Econ Final Exam
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Cost benefit analysis
comparing the cost of an action to its benefit
Opportunity cost
the most valued alternative you give up when you make a choice
Profit
money left over after costs of production (total revenue - total costs)
Incentive
attempt to change peoples behavior by offering a tangible reward
Circular Flow Chart
shows how money moves through the economy in a constant loop from producers to consumers
Economic Interdependence
working relationship between businesses, households, and the government
Free Enterprise (market economy)
supply, demand, and the price system help allocate resources and answer 3 basic questions (also called capitalism)
Command economies
a central authority (govt) makes most of the major economic decisions (socialism, communism)
Mixed economies
has some combination of command and/or market economies
Production possibilities frontier (PPF)
Shows possible alternatives of production
Illustrates trades offs and opportunity costs
What do you lose when you make a change.
Exports
when a country send goods/services to another country
Imports
when a country takes in gods and services sent in from another country
Specialization
focusing on a specific skill, activity, or production process,
Comparative Advantage
when a country can produce a good at a lower opportunity cost
absolute advantage
when a country can produce more of a good using the same quantity of resources.
balence of trade
Trade between countries consists of exporting and importing goods.
trade surplus
positive balance of trade = trade surplus (exports greater than imports)
trade deficit
negative balance of trade = trade deficit (exports less than imports)
free trade agreements pros vs. cons
pros: allows easier access to goods/services, spreads economic activity, countries can get foreign currency
cons: can destroy job sectors in other countries, make smaller nations economically dependent on larger ones
Trade Restrictions
Tariff - a tax placed on imports so they become more expensive
Quota - is a legal limit on the amount of a good that may be imported from other countries
Embargo - is a government order prohibiting the selling of goods to another country, usually because that country has bad/tyrannical/cruel leaders
How can the value of currency change
weak dollar - will lead to a trade surplus, make U.S. goods cheaper so exports will increase
strong dollar - U.S. good become more expensive, leading to fewer exports causing a trade deficit
Demand Shifters
If price stays the same…but for some reason more (or fewer) are being sold…then there has been a “shift in demand”, or a “change in demand”.
What are the demand shifers called?
N.I.C.E.S.T
Demand shifter #1: Number of buyers (N)
When more people immigrate to an area…or emigrate from an area.
Demand shifter #2: Income (I)
When people earn more or less money…they may buy more or less of a product (even though the price hasn’t changed)
Demand shifter #3: Price of complements (C)
Commonly purchased items together.
ex :Because printers are cheaper the quantity demanded will go up (price change).
Demand shifter #4: Expectations of future prices (E)
If people think the price of a good will change, they may either stop buying and wait for price to fall...or rush to buy before the price goes up.
Demand shifter #5: Price of substitutes (S)
Substitutes are used in place of another product. Usually with competitors
Price of one good can have an affect on another good.
Demand shifter #6: Taste/Preferences/Popularity (T)
refers to the popularity of a good. Fads or trends.
Demand
The willingness and ability to purchase an item.
Need both to have demand
Law of demand
As the price goes up quantity demanded goes down
demand schedule
a table that shows the quantity demanded of a good or service at different price levels
demand curve
a graph that shows the relationship between the price of a good/service and the quantity demanded within a specified time frame (Any time the price changes…the quantity demanded will change)
(supply to the sky, demand to the sand)
supply
Supply = How much of a product or a service will be produced and sold.
Businesses supply goods/services to buyers.
People supply their land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurial abilities.
a shift in supply
Sometimes price doesn’t change, yet supply does.
What are the supply shifters called?
T.W.I.N.G.E
Supply shifter #1: Technology/productivity
Technology allows companies to make things cheaper, and therefore increases supply
Technology lowers the per unit cost of producing the item. The cheaper it is to produce...the more they can produce
Per Unit Cost is the cost of making ONE item.
Supply shifter #2: Weather
Good weather usually increases supply (or at least keeps it the same)
Bad weather can decrease supply.
Supply shifter #3: Cost of input/resources
total cost of the resources needed to make the product. The price and cost of the resources and materials needed to make the product can have an impact on how much a business can supply.
Land, labor, capital.
If resource prices go up…supply will fall because it costs MORE to make the product
Supply shifter #4: Number of sellers
How many companies sell the product.
More companies selling means higher supply
Fewer companies means less supply.
Supply shifter #5: Government actions
The government can put rules, laws, and regulations on businesses that can increase or decrease supply.
ex:Subsidies are the opposite of taxes…the government PAYS companies to produce something
Tariffs, quotas, embargo
Supply shifter #6: expectations of future prices
If people think the price of a good will change, they may either stop buying and wait for price to fall...or rush to buy before the price goes up.
law of supply
Law of supply…as price goes up, quantity supplied goes up.
supply schedule
a table that shows the quantity supplied at each price
supply curve
a graph that shows how a change in the price of a good or service affects the quantity a seller supplies. (supply to the sky, demand to the sand)
surplus
supply is greater than demand - causes businesses to lower their prices
shortage
demand is greater than supply - causes businesses to increase their prices
equilibrium
the price on which the consumers and producers agree on
increase in supply graph
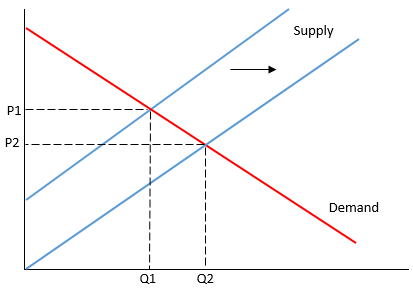
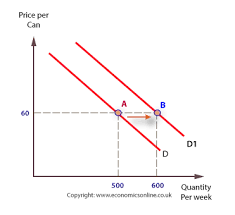
increase in demand
sole proprietorship
One individual, who makes all the decisions, takes all the losses...but makes all the profits
partnership
A business that is owned by two or more co-owners who share profits/debts of the business (firm).
