A&P I Lecture Exam 3
1/56
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
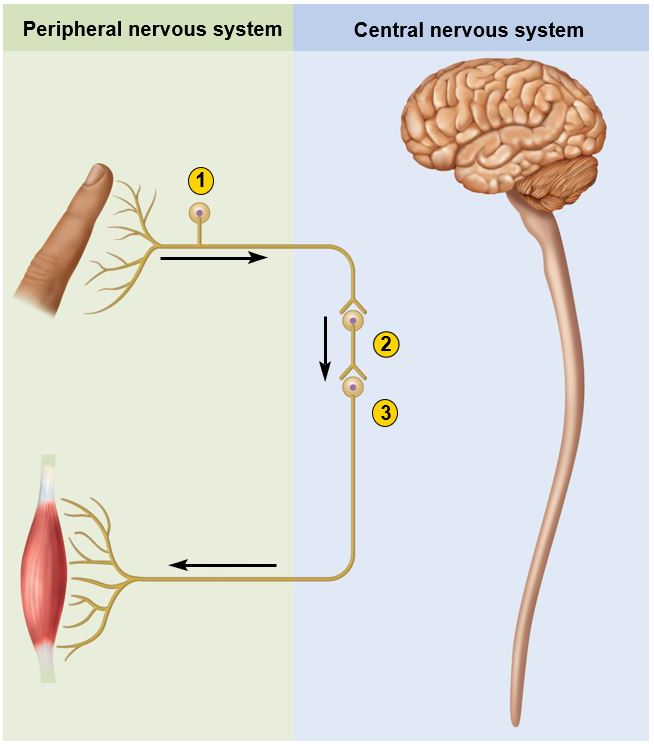
This figure shows the three main functional classes of neurons. Which option below correctly matches the types of neuron to the numeric labels on the figure?
1-Afferent neuron, 2-Interneuron, 3-Efferent neuron
1-Interneuron, 2-Afferent neuron, 3-Efferent neuron
1-Efferent neuron, 2-Afferent neuron, 3-Interneuron
1-Afferent neuron, 2-Efferent neuron, 3-Interneuron
1-Efferent neuron, 2-Interneuron, 3-Afferent neuron
1-Afferent neuron, 2-Interneuron, 3-Efferent neuron
If a neuron is prevented from sending a neurotransmitter across a synapse to another cell, which neuron property is being inhibited?
Secretion
What is another name for the autonomic nervous system?
Visceral motor division
Some antidepressant drugs act by inhibiting monoamine oxidase (MAO). What is the function of this enzyme?
It breaks down monoamines.
Parkinson disease is a progressive loss of motor function due to the degeneration of specific neurons. These neurons secrete an inhibitory neurotransmitter that prevents excessive activity in motor centers of the brain. What neurotransmitter is this?
Dopamine
While both systems maintain homeostasis, how does the nervous system differ from the endocrine system?
The nervous system releases neurotransmitters between cells, while the endocrine system releases hormones into the blood.
Where are axons surrounded by Schwann cells found?
In the PNS
A myelin sheath is composed primarily of _________.
lipids and proteins
Which of the following is true regarding axons in the PNS?
Astrocytes send extensions called perivascular feet to wrap each axon.
Satellite cells cluster around each axon to form a pseudo-myelin sheath.
A Schwann cells wraps its plasma membrane around each individual axon as it does in the CNS.
A Schwann cell folds its plasma membrane around several axons.
An oligodendrocyte cells wraps its plasma membrane around each axon as it does in the CNS.
A Schwann cell folds its plasma membrane around several axons.
The term "nerve fiber" refers to a(n) _________.
axon
What is the primary site on a neuron for receiving signals from other neurons?
The dendrites
The respiratory center gathers information from a variety of sources in order to set the rate and depth of breathing. This is an example of what type of neural circuit?
Convergent
The opening of _________ gates produces an _________.
chloride; IPSP
Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) are associated with which of the following?
Repolarization of the cell membrane
No change in the cell membrane potential
No change of the threshold
Hyperpolarization of the cell membrane
Depolarization of the cell membrane
Hyperpolarization of the cell membrane
Which of these happens first in a cholinergic synaptic transmission?
Acetylcholine diffuses across the synaptic cleft.
Sodium enters the postsynaptic cell.
The synaptic vesicles release acetylcholine.
A postsynaptic potential is produced.
The synaptic vesicles release acetylcholine.
All of the following are typical characteristics of neurotransmitters except _________.
they are synthesized by a presynaptic neuron
they alter the physiology of the postsynaptic cell
they are released in response to stimulation
they are released into the bloodstream before reaching the postsynaptic cell
they bind to specific receptors on the postsynaptic cell
they are released into the bloodstream before reaching the postsynaptic cell
Which of these is an example of an EPSP in a typical neuron?
A voltage change from -69.5 mV to -70 mV
A voltage change from 0 mV to +0.35 mV
A voltage change from -70 mV to -69.5 mV
A voltage change from +35 mV to 0 mV
A voltage change from -70 mV to -70.5 mV
A voltage change from -70 mV to -69.5 mV
What would be the best explanation for why myelinated axons conduct signals faster than unmyelinated axons?
Myelinated axons contain more sodium ions.
There are no sodium channels in unmyelinated axons.
Electrical signals spread faster through insulated (myelinated) regions of axon.
Myelinated axons have more sodium-potassium pumps in their membranes.
Active transport of sodium and potassium is faster in myelinated axons.
Electrical signals spread faster through insulated (myelinated) regions of axon.
A neuron receives a stimulus. Which of the following events happens next?
