SNC1W: Chemistry
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
What is matter?
Anything that has mass and occupies space.
What is a pure substance?
Matter that contains only one kind of particle.
What are the two types of pure substances?
An element and a compound.
What can a particle consist of?
either a singular type of atom or a singular type of compound.
What is the definition of an element?
A type of pure substance that can’t be broken down by chemical methods. Elements are made up of only one kind of atom.
What is a compound?
A pure substance made of two or more elements that are chemically combined.
What is a mixture?
Matter that contains more than one kind of particle.
What is a mechanical mixture?
When two or more pure substances are mixed together, and you can see more than one part.
What is a solution?
A homogeneous mixture where one substance is dissolved in another, but you can only see one part. It may involve a solute and solvent.
What is a solute?
The substance that is dissolved in a solution.
What is a solvent?
The substance doing the dissolving.
What is a physical property?
A characteristic of a substance that can be observed and measured without changing the chemical identity of the substance.
What is a qualitative physical property?
An observation without measurements.
What are the 9 types of qualitative properties?
colour, odour, state (of matter), taste, texture, lustre, malleability, ductility, opacity
What is opacity?
the transparency of a substance
What is malleability?
the ability of a substance to be shaped or bent.
What is ductility?
The ability of a substance to be drawn into a wire.
What is lustre?
how shiny something is
What is a quantitative physical property?
A property that can be measured with an number.
What is a melting point?
the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid.
what is a boiling point?
The temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas.
What is a chemical property?
The ability of a substance to react with another and form one or more new substance.
When are chemical properties shown?
During a chemical reaction.
What are the 4 major categories of chemical properties?
Reactivity, combustibility, stability, toxicity
What is stability?
how easily a substance decomposes/breaks down The more “stable” a substance is, the longer it will take to break down.
What is toxicity?
The ability of a substance to cause harm to animals/plants.
What is toxicity measured in?
the mass required per kg of body weight to cause death.
What is combustibility?
the ability of a substance to burn in air
What is a physical CHANGE?
A change in matter, but no new substances are formed.
New properties may appear, but the particles of the starting substances are the same.
What is a CHEMICAL CHANGE?
A reaction where one or more new substances are formed.
Atoms of the original compounds are rearranged to form new compounds.
What are the 5 SIGNS of a chemical CHANGE/reaction?
The formation of a gas
A change in temperature (gets hot or cold)
A change in colour
The formation of a solid (precipitate)
The production of light.
How do you know a formation of a gas has taken place?
bubbles/fizzing, an odour produced
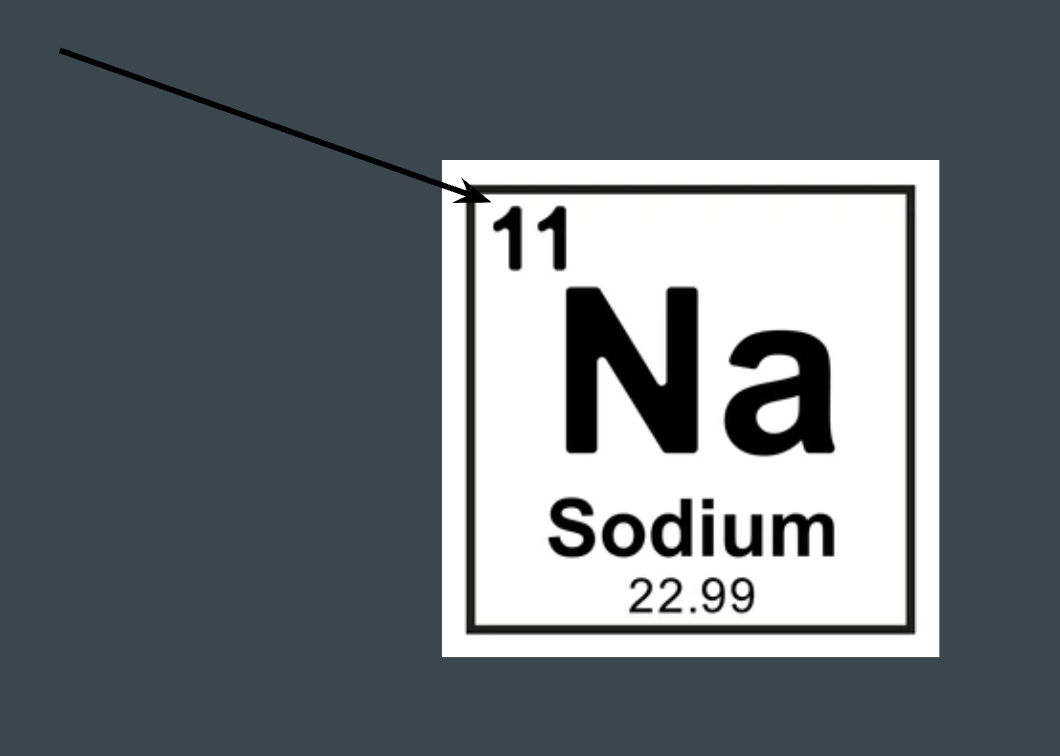
What does this number represent on the periodic table?
