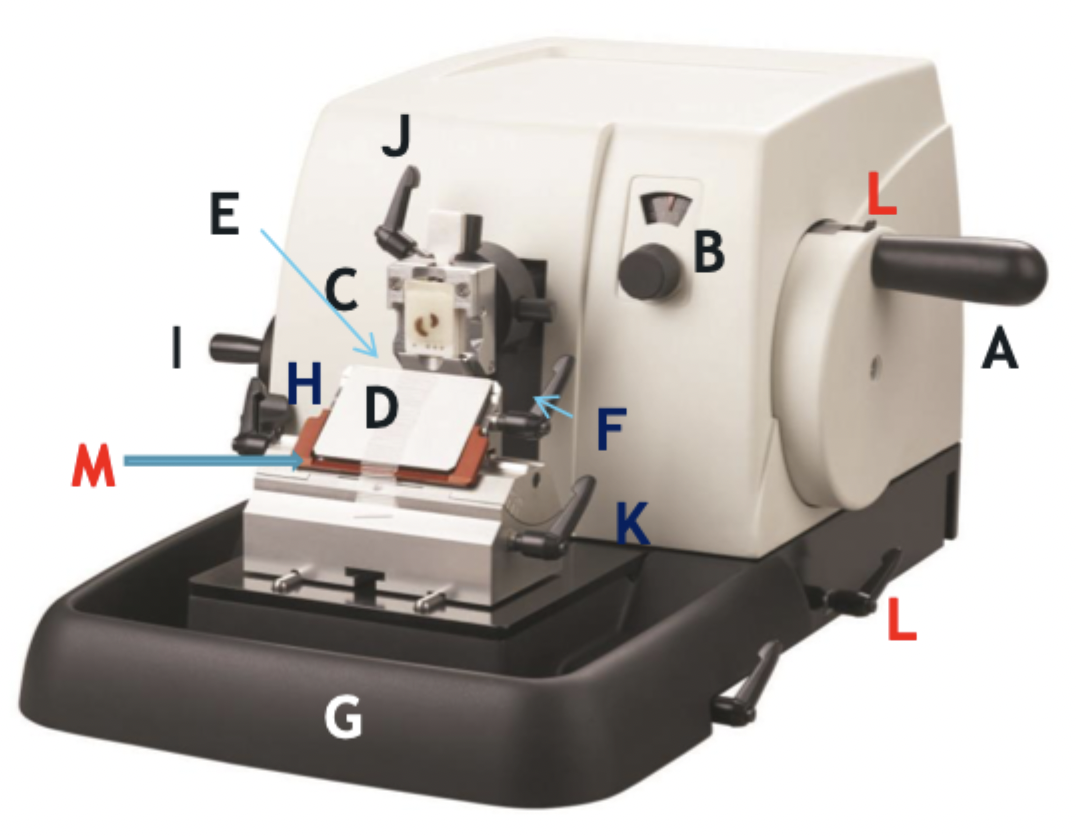
A
Wheel handle
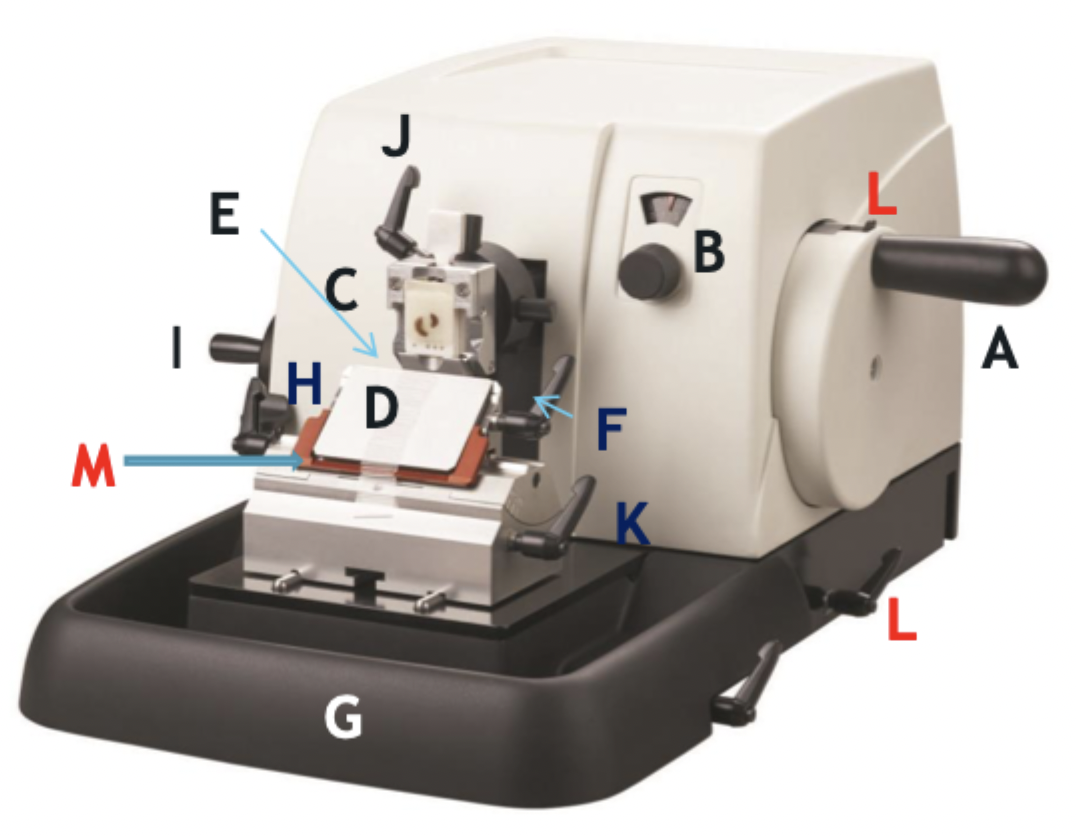
B
Micron selector
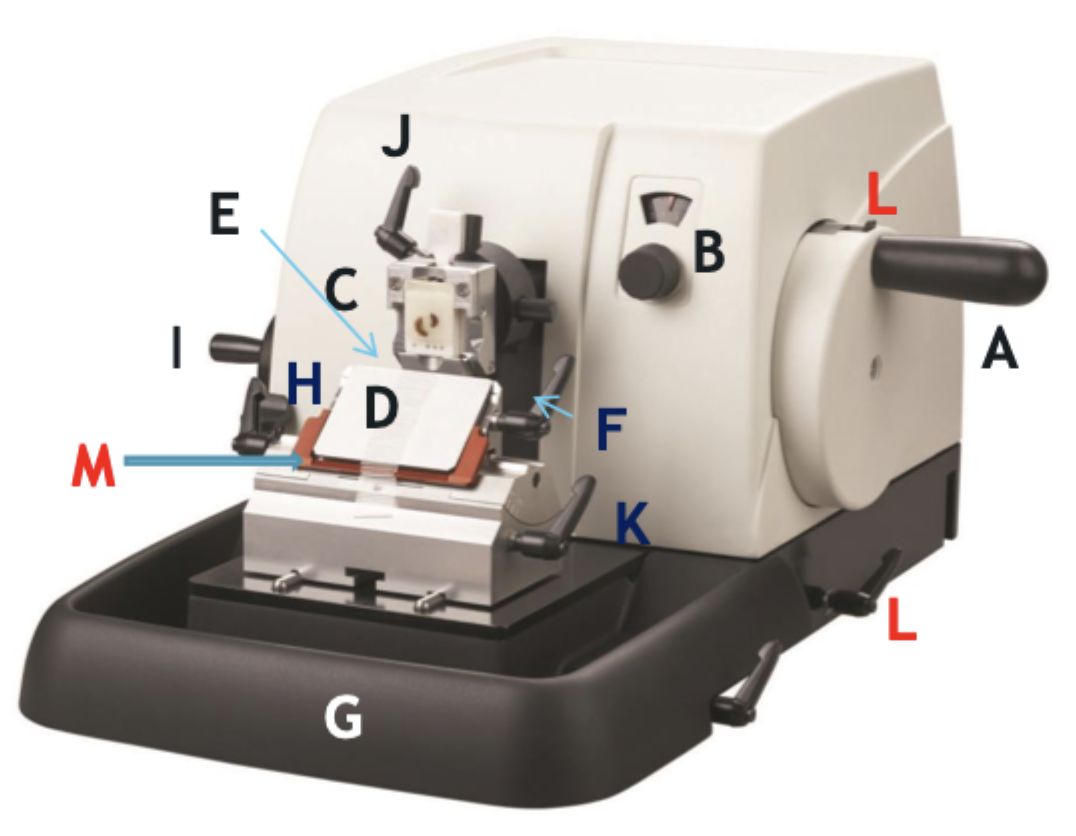
C
Chuck, block holder
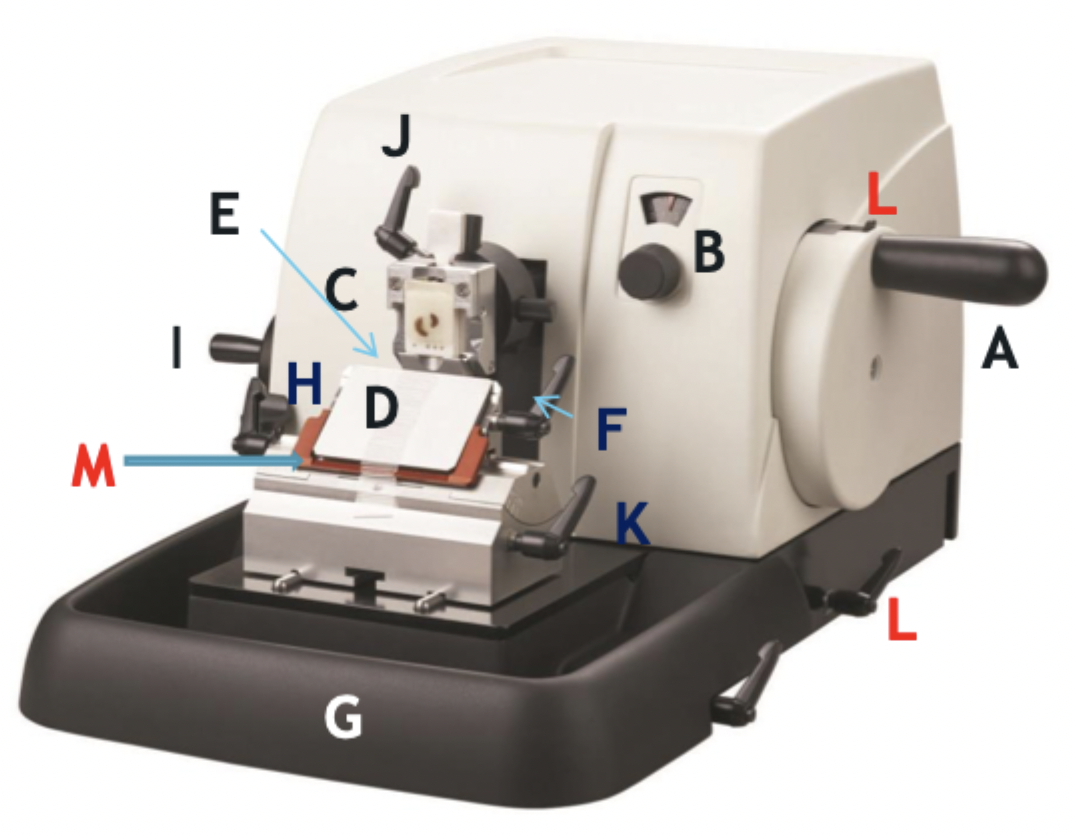
D
Steel knife holder

E
Knife
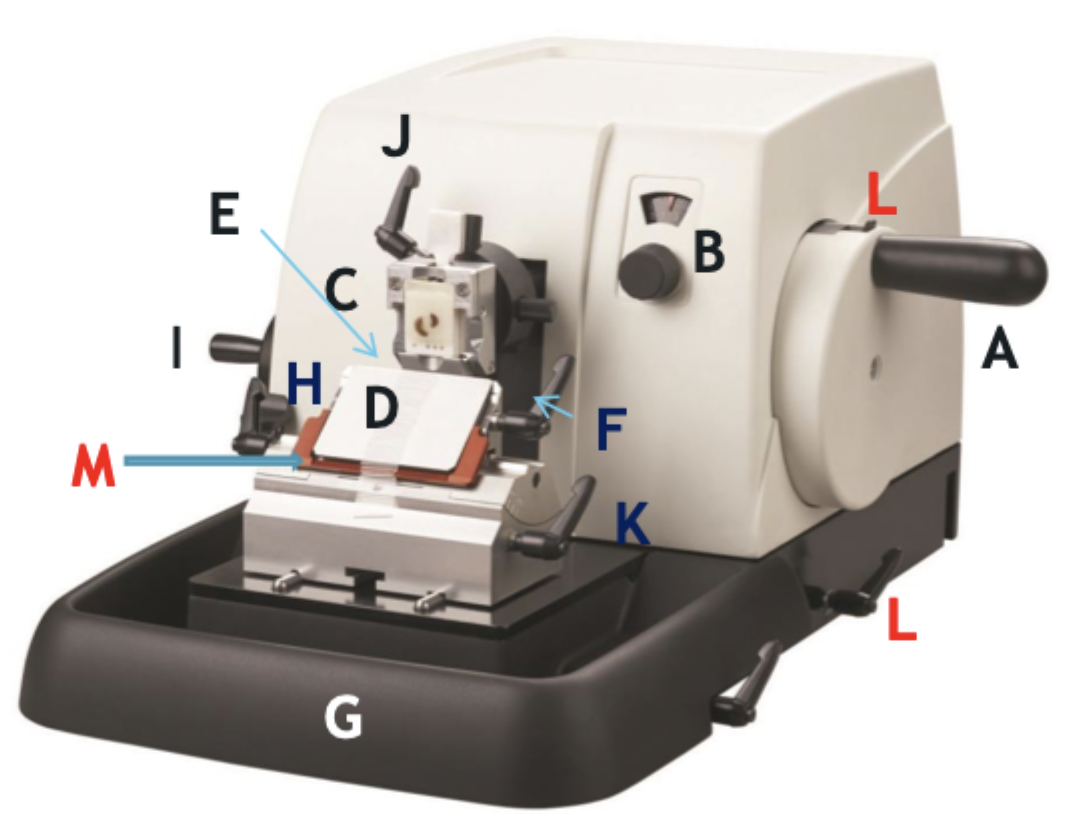
F
Knife holder mover
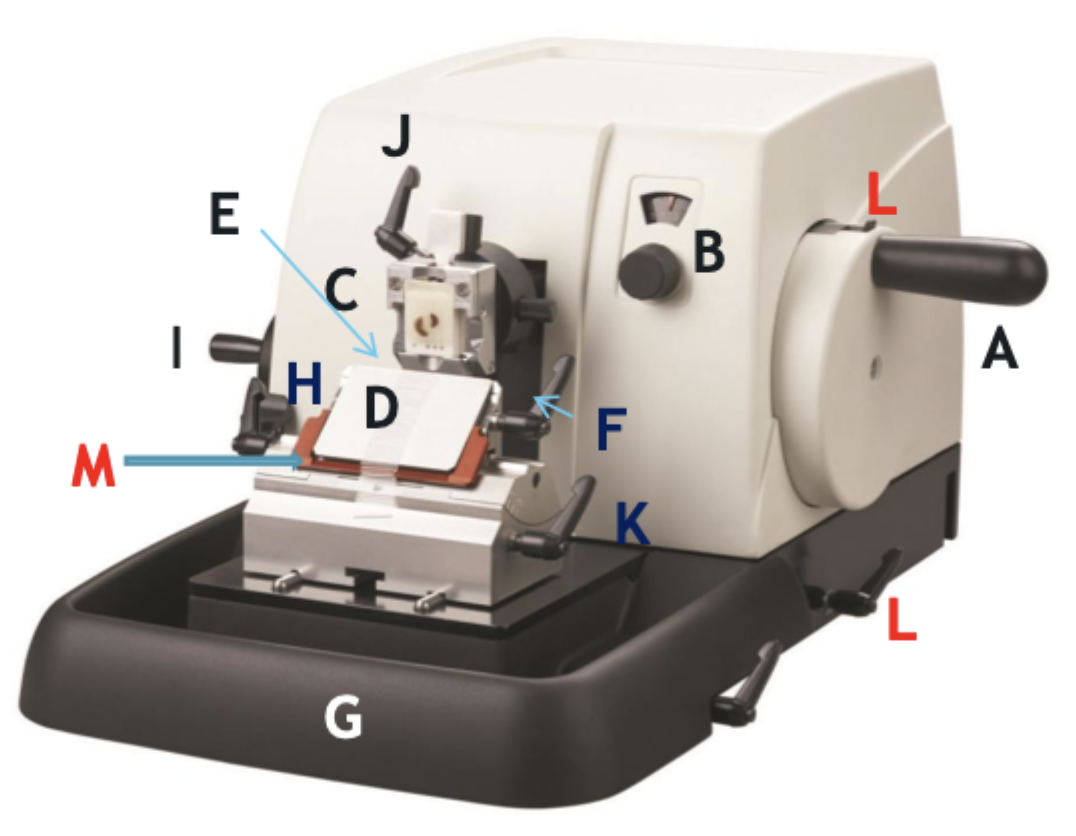
G
Paraffin wax shaving holder
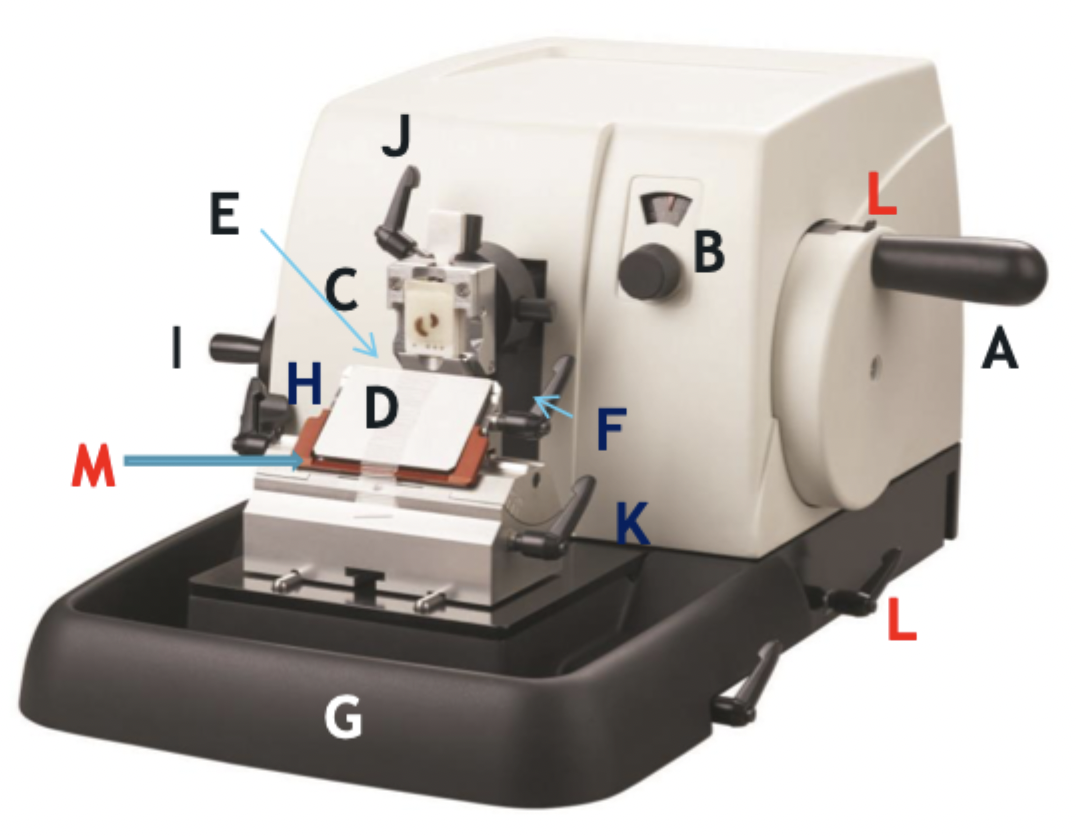
H
Coarse trimming lever
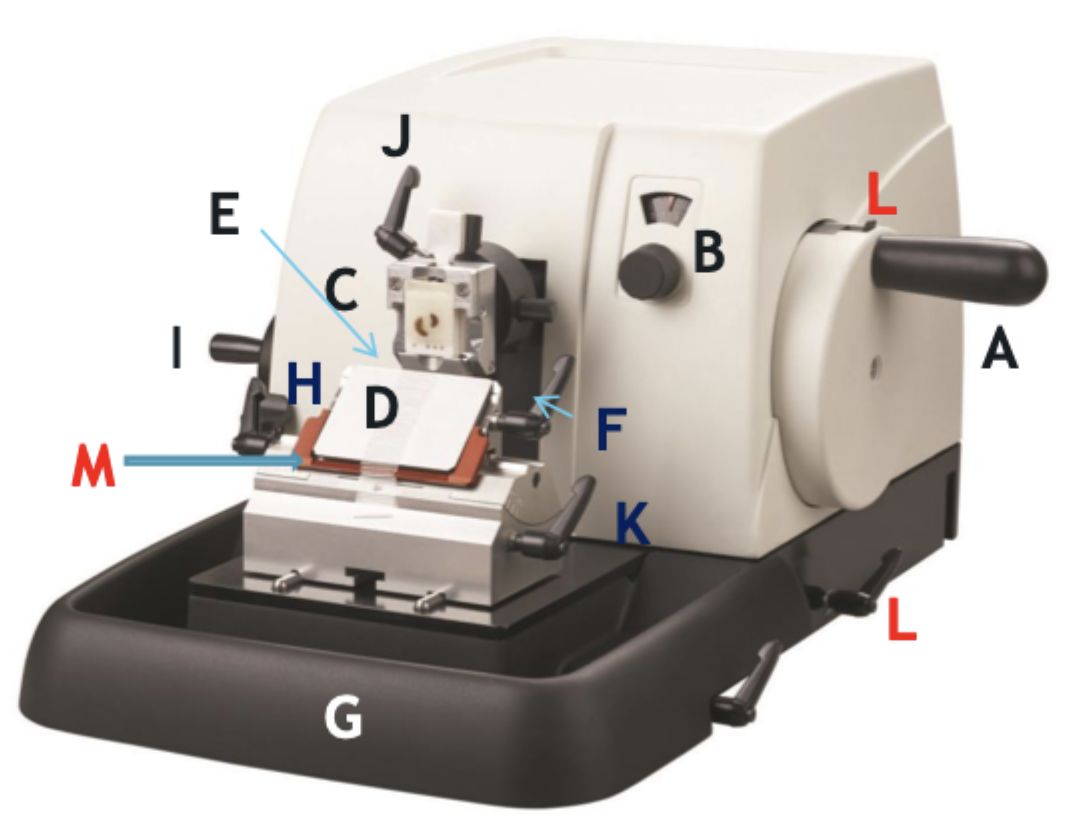
