1st Semester Final - Anatomy and Physiology
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Respiratory system and Directional terms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Functions of the Respiratory System
Provides area for gas exchange, filters and warms air, produces sound, and aids in sense of smell
Thoracic Cavity
Contains heart and lungs
Serous Membrane
Two membranes lining thoracic cavity and the organs
Visceral Pleura
Covers surface of organs
Parietal Pleural
Covers walls pf the cavity
What is the naval cavity made of?
Epithelial Tissue
Ciliated columnar epithelial tissue
Propels mucus towards throat where it can be swallowed
Paranasal Sinuses
Empty spaces in the frontal, sphenoid, and maxilla bones
Nasal Conchae
Force air flow over the largest surface area of the cilia possible (3 curved bones)
Pharynx is also called what?
Throat, for food and air
Nasopharynx
Superior part of the pharynx, below the nasal cavity
Oropharynx
Middle party of the pharynx
Laryngopharynx
Inferior part of the pharynx, above the larynx
Larynx is also called what?
The voicebox
Epiglottis
Flap that allows air to pass, opening when breathing and closed when eating
Vocal Cords
Vibrate to produce sound
Thyroid Cartilage
Anterior to larynx
Trachea
Windpipe
Cricoid Cartilage
Treachea cartilage, where they larynx joints trachea
Tracheal Cartilages
C-shaped, stiffen trachea and prevent closing
Bronchi
Lead to lungs
Right lung
Three lobes - Superior, middle, and inferior
Left Lung
Two lobes - Superior and Inferior
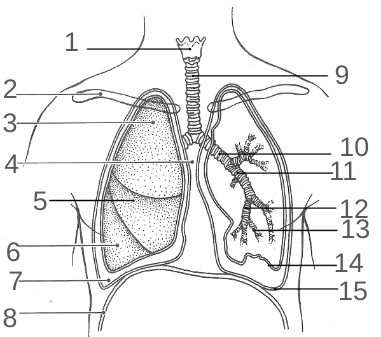
What is 1?
The Larynx
What is 2?
The Clavicle
What is 3?
The Superior Lobe
What is 4?
The Mediastinum
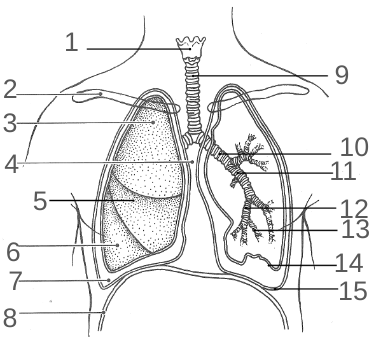
What is 5?
The Middle Lobe
What is 6?
The Inferior Lobe
What is 7?
The Pleural Space
What is 8?
The Diaphragm
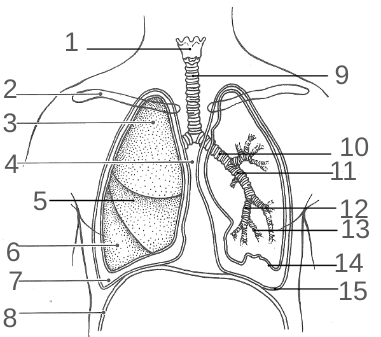
What is 9?
The Trachea
What is 10?
The Primary Bronchi
What is 11?
The Secondary Bronchi
What is 12?
The Tertiary Bronchi
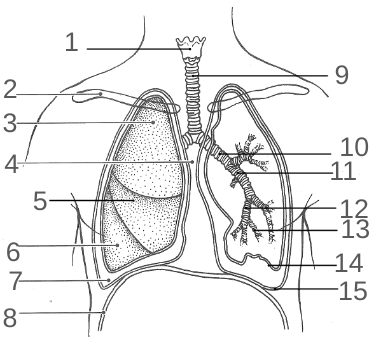
What is 13?
The Bronchiole
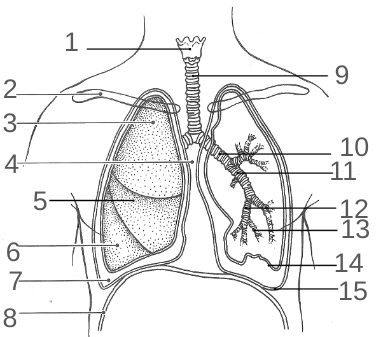
What is 14?
Visceral Pleura
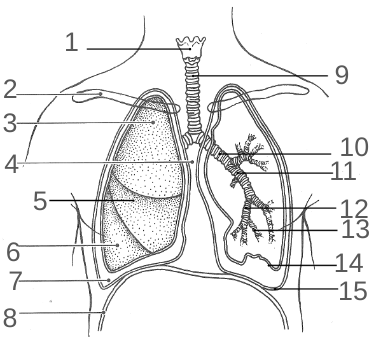
What is 15?
