Cell Division
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
What is metastasis?
A process where a tumor becomes malignant when its cells break loose and travel to other tissues and organs
At the end of meiosis two, how many chromosomes and chromatids are present?
23 chromosomes and 23 chromatids
At the end of meiosis, how many chromosomes and chromatids are there?
23 chromosomes and 46 chromatids
At the end of mitosis, how many chromosomes and chromatids are present?
46 chromosomes and chromatids
At the end of mitosis, there are now___ daughter cells
Two
Cell checkpoint occurs at the end of?
G 1
Mitosis occurs in what type of cells?
Stomatic cells
Meiosis occurs only in what type of cells?
In germ cells (gamete-producing cells)
What occurs to the cell in G1?
The cell begins to grow, increases in size, and protein synthesis starts for cell division
What are cells called when they are continuously dividing?
Labile cells
EX: Skin
What are cells called when they don’t usually divide, but can be stimulated as needed?
Quiescent Cells
E.X liver cells
What are cells called if they have no or little capacity for cell division?
Fixed Cells (Permanent)
What are cells called when they only divide when attached to an external surface?
Anchoring Dependent
Prevents cells from multiplying while floating throughout the body
What are chromosomes?
Dense packaging of chromatin existing during mitosis and meiosis
Dogs have 78 chromosomes, how many chromosomes are in the dog's haploid cells?
2n=78 so
n=39 ( half of 2n)
During meiosis 1, how many chromosomes and chromatids are in anaphase 1?
46 chromosomes and 92 chromatids
During prophase and metaphase of mitosis, chromosomes exist in a duplicated state. How many chromosomes and chromatids?
46 chromosomes and 92 chromatids
What is density-dependent inhibition?
When cells stop dividing due to their surrounding density reaching max
False or true: Drugs that disrupt microtubule formation will subsequently disrupt cell division?
True
What occurs in G 2
Consider the final preparation for mitosis. Organelles replicate, and cells continue to grow, and cell check is done
Genetic recombination occurs during what three events?
Crossing over, independent assortment, and random joining of gametes
Homologous chromosomes are found in what type of cell?
Diploid Cells
What is disjunction?
It is when homologous pairs are pulled to opposite poles
how many chromosomes and chromatids are present during anaphase in mitosis?
92 chromosomes and 92 chromatids
How many chromosomes and chromatids are present in anaphase 2 and telophase 2 in meiosis 2?
46 chromosomes and 46 chromatids
How many chromosomes and chromatids are present in prophase 2 and metaphase 2 in meiosis 2?
23 chromosomes and 46 chromatids
How many chromosomes and chromatids are present in telophase in mitosis?
92 chromosomes and chromatids
how many chromosomes are in egg and sperm?
23 (n)
Humans have ___ chromosomes because they have ___ homologous pairs
46; 23
If a tetrad failed to form, which process could not occur?
Genetic recombination
Important phase! All DNA is replicated during__ before mitosis, this is where sister chromatids are formed, centrosomes replicate, what phase is this?
S phase
Is cytokinesis part of mitosis or a separate step?
It's a separate phase
What is a chromatid?
Half of a duplicated chromosome
What is crossing over?
The process of genetic recombination produces chromosomes that are unique at the genetic level
What is the chiasmata?
The region of crossing over creating genetic diversity in offspring
separation of homologous chromosomes. Genetic recombination only occurs in
Meiosis 1
Separation of sister chromatids occurs in
Meiosis 2
What is interphase?
A sequence that occurs before the cell undergoes cell division, and where cells spend the most time
What occurs in G0?
The stage where cells are not actively dividing. They re-enter the cell cycle based on different environmental cues
The amount of DNA in each daughter cell is _____ at the end of mitosis?
Half the amount of the parent cell
The final checkpoint occurs?
During metaphase also known as spindle checkpoint
The second checkpoint occurs at the end of ?
G2
There are now four daughter cells, at the end of what?
Mitosis
What allows the chromosomes and chromatids to be separated during specific phases of cell division...?
Spindle Fibers
What are homologous chromosomes?
Two sets of every chromosome (one from each parent). Similar in length, gene position, and centromere position
What are the three cell-specific regulations?
Cell cycle checkpoints, density-dependent inhibition, and anchorage dependence
What are the two functional limitations of a cell?