I
Chuck advance and back wheel
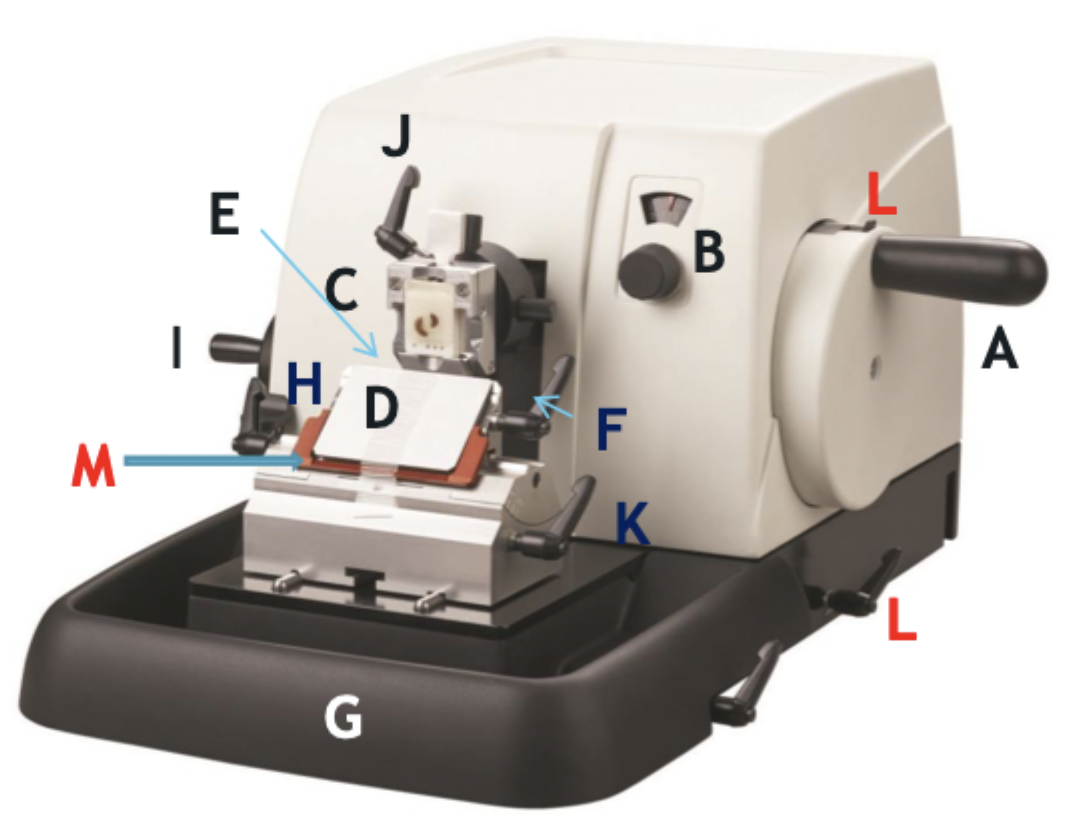
J
Chuck tilt lever
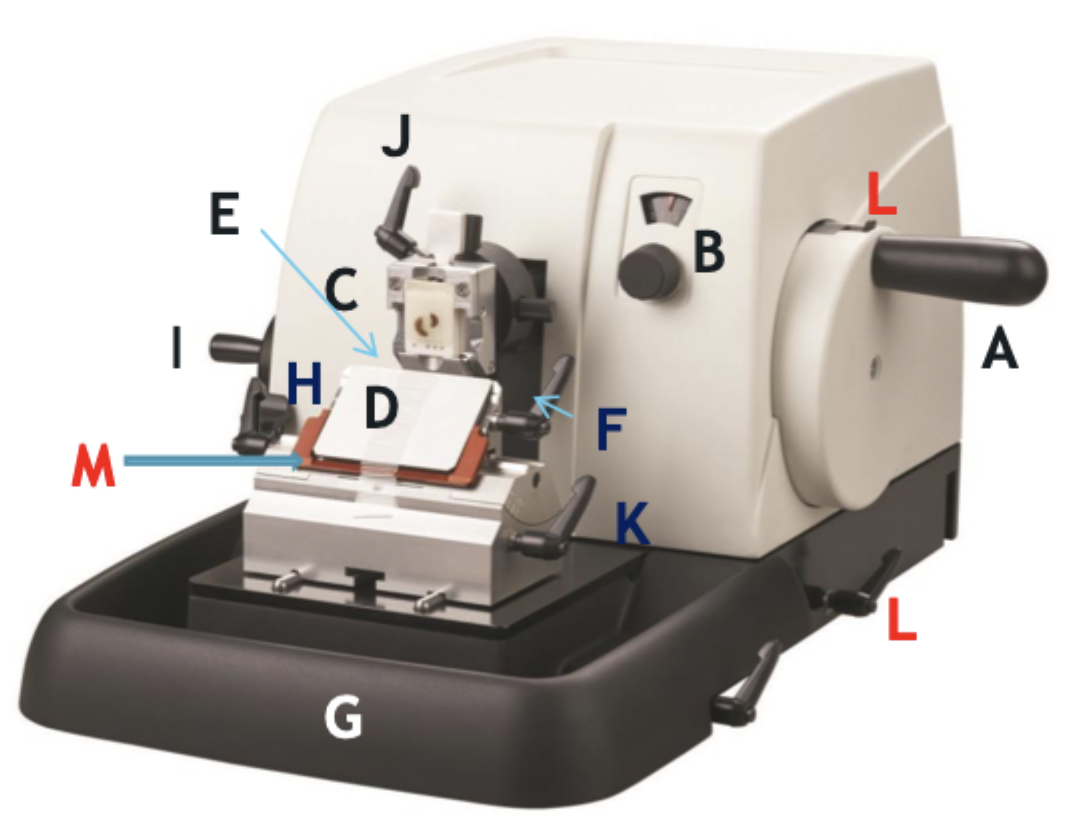
K
Angle change
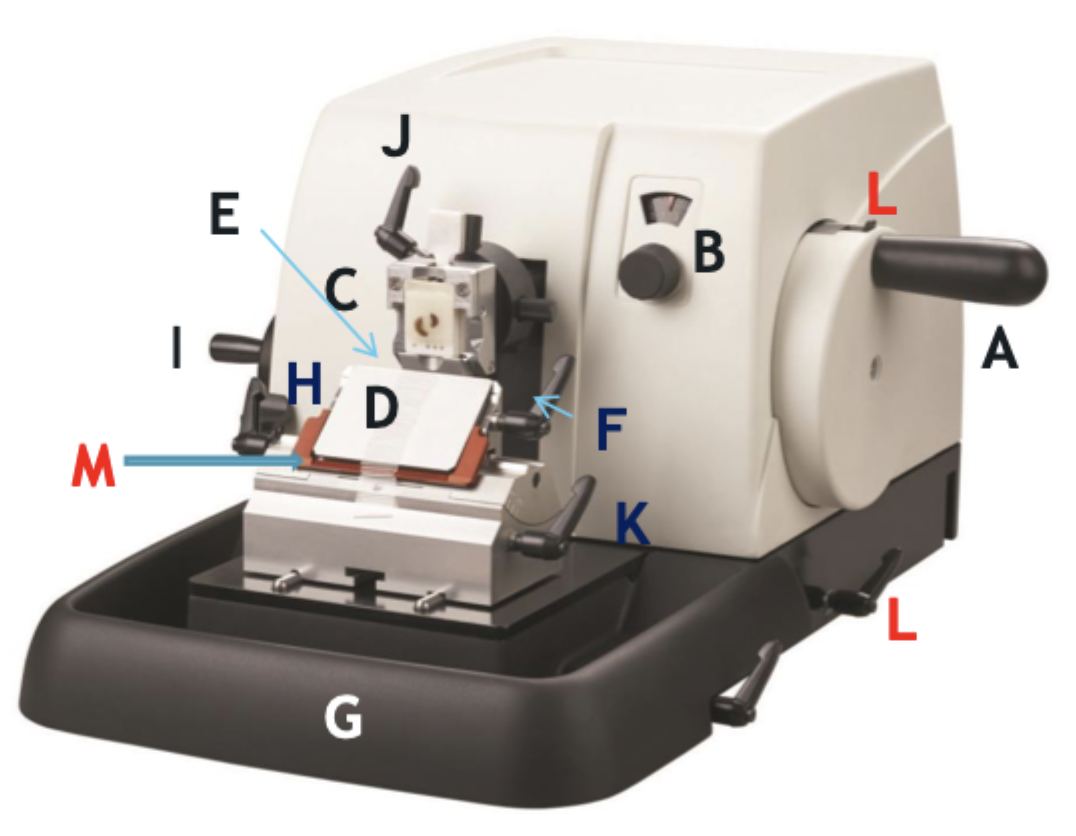
L
Wheel lock
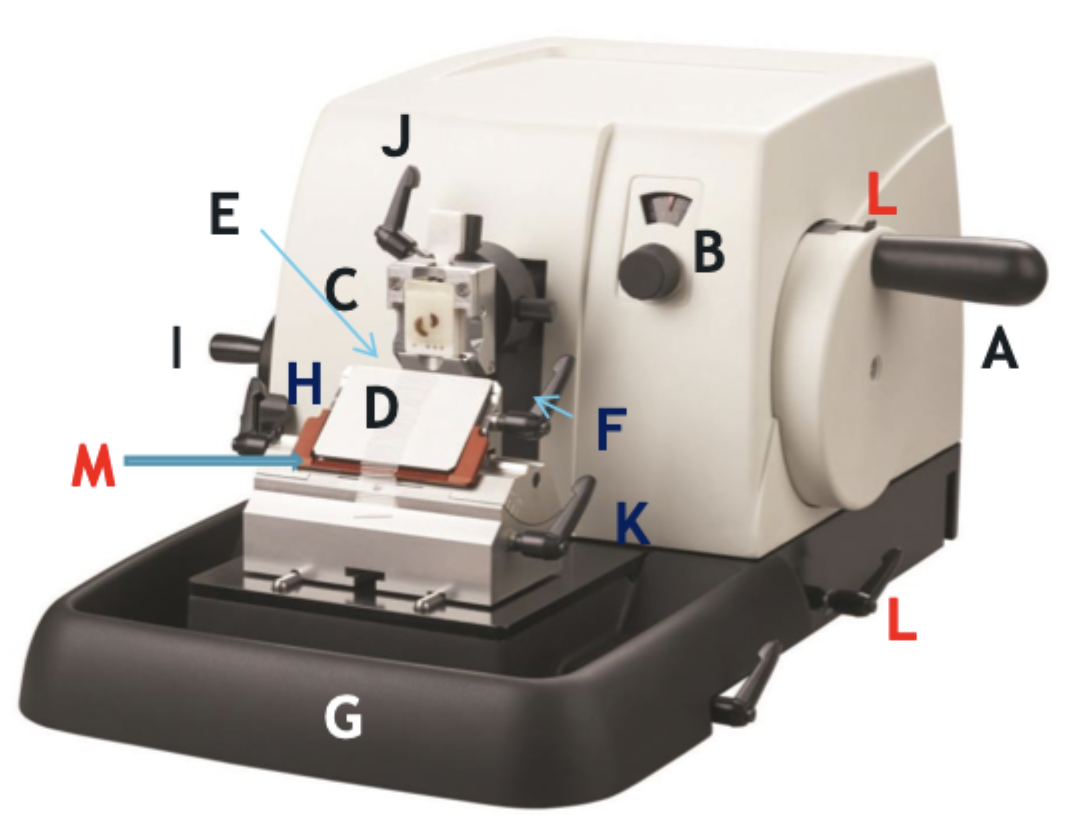
M
Knife guard
Rotary microtome advantages
Ability to cut 2–3 micron sections and cope with harder tissue,
Ideal for cutting serial sections
Tilt of knife is adjustable
Can cut resin using special holder
Manual microtome in cyostat