The Parietal Pleura
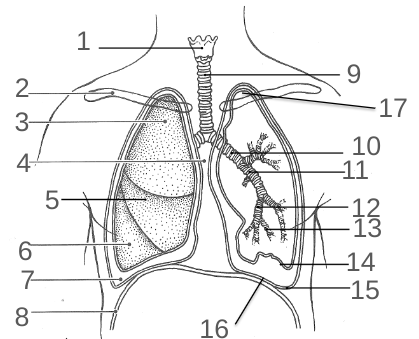
What is 16?
The Base
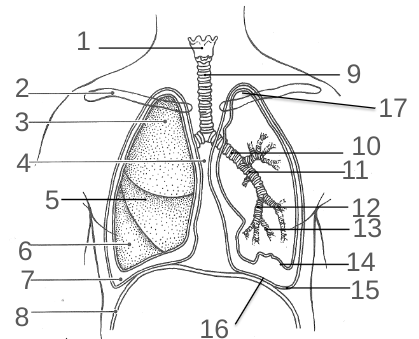
What is 17?
The Apex
Alveoli
Gas exchange area with capillaries
Surfactant-Secreating Cells
Produce lipid that reduces surface tension of water, prevents alveoli from sticking on the interior
Machrophages
White blood cells, ‘eat’ bacteria (endocytosis)
Capillaries
Very small and thin allows for gas exchange, red blood cells pass in single-file line
What do premature babies not produce?
Serfectant
Pleural Fluid
In pleural space (between layers of pleura), reduces friction
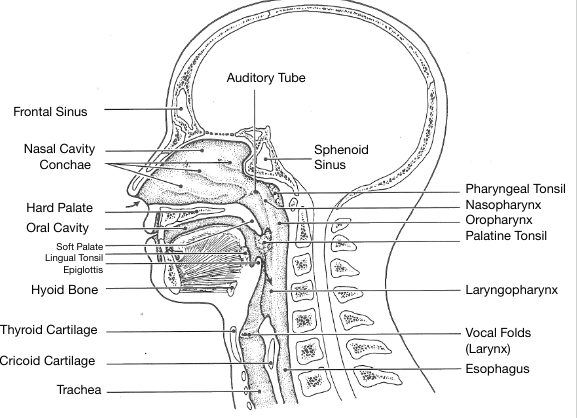
Now look at this…
Wow Bailey, you’re so amazing for making this awesome study guide for us!
Pulmonary Ventilation
Breathing (air in and out of lungs)
External Respiration
Gas exchange between blood and lungs
Respiratory Gas Transport
O2 and CO2 to and from cells
Internal Respiration
Gas exchange between blood and cells in body
Breathing in(inspiration)…
Volume of lungs increases, pressure drops allowing air in, diaphragm contracts and moves down, intercostal muscles/ ribs expand
Breathing out(expiration)…
Lung volume decreases, pressure increases forcing air out, diaphragm relaxes and moves up, intercostal muscles relax
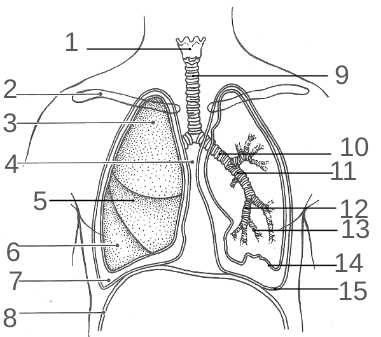
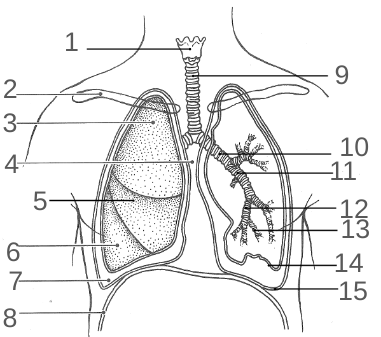
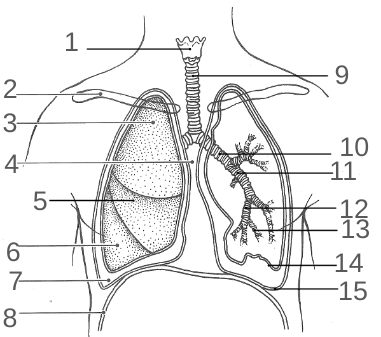
What should 2 be?
