Transcription
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
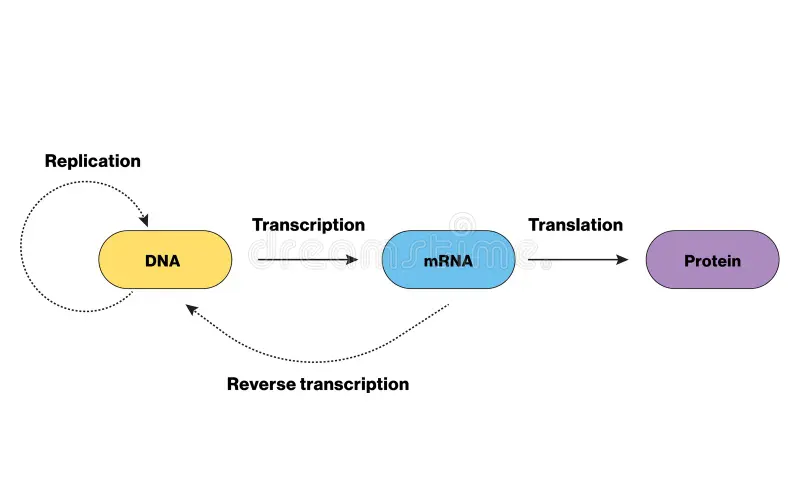
What is the central DNA dogma?
It references the inheritance mechanisms of molecular biology
What does DNA contain?
The molecular blueprint of every cell
What are genes?
Small segments of DNA located on a chromosome
What do genes store?
The information needed to make many things, including proteins
How do cells become specialized to carry out a particular function?
By making specific proteins
What are proteins?
The molecular workers of the cell
What do proteins control?
Cell shape, function, reproduction, and synthesis of biomolecules
What does a gene encode?
The information for the production and synthesis of a protein
Determines the order in which amino acids are linked together to make the primary structure of a protein
What carries protein synthesis out?
Ribosomes
Can DNA leave the nucleus?
No, so its message has to be carried from the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm by RNA, where the message will be translated into a protein
What are the two steps to protein synthesis?
(In the nucleus) Information in a DNA gene is copied into mRNA in the process of transcription
(In the cytoplasm) mRNA together with tRNA, animo acids, and a ribosome synthesize in the process of translation
What is transcription?
DNA acts as a template in the creation of messenger RNA (mRNA)
What is RNA polymerase and what does it do?
An enzyme that unzips DNA in the relevant region (wherever the necessary gene is) and acts to guide free nucleotides to align themselves (complimentary base pairing) along one of the unzipped strands to form the single strand of mRNA
What happens when transcription is complete?
The DNA molecule zips up again, then the mRNA moves from the nucleus and goes out into the cytoplasm through a nuclear pore
What is the first step of transcription?
Initiation
A DNA molecule is unwound (H-bonds are broken) and strands are separated at the beginning of the gene sequence
RNA polymerase binds to a promoter at the beginning of a gene on the template strand
What is a promoter?
A short sequence of DNA that promotes protein synthesis
What is step 2 of transcription?
Elongation
RNA polymerase synthesizes a sequence of RNA nucleotides along the DNA template strand
RNA polymerase moves along the template strand in the 3’ to 5’ direction, creating an RNA strand that is made in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
RNA bases are complimentary to the DNA template strand (except uracil replaces thymine)
What is step 3 in transcription?
Termination
RNA polymerase reaches a termination sequence/signal and releases the completed RNA strand
RNA polymerase detaches from the DNA molecule and is free to synthesize another RNA molecule
The DNA completely rewinds into a double helix
What is a DNA transcription unit composed of from its 3’ to 5’ direction?
An RNA coding region, flanked by a promoter region and a terminator region
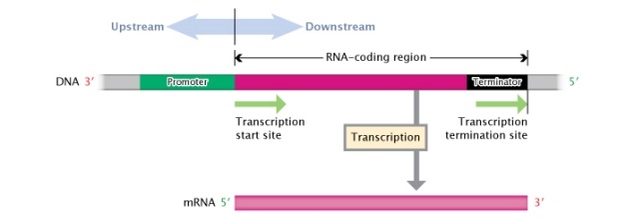
What is upstream in the DNA transcription unit?
Regions moving toward the 3’ end of the transcription site
What is downstream in the DNA transcription unit?
Regions moving towards the 5’ end of the transcription start site
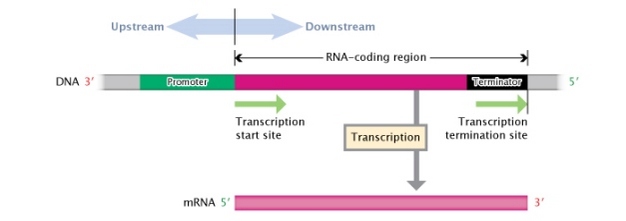
Which way does RNA polymerase read?