Surface to volume and genome to volume ratio
what are two words used to describe how many chromosomes there are?
Haploid 1 set of chromosomes (n)
Diploid 2 set of chromosomes (2n)
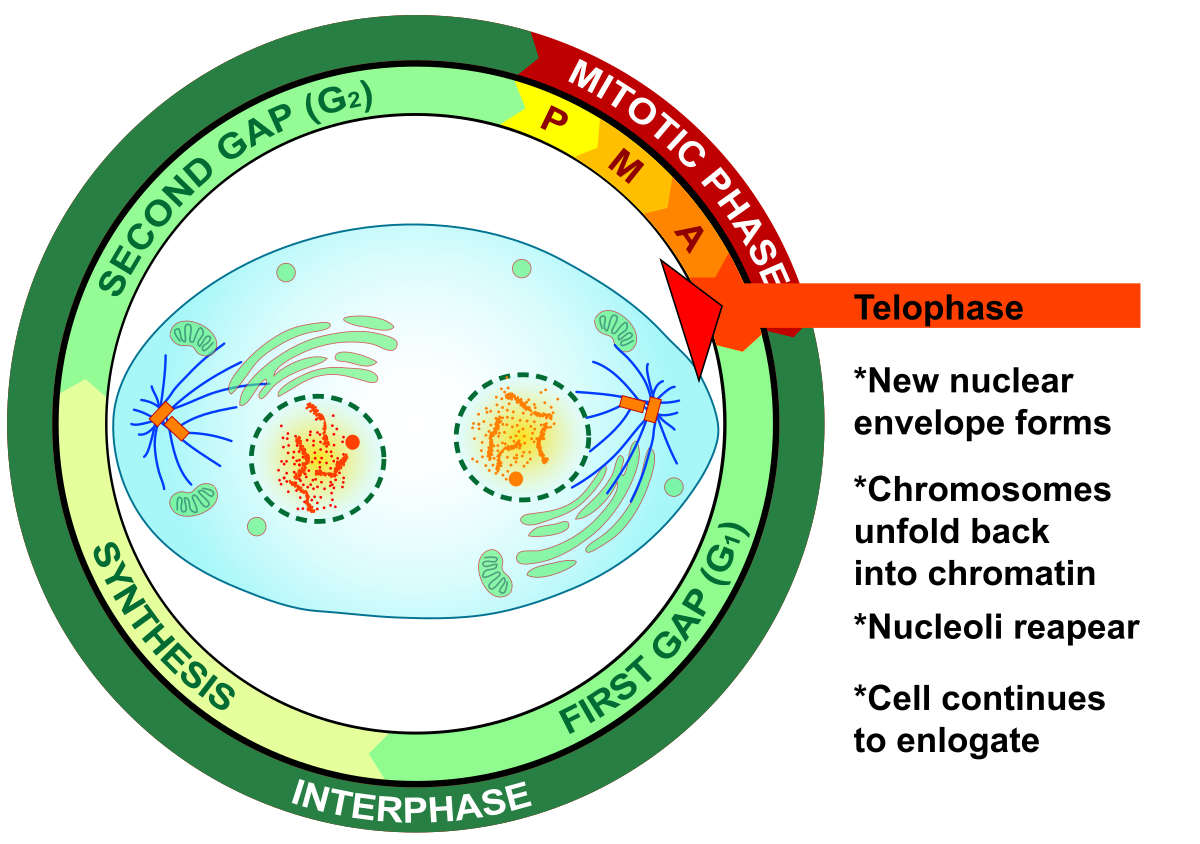
What is the fifth step of mitosis? What occurs here
Telophase
-Nucleoli reappear
-two nuclear envelopes develop
-chromosomes decondense back into chromatin