Nasal cavity
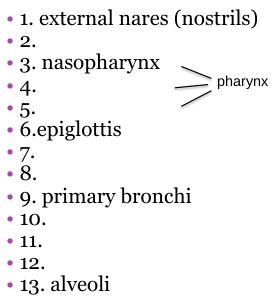
What should 4 be?
Oropharynx
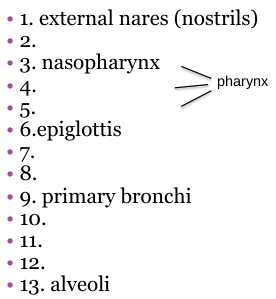
What should 5 be?
Laryngopharynx
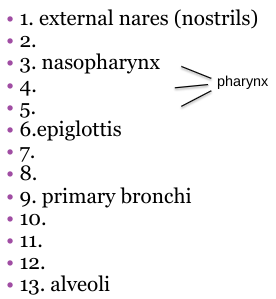
What should 7 be?
Larynx
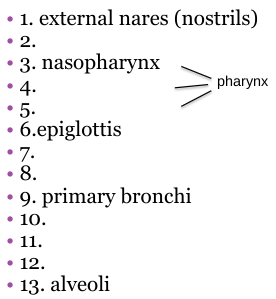
What should 8 be?
Trachea
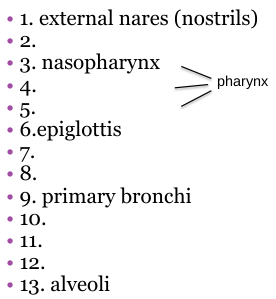
What should 10 be?
Secondary bronchi
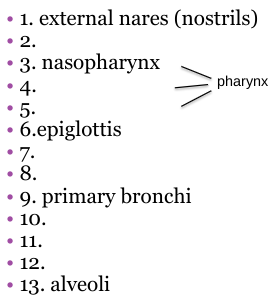
What should 11 be?
Tertiary bronchi
What should 12 be?
Bronchioles
Proximal
Closer to origin or point of attachment
Distal
Away from the origin of attachment
Inferior (Caudal)
Away from the head
Superior (Cranial)
Toward the head
Anterior (Ventral)
More toward the front of the body
Posterior (Dorsal)
More toward the back of the body
Lateral
Away from the body’s midline
Medial
Towards the midline of the body
Superficial (external)
Towards the body’s surface
Deep (Internal)
Further away from the body’s surface
Saggittal Plane
Divides body into left and right portions
Frontal Plan
Divides body into front and back
Transverse/Horizontal Plane
Divides body into top and bottom parts producing a cross section
Midsagittal
Sagittal division, equal left and right parts
Parasagittal
Sagittal division, UNequal left and right parts
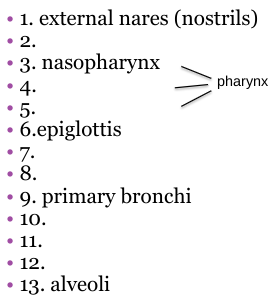
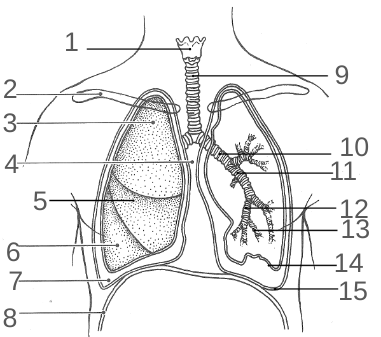
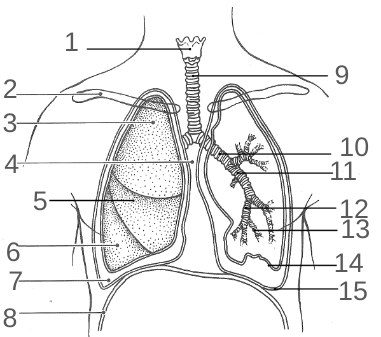
1-12 would are what?
Conductive passageways
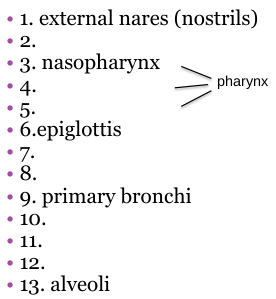
13 is also referred to what?
Respiratory membrane
The pallet
Separates the nasal and oral cavity
Functions for conductive passageways
Warms, moisten, and clean/ filter air
Charateristics of the right main bronchi
Larger diameter, more common to get clogged
Characteristics of left main bronichi
Longer, more horzontal
What constitute respiration?
Pulmonary ventalation, external ventilation, respiratory gas exchange, and internal respiration