corporation
A legal entity that can conduct business in its own name (as if it’s an individual)
Owned by stockholders
stockholders
owners of the corporations.
franchise
A company that allows people to buy and run a firm.
stock
certificate of ownership of a small piece of a corporation that can go up or down in value
limited liability
If your business fails, or if your business is losing money...courts cannot force you to pay debts with your personal assets.
unlimited liability
You are on the hook to pay any debts you owe...and you may be forced to use your own personal assets (like savings, or other holdings)
Pure/perfect competition
Type of Product = Identical
Barriers to Entry = No barriers
Control Over Prices = No control (price taker)
Advertising/product differentiation = no advertising and no product differentiation
Price takers: can sell all their output at the equilibrium price but can sell none of their output at any other price
ex: Farm Produce,Commodities (oil, gold), Stocks
monopolistic competition
Many buyers and sellers
Products are slightly/moderately different
Product Differentiation: Heavy use of advertising and nonprice differentiation
Easy to get in or out of market (low barriers to entry)
Price searchers...can change prices some…but can’t really go far beyond competitors price range
ex: Fast food, gas stations, car insurance, realtors, construction/carpenters, lawn care
Oligopoly
A few large companies
Similar/slightly different products
Product Differentiation: Fair amount of nonprice competition
Significant barriers to entry usually due to cost of entry and regulations
Price searchers: Have some control over prices, but can’t stray too far from competitors.
Potential for collusion/price-fixing
Examples: Auto companies, airline companies, Streaming services, health insurance, Cell phone carriers
monopoly
Number of Sellers = One
Type of Product = Unique
Barriers to Entry = Extremely High
Control over Prices = Total Control...but can’t go too high or nobody will purchase.
Advertising: None
Product Differentiation: None
Technically in the US they are illegal...unless the government allows them and control them.
Price Searchers: Chooses the price to make the most profit
Examples = Water, Electricity, First Class Mail
price searcher
can sell some of its products at various prices. The “range” of slightly higher or lower prices.
price taker
can sell all their output at the equilibrium price but can sell none of their output at any other price. Must sell at equalibrium
anti trust laws
Goal: Promote and preserve competition in the marketplace by regulating businesses and their practices.
Result: No monopolies unless the government allows. No price collusion.
wage rate
the wage level (dollar amount) that is paid to a worker for their service.
labor union
Organization seeking to increase the wages & improve the working conditions of its members…
price discrimination
When businesses charge different prices for different people
Age
Gender
Race
Generally illegal, except in some cases (allowed to give breaks to the elderly, the young…)
NOT allowed to discriminate based on race, religion, or gender in most cases.
externalities
Unintended side effects that can be positive or negative.
Positive side effect ex:public education (benefits all of society
Negative side effect ex: businesses polluting (hurts all of us)
money supply
How much money is in circulation. High interest rates lead to a lower supply. Low interest rates lead to a higher money supply.
interest rates
how much banks charge on loans to people or businesses. People like low interest rates so they can borrow and spend more money.
fractional reserve banking
When banks hold on to a “fraction” of people’s deposits and lend out the rest. Helps to increase the money supply.
The Federal Reserve System
Nation’s central bank. It controls the money supply and interest rates (which has an impact on the economy as a whole).
required reserves
the amount of money that a bank holds to ensure that it is able to meet liabilities in case of sudden withdrawals.
inflation
Caused by an increase in Aggregate Demand or a decrease in Aggregate Supply
caused by increase in wages, increase in the price of raw materials, increase in taxes, decline in productivity, increase in money supply
deflation
Caused by a decrease in Aggregate Demand. (An increase in supply COULD cause this but it’s rare)
caused by recession
aggregate demand
a measurement of the total amount of demand for all finished goods and services produced in an economy
Aggregate supply
total number of goods and services that producers make and are willing to sell at a certain price within a certain time.
business cycles
ups and downs of economy and GDP
Peak
high point of economy and GDP. (between the end of an economic expansion and the start of a recession in a business cycle.
Recession
economic indicators start to fall (GDP, housing, business earning, and unemployment rises)
Trough
economy bottoms out and starts to improve (before a rise/recovery)
Recovery
economy starts to improve (GDP rises, unemployment falls)
expansion/growth
an increase in the production of goods and services in an economy - GDP passes old peak and economy is growing bigger than previous
excess reserves
funds held at the bank that exceed the Federal Reserve's minimum requirement.
gross domestic product (GDP)
measure of U.S. economic activity
monetary policy
a set of actions to control a nation's overall money supply and achieve economic growth
expansionary fiscal policy
Goverment cuts taxes on people/businesses to allow them to have more money to spend
contractionary fiscal policy
government raises taxes and causes people to have less money to spend (decreases agg.demand)
exapnsionary monetary policy
expanding the money supply faster than usual or lowering short-term interest rates.
contractionary monetary policy
a type of monetary policy that is intended to reduce the rate of monetary expansion to fight inflation
national debt
the total amount of money that a country's government has borrowed
budget deficit
If the government spends more than it takes in with taxes for the year
budget surplus
if the government spends less than what it takes in
Credit scores (good)
Higher credit scores allow you to get loans at cheaper interest rates
Credit scores (bad)
If you have a bad credit score you may not get a loan, or it will be at a higher interest rate
Tariff
a tax placed on imports so they become more expensive
Quota
is a legal limit on the amount of a good that may be imported from other countries
Embargo
is a government order prohibiting the selling of goods to another country, usually because that country has bad/tyrannical/cruel leaders