-Spindle fibers disappear
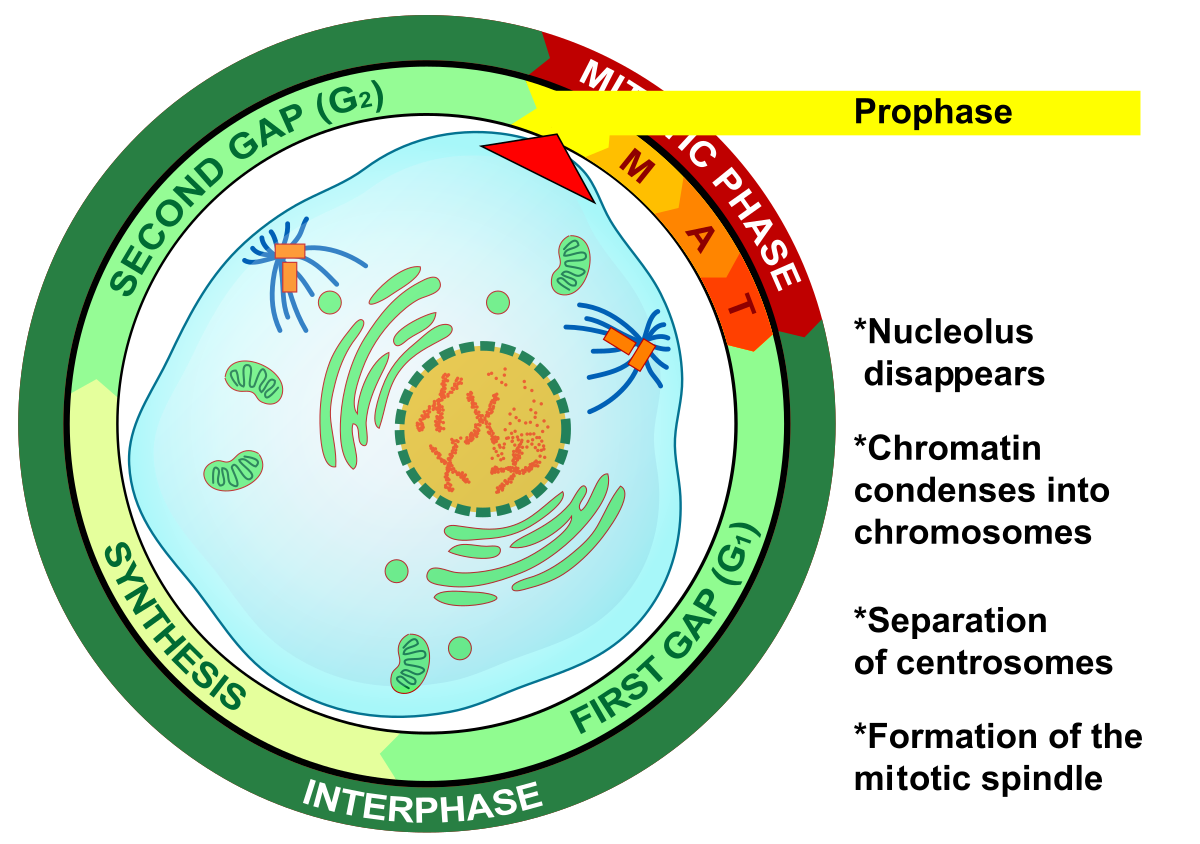
What is the first step of mitosis? Explain what happens here.
Prophase
-Chromatin condenses into chromosomes
- nucleolus disappears
-The miotic splindle begins to form
-Centrosomes begin to move towards opposite ends of the cell
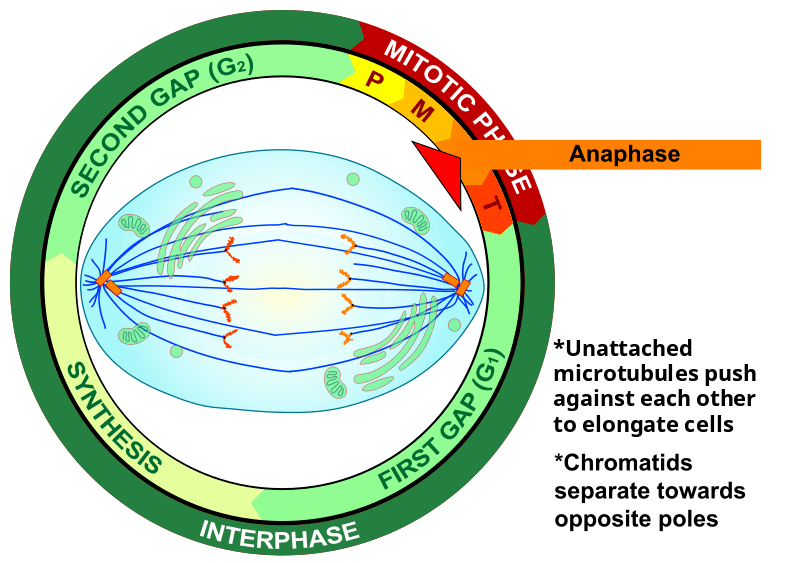
What is the fourth step of mitosis? What occurs here?