3’ to 5’, creating a strand made in the 5’ to 3’ direction
What does the processing of mRNA highlight?
The differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
How does the processing of mRNA in prokaryotes work?
The ribosomes begin translation of mRNA even as RNA polymerase is still elongating mRNA
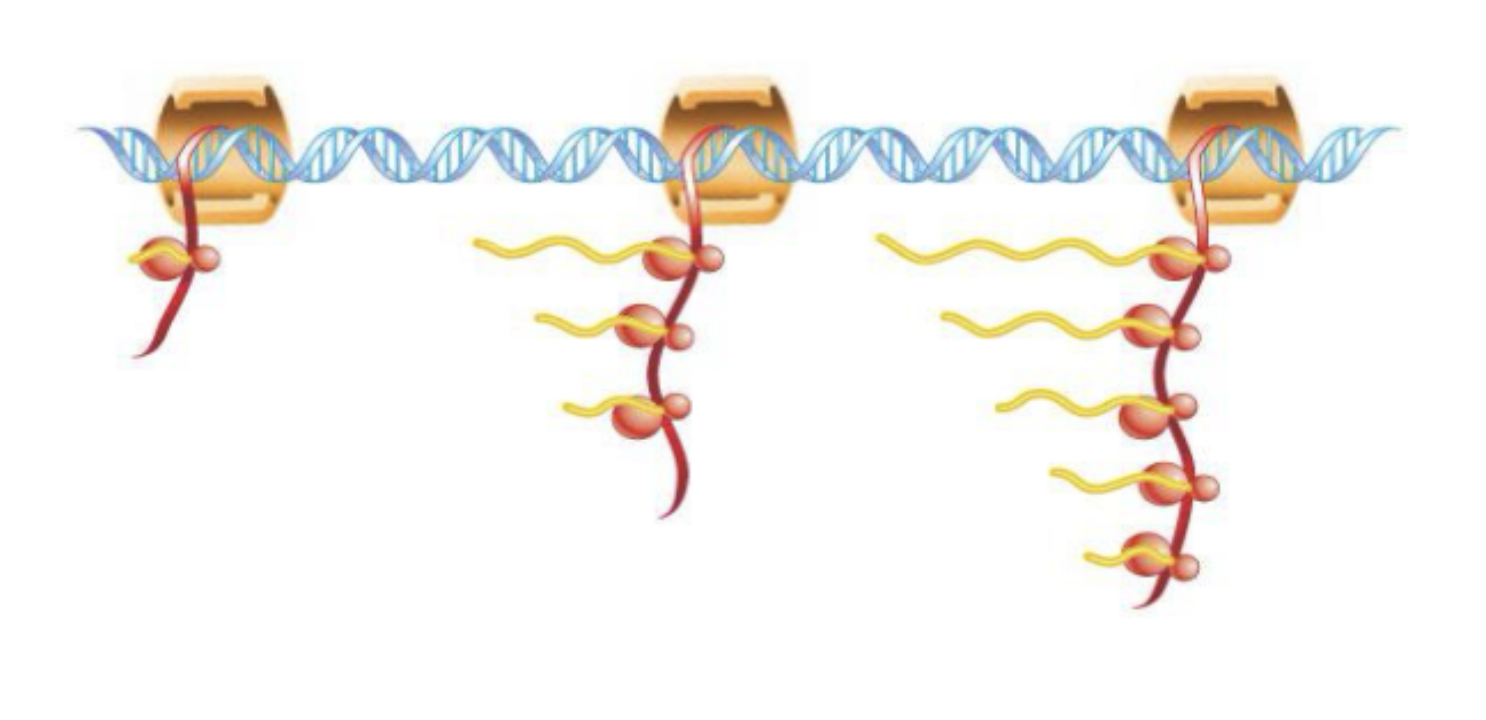
What is different about genes in prokaryotes?
All the nucleotides in a gene encode for the amino acids of a protein, there are no sequences that are not transcribed into RNA
How have prokaryotes made transcription and translation faster?
Genes for related functions are adjacent and transcribed together
What is different about transcription and translation in prokaryotes?
Transcription and translation are not separated in space or time as there is no nucleus
Why does mRNA need to be processed in eukaryotes?
Not all DNA is considered coding DNA, some stretched of DNA can be non-coding, so before mRNA can leave the nucleus, it must be processed before entering the cytoplasm
What is precursor mRNA (also called pre-mRNA or primary mRNA)?
mRNA containing all the bases complimentary to both intron and exon segments of DNA
How is mRNA processed in eukaryotic cells?