Atomic number
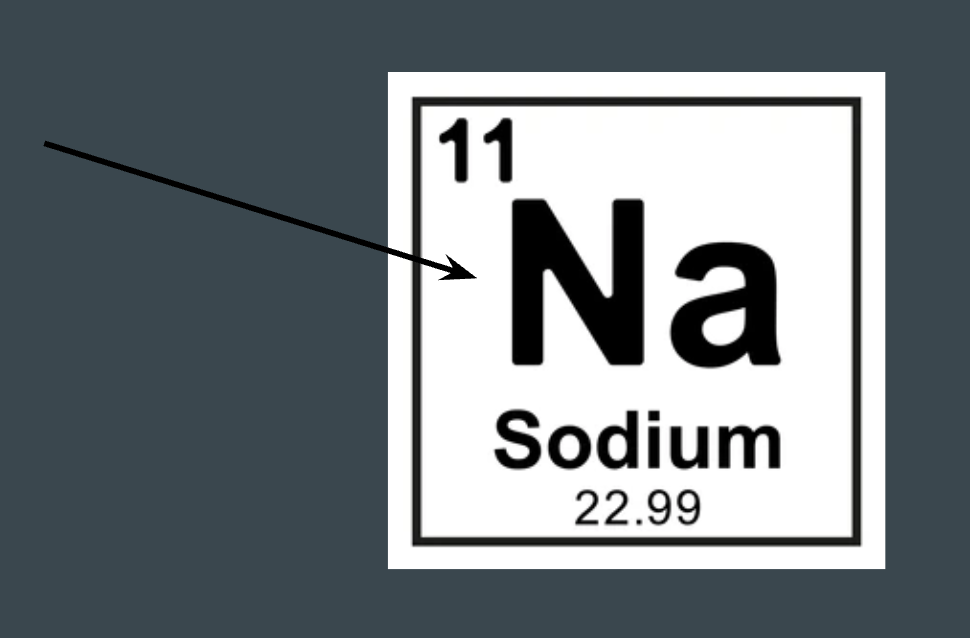
What does this represent on the periodic table?