Multiple Choice
Threshold is reached
A local potential develops
Repolarization of the membrane
A resting membrane potential is established
Hyperpolarization of the membrane
A local potential develops
During the absolute refractory period which of the following is true?
The signal grows weaker with distance.
The neuron fires at its maximum voltage if a stimulus depolarizes the neuron to threshold.
No stimulus of any strength will trigger a new action potential.
It is possible to trigger a new action potential, but only with an unusually strong stimulus.
If a neuron reaches threshold, the action potential goes to completion.
No stimulus of any strength will trigger a new action potential.
The _________ division carries signals to the smooth muscle in the large intestine.
visceral motor
Which cells form myelin sheaths in the spinal cord?
Oligodendrocytes
How does a neuron transport enzymes produced in the cell body to its axon terminals?
Along microtubules
Which neurotransmitter excites skeletal muscle and inhibits cardiac muscle?
Acetylcholine
Place the following events in synaptic transmission at a cholinergic synapse in order:
A - A postsynaptic potential is produced;
B - Voltage-gated calcium channels open and calcium enters the cell;
C - ACh is released and diffuses across the axon terminal;
D - A nerve signal arrives at an axon terminal;
E - Ligand-gated sodium channels open and sodium enters the cell.
D, B, C, E, A
Conduction of a nerve impulse would be the fastest in which of the following?
A small unmyelinated axon
A small diameter myelinated axon
A large unmyelinated axon
A large diameter myelinated axon
A small axon with multiple Schwann cells
A large diameter myelinated axon
In an action potential, which event directly follows repolarization?
Hyperpolarization of the membrane
Which of the following is most likely to cause a rapid depolarization?
Inactivation of sodium channels
Opening of chloride channels
Closing of sodium channels
Opening of potassium channels
Opening of sodium channels
Opening of sodium channels
Loss of muscle mass from lack of activity is called _________.
atrophy
Where is dystrophin, the protein that is defective in muscular dystrophy, normally found?
Between the outermost myofilaments and the sarcolemma of a muscle fiber
Why does one continue to breathe heavy after rigorous physical activity has stopped?
The body requires more oxygen to restore levels of ATP and creatine phosphate.
Which of the following is not a characteristic of a muscle cell?
Plasticity
Conductivity
Excitability
Contractility
Extensibility
Plasticity
Skeletal muscle is called _________, because it is usually subject to conscious control.
voluntary
When a skeletal muscle lengthens, its _________ helps resist excessive stretching and subsequent injury to the muscle.
collagen
A bundle of muscle fibers is known as a _________.
fascicle
Which of the following is an accurate comparison of skeletal muscle to smooth muscle?
Smooth muscle depends on an axon to supply the calcium needed for contraction.
Smooth muscle contracts more slowly but relaxes more rapidly.
Smooth muscle consumes more ATP to maintain a given level of muscle tension.
Smooth muscle contracts more rapidly but relaxes more slowly.
Smooth muscle contracts and relaxes more slowly.
Smooth muscle contracts and relaxes more slowly.
Which of the following would be caused by a contraction of smooth muscle?
Elevating the eyebrows
Blood leaving the left ventricle of the heart
Blinking the eyelids
Goose bumps
Deep inspiration
Goose bumps
Cardiac muscle has very little capacity for regeneration because it lacks _________.
satellite cells
Which of the following marks the boundaries of a sarcomere?
H bands
M lines
A bands
I bands
Z discs
Z discs
A myofilament that runs through the core of a thick filament and anchors it to a Z disc is called a(n) _________.
elastic filament
The protein that acts as a calcium receptor in skeletal muscle is _________.
troponin
Which of the following is true concerning isotonic eccentric contraction?
The muscle lengthens but tension remains constant.
The muscle shortens but tension remains constant.
The muscle lengthens and tension declines.
The muscle tenses but length remains unchanged.
The muscle tenses and shortens.
The muscle lengthens but tension remains constant.
How many somatic motor neurons stimulate one muscle fiber?
1
Which of the following best describes the resting membrane potential (RMP)?
The intracellular environment is negatively charged.
It has a voltage of about +75 mV.
The extracellular environment is negatively charged.
The intracellular environment has more positively charged sodium.
The intracellular environment is negatively charged.
When acetylcholinesterase outlasts the release of acetylcholine from the synaptic vesicles, the skeletal muscle _________.
relaxes
Which of the following is not a purpose of the excess postexercise oxygen consumption (EPOC) in muscle?
To replenish the phosphagen system
To oxidize lactate
To restore resting levels of ATP and CP
To neutralize carbon dioxide buildup
To serve elevated metabolic rate
To neutralize carbon dioxide buildup
Athletes who train at high altitudes increase their red blood cell count, which increases their oxygen supply during exercise. Increased oxygen supply results in _________
longer aerobic respiration
The transfer of phosphate from CP to ADP is catalyzed by _________.
creatine kinase
All muscle types will respond to an electrical stimulus because all muscle cells are _________.
excitable
Where would you expect to find numerous gap junctions in muscular tissue?
The intercalated discs of cardiac muscle
Which muscle type depends solely on the sarcoplasmic reticulum as its calcium source?
Skeletal muscle
Each T tubule is flanked by two _________.
terminal cisterns
Which of the following is predominately made up of myosin?
The elastic filament
The thin filament
The thick filament
F actin
G actin
The thick filament
Shortening a muscle while it maintains constant tension is called _________.
an isotonic contraction
What happens when acetylcholine stimulates its receptors in the neuromuscular junction?
The permeability of the sarcolemma to Na+ increases.
Increased calcium ion permeability of the presynaptic terminal cell membrane is caused by _________.
an action potential
Aerobic respiration produces a net yield of approximately _________ ATPs per glucose.
32