Rotary microtome disadvantages
Rotary motion of handle is tiring, risk of OOS (occupational overuse syndrome)
Types of knives
Steel (obsolete, tungsten tipped steal/diamond, glass, disposable (stainless steel coated)
Tungsten carbide/diamond knives
For very hard undecalcified bone, resin blocks
Tougher than steel, industrially sharpened
Glass knives
Mainly for resin blocks for light and electron microscopy, high quality knives made using special equipment, prepared just prior to use
Advantages of disposable knives
Widely used for microtomy of paraffin block, sharpening not required and is assured, easy to use, cost effective, replacement blades readily available, low and high profiles adaptable to variety of tissue and paraffintype, safe storage when not in use, safe disposal
Microtomy
Ability to cut extremely thin slices (sections) of tissue
Purpose of microtomy
Enables transparency of stained tissues and cells when viewing microscopically
Needed for microtomy
Thorough knowledge of equipment used and type of investigation required, good quality tissue (well fixed)
Routine histolofgy sections are cut at…
3–4μm thickness
Microtomy tools
Microtome, water bath (45°C), tissue paper, slide rack, forceps, disposable blades, cold plate/ice, slides ± adhesive, pencil, brush

Single full-face section
Single section

Serial section
Consecutive sections
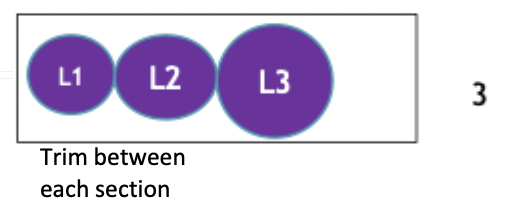
Stepped levels section
Sections at periodic levels
Type of slide depends on…