Element symbol
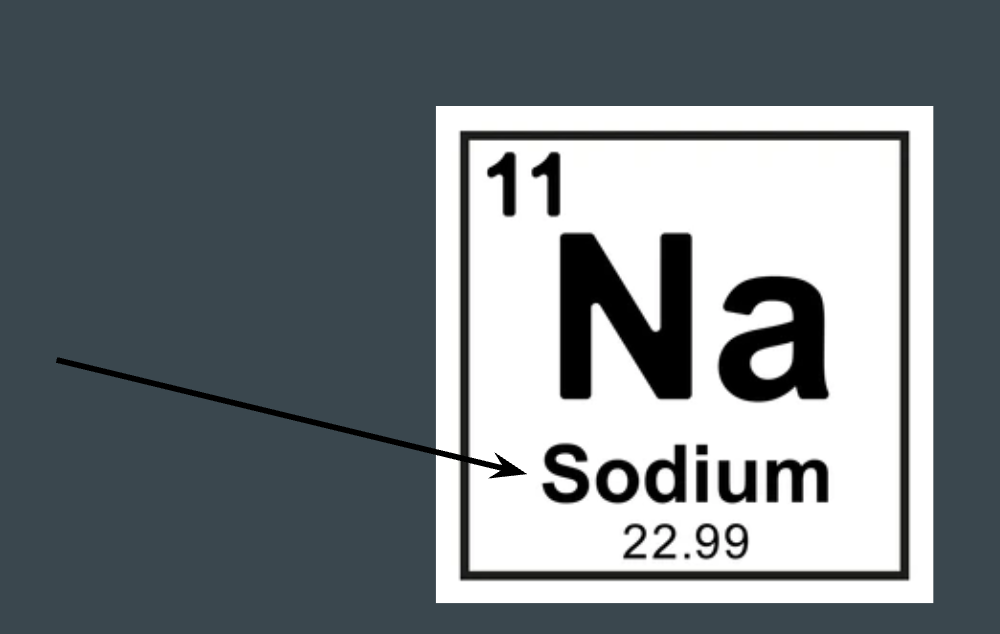
What does this represent on the periodic table?
Element name
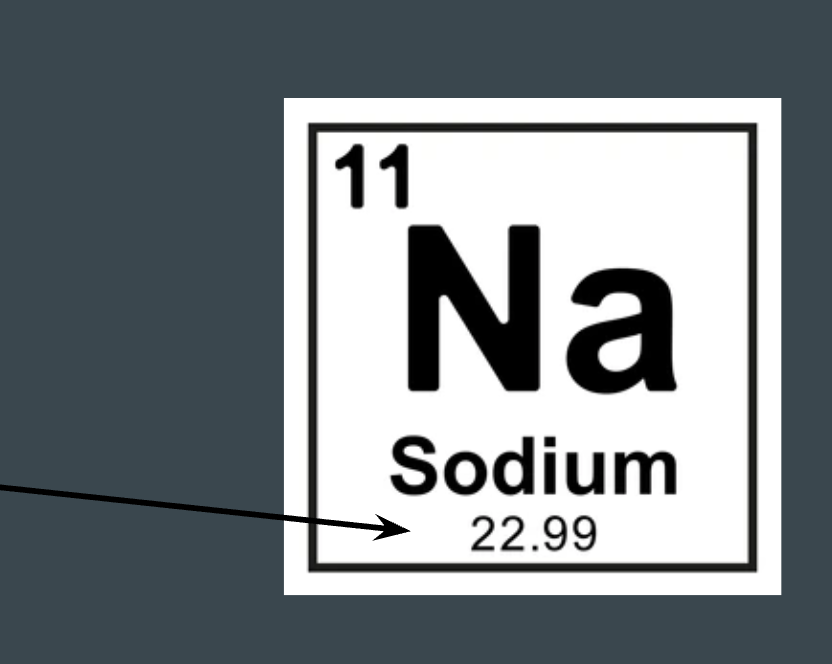
What does this represent on the periodic table?
Atomic mass/weight
What is a mass number?
The atomic mass after rounding.
how do you know how many protons in an atom using a periodic table?
Find the atomic number.
How do you know how many protons in an atom using a periodic table?
using the atomic number
How do you know how many neutrons in an atom using a periodic table?
Mass number - atomic number
How do you know how many electrons in an atom using a periodic table?
Equal to the number of protons
What is an isotopes?
A form of an element that has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
What does the atomic mass account for?
The average of the mass numbers of all isotopes.
What is the mass of all subatomic particles?
Electrons have a mass of 0, the others all have a mass of 1.