A cap and tail are added on either end, the intron sequences are removed, and the exon sequences are joined together
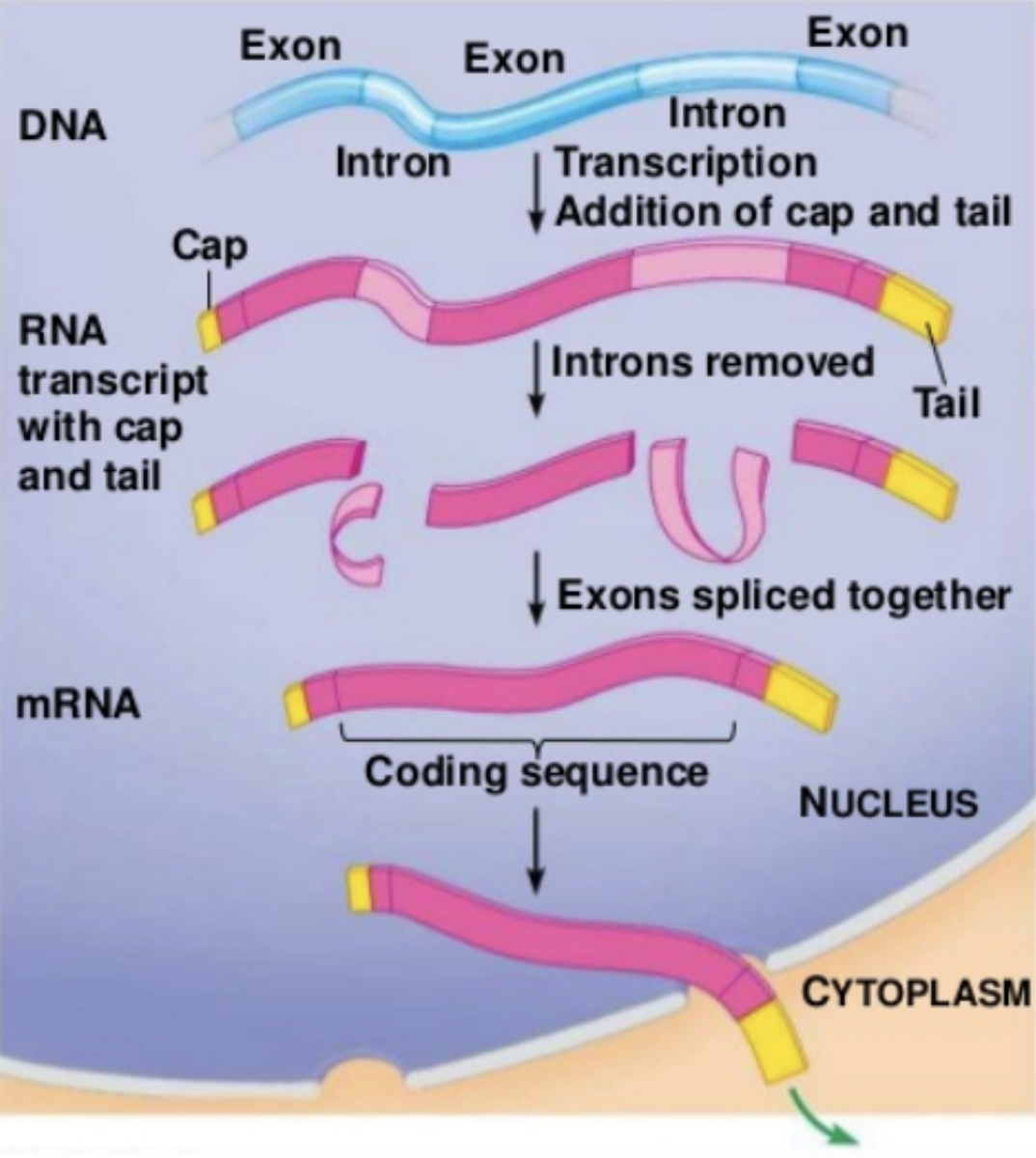
What is the cap and where is it added onto the mRNA?
A few RNA nucleotides are added on to the 5’ side, which is called the 5’ cap
What is the tail and where is it added onto the mRNA?
A few RNA nucleotides are added on to the 3’ side, which is called the poly-A tail
What does the 5’ cap do?
Helps bond the mRNA to the ribosome
What does the poly-A tail do?
Prevents cellular enzymes from breaking down the mRNA molecule once it leaves the nucleus
What cellular enzyme attempts to break down the mRNA molecule once it leaves the nucleus?
Exonuclease
What are introns?
Sequences of nucleotides that don’t code for proteins (intron = intragenic)
What does intragenic mean?
Within a gene
What are exons
Sequences of nucleotides that code for proteins (exon = expressed)
What removes the exons?
An enzyme called ribozymes
What happens after ribozymes remove the introns?
Exons are joined together to form a finished/processed mRNA molecule
Why is having introns and exons helpful?
All cells can make multiple proteins from a single gene, because it can make many different combinations of exons
Fragmented genes may provide a quick and efficient way for eukaryotes to evolve new proteins with new functions (which gives organisms genetic variation)