investigation
Plain/frosted end (noncoated) slides used for…
routine histology
Coated/adhesive slides
Commercially pre-coated, charged slides
Coated slides used for…
Sections exposed to strong alkali, cryostat (frozen) sections, immunochemistry and direct immunofluorescence studies, CNS tissues, blood clots, decalcified tissues
Slide drying purpose
Slide drying in…
hot place, laboratory oven
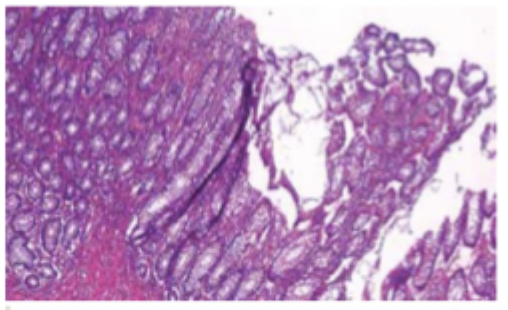
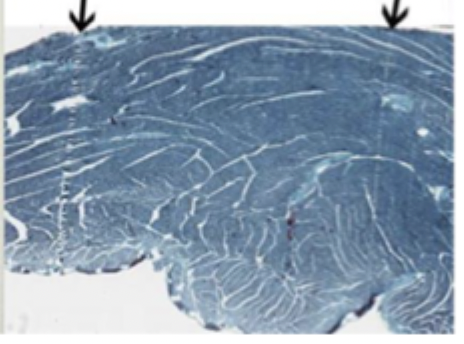