Physical Properties of metals (State at room temp, appearance, conductivity, Malleability/Ductility)
Solid, shiny, great conductor of heat and electricity, malleable and ductile
Physical Properties of nonmetals (State at room temp, appearance, conductivity, Malleability/Ductility)
Mix of gases and solids, dull, poor conductors, brittle
Physical Properties of metalloids (State at room temp, appearance, conductivity, Malleability/Ductility)
Solids at room temp, some are shiny others dull, semiconductors, neither
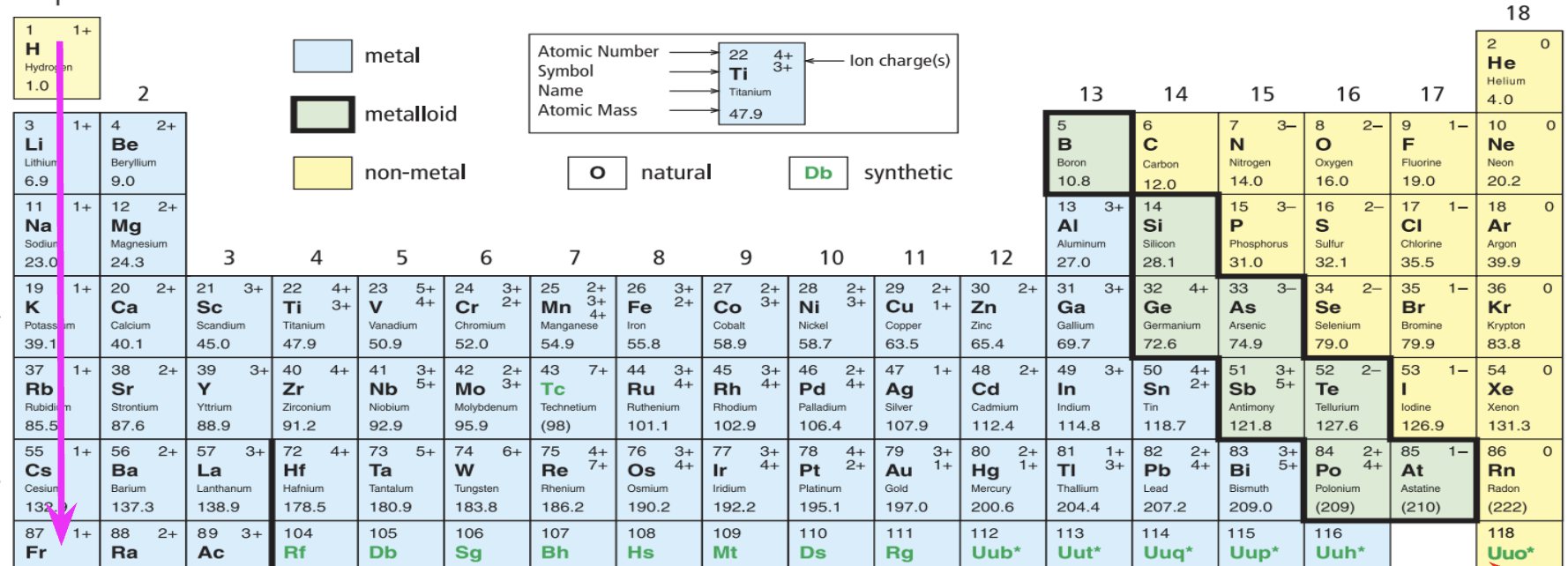
What does this arrow refer to? (verticle)
Groups
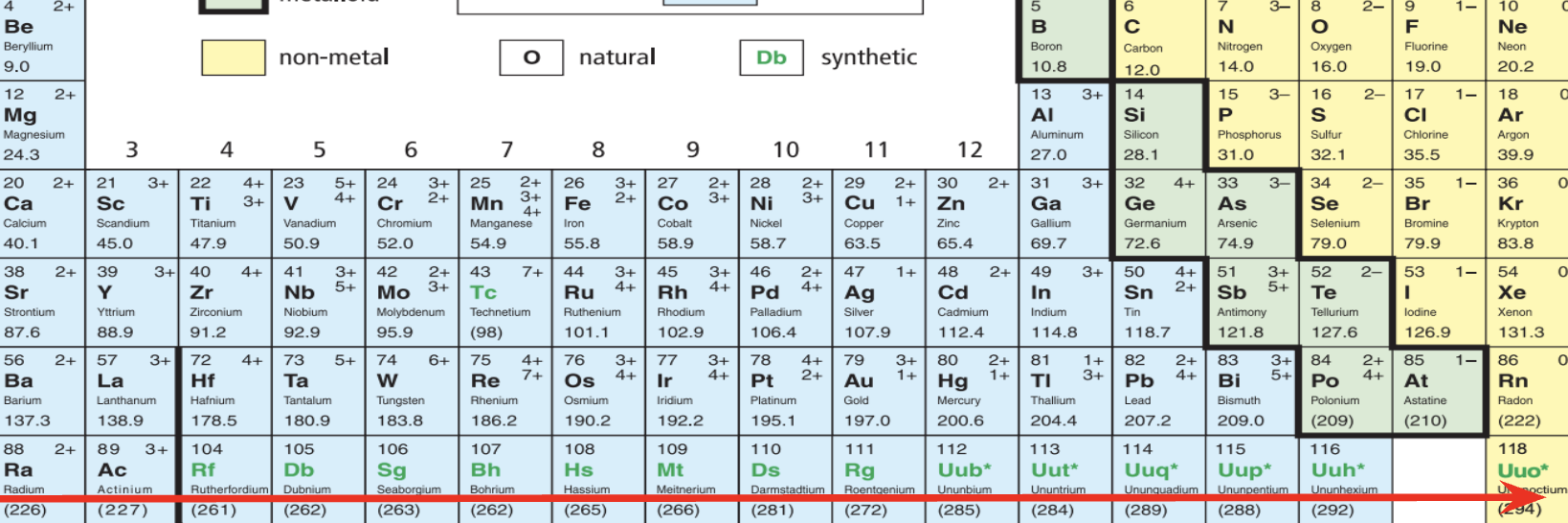
What does this arrow on refer to? (Horizontal)
Periods
What are the 4 main groups?
alkali metals (group 1), alkaline earth metals (group 2), halogens (group 17), nobel gases (group 18)
Describe the chemical and physical properties of alkali metals (melting point, hardness, reactivity)
Low melting point, soft enough to cut with a knife, highly reactive with air and water.
Describe the chemical and physical properties of alkaline earth metals (melting/boiling point, hardness, density, reactivity, colour)
Low boiling points and low melting points, very hard and dense, combustible (like to react with oxygen), silvery white in colour and shiny
Describe the chemical and physical properties of halogens (melting/boiling points, reactivity, corrosive, what it’s good for)
Highly reactive (with hydrogen), low melting and boiling points, extremely corrosive, very good for killing bacteria
What does it mean when a substance is corrosive?
Capable of eating away or destroying by chemical action.