Anaphase
-Microtubules shorten
-Chromatids are pulled apart
-Each sister chromatid is now considered to be an individual chromosome
-chromosomes are pulled to opposite ends of the cell
What is the order of the cell cycle?
G1, S , G2, M
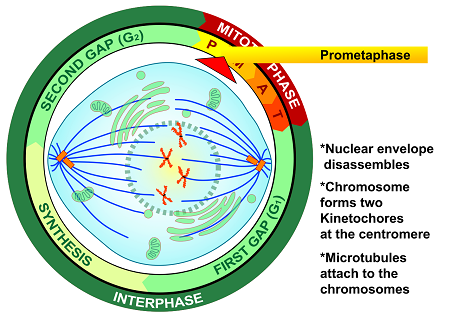
What is the second phase of mitosis? What occurs here?
Prometaphase
-Nucleus disassembles
-chromosomes condense even further
-Each chromatid is attached to a kinetochore
-mitotic spindle further develops
- Spindle fibers begin to attach to the kinetochores of chromosomes
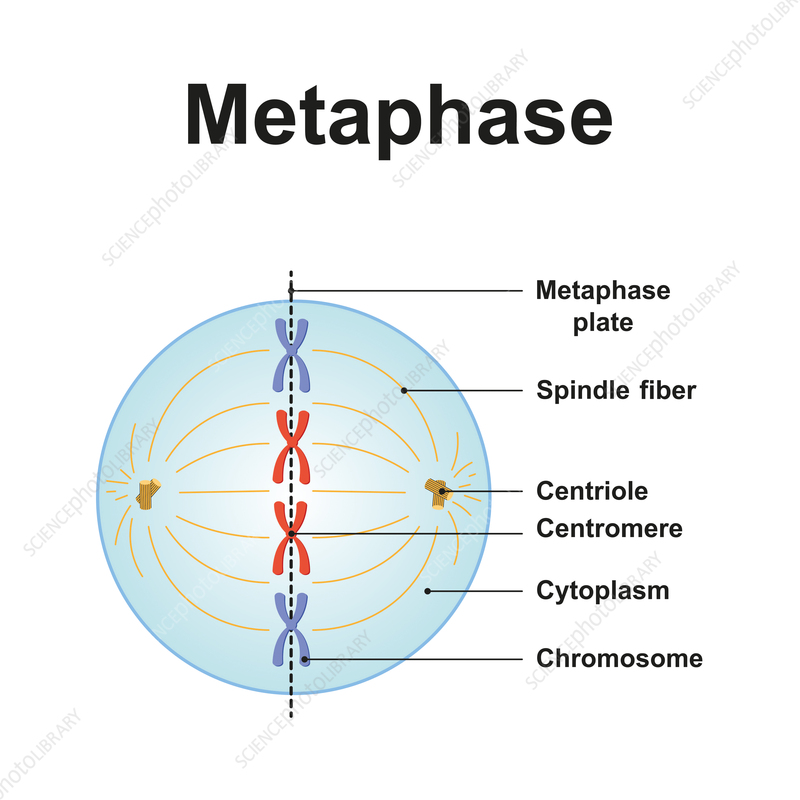
What is the third phase of mitosis? What occurs here?
Metaphase
-Chromosomes are lined up across the center of the cell
-Centrosomes have reached opposite ends of the cell
-The mitotic spindle is fully developed
-All chromosomes are attached to spindle fibers via kinetochores
-Karyotyping performed here
What makes prophase one unique?
The homologous chromosomes pair up (crossing over)
What occurs in telophase one and cytokinesis?
-Each new daughter cell has a new nucleus that has half the number of chromosomes
-diploid parent cells-> haploid daughter cells
-chromosomes are not genetically identical to the parent cell due to recombination
What gene limits cell division?
p53 gene, however mutation can cause over dividing
What is synapse?
When homologous chromosomes pair up into tetrads
Where do spindle fibers attach?
kinotochores they are proteins located on the chromosome region of the chromosome
Which cell division keeps the same number of chromosomes and chromatids, but changes at the end?
Meiosis 1