Folds
Knife marks
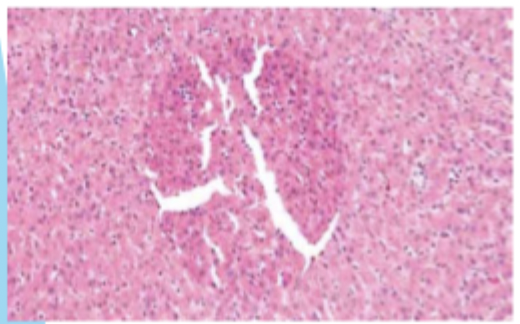
Bubbles under section
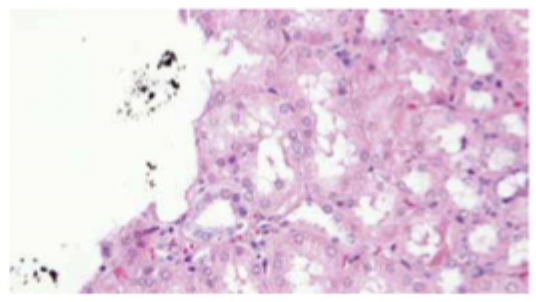
Dust present
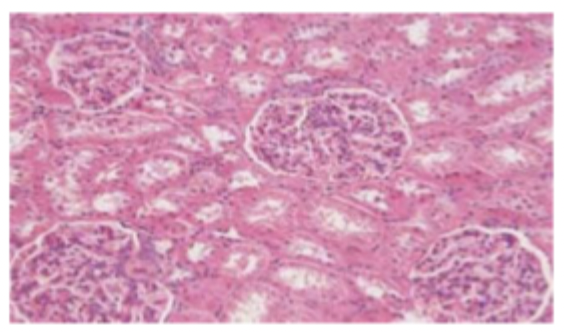
Excessive compression
Over expansion
Cause and remedy: Section ribbon curved
Knife is blunt
Change knife
Cause and remedy: Scoring or splitting of sections
Nick in knife edge, hard particles in tissue/wax
Change knife, use softening agent/remove hard particle and re-embed
Cause and remedy: Areas of tissue in block not present in section
Too vigorous trimming, incomplete trimming
Polish block, further trim block
Cause and remedy: Holes in section
Harsh or coarse trimming
Fine trim (polish) block to get rid of tough appearance
Cause and remedy: Blade hits into block and tissue is cut out
Tissue is loose in block, microtome part not clamped down, block is not secure in holder, aggressive trimming with rapid wheel rotation
Re-embed tissue, tighten clamps, re-secure block, slow down trimming