Describe the chemical and physical properties of nobel gases (colour, odour, reactivity, at what temp gases, under what )
Colourless and odourless gases, unlike the other three groups they are very unreactive, they are all gases at 20oC, they’re all nonmetals.
What are valence electrons?
Electrons in the most outer orbital.
What is the connection between valence electrons and reactivity?
Atoms close to acheiving stability (full outer orbital) will react more violently.
How do alkali metals achieve stability?
Get rid of one valence electrons
How do alkaline earth metals achieve stability?
Get rid of two valence electrons
How do halogens achieve stability?
They want to gain one valence electrons.
What happens to reactivity in a group and why?
Reactivity increases as you go down a group because the valence electrons are farther from the nucleus and can be lost easier.
Why do compounds form?
Since all atoms want to achieve stability, they combine with other atoms to gain a full valence orbital.
What is a chemical bond?
Unstable atoms must interact with each other to achieve stability through giving up, sharing, or gaining electrons.
What is an ionic compound?
When a metal and nonmetal bond.
What is an ion?
Charged atoms that have either lost or gain electrons.
What do metal atoms become in an ionic compound?
A cation (positively charged)
What do nonmetal atoms become in an ionic compound?
An anion (negatively charged)
Physical properties of ionic compounds
Solid at room temperature, high melting and boiling points, easy to dissolve
When are molecular compounds formed and what is it called?
When nonmetals share electrons to achieve a full outershell. Called a covalent bond.